-
3. 内核解压-确定解压信息
源码位置arch/arm/boot/compressed/head.S
- #ifdef CONFIG_AUTO_ZRELADDR
- /*
- * Find the start of physical memory. As we are executing
- * without the MMU on, we are in the physical address space.
- * We just need to get rid of any offset by aligning the
- * address.
- *
- * This alignment is a balance between the requirements of
- * different platforms - we have chosen 128MB to allow
- * platforms which align the start of their physical memory
- * to 128MB to use this feature, while allowing the zImage
- * to be placed within the first 128MB of memory on other
- * platforms. Increasing the alignment means we place
- * stricter alignment requirements on the start of physical
- * memory, but relaxing it means that we break people who
- * are already placing their zImage in (eg) the top 64MB
- * of this range.
- */
- mov r4, pc
- /* 128M对齐 */
- and r4, r4, #0xf8000000
- /* Determine final kernel image address. */
- /* arch/arm/Makefile
- * textofs-y := 0x00008000
- * TEXT_OFFSET := $(textofs-y)
- */
- add r4, r4, #(TEXT_OFFSET & 0xffff0000)
- add r4, r4, #(TEXT_OFFSET & 0x0000ffff)
- #else
- ldr r4, =zreladdr
- #endif
以rv1126为例,uboot会把内核拷贝到0x2008000这个地址,pc的值也就是在这个范围内,与上0xf8000000值为0,所以说内核解压地址是0x8000.
TEXT_OFFSET的值可以是不同的,平台商设置, r4中存放的是解压后的内核的地址

下面的代码其实只有一个目的,创建页表的时候,不要覆盖解压代码。
比如页表位置和未解压的源码位置重合这种情况
- /*
- * Set up a page table only if it won't overwrite ourself.
- * That means r4 < pc || r4 - 16k page directory > &_end.
- * Given that r4 > &_end is most unfrequent, we add a rough
- * additional 1MB of room for a possible appended DTB.
- */
- mov r0, pc
- /* 将当前运行的地址和内核解压地址比较
- * r0小于r4的时候才会执行下面的有cc的指令
- * cmp会影响C标志位
- */
- cmp r0, r4
这里有2种情况
(1) R0 > R4,页表不会覆盖正在执行的解压代码,这里会直接跳到cache_on函数
cache_on会创建页表,所以这里可以执行

(2) R0 < R4,页表有可能覆盖执行的解压代码


对于情况(2)继续执行下面的代码
- /* LC0+32对应的是 _end - restart + 16384 + 1024*1024
- * 程序长度+16k的页表长+1M的DTB空间
- * 其中 _end - restart是程序长度,包含了piggydata
- */
- ldrcc r0, LC0+32
- /* pc + 程序的大小后再次和内核解压地址进行比较 */
- addcc r0, r0, pc
- cmpcc r4, r0
- ...
- .align 2
- .type LC0, #
- LC0: .word LC0 @ r1
- .word __bss_start @ r2
- .word _end @ r3
- .word _edata @ r6
- .word input_data_end - 4 @ r10 (inflated size location)
- .word _got_start @ r11
- .word _got_end @ ip
- .word .L_user_stack_end @ sp
- .word _end - restart + 16384 + 1024*1024
- .size LC0, . - LC0
这里又会出现2种情况,注意这里r0 记录的是总镜像包的结束地址
(3)R4 < R0 覆盖解压代码

