-
非零基础自学Java (老师:韩顺平) 第12章 异常 - Exception
非零基础自学Java (老师:韩顺平)
✈【【零基础 快速学Java】韩顺平 零基础30天学会Java】
第12章 异常 - Exception
文章目录
12.1 举个栗子
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: Exception01 * date: 2022/9/4 14:25 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class Exception01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; int res = num1 / num2; System.out.println("程序继续运行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
运行结果

因为我们把0作除数了
12.2 解决方案 - 异常捕获
对异常进行捕获,保证程序可以继续运行
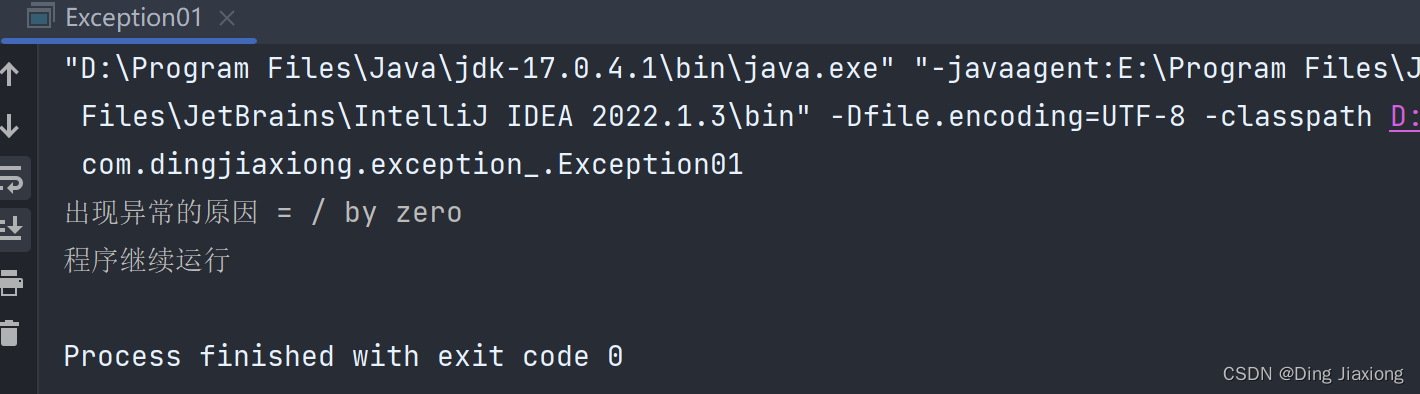
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: Exception01 * date: 2022/9/4 14:25 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class Exception01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; try { int res = num1 / num2; }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("出现异常的原因 = " + e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("程序继续运行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
运行结果
12.3 异常介绍
12.3.1 基本概念
Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称为“异常”。
(开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常)
12.3.2 执行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两大类
- Error(错误):Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。比如: StackOverflowError[栈溢出]和OOM(out of memory). Error是严重错误,程序会崩溃。
- Exception:其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。例如空指针访问,试图读取不存在的文件,网络连接中断等等,Exception 分为两大类:运行时异常[程序运行时,发生的异常]和编译时异常[编程时,编译器检查出的异常]。
12.4 异常体系图一览
12.4.1 异常体系图
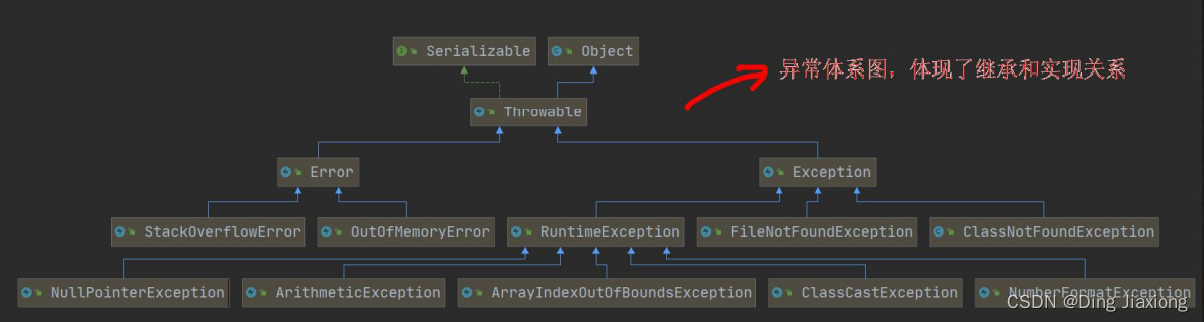
12.4.2 异常体系图小结
- 异常分为两大类,运行时异常和编译时异常.
