-
MySQL索引介绍
索引主要是用来提高数据库的查询效率的,它对指定的列或列的集合生成索引,然后可以通过索引来检索目标数据,就像目录一样,缩小了扫描范围,大大提高了查询效率。
如果不使用索引,MySQL服务器会从第一行开始查询,直到找到相关行,数据表越大,耗费时间就越多。本文将介绍索引的一些基本原理,了解它是如何优化数据库性能的。
简介
MyISAM存储引擎使用三个文件来表示每个表:
- frm文件:格式文件,存储表结构的定义
- MYD文件:数据文件,存储表行数据
- MYI文件:索引文件,存储表上索引
InnoDB存储引擎的存储文件包括两个文件:frm 和 ibd
- frm文件存储表结构定义
- ibd文件存储表的内容,存储数据和索引
MEMORY存储引擎也frm格式文件存储表结构,而数据及索引存储在内存中,因此它的查询速度更快。
MySQL索引是在存储引擎层实现的,因此不同引擎数据库的底层的实现可能不同,列举几种实现索引的数据结构:
- 哈希表:键-值(key-value)方式存储数据,需要注意出现**哈希碰撞(Hash Collisions)**的情况。另外哈希表的 Hash 码不是按顺序存放的,因此哈希索引更适用于等值查询,对于范围查找就不适合了。
- 二叉搜索树:查询的时间复杂度O(log(N)),由于在数据量大的情况下会使用大量的数据块,频繁读取磁盘,导致查询效率变慢。因此实际使用中通常会使用N叉树。
- B树:B树就是一种N叉树,树的高度降低了。每个节点存储Key值和数据。
- B+树:B+树是对B树的改进,数据存储在同一层的叶子节点上,并且按顺序排列,非叶子节点不再存储数据,只存储key的信息。这是目前MySQL索引最常用的数据结构。
- 其他:当然还有其它数据结构也可以用来保存索引,比如有序数组,跳表、LSM 树等。
InnoDB 存储引擎使用的索引数据结构为B+树,InnoDB也是最常用的MySQL数据库引擎,下面来介绍以下B+树索引模型。
B+ 树索引模型
先创建一个使用InnoDB 存储引擎的表departments,主键为id,辅助索引dept_name:
create table departments( id int not null primary key, dept_no char(4) null, dept_name varchar(40) null, unique index dept_name(dept_name)) engine=InnoDB; insert into departments values(2,'d001', 'Marketing'),(5,'d002','Finance'),(6,'d003','Human Resources'),(7,'d004','Production'),(10,'d005','Development'),(12,'d006','Quality Management'),(17,'d007','Sales'),(18,'d008','Research'),(22,'d009','Customer Service');- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
查询数据:
mysql> select * from departments; +----+---------+--------------------+ | id | dept_no | dept_name | +----+---------+--------------------+ | 2 | d001 | Marketing | | 5 | d002 | Finance | | 6 | d003 | Human Resources | | 7 | d004 | Production | | 10 | d005 | Development | | 12 | d006 | Quality Management | | 17 | d007 | Sales | | 18 | d008 | Research | | 22 | d009 | Customer Service | +----+---------+--------------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
查看索引:
