-
springboot原理初探
前言
- 本文是作者的入门笔记,学习狂射说,其中的主要知识,借鉴自狂神的课堂笔记。
- 本文章仅供学习和参考使用,没有任何商业的用途。如果对原作者造成损失,希望大家及时通知作者,我一定会及时处理。
- 虽然,学习的是老的课程,但是本质还是不变的,然后我是用的是比较新的东西,在组织博客,相当于再学习一遍
运行原理探究
起源·pom.xml
父依赖:主要是管理项目的资源过滤及插件
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> <version>2.7.3version> <relativePath/> parent>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
点进spring-boot-starter-parent,发现还有一个父依赖
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId> <version>2.7.3version> parent>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
点进spring-boot-dependencies:真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot的版本控制中心
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId> <version>2.7.3version>- 1
- 2
- 3

- 结论
- 导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了。
启动器 ·spring-boot-starter
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
- spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件。
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可
主启动类·SpringbootApplication
默认的主启动类
//@SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类 , 说明这是一个Spring Boot应用 @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //启动了一个方法,其实启动了一个服务 SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
注解·@SpringBootApplication
- 作用:标注在某个类上说明这个类是SpringBoot的主配置类 , SpringBoot就可以运行这个类的main方法来启动SpringBoot应用
点进@SpringBootApplication:可以看到如下
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { //······ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
注解·@ComponentScan
- 这个注解在Spring中很重要 ,它对应XML配置中的元素。
- 作用:自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
- @ComponentScan(param)告诉Spring 哪个packages 的用注解标识的类 会被spring自动扫描并且装入bean容器,param即用来指定扫描包的范围。
- 此注解一般和@Configuration注解一起使用,指定Spring扫描注解的package。如果没有指定包,那么默认会扫描此配置类所在的package。
- @Configuration注解申明当前类是一个配置类,相当于xml配置文件。
- @ComponentScan和@Configuration一起使用的原因就是基于Spring2.0中的注解配合xml配置文件的实现一样,即在xml配置文件配置ComponentScan包扫描属性。
注解·@SpringBootConfiguration
- 作用:SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示这是一个SpringBoot的配置类
点进@SpringBootConfiguration
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration @Indexed public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { @AliasFor( annotation = Configuration.class ) boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- @Configuration,说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件
- @Component 这就说明,启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用
注解·@EnableAutoConfiguration
- @EnableAutoConfiguration :开启自动配置功能
