-
Netty源码剖析之数据通信流程
Selector监听的事件
NIO事件/感兴趣事件
OP_REGISTER = 0 通道注册事件
OP_READ = 1 << 0
OP_WRITE = 1 << 2
OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3
OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4

执行流程
1、客户端与服务器建立连接, BossGroupNioEventLoop 监听到有IO事件,那么处理选择的key ----processSelectedKeys()
/** * NIOEventLoop执行核心 */ @Override protected void run() { int selectCnt = 0; // 阻塞选择次数 // 从NioEventLoop中的 taskQueue中 判断是否存在事件 for (;;) { // 轮训注册到selector的IO事件 为什么for(;;)比while(1)好?因为for(;;)底层的指令更少,效率更高 try { int strategy; // strategy = 0 default try { strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks()); // 获取策略。如果有任务则使用非阻塞方式 switch (strategy) { case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE: continue; case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT: // fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIO case SelectStrategy.SELECT: // select事件执行 long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos(); // 当前截止时间 if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) { // 表明没有定时任务 curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar } nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos); try { if (!hasTasks()) { // 如果没有任务,则select阻塞等待任务 任务存放在SingleThreadEventLoop // TODO 测试 System.err.println("[CurrentThread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]I'm selecting... waiting for selectKey or tasks!"); strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos); } } finally { // This update is just to help block unnecessary selector wakeups // so use of lazySet is ok (no race condition) // 标记未唤醒状态 nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE); } // fall through default: } } catch (IOException e) { // If we receive an IOException here its because the Selector is messed up. Let's rebuild // the selector and retry. https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566 rebuildSelector0(); selectCnt = 0; handleLoopException(e); continue; } System.err.println("[CurrentThread = " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] select() 调用完了,此时已经有事件进来了?"); selectCnt++; // 选择次数+1 cancelledKeys = 0; needsToSelectAgain = false; final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio; // 这里的ioRatio默认是50 boolean ranTasks; if (ioRatio == 100) { try { if (strategy > 0) { processSelectedKeys(); // 处理选择key,处理io相关的逻辑 } } finally { ranTasks = runAllTasks(); // 处理外部线程扔到taskQueue里的任务,这里的taskQueue是一个mpscQueue } } else if (strategy > 0) { final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); // 计算处理选择key的时间 try { processSelectedKeys(); } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime; ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); } } else { /** * 在Netty中,有两种任务,普通任务和定时任务。在执行任务的时候,会把定时任务队列里的task扔进普通任务队列里, * 这里的普通任务队列就是mpscQueue,接着就挨个执行mpscQueue里的任务。 * * 任务:普通任务 、定时任务 * 队列:普通任务队列mpscQueue 、 定时任务队列 * */ ranTasks = runAllTasks(0); // This will run the minimum number of tasks } if (ranTasks || strategy > 0) { if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS && logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.", selectCnt - 1, selector); } selectCnt = 0; } else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) { // Unexpected wakeup (unusual case) 解决空轮训Bug,重置selectCnt,重新生成selector selectCnt = 0; } } catch (CancelledKeyException e) { // Harmless exception - log anyway if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?", selector, e); } } catch (Error e) { throw (Error) e; } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } finally { // Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception. try { if (isShuttingDown()) { closeAll(); if (confirmShutdown()) { return; } } } catch (Error e) { throw (Error) e; } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
2、获取到当前NioEventLoop中 通道(ServerSocketChannel)注册到selector 产生的所有令牌 SelectionKeySet,获取到ServerSocketChannel,来处理这个IO事件(建立连接事件)