- 运行时异常,编译器检查不出来。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该避免其出现的异常。java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子类都是运行时异常
- 对于运行时异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响
- 编译时异常,是编译器要求必须处置的异常。
12.5 常见的运行时异常
12.5.1 常见的运行时异常包括
- NullPointerException : 空指针异常
- ArithmeticException :数学运算异常
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException : 数组下标越界异常
- ClassCastException : 类型转换异常
- NumberFormatException : 数字格式不正确异常
12.5.2 常见的运行时异常举栗子
【NullPointerException 空指针异常】
当应用程序试图在需要对象的地方使用 null 时,抛出该异常
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: NullPointerException_ * date: 2022/9/4 14:33 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class NullPointerException_ { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = null; System.out.println(name.length()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
运行结果

【ArithmeticException 数学运算异常】
当出现异常的运算条件时,抛出此异常
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: NumberFormatException_ * date: 2022/9/4 14:34 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class NumberFormatException_ { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "韩老师666"; int num = Integer.parseInt(name); System.out.println(num); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行结果

【ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常】
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_ * date: 2022/9/4 14:35 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_ { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1 ,2 ,4}; for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行结果

【ClassCastException 类型转换异常】
当试图将对象强制转换为不是实例的子类时,抛出该异常
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: ClassCastException_ * date: 2022/9/4 14:37 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class ClassCastException_ { public static void main(String[] args) { A b = new B(); //向上转型 B b2 = (B) b; //向下转型 C c2 = (C) b; } } class A { } class B extends A { } class C extends A { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
运行结果

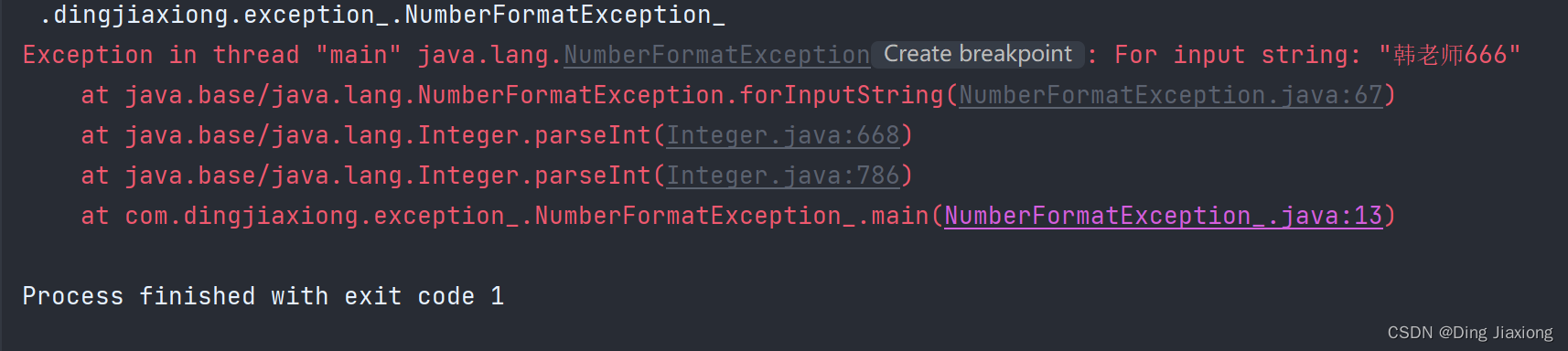
【NumberFormatException 数字格式不正确异常】
当应用程序试图将字符串转换成一种数值类型,但该字符串不能转换为适当格式时,抛出该异常
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: NumberFormatException_ * date: 2022/9/4 14:34 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class NumberFormatException_ { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "韩老师666"; int num = Integer.parseInt(name); System.out.println(num); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
运行结果
12.6 编译异常
12.6.1 介绍
编译异常是指在编译期间,就必须处理的异常,否则代码不能通过编译。
12.6.2 常见的编译异常
- SQLException//操作数据库时,查询表可能发生异常
- IOException//操作文件时,发生的异常
- FileNotFoundException //当操作一个不存在的文件时,发生异常
- ClassNotFoundException//加载类,而该类不存在时,异常
- EOFException//操作文件,到文件未尾,发生异常
- lllegalArguementException//参数异常
12.6.3 案例说明
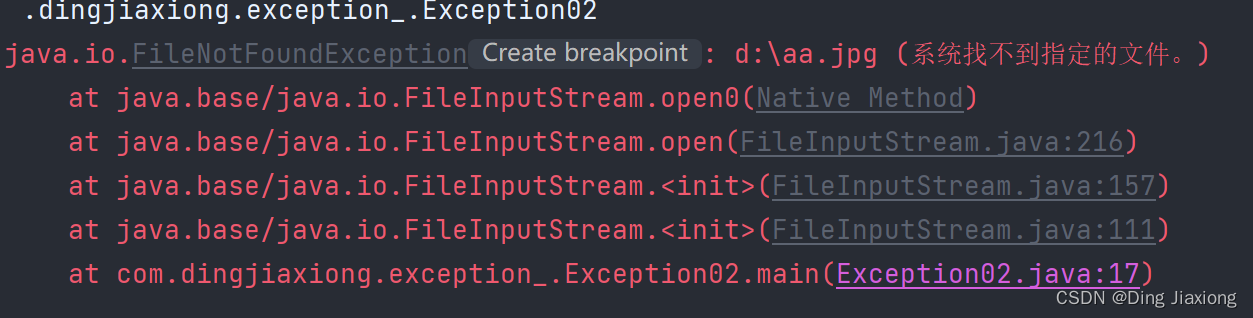
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * ClassName: Exception02 * date: 2022/9/4 14:44 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class Exception02 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileInputStream fis; fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.jpg"); int len; while ((len = fis.read()) != -1){ System.out.println(len); } fis.close(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
运行结果
12.8 异常处理
12.8.1 基本介绍
异常处理就是当异常发生时,对异常处理的方式。
12.8.2 异常处理的方式
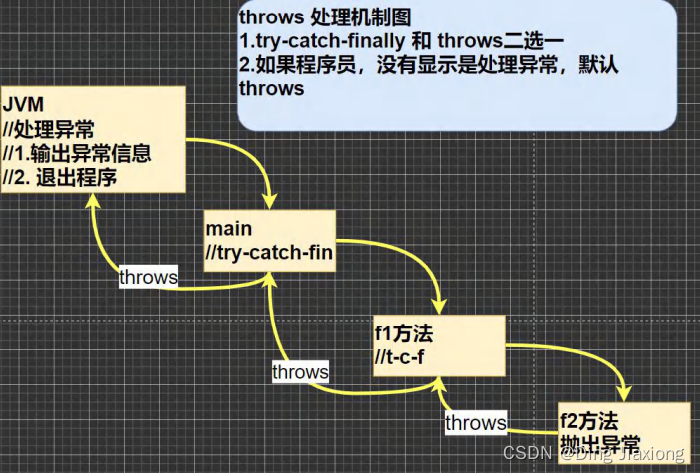
- try-catch-finally
程序员在代码中捕获发生的异常,自行处理 - throws
将发生的异常抛出,交给调用者(方法)来处理,最顶级的处理者就是JVM
12.8.3 示意图

