-
js数据结构【树结构】二叉树 二叉搜索树。
生活中真实的树
树的特点
- 树通常有一个,连接着根的是树干。
- 树干到上面会进行分叉成树枝,树枝还会分叉成更小的树枝。
- 树枝的最后是树叶。

树叶状结构也可以运用到生活中。
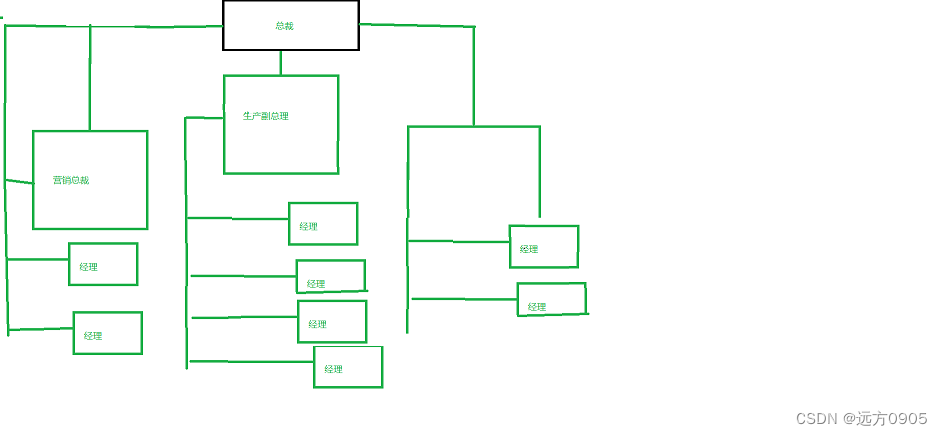
树结构
将里面的数据移除,仅仅抽象出来结构,就是树结构。
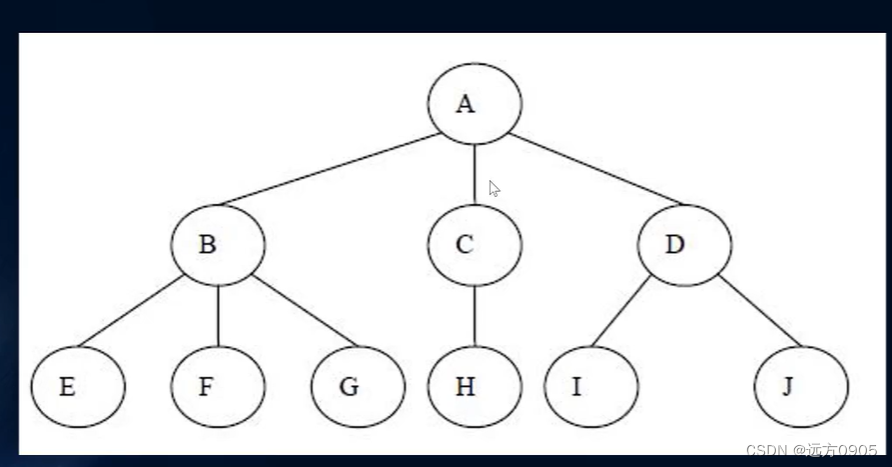
树结构的优点
- 查找比数组跟链表快,但是比哈希表慢。
- 空间利用率高,可以有序,可以查找最值。
每种数据结构都有自己特定的应用场景。
树的术语
树(tree)的定义
- n( n >= 0 )个节点构成的有限集合。
- 当n 等于0的时候,成为空树。
- 对于任何一个空树。
a. 树中有一个称为 “跟(root)”的特殊节点,用r来表示。
b. 其余节点可分别为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集 T1,T2,T3 , Tm 其中每个集合本身又是一棵树,称之为原来的子树(SubTree)
数的术语(部分)
- 节点的度(Degree):节点的子树个数。
- 树的度:树的所有节点中最大的度数。
- 叶节点(Leaf):度为0的节点。(也称为叶子节点)。
- 父节点(Parent):有子树的节点是其子树的根节点的父节点。
- 子节点 (Child):若A节点是B节点的父节点,则称B节点是A节点的子节点;子节也称为孩子节点。
- 兄弟节点(Sibling):具有同一父节点的各节点彼此是兄弟结点。
- 路径和路径长度:从节点n1到nk的路径为一个节点序列 n1 ,n2 ,nk, ni 都是ni + 1 的父节点。路径包含边的个数为路径的长度。
- 节点的层次(Level):规定根节点在1层,其它任一节点的层数是其父节点的层数加1.