* 优化过后处理SelectedKey方法 */ private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() { // 迭代selectedKey数组 for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) { final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i]; // null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/236 // 这种感兴趣的事件只处理一次就行 selectedKeys.keys[i] = null; // 获取注册到NioEventLoop里的channel // 获取出 attachment,默认情况下就是注册进Selector时,传入的第三个参数 this===> NioServerSocketChannel // 一个Selector中可能被绑定上了成千上万个Channel, 通过K+attachment 的手段, 精确的取出发生指定事件的channel, 进而获取channel中的unsafe类进行下一步处理 final Object a = k.attachment(); if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { // 这里为啥要将NioServerSocketChannel强转为AbstractNioChannel呢? // 这里强转为AbstractNioChannel是为了准备调用jdk channel的accept方法 processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a); } else { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a; processSelectedKey(k, task); } // 疑问:什么情况下这里会出现true的情况,需要重新select? // 答:每当256个channel从Selector上移除时,就标记needsToSelectAgain为true,表示需要再次轮询 if (needsToSelectAgain) { // null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363 selectedKeys.reset(i + 1); selectAgain(); i = -1; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
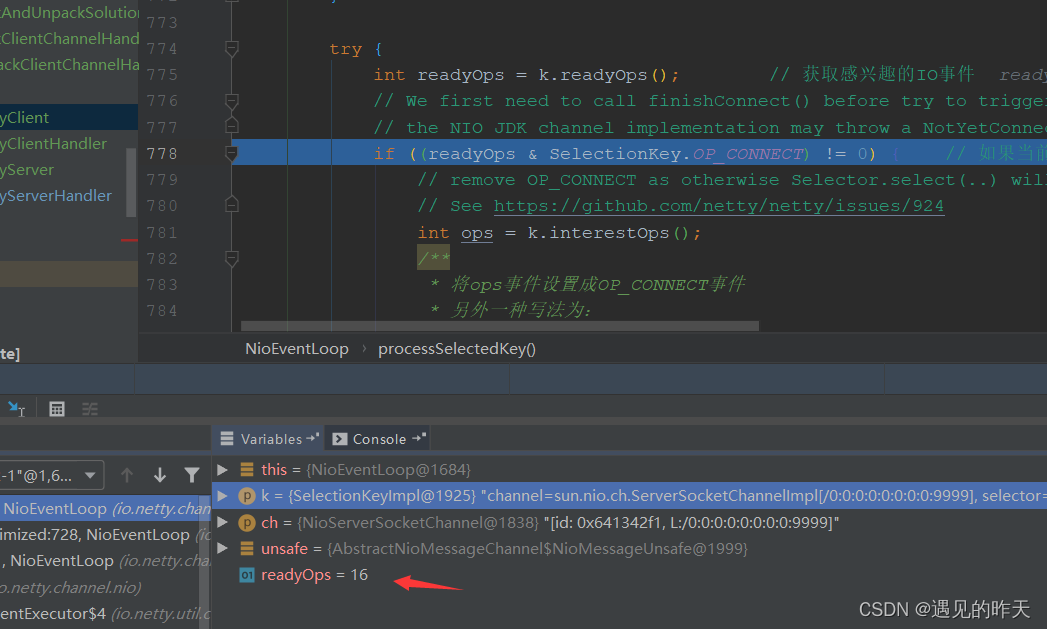
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) { final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe(); // 获取channel内部的unsafe方法 if (!k.isValid()) { // 如果key不合法 final EventLoop eventLoop; try { eventLoop = ch.eventLoop(); } catch (Throwable ignored) { // If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this // because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority // to close ch. return; } // Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop // and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is // still healthy and should not be closed. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125 if (eventLoop == this) { // close the channel if the key is not valid anymore // 关闭通道,如果key是非法的 unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } return; } try { int readyOps = k.readyOps(); // 获取感兴趣的IO事件 // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { // 如果当前感兴趣事件不是连接事件 // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924 int ops = k.interestOps(); /** * 将ops事件设置成OP_CONNECT事件 * 另外一种写法为: * * k.interestOps(readyOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) * OP_CONNECT是8,即1000,取反则为:111,如果k是0,则 000 & 111 = 000 * */ ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; k.interestOps(ops); unsafe.finishConnect(); } // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write ch.unsafe().forceFlush(); } // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead // to a spin loop // readyOps = 0 表示的是channel注册事件 // 如果是workerGroup,可能是OP_READ的IO事件,如果是bossGroup,可能是OP_ACCEPT的IO事件 if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { // 负责读,接受连接事件 unsafe.read(); } } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) { unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
感兴趣事件 161、获取通道 NioMessageUnsafe 主要负责服务端读写数据的 非常重要
2、判断ServerSocketChannel是否合法,不合法关闭
3、获取 channel 注册到 Selector 指定监听的事件,这里是 ON_ACCEPT 建立连接事件
4、调用NioMessageUnsafe 处理事件/** * read()方法的核心三个步骤: * 1. doReadMessages(readBuf) * 2. allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead) * 3. pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i)) * */ @Override public void read() { assert eventLoop().inEventLoop(); final ChannelConfig config = config(); // 服务端的Config final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline(); // pipleline管道 final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle(); // 用于查看服务端接受的速率, 说白了就是控制服务端是否接着read 客户端的IO事件 allocHandle.reset(config); // 重置配置 boolean closed = false; Throwable exception = null; try { try { do { // 往readBuf 添加客户端socketChannel int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf); if (localRead == 0) { break; } if (localRead < 0) { closed = true; break; } // 简单的计数 allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead); } while (allocHandle.continueReading()); } catch (Throwable t) { exception = t; } int size = readBuf.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) { readPending = false; // 处理新的连接之后,让pipeline中发生事件传播 // 这里的pipeline是服务端的 // 事件是如何传播的?head --> ServerBootStrapAcceptor --> tail 依次传播 // 这里传播的什么事件? ChannelRead, 也就是说,会去调用 ServerBootStraptAcceptor的ChannelRead方法 // readBuf.get(i)这里获取到的是NioSocketChannel对象 // TODO 是这里把新的NioSocketChannel注册进workerGroup里的,需要注意的是workerGroup注册完之后,只有16个NioEventLoop,但是 // TODO 没有NioSocketChannel pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i)); // 链式调用channelRead } readBuf.clear(); allocHandle.readComplete(); // 传播channelReadComplete事件 pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete(); // 链式调用ChannelReadComplete if (exception != null) { closed = closeOnReadError(exception); // 传播exceptionCaught事件 pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception); } if (closed) { inputShutdown = true; if (isOpen()) { close(voidPromise()); } } } finally { // Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet. // This could be for two reasons: // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254 if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) { removeReadOp(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
1、NioEventLoop Selector监听到有连接事件,调用ServerSocketChannel accpt方法接收封装成NioSocketChannel到list中,这不会堵塞当前线程,没有客户端建立连接直接返回null,普通的accept方法会堵塞当前线程。