(4) R0 < R4 不覆盖页表,注意R0其实多加了一个页表的大小
 对于(2)(3)的情况,页表覆盖解压代码,暂时跳过cache_on函数,需要搬运操作,执行下面的操作
对于(2)(3)的情况,页表覆盖解压代码,暂时跳过cache_on函数,需要搬运操作,执行下面的操作orrcc r4, r4, #1 @ remember we skipped cache_on对于(1)和(2)(4)情况都不会出现覆盖页表的情况,则执行下面的代码
blcs cache_on暂时跳过cache_on函数,继续分析
- restart: adr r0, LC0
- ldmia r0, {r1, r2, r3, r6, r10, r11, r12}
- ldr sp, [r0, #28]
这里的sp的值是这样计算的,r0 + 28指向的是.L_user_stack_end
栈的定义如下,大小4k:
- .align
- .section ".stack", "aw", %nobits
- .L_user_stack: .space 4096
- .L_user_stack_end
到目前为止
- * r0 = LC0当前运行地址
- * r1 = LC0链接地址
- * r2 = BSS start
- * r3 = BSS end
- * r4 = final kernel address (possibly with LSB set)
- * r5 = ?
- * r6 = _edata
- * r7 = architecture ID
- * r8 = atags/device tree pointer
- * r9 = ?
- * r10 = ?
- * r11 = GOT start
- * r12 = GOT end
- * sp = .L_user_stack_end
注意这里的r10,也就是input_data_end - 4
首先input_data_end是什么?变量定义在 arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.S
- section .piggydata,#alloc
- .globl input_data
- input_data:
- .incbin "arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy_data"
- .globl input_data_end
- input_data_end:
1. incbin指令作用?
被汇编的文件内包含一个文件。 该文件按原样包含,没有进行汇编
2. piggy_data是什么?
该系列第一篇文章已经讲了 1. 内核镜像组成及编译
那么现在可以知道r10里面存的是压缩前内核的大小的地址,注意这个地址是链接地址
更新一下当前已知信息
- * r0 = LC0当前运行地址
- * r1 = LC0链接地址
- * r2 = BSS start
- * r3 = BSS end
- * r4 = final kernel address (possibly with LSB set) 解压地址
- * r5 = ?
- * r6 = _edata
- * r7 = architecture ID
- * r8 = atags/device tree pointer
- * r9 = ?
- * r10 = 镜像的结束位置 *** 临时用于获取压缩前Image大小
- * r11 = GOT start
- * r12 = GOT end
- * sp = stack pointer
继续看代码
- /*
- * We might be running at a different address. We need
- * to fix up various pointers.
- */
- sub r0, r0, r1 @ calculate the delta offset
- add r6, r6, r0 @ _edata
- add r10, r10, r0 @ inflated kernel size location
根据上面知道
r0是LC0的运行地址,r1是LC0的链接地址
那么r0-r1就是2者的差值,保存在r0中,那么r10+r0就得到了保存压缩前内核的大小的运行地址,地址中记录了压缩前的内核的大小
计算方式如下:
首先dump方式看看大小是多少
- # ls arch/arm/boot/Image -l
- -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 13940060 Apr 9 01:02 arch/arm/boot/Image
- # hexdump arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy_data -s 6043023
- 05c358f b55c 00d4
- 05c3593
代码中计算如下
- /*
- * The kernel build system appends the size of the
- * decompressed kernel at the end of the compressed data
- * in little-endian form.
- */
- ldrb r9, [r10, #0] //r9 = 0x5c
- ldrb lr, [r10, #1] //lr = 0xb5
- orr r9, r9, lr, lsl #8 //r9 = 0xb55c
- ldrb lr, [r10, #2] //lr = 0xd4
- ldrb r10, [r10, #3] //r10 = 0
- orr r9, r9, lr, lsl #16 //r9 = 0xd4b55c
- orr r9, r9, r10, lsl #24 //r9 = 0x00d4b55c
13940060 = 0x00d4b55c
继续分析
- #ifndef CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM
- /* malloc space is above the relocated stack (64k max) */
- add sp, sp, r0
- add r10, sp, #0x10000
- #else
- /*
- * With ZBOOT_ROM the bss/stack is non relocatable,
- * but someone could still run this code from RAM,
- * in which case our reference is _edata.
- */
- mov r10, r6
- #endif
sp变成运行地址,同时r10加上malloc空间的大小
源码中有这样的注释,r10这个时候是end of this image, including bss/stack/malloc space if non XIP
注意这里的r10是一个运行地址,里面包含了压缩内核,bss,stack,malloc space
这里为什么要考虑bss stack malloc space? 因为解压的时候代码是c语言的,需要这个基本的环境
上面的判断主要是判断解压后页表会不会被覆盖,下面的则是判断解压后会不会覆盖当前运行的代码。
那么如果要解压,解压的地址肯定不能覆盖当前运行的代码,如果会覆盖,那么就需要搬运
- add r10, r10, #16384
- cmp r4, r10
- bhs wont_overwrite
r4大于r10的情况如下,解压不会出现覆盖,那么就会去执行wont_overwrite

r9之前已经分析了,记录的是压缩前的内核镜像的大小
- add r10, r4, r9
- adr r9, wont_overwrite
- cmp r10, r9
- bls wont_overwrite

wont_overwrite部分的代码主要是用于代码搬运及内核解压
所以解压内核的时候是不能覆盖wont_overwrite后面的代码
对于其之前的部分没有影响,因为那部分代码不会执行解压
如果继续向下执行,则说明当前是会覆盖wont_overwrite代码,比如这种