- 树的深度(Depth):书中所有的节点中的最大层次 是这棵树的深度。
二叉树
二叉树的概念
- 如果树中的每个节点最多只能有两个子节点,这样的树就称为 二叉树。
- 其实所有的树本质上都可以使用二叉树模拟出来。
二叉树的定义
- 二叉树可以为空,也就是没有节点。
- 若不为空,则它是由根节点和称为其左子树TL和右子树TR的两个不相交的二叉树组成。
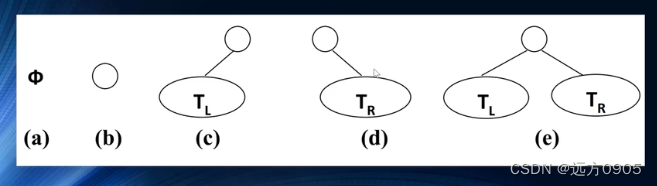
二叉树的五种形态
- 二叉树是一个空树。
- 二叉树只有一个根节点。
- 二叉树只有一个左子节点。
- 二叉树只有一个右子节点。
- 二叉树有两个子节点。
二叉树的特性
- 一个二叉树的第 i 层的最大节点数为:2^(i-1) , i>=1;
- 深度为k的二叉树有最大的节点总数为 2^(k-1), k >=1;
- 对于任何非空二叉树T,若n0表示叶节点的个数,n2是度为2的非叶节点个数,那么两者满足关系n0 = n2 + 1;
完美二叉树
完美二叉(满二叉树):在二叉树中,除了最下一层的叶节点外,每层节点都有2个子节点,就构成了满二叉树。
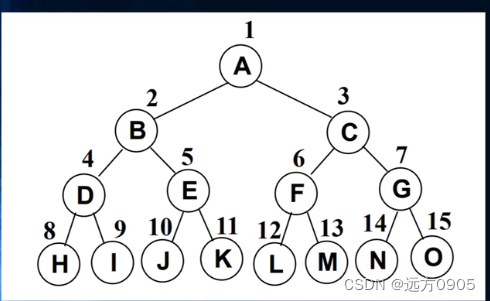
完全二叉树
- 除了二叉树最后一层外,其他各层的节点数都达到最大个数。
- 且最后一层从左向右的叶节点连续存在,只能缺右侧若干节点。
- 完美二叉树是特殊的完全二叉树。
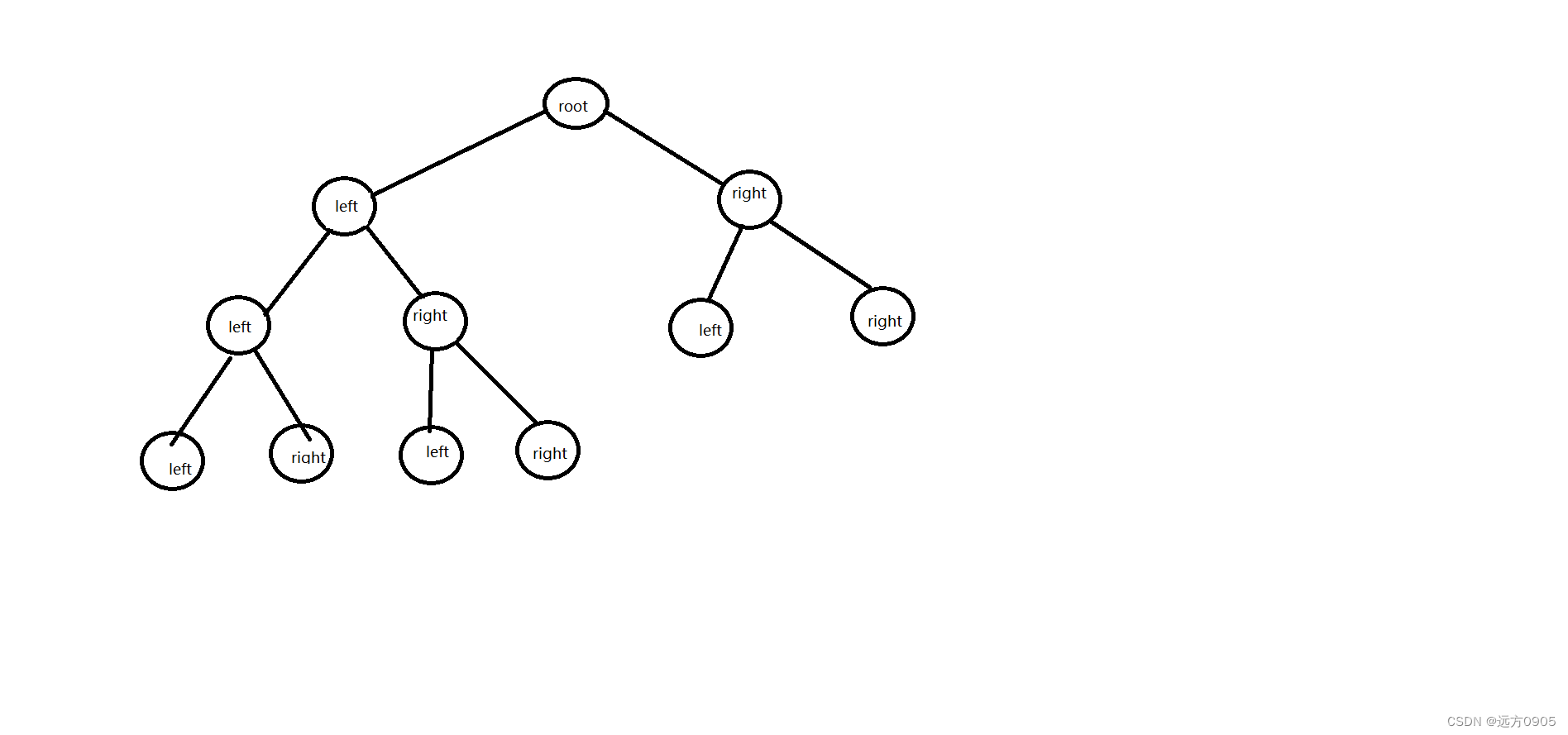
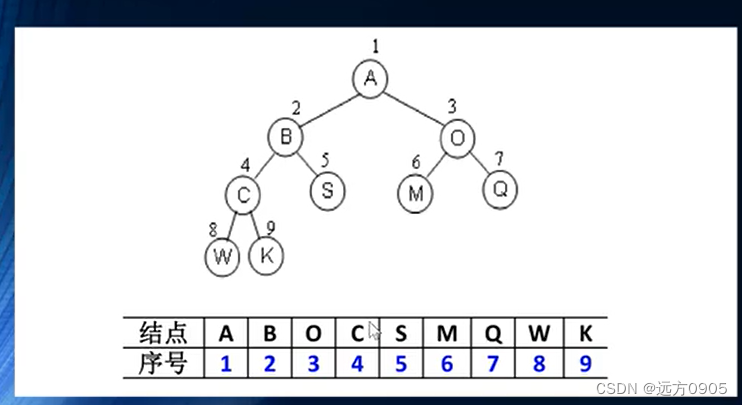
二叉树的存储
使用数组
完全二叉树 按从上至下、从左到右顺序存储。
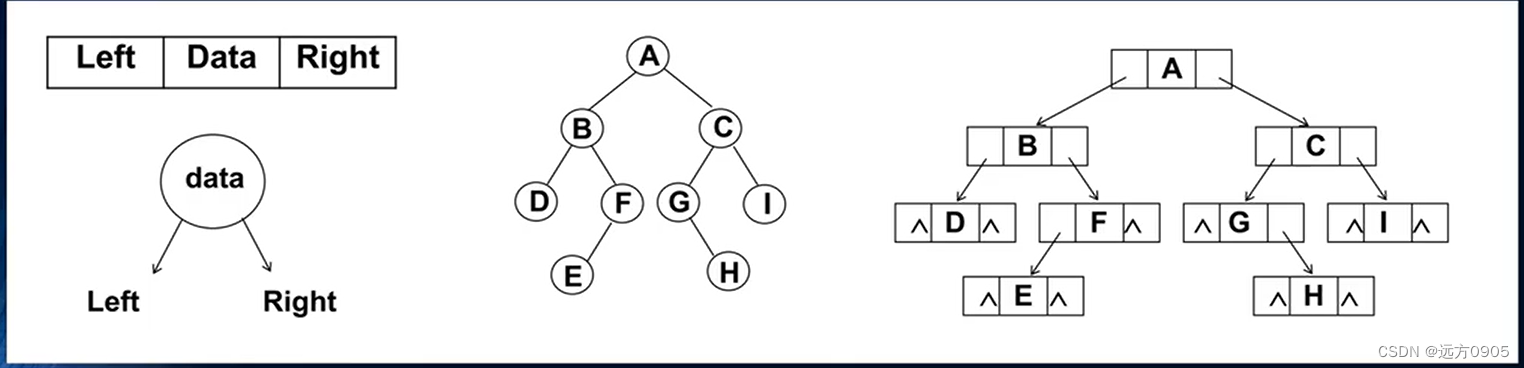
链表存储
- 二叉树常见的存储方式是使用链表做存储。
- 每个节点封装成一个Node ,Node中包含存储的数据,左节点的引用,右节点的引用。
