-
PCL RANSAC拟合球面和平面
一、概述
PCL中 RANSAC拟合球面和平面的简单使用案例。
二、代码
random_sample_consensus.cpp#include#include #include #include // for PointCloud #include // for copyPointCloud #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std::chrono_literals; pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr simpleVis (pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr cloud) { // -------------------------------------------- // -----Open 3D viewer and add point cloud----- // -------------------------------------------- pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer ("3D Viewer")); viewer->setBackgroundColor (0, 0, 0); viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud, "sample cloud"); viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "sample cloud"); //viewer->addCoordinateSystem (1.0, "global"); viewer->initCameraParameters (); return (viewer); } int main(int argc, char** argv) { // initialize PointClouds pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr final (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // populate our PointCloud with points cloud->width = 500; cloud->height = 1; cloud->is_dense = false; cloud->points.resize (cloud->width * cloud->height); for (pcl::index_t i = 0; i < static_cast<pcl::index_t>(cloud->size ()); ++i) { if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-s") >= 0 || pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= 0) { (*cloud)[i].x = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); (*cloud)[i].y = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); if (i % 5 == 0) (*cloud)[i].z = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); else if(i % 2 == 0) (*cloud)[i].z = sqrt( 1 - ((*cloud)[i].x * (*cloud)[i].x) - ((*cloud)[i].y * (*cloud)[i].y)); else (*cloud)[i].z = - sqrt( 1 - ((*cloud)[i].x * (*cloud)[i].x) - ((*cloud)[i].y * (*cloud)[i].y)); } else { (*cloud)[i].x = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); (*cloud)[i].y = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); if( i % 2 == 0) (*cloud)[i].z = 1024 * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); else (*cloud)[i].z = -1 * ((*cloud)[i].x + (*cloud)[i].y); } } std::vector<int> inliers; // created RandomSampleConsensus object and compute the appropriated model pcl::SampleConsensusModelSphere<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr model_s(new pcl::SampleConsensusModelSphere<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud)); pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr model_p (new pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud)); if(pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-f") >= 0) { pcl::RandomSampleConsensus<pcl::PointXYZ> ransac (model_p); ransac.setDistanceThreshold (.01); ransac.computeModel(); ransac.getInliers(inliers); } else if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= 0 ) { pcl::RandomSampleConsensus<pcl::PointXYZ> ransac (model_s); ransac.setDistanceThreshold (.01); ransac.computeModel(); ransac.getInliers(inliers); } // copies all inliers of the model computed to another PointCloud pcl::copyPointCloud (*cloud, inliers, *final); // creates the visualization object and adds either our original cloud or all of the inliers // depending on the command line arguments specified. pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer; if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-f") >= 0 || pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= 0) viewer = simpleVis(final); else viewer = simpleVis(cloud); while (!viewer->wasStopped ()) { viewer->spinOnce (100); std::this_thread::sleep_for(100ms); } return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
三、结果
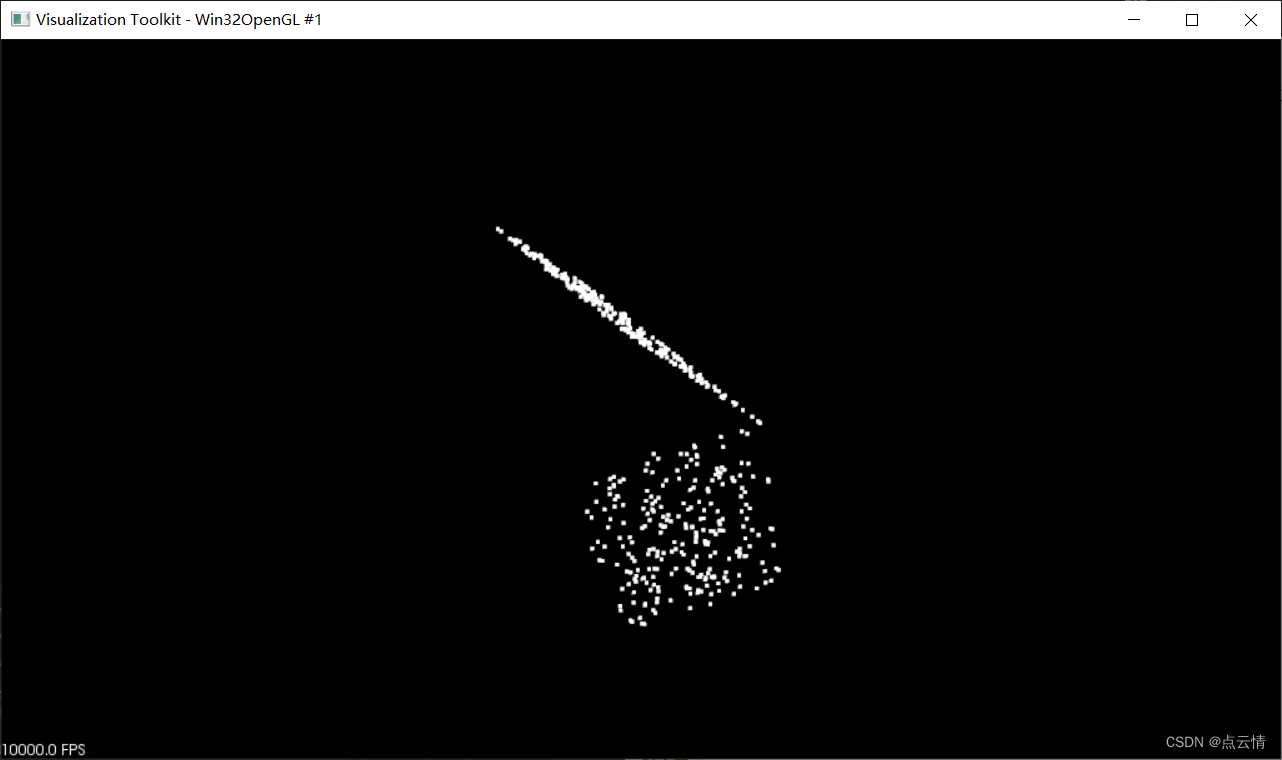
-
相关阅读:
nginx+lua+redis实现灰度发布
Java并发—ReetrantLock详解及应用
armv8/armv9/aarch64/arm64/A64/架构/IP你不知道的那些事
Spring基础元注解@Target、@Retention、@Documented、@Inherited
【分享贴】VUCA环境下实现价值交付,PMO亟待转型
LabVIEW通讯-GPIB
nginx的负载均衡包括哪些策略配置?Java如何结合nginx实现负载均衡?
Go-知识map
Vue操作数组的几种常用方法(map、filter、forEach、find 和 findIndex 、some 和 every)
Portraiture3.5升级版磨皮滤镜插件使用效果教程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51204289/article/details/126915570