-
关于模糊理论及简单应用
关于模糊理论及简单应用
1.开始
最近导师让我了解一下模糊理论,思考能不能结合现有技术实现创新点.这篇博客主要记录一下这两天对模糊理论的学习,以及做的一个小demo,希望如果有研究相关方面的大佬能留言相互交流学习.
之前用模糊c均值聚类的时候了解过scikit-fuzzy,这次发现它更大的作用是构建模糊系统,因此以它为主要工具来实现下面的内容
安装:pip install scikit-fuzzy2.正文
2.1 关于模糊理论应用
流程:
- 输入,某个连续逻辑值
- 选择合适的隶属度函数
- 制定模糊规则,根据隶属度函数选择成员的隶属程度,构建模糊集
- 去模糊化得到结果
一些小知识,在模糊理论中,也存在着类似与或操作,分别对应取小,取大.类似的,在模糊控制矩阵中,矩阵乘法中元素乘对应了取小操作,元素加对应取大操作.
下面来看看常规的隶属度函数
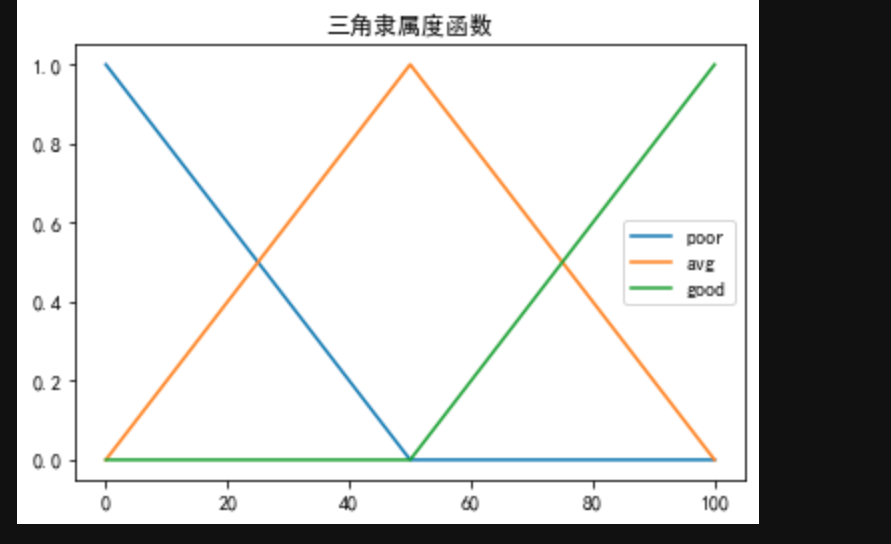
以三角隶属函数为例
曲线形状由输入x,以及a,b,c确定,函数表达式如下
f ( x , a , b , c ) = { 0 x ≤ a x − a b − a a ≤ x ≤ b c − x c − b b ≤ x ≤ c 0 x ≥ c f(x,a,b,c)={0x≤ax−ab−aa≤x≤bc−xc−bb≤x≤c0x≥cf(x,a,b,c)=⎩ ⎨ ⎧0b−ax−ac−bc−x0x≤aa≤x≤bb≤x≤cx≥c也就是中间输入值b代表波峰,而a,c代表三角的两个底,实际运用中可以调用skfuzzy.trimf(),代码如下

import numpy as np import skfuzzy as fuzz import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['font.family']='simhei' x=np.arange(0,101,1) poor=fuzz.trimf(x,[0,0,50]) avg=fuzz.trimf(x,[0,50,100]) good=fuzz.trimf(x,[50,100,100]) plt.figure() plt.title("三角隶属度函数") plt.plot(x,poor,label="poor") plt.plot(x,avg,label="avg") plt.plot(x,good,label="good") plt.legend() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
当然还有很多其他形式隶属函数可以参考这个链接隶属函数,相应的在skfuzzy中都有实现
2.2 小例子
熟悉简单的skfuzzy构建接近生活事件的模糊控制器
假设下面这样的场景,我们希望构建一套模糊控制系统,通过室外温度和风的大小来判断穿几件衣服
- 室外温度的范围设置为0-40度,虽然今年夏天超过40度在我们这边很平常,但是我们这里还是以40度为最高界限
- 风的大小范围0-10,这里不是风的级数,而是我自己构建的大小.模糊理论奥妙就在于不需要精确的逻辑值,可以模糊描述.比如小风我设置为1-3,然后有点大的风等等,都是比较抽象的描述,但是经过隶属函数可以看出,往往某个值是在多个状态叠加.