二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树(BST,Binary Search Tree),也称二叉排序树或二叉搜索树。
- 二叉搜索树是一颗二叉树,可以为空;
- 如果不为空,满足以下性质。
a. 非空左子树的所有键值小于其根节点的键值。
b. 非空右子树的所有键值大于其根节点的键值。
c. 左、右子树本身也都是二叉搜索树。
二叉搜索树的封装
<script> // 封装二叉搜索树 function BinarySearchTree() { //节点类 function Node(key) { this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; } // 属性 this.root = null // 方法 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
二叉搜索树的操作
- insert(key) :向树中插入一个新的键。
- search(key) 在树种查找一个键,如果节点存在,则返回true;如果不存在,则返回false;
- inOrederTraverse :通过中序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- preOrederTraverse :通过先序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- postOrederTraverse : 通过后序遍历方式遍历所有节点。
- min:返回树中最小的值 / 键。
- max:返回树中最大的值 / 键。
- remove(key):从树中移除某个键。
// insert 插入方法 BinarySearchTree.prototype.insert = function (key) { // 1. 根据key创建节点 let newNode = new Node(key); // 2. 判断根节点是否有值 if (this.root == null) { this.root = newNode; } else { this.insertNode(this.root, newNode) } } // 递归去向右去查询 BinarySearchTree.prototype.insertNode = function (node, newNode) { if (newNode.key < node.key) { //向左边查找 if (node.left == null) { node.left = newNode; } else { this.insertNode(node.left, newNode) } } else { if (node.right == null) { node.right = newNode; } else { this.insertNode(node.right, newNode) } } } //测试数据 let bts = BinarySearchTree(); bst.insert(11); bst.insert(7); bst.insert(15); bst.insert(5); bst.insert(3); bst.insert(9); bst.insert(8); bst.insert(10); bst.insert(13); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(14); bst.insert(20); bst.insert(18); bst.insert(25); bst.insert(6); //结果在图。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
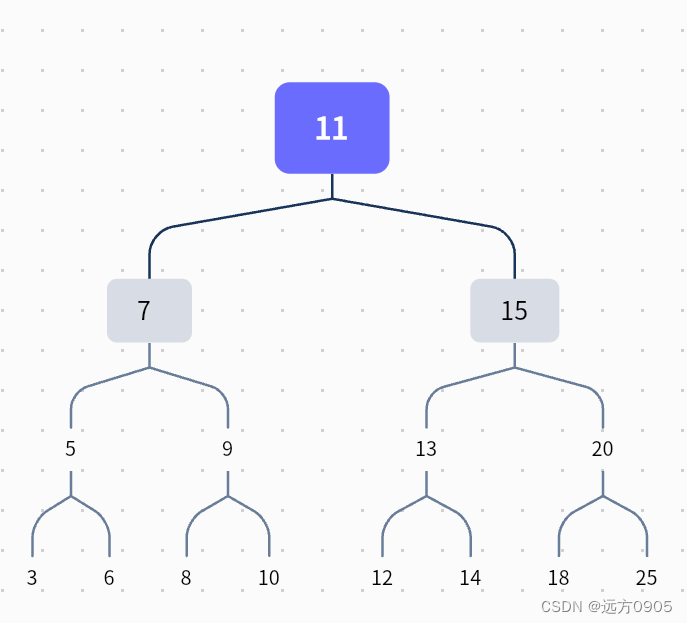
遍历二叉搜索树(所有的二叉树通用)
树的遍历
- 遍历一棵树是指访问树的每一个节点(也可以对每个节点进行某些操作,这里是简单的打印)。
- 但是树和 线性结构不一样, 线序结构我们通常按照从先到后的顺序遍历,书该如何遍历?