- /*
- * Relocate ourselves past the end of the decompressed kernel.
- * r6 = _edata
- * r10 = end of the decompressed kernel
- * Because we always copy ahead, we need to do it from the end and go
- * backward in case the source and destination overlap.
- */
- /*
- * Bump to the next 256-byte boundary with the size of
- * the relocation code added. This avoids overwriting
- * ourself when the offset is small.
- */
- /* 执行到这里的时候 r10记录的是解压后内核的结束地址
- * 计算reloc_code_end到restart的大小,256字节对齐
- * 这里其实就是代码段的大小
- * 更新r10的值,此时r10的值是搬移后代码的结束地址
- * 这里对解压内核的结束地址进行了一个拓展,为什么要拓展?
- */
- add r10, r10, #((reloc_code_end - restart + 256) & ~255)
- bic r10, r10, #255

接着分析
- /* Get start of code we want to copy and align it down. */
- /* r5中记录restart的运行地址 */
- adr r5, restart
- /* 4字节对齐 */
- bic r5, r5, #31
- /* 忽略 VIRT相关 */
- /* r6 的值是_edata
- * r9 = r6 - r5 这部分大小包含了代码段,数据段,不包含bss和堆栈
- */
- sub r9, r6, r5 @ size to copy
- /* 4字节对齐 */
- add r9, r9, #31 @ rounded up to a multiple
- bic r9, r9, #31 @ ... of 32 bytes
- /* r5 要拷贝的源起始地址
- * r9 要拷贝的大小
- * r6 就是拷贝结束地址
- */
- add r6, r9, r5
- /* r9变成目的结束地址 */
- add r9, r9, r10
- /* ldm: 多数据加载,将地址上的值加载到寄存器上
- * stm: 多数据存储,将寄存器的值存到地址上
- * db: 每次传送钱地址减4
- * !:表示最后地址写回寄存器中
- */
- 1: ldmdb r6!, {r0 - r3, r10 - r12, lr}
- cmp r6, r5
- stmdb r9!, {r0 - r3, r10 - r12, lr}
- bhi 1b
- /* Preserve offset to relocated code. */
- /* r6中保存偏移量 */
- sub r6, r9, r6
- #ifndef CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM
- /* cache_clean_flush may use the stack, so relocate it */
- add sp, sp, r6
- #endif
这样就得到了能正常解压的环境

这里解释一下上面的疑惑,为什么要拓展?