- 衣服的件数我设置为1-6(不能一件衣服不穿),如果按照本人自己的爱好,我最多也只穿三件.不过考虑到实际还是设一个大点的范围
后续的模糊规则我写到那里再来设置,首先创建这几个范围
import numpy as np import skfuzzy as fuzz import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['font.family']='simhei' x_temp=np.arange(0,41,1) x_wind=np.arange(0,11,1) x_clothes=np.arange(1,7,1) x_temp,x_wind,x_clothes- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
模糊规则与隶属度
-
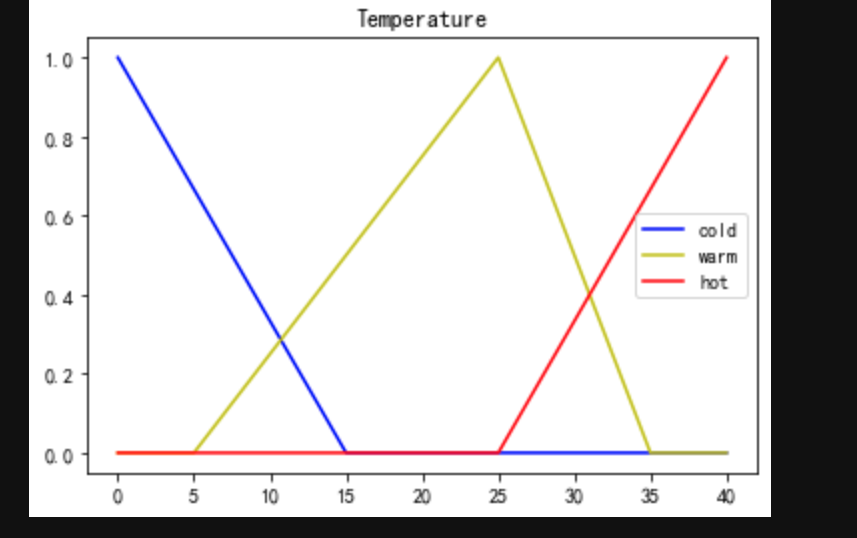
对于温度,寒冷,温暖,炎热
-
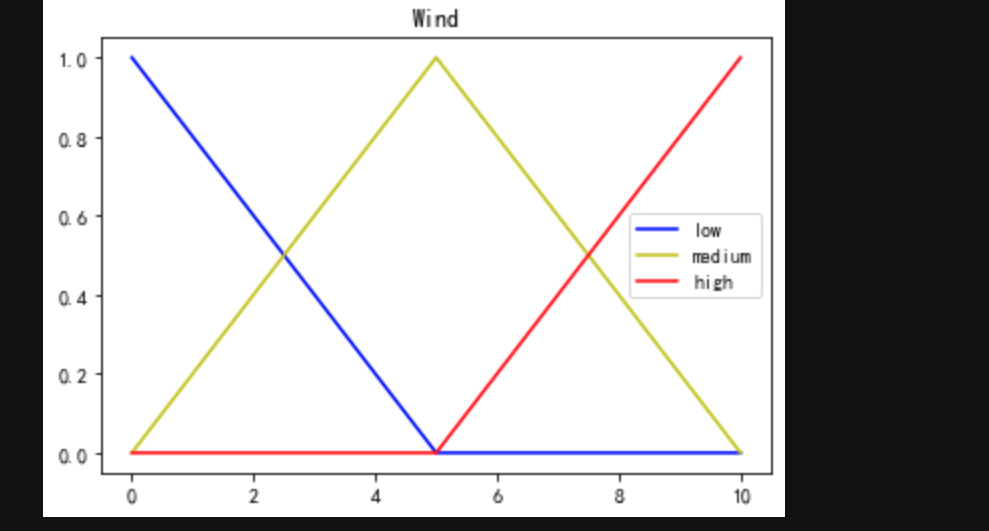
对于风的大小,小风,中等风,大风
-
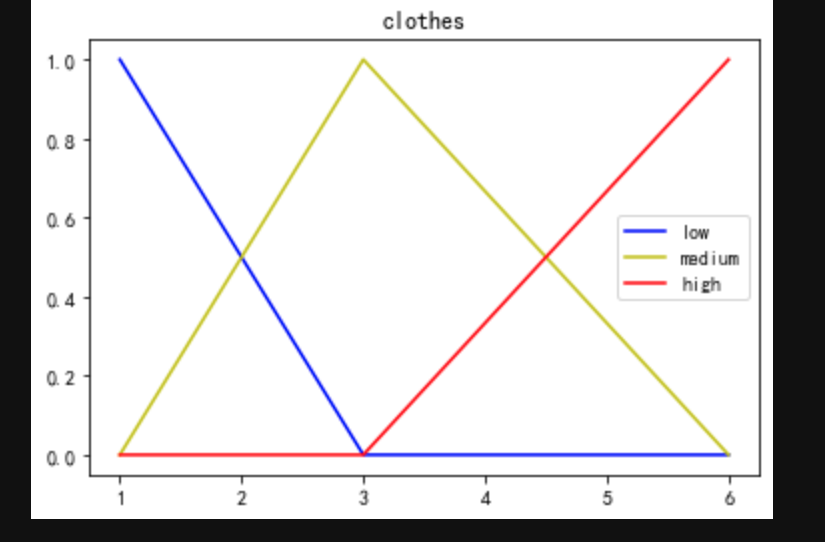
对于衣服件数类似,分为少,合适,多三种
-
当风小或者温度高的时候我们穿很少的衣服
-
当温度中等,比较温暖的时候我们穿得稍微多点
-
当温度很低或者风很大的时候,那我们就需要穿很多衣服了
应用这三个模糊规则,去隶属度函数中找成员
# 将三角隶属度函数对各个量进行隶属度映射 temp_cold=fuzz.trimf(x_temp,[0,0,15]) temp_warm=fuzz.trimf(x_temp,[5,25,35]) temp_hot=fuzz.trimf(x_temp,[25,40,40]) plt.figure() plt.title("Temperature") plt.plot(x_temp,temp_cold,'b',label='cold') plt.plot(x_temp,temp_warm,'y',label='warm') plt.plot(x_temp,temp_hot,'r',label='hot') plt.legend() plt.show() wind_low=fuzz.trimf(x_wind,[0,0,5]) wind_medium=fuzz.trimf(x_wind,[0,5,10]) wind_high=fuzz.trimf(x_wind,[5,10,10]) plt.figure() plt.title("Wind") plt.plot(x_wind,wind_low,'b',label='low') plt.plot(x_wind,wind_medium,'y',label='medium') plt.plot(x_wind,wind_high,'r',label='high') plt.legend() plt.