- 从左开始还是从右开始,还是从中间开始呢。
- 先序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
先序遍历
先序遍历会先访问节点本身,然后再访问它的左侧子节点,最后是右侧子节点,
遍历过程- 访问根节点
- 先序遍历其左子树
- 先序遍历其右子树
应用场景: 先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档。
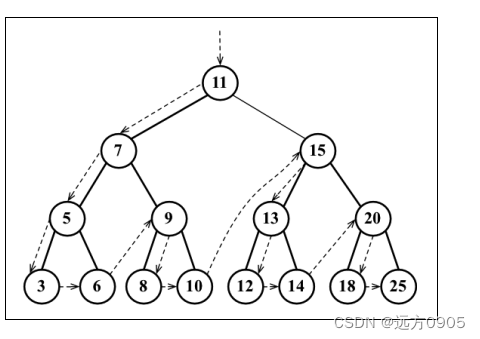
//原理 递归调用函数 处理节点 先访问根节点 然后 递归去访问左节点 BinarySearchTree.prototype.preOrderTraversal = function () { let arr = []; this.preOrderTraversalNode(this.root, arr); return arr; } // 第一次 node -> 根节点 11 // 第二次: node -> 根的左节点 7 // 第三次: node -> 7的左节点 5 // 第四次: node -> 5的左节点 null // BinarySearchTree.prototype.preOrderTraversalNode = function (node, arr) { // 比如 根节点 为11 上图 11 然后 开始执行, node不为空 然后去 递归调用把 第二行代码把左子节点 传入进去 等左子节点的 node ==null // 开始返回上一层 然后 执行滴 三行代码 this.preOrderTraversalNode(node.right, arr) 继续向下遍历 每次把 node.key传入 arr中。 if (node != null) { // 1. 处理经过的节点 // handler(node.key) arr.push(node.key) // 2. 处理经过的左子节点 this.preOrderTraversalNode(node.left, arr) // 3. 处理经过节点的右子节点 this.preOrderTraversalNode(node.right, arr) } } // 测试代码。 console.log(bst.preOrderTraversal());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
中序遍历
中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问BST所有节点的遍历方式,也就是以从最小到最大的顺序访问所有节点。
- 处理左子树的 节点
- 处理节点
- 处理右子树的节点
应用场景: 中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作。
原理图
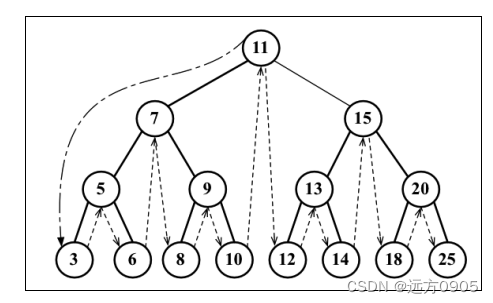
BinarySearchTree.prototype.midOrderTraversal = function () { let arr = []; this.midOrderTraversalNode(this.root, arr) return arr; } BinarySearchTree.prototype.midOrderTraversalNode = function (node, arr) { if (node != null) { // 1. 处理左子树的 节点 this.midOrderTraversalNode(node.left, arr) //2. 处理节点 arr.push(node.key); // 3.处理右子树的节点 this.midOrderTraversalNode(node.right, arr) } } // 测试代码: // console.log(bst.midOrderTraversal());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
后序遍历
后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。
- 查找左子树中的节点
- 查找右子树的节点
- 访问根节点
应用场景:后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目录和它的子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小。
//基本原理跟先序遍历一样 BinarySearchTree.prototype.postOrderTraversal = function () { let arr = []; this.postOrderTraversalNode(this.root, arr); return arr; } BinarySearchTree.prototype.postOrderTraversalNode = function (node, arr) { if (node != null) { // 1.查找左子树中的节点 this.postOrderTraversalNode(node.left, arr); //2. 查找右子树的节点 this.postOrderTraversalNode(node.right, arr); // 3.访问根节点 arr.push(node.key); } } //测试代码 : // console.log(bst.postOrderTraversal());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
查找最值
// 4. 寻找最值 // 4.1 最大值 BinarySearchTree.prototype.max = function () { // 1.获取根节点 let node = this.root; let key = null //2. 依次向右不断地查找,直到节点 为 null while (node != null) { key = node.key; node = node.right; } return key; } // 4.2 最小值 BinarySearchTree.prototype.min = function () { // 1.获取根节点 let node = this.root; let key = null; //2. 依次向右不断地查找,直到节点 为 null while (node != null) { key = node.key; node = node.left; } return key; } // 测试代码。 console.log(bst.max()); console.log(bst.min());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
