-
ssm框架之spring:xml如何配置创建对象
本篇就简单了聊一下spring中Bean管理和操作。
首先说一下spring中管理操有两种方式:
- 基于xml配置文件方式,这个在初体验中使用的就是这种方式。
- 基于注解方式实现
现在就聊一下xml配置的文件的不同配置方式的不同效果。
其实一直说bean,简单的说就是java对象。
因为后面很多时候会使用配置文件,格式:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
创建对象和set注入属性
创建对象
无参创建对象
首先来一个无参创建对象,这个很简单。
这个时候简单的时候创建一个类:
package com.xzd.test; public class Person { public void play(){ System.out.println("我是喜欢运动小仙女,所以才玩飞盘的"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
然后下xml中进行配置信息:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
然后体验一下:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("personbean.xml"); Person person1= (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");// 这里会增加一个强制转换或者如下 Person person2= applicationContext.getBean("person",Person.class);// 这里可以通过参数来确定这个spring创建的对象是什么类型 person1.play(); person2.play(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

补充XML标签解释:
- bean标签,就是创建一个对象的需要使用的标签。但是可以看出标签里面可以添加对应属性。
- bean属性:
- id : 这个唯一的标识,可以看出id=“person” 然后test类中applicationContext.getBean(“person”)。一般的时候会创建于对象相同的名字,毕竟好识别。
- class: 这个属性其实就是说明了要创建这个id代表的是那个类,这个类的具体所在位置,其实是class=“com.xzd.test.Person”,
- name: 当然还有一个name属性,不过其意义与id的差不多,所以直接使用id即可。
但是这种创建的对象,可以看出创建的对象其没有属性的或者是无参构造对象。
有参创建对象
演示一下:
package com.xzd.test; public class Person { String personname; int age; public Person(String personname, int age) { this.personname = personname; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person={\"name\":"+this.personname+",\"age\":"+this.age+"}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
然后配置xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person"> <constructor-arg name="personname" value="我是张三啊">constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="age" value="18">constructor-arg> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
然后调用:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("personbean.xml"); Person person= applicationContext.getBean("person",Person.class);// 这里可以通过参数来确定这个spring创建的对象是什么类型 System.out.println(person.toString()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
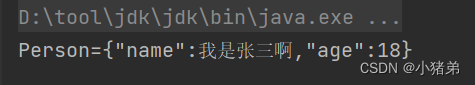
解释补充:
- constructor-arg : 配置了意思有参构造参数。当然可以通过name和value对参数和值进行设置。
set注入属性
对于属性,前面在创建对象的时候,通过构造参数进行属性,赋值,但是在前面也是可以同set进行属性赋值没说白了就是:
public class Person { String personname; int age; public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void setPersonname(String personname) { this.personname = personname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person={\"name\":"+this.personname+",\"age\":"+this.age+"}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
但是既然聊spring,自然就不能使用创建对象后使用setPersonname,现在演示:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person"> <property name="personname"> <value>我是张三啊value> property> <property name="age" value="18">property> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
然后试一下:
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("personbean.xml"); Person person= applicationContext.getBean("person",Person.class);// 这里可以通过参数来确定这个spring创建的对象是什么类型 System.out.println(person.toString()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

标签补充:
-
property : 这个是对属性的进行配置,但是这种配置还有一前提,那就是需要在对象中记得些setter方法,不然ide会提示。
-
property的属性(简单列出两个,其实有很多在后面补充):
- name : 这个需要和对象属性一样。
- value :这个是为属性赋值,这样就不需要创建对象然后调用setPersonname了。这个当然也可以单独拿出来作为标签来使用
补充p标签
对于set的注入属性,还可以更加简单的,进行配置,现在只需要将配置文件增加p标签即可:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person" p:personname="我是张三啊" p:age="18"> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10