show() cloth_low=fuzz.trimf(x_clothes,[1,1,3]) cloth_medium=fuzz.trimf(x_clothes,[1,3,6]) cloth_high=fuzz.trimf(x_clothes,[3,6,6]) plt.figure() plt.title("clothes") plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_low,'b',label='low') plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_medium,'y',label='medium') plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_high,'r',label='high') plt.legend() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
设置场景:比如今天,外面40度,但是风很小,设置temp=40,wind=2然后进行测试
temp_level_cold=fuzz.interp_membership(x_temp,temp_cold,40) temp_level_warm=fuzz.interp_membership(x_temp,temp_warm,40) temp_level_hot=fuzz.interp_membership(x_temp,temp_hot,40) wind_level_low=fuzz.interp_membership(x_wind,wind_low,2) wind_level_medium=fuzz.interp_membership(x_wind,wind_medium,2) wind_level_high=fuzz.interp_membership(x_wind,wind_high,2) # 之前说过,或运算取最大值 rule1=np.fmax(temp_level_hot,wind_level_low) cloth_res_low=np.fmin(rule1,cloth_low) cloth_res_medium=np.fmin(temp_level_warm,wind_level_medium) rule2=np.fmax(temp_level_cold,wind_level_high) cloth_res_high=np.fmin(rule2,cloth_high) clothes=np.zeros_like(x_clothes) # vis plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3)) plt.title("结果") plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_low,'b') plt.fill_between(x_clothes,0,cloth_res_low) plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_medium,'g') plt.fill_between(x_clothes,0,cloth_res_medium) plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_high,'r') plt.fill_between(x_clothes,0,cloth_res_high) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
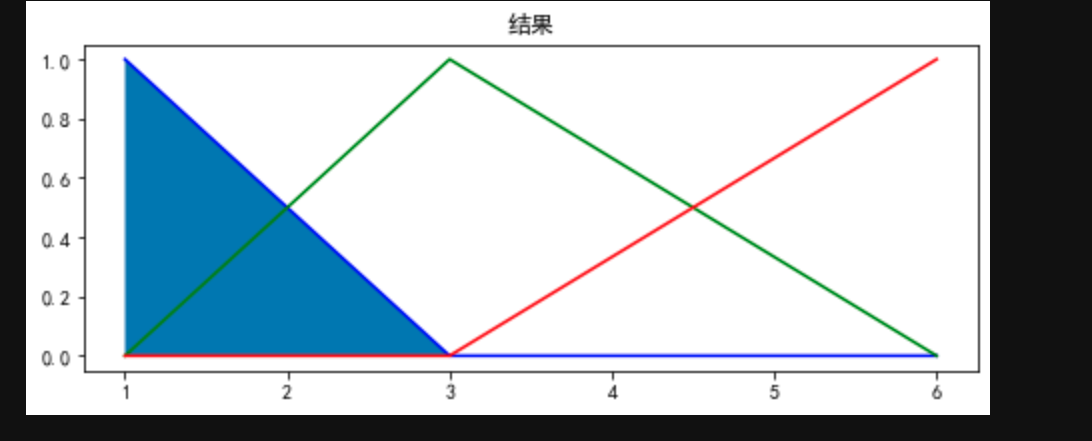
然后对应用规则后的结果去模糊,得到我们想要的值(将模糊值转为具体值)
# 去模糊 aggregated=np.fmax(cloth_res_low,np.fmax(cloth_res_medium,cloth_res_high)) # 去模糊方法:centroid,bisector,mom,som,lom cloth=fuzz.defuzz(x_clothes,aggregated,'mom') cloth_res=fuzz.interp_membership(x_clothes,aggregated,cloth) plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3)) plt.title(f"去模糊化结果cloth:{cloth}") plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_low,'b') plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_medium,'g') plt.plot(x_clothes,cloth_high,'r') plt.fill_between(x_clothes,0,aggregated,facecolor='orange') plt.plot([cloth,cloth],[0,cloth_res],'k') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
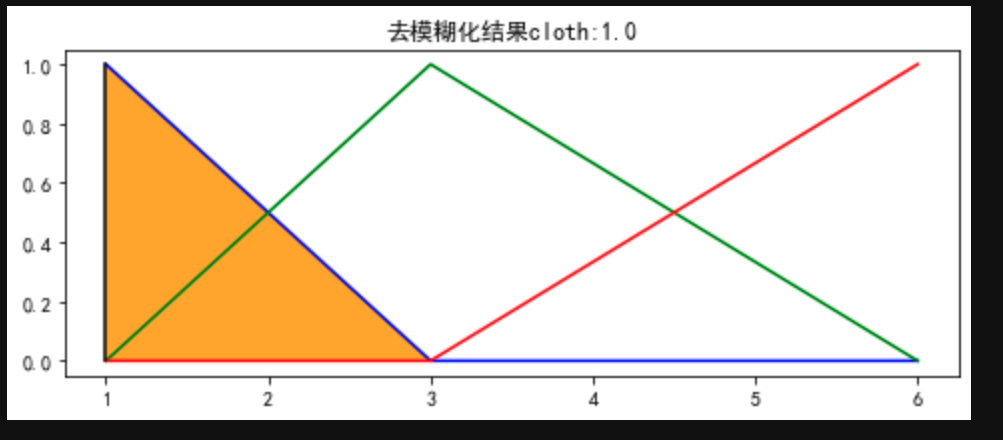
去模糊化方法有很多,我用的是取最大隶属的方法,下面是其他方法及介绍
- centroid 面积重心法
- bisector 面积等分法
- mom 最大隶属度平均法
- som 最大隶属度取最小法
- lom 最大隶属度取最大法
2.3 更简单的创建模糊系统
如果觉得我们一点点编辑规则,然后根据隶属函数找成员变量,再去模糊化这套流程太复杂,也可以试试下面简单的封装方法.