搜索某一个key 是否存在
// 5.搜索某一个key BinarySearchTree.prototype.search = function (key) { // 1.获取节点 let node = this.root; // 2. 循环搜索key while (node != null) { if (key < node.key) { node = node.left } else if (key > node.key) { node = node.right } else { return true; } } return false }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
二叉搜索树的删除
删除节点要从查找要删的节点开始,找到节点后,需要考虑的情况
- 删除叶子节点。
- 删除只有一个子节点的节点。
- 删除有两个子节点的节点。
// 删除节点 BinarySerachTree.prototype.remove = function(key){ //1.1 寻找要删除的节点 let current = this.root; let parent = null; let isLeftChild = true; //1.2. 开始寻找删除节点。 while (current.key != key){ parent = current if(key < current.key){ isLeftChild = true; current = current.left; }else { isLeftChild = false; current = current.right } // 某种情况: 已经找到最后的节点,依然没有找到相等的key if(current == null) return false; } //2. 根据对应的情况删除节点 //2.1. 删除的节点是叶子节点(没有子节点) if(current.left == null && current.right == null) { if (current == this.root) { this.root = null; }else if (isLeftChild) { parent.left = null; } else { parent.right = null; } } //2.2. 删除的节点有一个子节点 else if (current.right = null){ if(isLeftChild){ parent.left = current.left }else if{ parent.right = current.left } }else if (current.left == null){ if (current == this.root ){ this.root = current.right; } else if (current == this.root){ this.root = current.left; } if(isLeftChild){ parent.left = current.right } else { parent.right = current.right; } } //2.3 删除的节点有两个子节点。 // 找到了current.key == key 的情况。 else { // 1. 获取后继节点 let successor = this.getSuccssor(current); // 2.判断是否为根节点 if(current == this.root){ this.root = successor } else if (isLeftChild) { parent.left = successor }else { parent.right = successor } // 3. 将删除节点的左子树 = current.left successor.left = current.left; } // 找后继的方法 BinarySerachTree.prototype.getSuccssor = function (del ){ // 1. 定义变量,保存找到的后继 let successor = delNode; let current = delNode.right; let successorParent = delNode; //2. 循环查找 while(current != null){ successorParent = successor; successor = current current = current.left; } //3. 判断寻找的后继节点是否就是delNode的right节点 if(successor != delNode.right){ successorParent.left = successor.right; successor.right = delNode.right; } return successor } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
-
相关阅读:
关于架构的一些理念
Python学习笔记七之文件操作:打开与写入、创建与删除、遍历文件夹批处理等
Ladybug 全景相机, 360°球形成像,带来全方位的视觉体验
使用python第三方库Parameterized进行接口参数化测试
java中的线程池
C++保留小数点后两位(floor&ceil&round)详解
界面控件DevExpress WinForm v22.2——即将拥有新的HTML & CSS模板
【MATLAB教程案例50】通过VisualSFM工具箱提取360度等间隔环绕拍摄得到的图像序列点云数据,并进行目标三维重建matlab仿真
认识和使用差分数组
.NET现代应用的产品设计 - DDD实践
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43198727/article/details/126547840