2、获取ServerSocketChannel的pipeline,通过 ServerBootstrapAcceptor (ChannelHandler)将客户端SocketChannel 注册到workerGroup中
客户端SocketChannel 注册流程 跟 ServerSocketChannel一致,这里就不赘述了
ServerBootstrapAcceptor 负责将客户端SocketChannel 交由 workGroup线程组处理
childGroup 就是 WorkerGroup,内部会遍历选出一个WorkerNioEventLoop,获取其中的Selector ,将当前客户端SocketChannel绑定上去,并监听 read/write 事件
后续客户端SocketChannel 数据通信 交由服务器端WorkerNioEevntLoop进行数据处理
3、WorkerNioEevntLoop读取SocketChannel 数据

Selector 监听到 通道有IO事件,处理选择的key
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) { final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe(); // 获取channel内部的unsafe方法 if (!k.isValid()) { // 如果key不合法 final EventLoop eventLoop; try { eventLoop = ch.eventLoop(); } catch (Throwable ignored) { // If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this // because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority // to close ch. return; } // Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop // and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is // still healthy and should not be closed. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125 if (eventLoop == this) { // close the channel if the key is not valid anymore // 关闭通道,如果key是非法的 unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } return; } try { int readyOps = k.readyOps(); // 获取感兴趣的IO事件 // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { // 如果当前感兴趣事件不是连接事件 // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924 int ops = k.interestOps(); /** * 将ops事件设置成OP_CONNECT事件 * 另外一种写法为: * * k.interestOps(readyOps & ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) * OP_CONNECT是8,即1000,取反则为:111,如果k是0,则 000 & 111 = 000 * */ ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; k.interestOps(ops); unsafe.finishConnect(); } // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write ch.unsafe().forceFlush(); } // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead // to a spin loop // readyOps = 0 表示的是channel注册事件 // 如果是workerGroup,可能是OP_READ的IO事件,如果是bossGroup,可能是OP_ACCEPT的IO事件 if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { // 负责读,接受连接事件 unsafe.read(); } } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) { unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
SelectionKey 中存储的感兴趣的事件 1 ,及读取数据事件,通知WorkerNioSocketChannel中的NioSocketChannelUnsafe读取数据。
NioSocketChannelUnsafe主要负责读取客户端的数据,想客户端写数据。
ServerSocketChannel数据读写类是NioMessageUnsafe注意这两个不一样哦!!!/** * 客户端channel的读,读取的是数据 * 如果数据量大,数据会分为多次读,最多为16次 */ @Override public final void read() { final ChannelConfig config = config(); if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) { clearReadPending(); return; } final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline(); final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator(); // 自适应数据大小的分配器,在io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelConfig中设置的RecvByteBufAllocator,默认是AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle(); allocHandle.reset(config); ByteBuf byteBuf = null; boolean close = false; try { do { byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator); // 尽可能分配合适的大小: guess()方法很形象,猜下系统分配了多少? allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf)); // 读并且记录读了多少,如果读满了,下次continue的话就直接扩容 if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) { // nothing was read. release the buffer. byteBuf.release(); byteBuf = null; close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0; if (close) { // There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF. readPending = false; } break; } allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1); // 表示读了一次 readPending = false; /** * 触发pipeline中的chanelRead,把读取到的数据传播出去 */ pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf); byteBuf = null; } while (allocHandle.continueReading()); allocHandle.readComplete(); // 记录这次读事件总共读了多少数据,计算下次分配大小 pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete(); // 相当于完成本次读事件的处理 if (close) { closeOnRead(pipeline); } } catch (Throwable t) { handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle); } finally { // Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet. // This could be for two reasons: // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254 if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) { removeReadOp(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
1、
allocHandle.allocate(allocator);拿到分配处理器,获取一个大小为2048 的 byteBuf 来存放客户端发送来的数据