- SpringBoot可以自动帮我们配置 ;*** @EnableAutoConfiguration告诉SpringBoot开启自动配置功能,自动配置才能生效***
点进@EnableAutoConfiguration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage { //······ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- @AutoConfigurationPackage : 自动配置包
- @import :Spring底层注解@import , 给容器中导入一个组件
- Registrar.class 作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器
注解·@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
- 作用:给容器导入组件
- @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) :给容器导入组件
点进AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class
- CTRL+F在本源文件中快速查找
- 可以找到以下代码【181–189行】
// 获得候选的配置 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { //这里的getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法 //返回的就是我们最开始看的启动自动导入配置文件的注解类;EnableAutoConfiguration List<String> configurations = new ArrayList<>( SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader())); ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, getBeanClassLoader()).forEach(configurations::add); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories nor in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
这个方法又调用了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法【126–1333行】
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader; if (classLoaderToUse == null) { classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader(); } String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName(); //这里它又调用了 loadSpringFactories 方法 return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
点进 loadSpringFactories【135–169行】
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) { //获得classLoader , 我们返回可以看到这里得到的就是EnableAutoConfiguration标注的类本身 Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } result = new HashMap<>(); try { /* 去获取一个资源 "META-INF/spring.factories" public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; */ Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION); //将读取到的资源遍历,封装成为一个Properties while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue()); for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) { result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>()) .add(factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } // Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct() .collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList))); cache.put(classLoader, result); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } return result; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