12.9 try-catch异常处理
12.9.1 try-catch方式处理异常说明
Java提供try和catch块来处理异常。
try块用于包含可能出错的代码。
catch块用于处理try块中发生的异常。
可以根据需要在程序中有多个try…catch块。
【基本语法】
try{ //可疑代码 //将异常生成对应的异常对象,传递给catch块 }catch(异常){ //对异常进行处理 } //如果没有finally,语法可以通过- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
12.9.2 try-catch 方式处理异常-快速入门
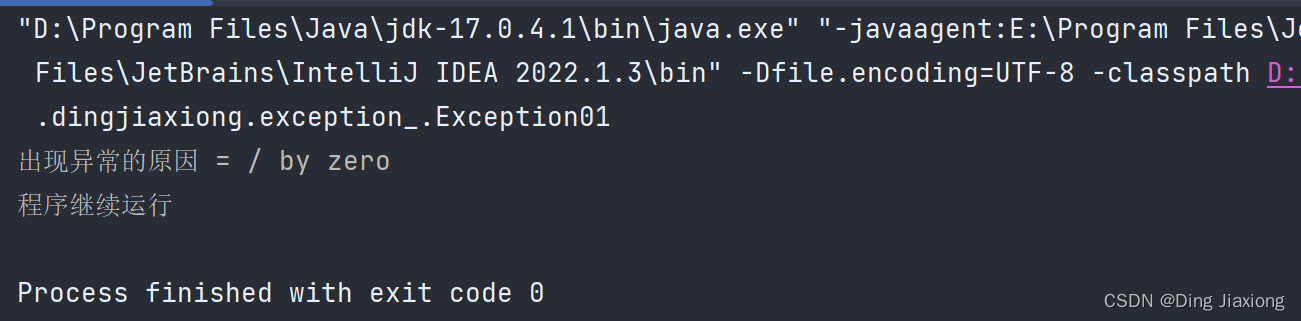
package com.dingjiaxiong.exception_; /** * ClassName: Exception01 * date: 2022/9/4 14:25 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class Exception01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 0; try { int res = num1 / num2; }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("出现异常的原因 = " + e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("程序继续运行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
运行结果
12.9.3 try - catch 方式处理异常 - 注意事项
- 如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到catch块.
- 如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行try的代码块,不会进入到catch.
- 如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finally {}
try{ //可疑代码 //将异常生成对应的异常对象,传递给catch块 }catch(异常){ //对异常进行处理 }finally{ //释放资源等 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
【举个栗子】
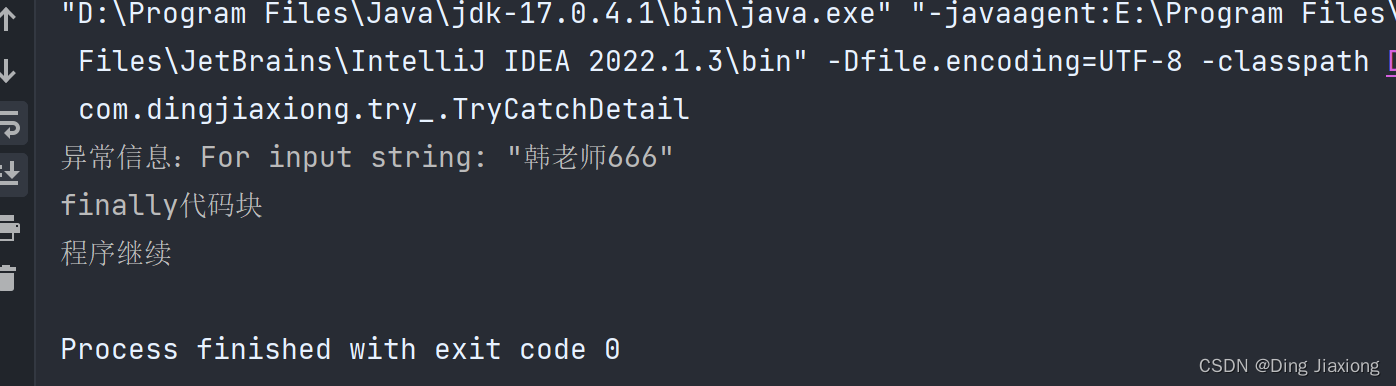
package com.dingjiaxiong.try_; import com.dingjiaxiong.exception_.NumberFormatException_; /** * ClassName: TryCatchDetail * date: 2022/9/4 14:54 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class TryCatchDetail { public static void main(String[] args) { try { String str = "韩老师666"; int a = Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println("数字 : " + a); }catch (NumberFormatException e){ System.out.println("异常信息:" + e.getMessage()); }finally { System.out.println("finally代码块"); } System.out.println("程序继续"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