内存缓存区分配器netty具体实现有两种:- 堆内字节缓冲分配器
- 堆外字节缓冲分配器
默认使用的好像是堆外内存
那么堆内堆外内存区别在哪???,先留着

2、记录读取的数据量,方便扩容

3、记录数据读取次数

4、调用workerNioEventLoop的 pipeLine 链式调用 channelRead
这里会走到我们定义的ChannelHandler ChannelRead 方法哦

这里会通过while判断是否继续读,没读完继续读,最多读16次
5、链式调用 ChannelReadComplete()
表示客户端的数据读完了

4、WorkerNioEevntLoop 向 SocketChannel 写数据

我们通过ChannelHandlerContext 来向通道写数据

Unpooled.copiedBuffer("叫我靓仔!!!".getBytes())数据转字节数组,通过Unpooled封装成 堆内缓冲区 heapByteBuf


写数据本质上就是获取到当前NioSocketChannelUnsafe 往通道写数据

/** * 向客户端socket最终写的方法,底层调用的是JDK底层的IOUtil#write * @param in * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void doWrite(ChannelOutboundBuffer in) throws Exception { // jdk channel SocketChannel ch = javaChannel(); // 写自旋次数,默认为16次 int writeSpinCount = config().getWriteSpinCount(); do { if (in.isEmpty()) { // All written so clear OP_WRITE clearOpWrite(); // Directly return here so incompleteWrite(...) is not called. return; } // Ensure the pending writes are made of ByteBufs only. int maxBytesPerGatheringWrite = ((NioSocketChannelConfig) config).getMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(); /** * 将ChannelOutboundBuffer中的ByteBuf转为ByteBuffer数组 */ ByteBuffer[] nioBuffers = in.nioBuffers(1024, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); int nioBufferCnt = in.nioBufferCount(); // Always use nioBuffers() to workaround data-corruption. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2761 switch (nioBufferCnt) { case 0: // We have something else beside ByteBuffers to write so fallback to normal writes. writeSpinCount -= doWrite0(in); break; case 1: { // Only one ByteBuf so use non-gathering write // Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need // to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero. ByteBuffer buffer = nioBuffers[0]; int attemptedBytes = buffer.remaining(); /** * 调用jdk底层channel的write */ final int localWrittenBytes = ch.write(buffer); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { incompleteWrite(true); return; } adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite(attemptedBytes, localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } default: { // Zero length buffers are not added to nioBuffers by ChannelOutboundBuffer, so there is no need // to check if the total size of all the buffers is non-zero. // We limit the max amount to int above so cast is safe long attemptedBytes = in.nioBufferSize(); final long localWrittenBytes = ch.write(nioBuffers, 0, nioBufferCnt); if (localWrittenBytes <= 0) { incompleteWrite(true); return; } // Casting to int is safe because we limit the total amount of data in the nioBuffers to int above. adjustMaxBytesPerGatheringWrite((int) attemptedBytes, (int) localWrittenBytes, maxBytesPerGatheringWrite); in.removeBytes(localWrittenBytes); --writeSpinCount; break; } } } while (writeSpinCount > 0); incompleteWrite(writeSpinCount < 0); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
写完后将数据刷新出去就行了
问题
1、workerGroup如果定义了16个NioEvetLoop ,在创建NioEvetLoop中会直接创建线程执行嘛?
我的理解是不会!只有当客户端与服务端建立连接的时候,ServerSocketChannel所在NioEventLoop将 接收到的SocketChannel通过 ServerBootAcceptor 交由 WorkerGroup NioEventLoop注册通道的时候,才会拿到这个WorkerNioEventLoop 创建线程,进行Selector监听。2、netty服务端数据 怎么接收,数据存放的内存通过什么分配?怎么分配?