然后看一下这样也可以注解的也可以完成这个配置。
补充注入特殊符号
有时候创建对象的时候,会赋值属性的时候会是特殊符号,当然spring也可以注入属性为特殊符号。
- 注入空值如何注入:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person"> <property name="personname"> <null/> property> <property name="age" value="18">property> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
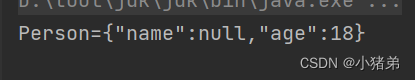
**
**可以直接问属性进行赋值为空值。 -
特殊符号
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person"> <property name="personname"> <value>value> property> <property name="age" value="18">property> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
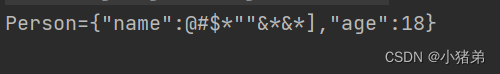
如何使用****
注入bean
注入内部bean
其实属性除了是简单字符串或者数字,但是有些对象的属性,本身就是一个对象,比如这样
package com.xzd.test; public class Person { String personname; int age; public void setPersonname(String personname) { this.personname = personname; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
package com.xzd.test; public class Student { String school; Person person; // 两 public Student(String school, Person person) { this.school = school; this.person = person; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student={\"name\":" + person.personname + ",\"age\":" + person.age + ",\"school\":"+this.school+"}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="student" class="com.xzd.test.Student"> <constructor-arg name="school" value="游戏学院">constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="person"> <bean id="person" class="com.xzd.test.Person"> <property name="personname" value="张三">property> <property name="age" value="18">property> bean> constructor-arg> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("personbean.xml"); Student student= applicationContext.getBean("student", Student.class);// System.out.println(student.toString()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
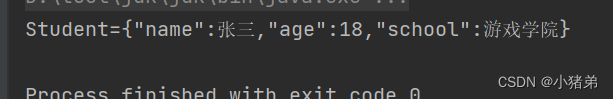
注入外部bean
比如还有就是业务中service中引用dao的方法一样。一句话来说就是在一个对象类中注入一到一个对象类中 ,前面内部注入,在bean标签中套用一个bean标签,但是外部注入式两个bean标签没套用,而通过属性进行引入,所以这个是外部注入。如下演示:
package com.xzd.test.service; import com.xzd.test.dao.SaveDao; public class SaveService { SaveDao saveDao; public void setSaveDao(SaveDao saveDao) { this.saveDao = saveDao; } public void save() { System.out.println("service调用dao"); saveDao.save(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
package com.xzd.test.dao; public class SaveDao { public void save(){ System.out.println("dao添加到数据库中了"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="SaveService" class="com.xzd.test.service.SaveService"> <property name="saveDao" ref="saveDao">property> bean> <bean id="saveDao" class="com.xzd.test.dao.SaveDao"> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("servicetest.xml"); SaveService saveService= applicationContext.getBean("SaveService", SaveService.class);// saveService.save(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
可以看结果
其实可以看出在property标签中,通过rel为name赋值,而rel的值就是创建的要引入的bean中id即可。
注入集合数据
注入普通的数据
毕竟有些bean的属性值,还有可能是集合,比如数字,list,map等
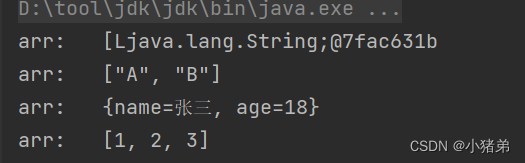
package com.xzd.test; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; public class CollectionTest { String arr[]; Map map; Set set; List list; public void setArr(String[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } public void setMap(Map map) { this.map = map; } public void setSet(Set set) { this.set = set; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public void testToString(){ System.out.println("arr: "+this.arr); System.out.println("set: "+this.set); System.out.println("map: "+this.map); System.out.println("list: "+this.list); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="collectiontest" class="com.xzd.test.CollectionTest"> <property name="arr"> <array> <value>"a"value> <value>"b"value> <value>"c"value> array> property> <property name="list"> <list> <value>1value> <value>2value> <value>3value> list> property> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="name" value="张三">entry> <entry key="age" value="18">entry> map> property> <property name="set"> <set> <value>"A"value> <value>"B"value> set> property> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("collectiontest.xml"); CollectionTest collectionTest= applicationContext.getBean("collectiontest", CollectionTest.class);// collectionTest.testToString(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
补充注入的util
package com.xzd.test; import java.util.List; public class CollectionTest { List<String> list; public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public String toString() { return "CollectionTest{" + "list=" + list + '}'; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
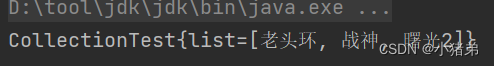
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <bean id="collectiontest" class="com.xzd.test.CollectionTest"> <property name="list" ref="s_list">property> bean> <util:list id="s_list"> <value>老头环value> <value>战神value> <value>曙光2value> util:list> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("collectiontest.xml"); CollectionTest collectiontest= applicationContext.getBean("collectiontest", CollectionTest.class); System.out.println(collectiontest.toString()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

可以看出可以如下设置,通过util标签进行设置。
注入集合中带有bean
package com.xzd.test; public class Course { String courseName; String teacherName; public Course(String courseName, String teacherName) { this.courseName = courseName; this.teacherName = teacherName; } @Override public String toString() { return "{name:"+this.courseName+" teachername: "+this.teacherName+"}"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
public class Student { String name; List<Course> listcourse; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setListcourse(List<Course> listcourse) { this.listcourse = listcourse; } public void testToString(){ System.out.println("name: "+this.name+"list: "+this.listcourse); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="student" class="com.xzd.test.Student"> <property name="name" value="张三">property> <property name="listcourse" > <list> <ref bean="course1">ref> <ref bean="course2">ref> list> property> bean> <bean id="course1" class="com.xzd.test.Course"> <constructor-arg name="courseName" value="老头环无伤通关">constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="teacherName" value="宫崎老贼">constructor-arg> bean> <bean id="course2" class="com.xzd.test.Course"> <constructor-arg name="courseName" value="v社不会数学尤其是三">constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="teacherName" value="亏本的v胖">constructor-arg> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("student.xml"); Student student= applicationContext.getBean("student", Student.class); student.testToString(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

-
相关阅读:
云原生强大且灵活的持续集成CI开源框架Tekton实战-上
爬虫与云服务器云数据库
【muduo源码剖析】EventLoop设计分析
$attrs,$listeners
DropWizard的AOP扩展点最佳实践
Java——break、continue(学习笔记)
优测云测试平台 | 有效的单元测试
08_Linux基础-vim-tmux-字符编码
【LIN总线测试】——LIN主节点网络管理测试
PIE-engine 教程 ——影像集合的使用map()映射函数(北京市NDVI计算)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u011863822/article/details/126990582