运行结果
【可以有多个catch语句,捕获不同的异常(进行不同的业务处理)】
要求父类异常在后,子类异常在前,比如(Exception在后,NullPointerException在前),如果发生异常,只会匹配一个catch
【举个栗子】
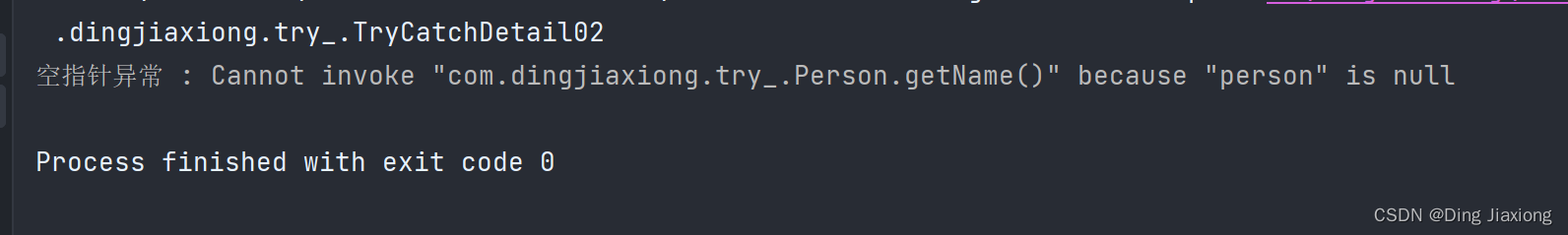
package com.dingjiaxiong.try_; import com.dingjiaxiong.exception_.NullPointerException_; import com.dingjiaxiong.exception_.NumberFormatException_; /** * ClassName: TryCatchDetail02 * date: 2022/9/4 14:56 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class TryCatchDetail02 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Person person = new Person(); person = null; System.out.println(person.getName()); //NullPointerException int n1 = 10; int n2 = 0; int res = n1 / n2; //ArithmeticException }catch (NullPointerException e){ System.out.println("空指针异常 : " + e.getMessage()); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("算术异常 : " + e.getMessage()); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } finally { } } } class Person{ private String name = "Jack"; public String getName() { return name; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
运行结果
【可以进行try-finally配合使用,这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,都必须执行某个业务逻辑】
package com.dingjiaxiong.try_; /** * ClassName: TryCatchDetail03 * date: 2022/9/4 15:04 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class TryCatchDetail03 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int n1 = 10; int n2 = 0; System.out.println(n1 / n2); }finally { System.out.println("执行了finally..."); } System.out.println("程序继续执行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行结果

12.9.5 try - catch -finally执行顺序小结
- 如果没有出现异常,则执行try块中所有语句,不执行catch块中语句,如果有finally,最后还需要执行finally里面的语句
- 如果出现异常,则try块中异常发生后,try块剩下的语句不再执行。将执行catch块中的语句,如果有finally,最后还需要执行finally里面的语句!