/** * 内存分配管理器接口抽象,负责分配所有的内存 * * 在Netty中可以分为两类内存缓冲分配器:1. 基于内存池的字节缓冲区分配器;2. 非内存池的字节缓冲区分配器; * * Implementations are responsible to allocate buffers. Implementations of this interface are expected to be * thread-safe. */ public interface ByteBufAllocator { ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT = ByteBufUtil.DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR; /** * 负责分配一块内存 * 具体分配一块堆内存还是堆外内存,由具体的实现类来决定 * * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf}. If it is a direct or heap buffer * depends on the actual implementation. */ ByteBuf buffer(); /** * 分配一个初始化容量为initialCapacity的字节缓冲区 * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity. * If it is a direct or heap buffer depends on the actual implementation. */ ByteBuf buffer(int initialCapacity); /** * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity and the given * maximal capacity. If it is a direct or heap buffer depends on the actual * implementation. */ ByteBuf buffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); /** * 分配一个DirectByteBuffer,因为DirectByteBuffer的IO操作性能更高 * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf}, preferably a direct buffer which is suitable for I/O. */ ByteBuf ioBuffer(); /** * 负责分配一块指定容量initialCapacity的DirectByteBuffer区域用于IO * * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf}, preferably a direct buffer which is suitable for I/O. */ ByteBuf ioBuffer(int initialCapacity); /** * 负责分配一块directBuf区域用于IO * * Allocate a {@link ByteBuf}, preferably a direct buffer which is suitable for I/O. */ ByteBuf ioBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); /** * Allocate a heap {@link ByteBuf}. */ ByteBuf heapBuffer(); /** * Allocate a heap {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity. */ ByteBuf heapBuffer(int initialCapacity); /** * Allocate a heap {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity and the given * maximal capacity. */ ByteBuf heapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); /** * Allocate a direct {@link ByteBuf}. */ ByteBuf directBuffer(); /** * Allocate a direct {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity. */ ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity); /** * Allocate a direct {@link ByteBuf} with the given initial capacity and the given * maximal capacity. */ ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); /** * 可以将heapBuf和DirectBuf合并到一个地方去使用,既CompositeByteBuf * * Allocate a {@link CompositeByteBuf}. * If it is a direct or heap buffer depends on the actual implementation. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeBuffer(); /** * Allocate a {@link CompositeByteBuf} with the given maximum number of components that can be stored in it. * If it is a direct or heap buffer depends on the actual implementation. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeBuffer(int maxNumComponents); /** * Allocate a heap {@link CompositeByteBuf}. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeHeapBuffer(); /** * Allocate a heap {@link CompositeByteBuf} with the given maximum number of components that can be stored in it. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeHeapBuffer(int maxNumComponents); /** * Allocate a direct {@link CompositeByteBuf}. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeDirectBuffer(); /** * Allocate a direct {@link CompositeByteBuf} with the given maximum number of components that can be stored in it. */ CompositeByteBuf compositeDirectBuffer(int maxNumComponents); /** * Returns {@code true} if direct {@link ByteBuf}'s are pooled */ boolean isDirectBufferPooled(); /** * Calculate the new capacity of a {@link ByteBuf} that is used when a {@link ByteBuf} needs to expand by the * {@code minNewCapacity} with {@code maxCapacity} as upper-bound. */ int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
总结


总体流程图(缺少一部分)

-
相关阅读:
带你深入浅出Vue
运维学习笔记——arthas 线上
树论_1.
js 锚点定位的方法
CCRC-DSO学员分享:数据安全官——导师与朋友的双重身份
C++11包装器
Map集合中,当添加一个键值对元素时,HashMap发生了什么?
P01 Swing综述
2022年,你还在犯这些Python错误吗?
SpringCloudAlibaba:1.体系概述
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44787816/article/details/126872920