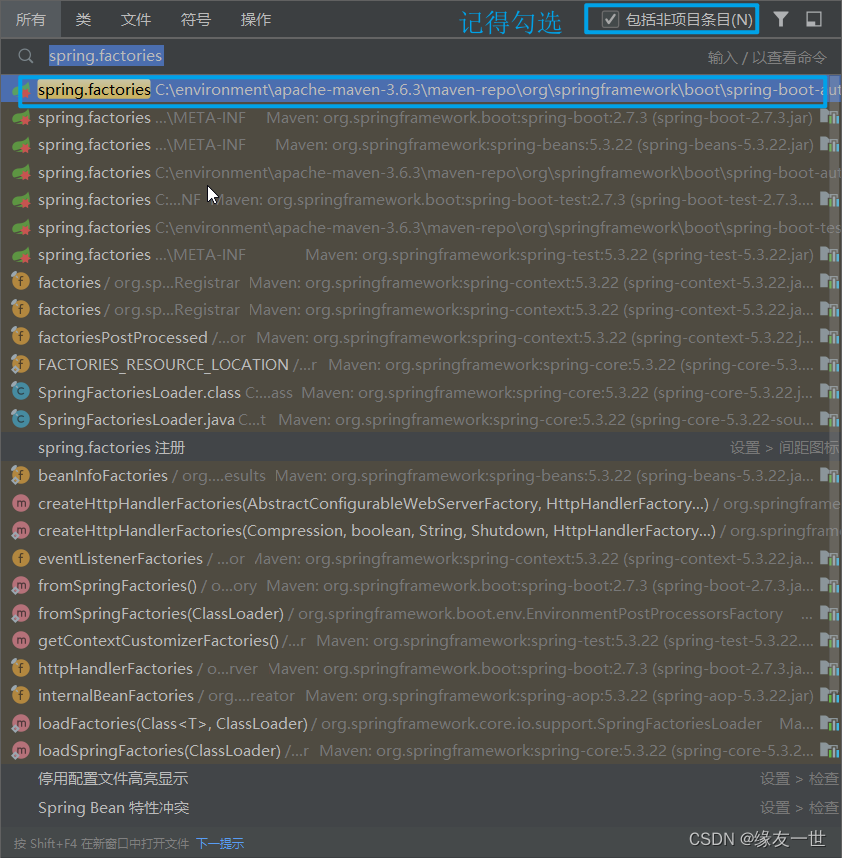
全局搜索META-INF下的:spring.factories
-
IDEA全局搜索快捷键:shift+shift
-
spring.factories 自动配置根源所在
-
也可以在外部库中查找

-
有很多很多自动配置的文件
遗憾·疑问spring.factories源码【看不到大量的自动装配源码】
-
为什么spring boot2.7.3中找到的spring.factories与下图相差甚远?
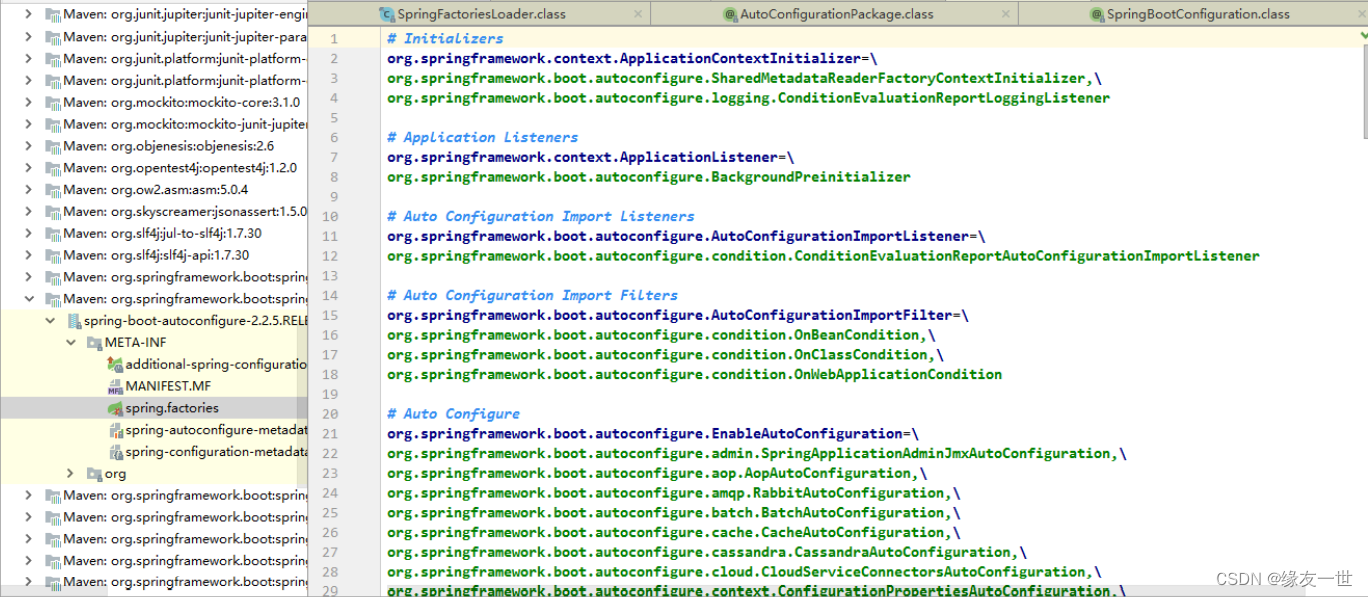
-
甚至找不到WebMvcAutoConfiguration的自动装配,但却是存在这个WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java文件
-
本来按照狂神说的,可以在里面找到WebMvcAutoConfiguration,然后找到WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java

- 可以看到这些一个个的都是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean。
- 所以,自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
结论
- SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
- 将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作;
- 整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中;
- 它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件 ;
- 有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
不平凡方法·SpringApplication
@SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
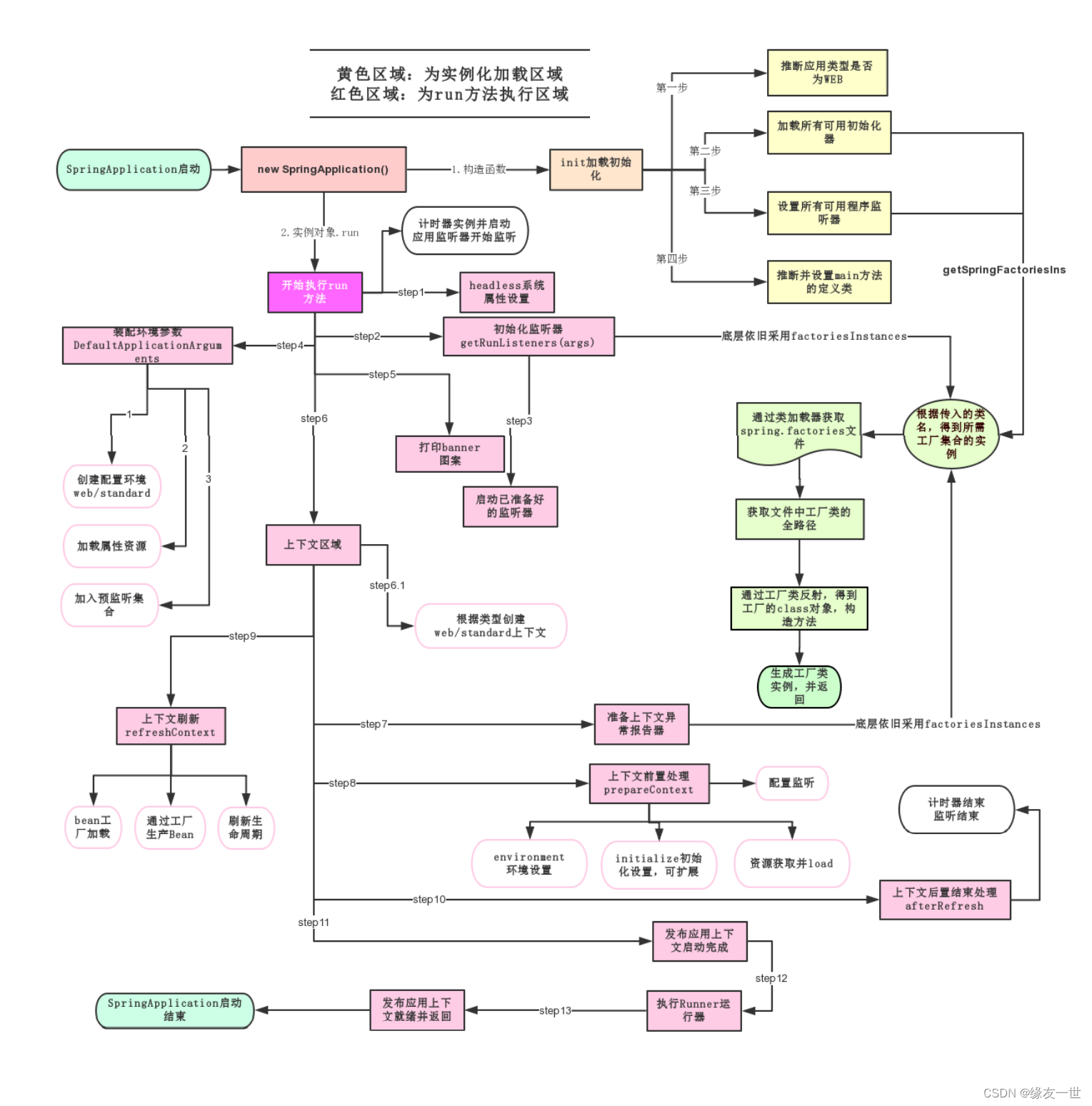
SpringApplication.run分析
- 分析该方法主要分两部分
- 一部分是SpringApplication的实例化
- 二是run方法的执行;
- SpringApplication
-
- 推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
-
- 查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
-
- 找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
-
- 推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
-
- 查看构造器
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.sources = new LinkedHashSet(); this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE; this.logStartupInfo = true; this.addCommandLineProperties = true; this.addConversionService = true; this.headless = true; this.registerShutdownHook = true; this.additionalProfiles = Collections.emptySet(); this.isCustomEnvironment = false; this.lazyInitialization = false; this.applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT; this.applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT; this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class)); this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- run方法
-
相关阅读:
Java面试笔记:CopyOnWriteArrayList是怎么保证线程安全的?
处理前端富文本渲染图片自适应(css方法)
从0开始做公众号|零基础如何运营一个公众号?
linux系统java环境变量的下载与安装
绥化学院学报杂志绥化学院学杂志社绥化学院学报编辑部2022年第9期目录
再也不用担心忘记密码了!如何在Windows 10或11中重置被遗忘的密码
python sqlalchemy(ORM)- 02 表关系
人工智能科技出海服务公司ADVANCE.AI助力企业开拓尼日利亚市场
jenkins CSV编码导致乱码问题解决
Vue3+Typescript+Axios封装网络请求
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yang2330648064/article/details/126909898