可以看到如果不拓展解压部分的代码是会被覆盖掉的
但是实际拷贝是从后向前拷贝的,即使覆盖了也没有关系
对于这里找了历史提交 adcc25915b98e5752d51d66774ec4a61e50af3c5
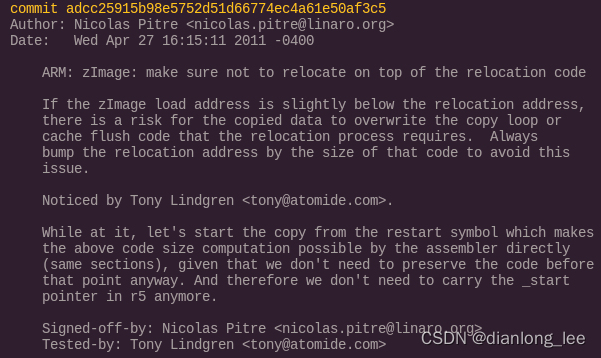
如果zImage加载地址略低于重定位地址,则复制的数据有覆盖重定位过程所需的复制循环或缓存刷新代码的风险。始终将重定位地址与该代码的大小相冲突,以避免此问题。
- bl cache_clean_flush
- badr r0, restart
- add r0, r0, r6
- mov pc, r0
对于cache这里先忽略
r6保存的是搬移之后的偏移,这里更新到搬移之后的restart重新执行。
再次执行resart的时候,肯定不会再出现覆盖的情况了,会执行打开cache的操作,所以下节内容开始分析cache。
restart重新执行的话,肯定会执行wont_overwrite
- wont_overwrite:
- /*
- * If delta is zero, we are running at the address we were linked at.
- * r0 = delta
- * r2 = BSS start
- * r3 = BSS end
- * r4 = kernel execution address (possibly with LSB set)
- * r5 = appended dtb size (0 if not present)
- * r7 = architecture ID
- * r8 = atags pointer
- * r11 = GOT start
- * r12 = GOT end
- * sp = stack pointer
- */
- /* 无论有没有发生搬运,都会执行restart
- * 此时r0的值是链接地址和实际运行地址的差值,如果这个值为0
- * 说明链接地址和运行地址一样
- * r5里面保存的是appended dtb的大小,这里为0 dtb和kernel是分开的
- */
- orrs r1, r0, r5
- beq not_relocated
- /* 获取GOT表的开始和结束的运行地址 */
- add r11, r11, r0
- add r12, r12, r0
- #ifndef CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM
- /*
- * If we're running fully PIC === CONFIG_ZBOOT_ROM = n,
- * we need to fix up pointers into the BSS region.
- * Note that the stack pointer has already been fixed up.
- */
- /* 获取BSS的开始和结束的运行地址 */
- add r2, r2, r0
- add r3, r3, r0
- /*
- * Relocate all entries in the GOT table.
- * Bump bss entries to _edata + dtb size
- */
- /* 获取GOT表里面的条目 */
- 1: ldr r1, [r11, #0] @ relocate entries in the GOT
- /* 将条目的地址改成实际的运行地址 */
- add r1, r1, r0 @ This fixes up C references
- /* 看下面的c语言部分*/
- cmp r1, r2 @ if entry >= bss_start && --- 1
- cmphs r3, r1 @ bss_end > entry
- addhi r1, r1, r5 @ entry += dtb size
- str r1, [r11], #4 @ next entry --- 2
- cmp r11, r12
- blo 1b
- /* C code */
- /* 这里在bss的情况说明got表中有bss中的相关地址?全局变量? */
- if ((r1 >= r2) && (r3 > r1)) { --- 1
- /* 由于dtb大小不为0,所以解压后的内核后面就是dtb
- * 防止bss覆盖dtb,所以bss向后移动dtb的大小
- * 对应的bss内的变量的实际运行地址也要加上dtb的大小
- */
- r1 += r5
- }
- *r11 = r1
- r11 += 4 --- 2
- /* GOT表可以看这个: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77406732 */
- /* bump our bss pointers too */
- /* 更新bss大小 */
- add r2, r2, r5
- add r3, r3, r5
- #else
- /*
- * Relocate entries in the GOT table. We only relocate
- * the entries that are outside the (relocated) BSS region.
- */
- 1: ldr r1, [r11, #0] @ relocate entries in the GOT
- cmp r1, r2 @ entry < bss_start ||
- cmphs r3, r1 @ _end < entry
- addlo r1, r1, r0 @ table. This fixes up the
- str r1, [r11], #4 @ C references.
- cmp r11, r12
- blo 1b
- #endif
- not_relocated: mov r0, #0
- 1: str r0, [r2], #4 @ clear bss
- str r0, [r2], #4
- str r0, [r2], #4
- str r0, [r2], #4
- cmp r2, r3
- blo 1b
- /*
- * Did we skip the cache setup earlier?
- * That is indicated by the LSB in r4.
- * Do it now if so.
- */
- /* 之前没有开启cache的话 这里开启 */
- tst r4, #1
- bic r4, r4, #1
- blne cache_on
-
相关阅读:
HarmonyOS鸿蒙原生应用开发设计- HarmonyOS Sans 字体
Java工程师常见面试题集锦
Linux系统编程_文件编程第1天:打开、写入、读取、关闭文件等编程
CTF中的一些图形密码
白天建筑师,晚上CG艺术家,他将建筑的华丽发挥极致
求先序遍历序列中第(1<=k<=二叉树中结点个数)个结点的值
程序调试技巧
大学生期末大作业之购物网站
【DETR 论文笔记】 End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers
设计模式-开闭原则和迪米特法则
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ldl617/article/details/126935949