mysql> show index from departments; +-------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression | +-------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ | departments | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 9 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL | | departments | 0 | dept_name | 1 | dept_name | A | 9 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | YES | NULL | +-------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.13 sec) mysql> desc departments; +-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | dept_no | char(4) | YES | | NULL | | | dept_name | varchar(40) | YES | UNI | NULL | | +-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
可以看到有两个索引:主键索引id和唯一索引dept_name,每一个索引在 InnoDB 里面对应一棵 B+树。
关于B+树的特性这里就不介绍了,主键索引示意图如下:
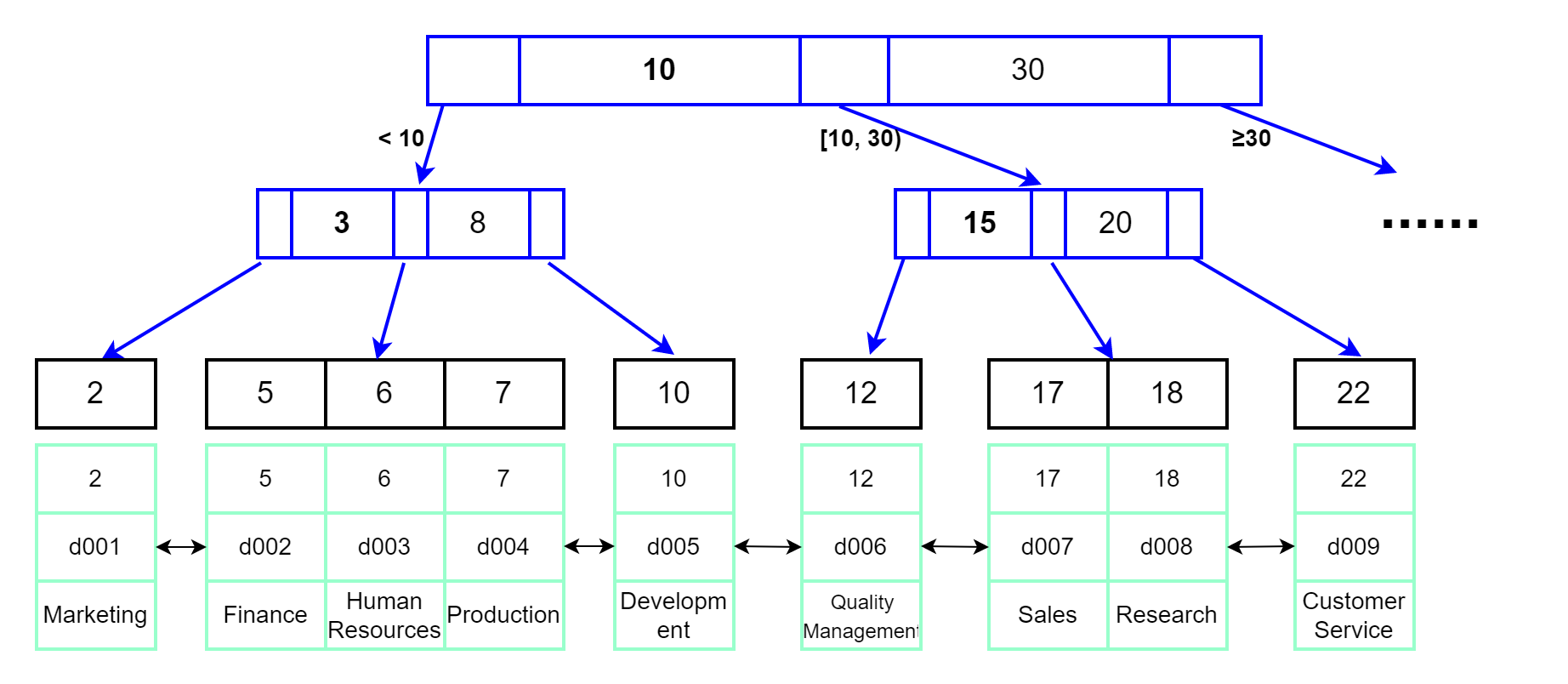
唯一索引dept_name示意图如下:
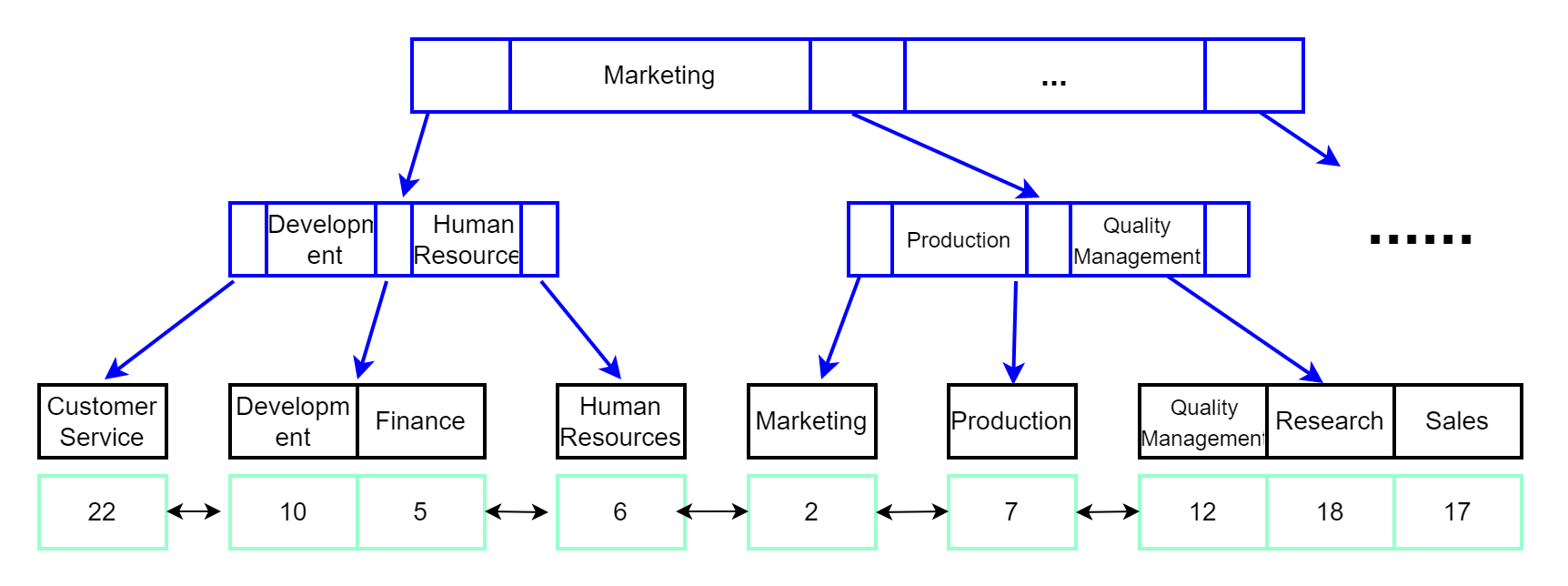
图中的数据页之间通常使用双向链表进行连接,可以减少查询时间,特别是区间查询时。
回表
主键索引就是在主键上添加的索引,它的叶子节点保存了整行数据。
辅助索引是主键之外的索引,也被称为二级索引(secondary index)。InnoDB引擎的辅助索引引用主键作为data域,也就是说,使用辅助索引的需要先搜索当前辅助索引树,得到主键值后,再到主键索引搜索一次,通过主键索引查找到目标数据,这个过程称为回表。因此,在实际使用过程中,如果能使用主键查询就应该优先选择它。
比如通过辅助索引dept_name查询部门名称为Research的dept_no:
select dept_no from departments where dept_name='Research';- 搜索dept_name索引树,得到dept_name为Research的id为18;
- 通过id索引树查询id为18的行记录。
如果知道id,直接使用id查询,效率会更高。
mysql> select dept_no from departments where dept_name='Research'; +---------+ | dept_no | +---------+ | d008 | +---------+ 1 row in set (0.04 sec) mysql> select dept_no from departments where id=18; +---------+ | dept_no | +---------+ | d008 | +---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
聚簇索引和非聚簇索引
上面介绍的是InnoDB存储引擎的主键索引和辅助索引,MyISAM引擎的索引结构与它有一定差异。MyISAM存储引擎使用MYD文件存储表行数据,使用MYI文件存储表上索引。InnoDB存储引擎使用ibd文件存储表数据和索引。
InnoDB引擎的索引和数据是存储在一起的,称为聚簇索引(clustered index)。
MyISAM的索引和数据是分开存储的,这种称为非聚簇索引(unclustered index)。非聚簇索引只存储索引字段和记录所在的位置,通过索引找到记录所在的位置,然后再根据位置去获取记录。因此MyISAM引擎的主键索引和辅助索引在结构上没有什么差别,叶子节点都使用一个地址指向真正的表数据。
聚簇索引的查找效率要比非聚簇索引快,因为聚簇索引查找到索引就查找到了数据位置,而非聚簇索引查找到索引之后,根据记录的数据地址,再去查找数据;
由于MyISM使用非聚簇索引,主键索引和辅助索引树是独立的,因此通过辅助索引查询时不需要访问主键的索引树。
页分裂
虽然聚簇索引查询速度相对更快,但聚簇索引对写入效率影响更大。为了保证B+树中索引的有序性,在进行插入和删除操作的时候需要对索引进行维护。
上面的示意图是3阶B+树,如果要插入一个id为11的记录,直接在10后面插入就可以了。而要插入id为4的记录,就需要挪动后面的数据来空出位置,这个过程称为页分裂。
如果相邻两个页由于删除了数据空出大量空间,通常还会对数据页进行合并。因此删除、插入操作可能会出现大量的索引分裂和合并,严重影响效率。
那么有什么解决方案呢?最好的解决方案就是使用递增主键,这样在插入记录时,不会进行索引分裂,直接追加在后面就可以。因此,选择主键时最好采用自增主键。
联合索引
联合索引是对两个或者更多的列添加索引,B+树中的key值变成了多个,MyISAM和InnoDB引擎限制最多列数为16。