还是以上面的案例为例子import numpy as np import skfuzzy as fuzz from skfuzzy import control as ctrl temp=ctrl.Antecedent(np.arange(0,41,1),'temp') wind=ctrl.Antecedent(np.arange(0,11,1),'wind') clothes=ctrl.Consequent(np.arange(1,7,1),'clothes') # 自动找成员函数,分为三类 temp.automf(3) wind.automf(3) # 设置目标的模糊规则 clothes['low']=fuzz.trimf(clothes.universe,[1,1,3]) clothes['medium']=fuzz.trimf(clothes.universe,[1,3,6]) clothes['high']=fuzz.trimf(clothes.universe,[3,6,6]) rule1 = ctrl.Rule(temp['good'] | wind['poor'], clothes['low']) rule2 = ctrl.Rule(temp['average'], clothes['medium']) rule3 = ctrl.Rule(temp['poor'] | wind['good'], clothes['high']) rule1.view() rule2.view()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
# 创建控制系统,应用编写好的规则 cloth_ctrl=ctrl.ControlSystem([rule1,rule2,rule3]) # 创建控制仿真器 cloth_num=ctrl.ControlSystemSimulation(cloth_ctrl) # 输入测试数据 cloth_num.input['temp']=40 cloth_num.input['wind']=2 # 设置去模糊方法 clothes.defuzzify_method='mom' # 计算结果 cloth_num.compute() cloth_num_res=cloth_num.output['clothes'] print(f"The result of clothes: {cloth_num_res}") # 可视化 clothes.view(sim=cloth_num)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
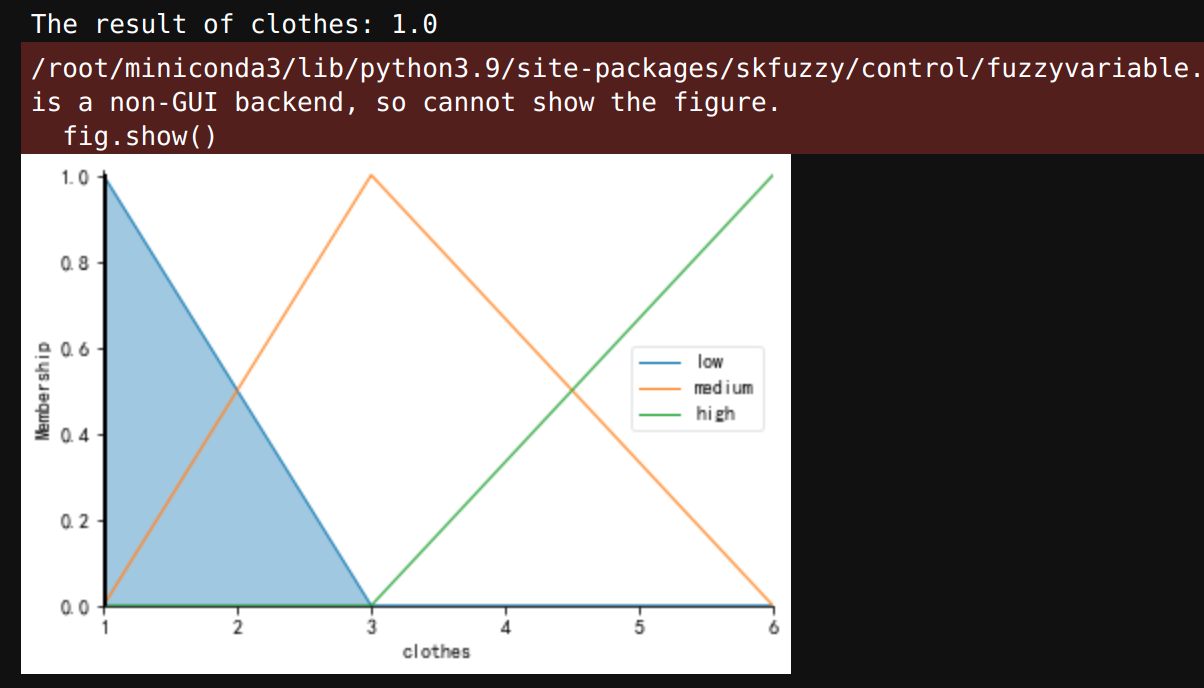
3. 总结
模糊理论可以将输入的实际中的逻辑值转换为一种日常中的抽象化表示,根据隶属度区分成员,设置好模糊规则构建模糊集合,最终去模糊化得到结果.创新点可以在隶属度函数上改进,模糊最大的好处是不用进行训练,而是抽象化的包含隶属.如果用机器学习等方法,也可以实现上面案例的功能,但是需要构建训练数据.很多实际问题很难或者不太好找到真实表示的数据,毕竟生活中的抽象描述占主要部分.
-
相关阅读:
Python 工匠 第三章 容器类型
【文件I/O】标准IO:库函数
较真儿学源码系列-PowerJob启动流程源码分析
如何将中文翻译成荷兰语?
uniapp da-tree插件 代码和结构分析
K8s 之 ApiServer 组件风险
Java 使用Velocity引擎生成代码
Tomcat - mac - 部署web项目
Linux 最常用命令
OWASP-TOP10漏洞-注入漏洞
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/shelgi/article/details/126908418