12.10 throws异常处理
12.10.1 基本介绍
如果一个方法(中的语句执行时)可能生成某种异常,但是并不能确定如何处理这种异常,则此方法应显示地声明抛出异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理。
在方法声明中用throws语句可以声明抛出异常的列表,throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类。
12.10.2 快速入门案例
举个栗子
package com.dingjiaxiong.throws_; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; /** * ClassName: Throws01 * date: 2022/9/4 15:11 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class Throws01 { public static void main(String[] args) { } public void f2() throws FileNotFoundException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.txt"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
读文件的操作可能产生FileNotFoundException类型的异常
12.10.3 注意事项和使用细节
- 对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如try-catch或者throws
- 对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理
- 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常的类型的子类型
- 在throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch,就相当于处理异常,就可以不必throws
【举个栗子】
package com.dingjiaxiong.throws_; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PipedInputStream; /** * ClassName: ThrowsDetail * date: 2022/9/4 15:13 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class ThrowsDetail { public static void main(String[] args) { f2(); } public static void f2(){ //1.对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws //2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是 throws 的方式处理 int n1 = 10; int n2 = 0; double res = n1 / n2; } public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException { //f3()抛出的是一个编译异常,f1就必须要处理 f3(); } public static void f3() throws FileNotFoundException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://a.txt"); } public static void f4(){ //f4之所以不用处理f5的异常,是因为f5抛出的是一个运行异常,有默认处理机制 f5(); } public static void f5() throws ArithmeticException{ } } class Father{ //父类 public void method() throws RuntimeException{} } //子类重写父类方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法 //所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常类型的子类型 class Son extends Father{ //子类 @Override public void method() throws ArithmeticException{ } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
运行结果

12.11 自定义异常
12.11.1 基本概念
当程序中出现了某些“错误”,但该错误信息并没有在Throwable子类中描述处理,这个时候可以自己设计异常类,用于描述该错误信息。
12.11.2 自定义异常的步骤
-
定义类:自定义异常类名(程序员自己写)继承Exception或RuntimeException
-
如果继承Exception,属于编译异常
-
如果继承RuntimeException,属于运行异常(一般来说,继承RuntimeException)
12.11.3 自定义异常举个栗子
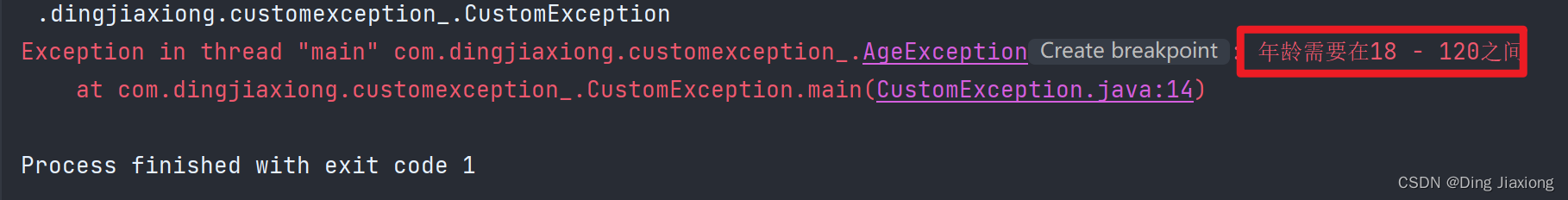
package com.dingjiaxiong.customexception_; /** * ClassName: CustomException * date: 2022/9/4 15:22 * * @author DingJiaxiong */ public class CustomException { public static void main(String[] args) { int age = 180; if (!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)){ throw new AgeException("年龄需要在18 - 120之间"); } System.out.println("你的年龄范围正确"); } } class AgeException extends RuntimeException{ public AgeException(String message){ super(message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
运行结果
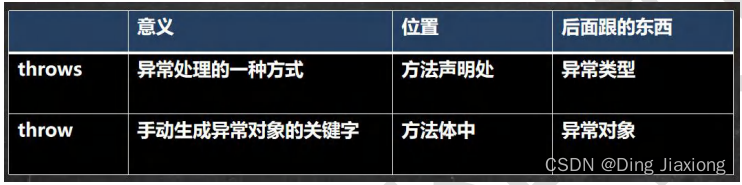
12.12 throw 和 throws 的区别
-
相关阅读:
01- ROS初识
【Spring】Spring学习入门案例
24.Semaphore的作用和原理
推荐系统中deepfm算法的pytorch实现
中国水稻行业供需现状发展趋势分析 国稻种芯百团计划行动
Sentinel-1主动微波数据下载
反向代理原理
JavaScript基础 事件处理一 事件处理方式和事件流(事件冒泡和事件捕获)
晶振在单片机中扮演着什么角色?晶振坏了单片机还能运行程序吗?
WhatsApp 群发了解这些能事半功倍!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44226181/article/details/126913735