联合索引查询时遵循“最左前缀”原则,即使用 where 条件查询时最左边的为起点索引都能匹配上。所以在创建联合索引时,通常将使用最频繁的列放在最左边。下面看一个示例:
student表数据如下:
mysql> select * from student; +----+------+-----+-----+--------+ | id | name | sex | age | dept | +----+------+-----+-----+--------+ | 1 | 李四 | 男 | 21 | 通信 | | 2 | 张三 | 男 | 21 | 通信 | | 3 | 王二 | 男 | 23 | 计算机 | | 4 | 小花 | 女 | 23 | 计算机 | | 7 | 小王 | 男 | 28 | 通信 | +----+------+-----+-----+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.14 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
添加一个
(name, age)的联合索引:alter table student add index name_age(name,age);mysql> alter table student add index name_age(name,age); Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.30 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> show index from student; +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression | +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ | student | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL | | student | 1 | name_age | 1 | name | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL | | student | 1 | name_age | 2 | age | A | 4 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL | +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+ 3 rows in set (0.08 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
查询时如果想要使用到创建的联合索引,可以使用
name、(name,age)或者(age,name)这几种组合:select * from student where name='张三'; select * from student where name='张三' and age=21; select * from student where age=21 and name='张三';- 1
- 2
- 3
mysql> explain select * from student where name='张三'; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | student | NULL | ref | name_age | name_age | 32 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from student where name='张三' and age=21; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | student | NULL | ref | name_age | name_age | 33 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from student where age=21 and name='张三'; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | student | NULL | ref | name_age | name_age | 33 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from student where age=21; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | student | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 25.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
可以看到
select * from student where age=21;没有使用到索引。语句
select * from student where age=21 and name='张三';也能使用到索引的原因是SQL查询时分析器会对查询语句进行优化,选择效率最高的索引查询顺序。(SQL查询顺序可参考MySQL基础架构:SQL查询语句执行过程)索引语法
下面来介绍一些常用的MySQL索引语法。
创建索引
建表时创建索引:
CREATE TABLE tbl_name( id int not null primary key, name varchar(40) null, age int null, INDEX index_name(字段名)) engine=InnoDB;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
新建索引:
CREATE INDEX index_name ON tbl_name(字段名);- 1
修改表结构新建索引:
ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD INDEX index_name ON 字段名;- 1
创建唯一索引:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON tbl_name(字段名); ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD UNIQUE index_name ON 字段名; -- 建表时指定 CREATE TABLE tbl_name( id int not null primary key, name varchar(40) null, age int null, UNIQUE INDEX index_name(字段名)) engine=InnoDB;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
注意唯一索引索引列的值必须唯一,允许为NULL。
创建主键时会自动创建主键索引,一张表只能有一个主键索引,不允许重复,不允许为 NULL;另外,加有 unique 约束的字段上会自动创建索引。
创建组合索引:
CREATE INDEX index_name ON tbl_name(字段1,字段2); ALTER TABLE tbl_name ADD INDEX index_name(字段1,字段2); -- 建表时指定 INDEX index_name(字段1,字段2)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
显示索引
SHOW INDEX FROM tbl_name;- 1
删除索引
ALTER TABLE tbl_name DROP INDEX index_name; DROP INDEX index_name ON tbl_name;- 1
- 2
不能删除主键索引。
重命名索引
ALTER TABLE tbl_name RENAME INDEX index_name TO new_index_name;- 1
总结
本文简单介绍了常用的B+树索引模型,B+树只有叶子节点才会存储数据,非叶子节点只存储键值,最底层的叶子节点形成了一个双向有序链表。另外要注意聚簇索引和非聚簇索引的区别,它们在数据存储方式上有差异。
联合索引查询时需要遵循“最左前缀”原则,因此在创建和使用联合索引时需要考虑到这一点。
参考:
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/innodb-limits.html
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/myisam-storage-engine.html
--THE END-- 一切都稍纵即逝,一切又都亘古长存。——[英]凯特·阿特金森《生命不息》
-
相关阅读:
算法竞赛进阶指南:奇怪的汉诺塔(Python)
查看已退出docker容器的日志
imu测试--UDP、PTP
如何测试和调试Android应用程序
【跨境电商卖家】Instagram营销初学者指南(一):重要性、优势
Window MongoDB安装
SpringCloud-nacos基础
MySQL和Navicat的安装与配置
配置鼠标右键edit with notepad
LayaBox---TypeScript---泛型
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u010698107/article/details/126693685
