-
vuex状态管理(二)超级详细使用教程(包含辅助函数map的使用),一看就会,一学就懂
vuex状态管理(一)原理以及使用注意事项_无围之解的博客-CSDN博客
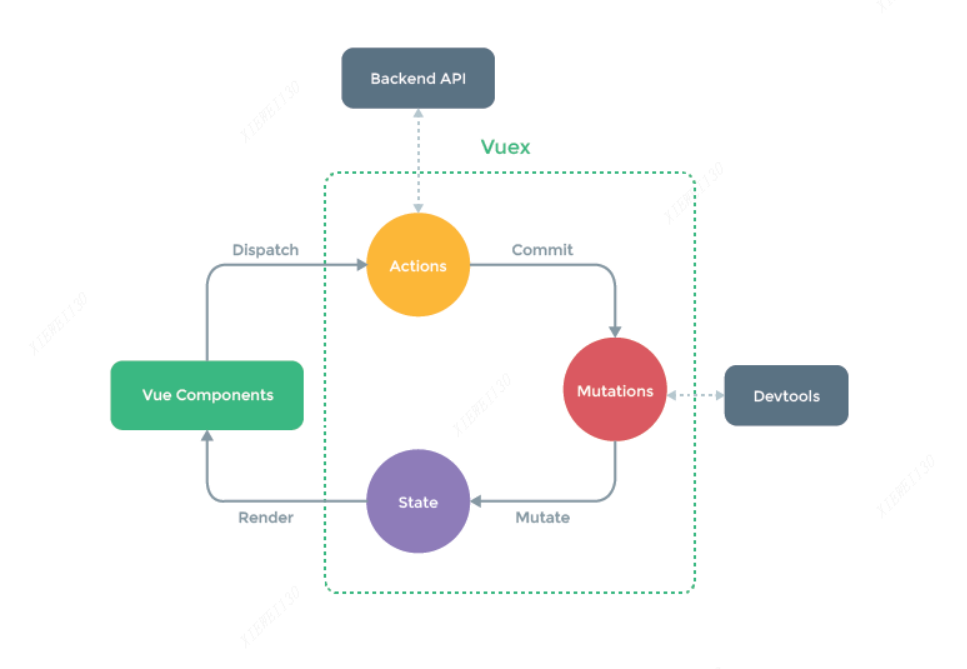
原理上一篇文章已经写了
1 本文默认首先项目已经安装了vuex,没有安装的参考官网安装一下
2 先看看正常的结构
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- //定义数据
- state: {
- },
- //同步操作
- mutations: {
- },
- //异步操作
- actions: {
- },
- modules: {}
- })
3 这几个主要的名词解释
3.1 state中主要是定义公共使用的数据,对象或这单个字符串,数组等等。
3.2 mutations 主要是数据的更改状态提交提交。只有这一种方式提交修改的数据才能追踪。
当你修改数据时,就需要通过commit提交, mutations会记录它的修改动作,便于跟踪管理。
3.3 actions主要时异步操作获取更改数据,但是也要最后通过dispatch就行数据提交,最终还是要通过mutations才能提交数据
3.4 mapState, mapMutations, mapActions 这些辅助函数,写法简单,用起来方便
3.5 页面获取数据 $store.state.obj1
4 下面看实例
4.1先在state中写2个数据
- state: {
- //直接使用
- obj1: {
- name: "张三儿1",
- id: "obj1"
- },
- //辅助函数
- obj2: {
- name: "张三儿2",
- id: "obj2"
- }
- },
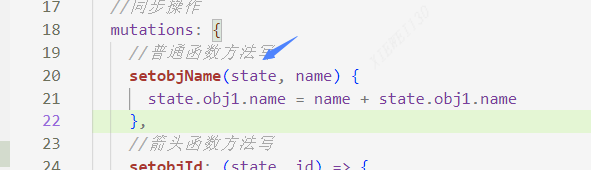
4.2然后mutations中写两个修改数据的方法
state.obj1.name = name + state.obj1.name
state.obj1.name就可以拿到state中的要操作的数据,同时可以传递一个参数name(或者多个参数)
- mutations: {
- //普通函数方法写
- setobjName(state, name) {
- state.obj1.name = name + state.obj1.name
- },
- },
4.3 然后去页面修改 app.vue, test.vue, profile.vue页面 分别获取obj1.name,和obj2的属性id 看下图页面渲染效果
- <h2>
- <div>name:{{ $store.state.obj1.name }}</div>
- <div>id:{{ $store.state.obj2.id }}</div>
- </h2>
我们看test.vue页面
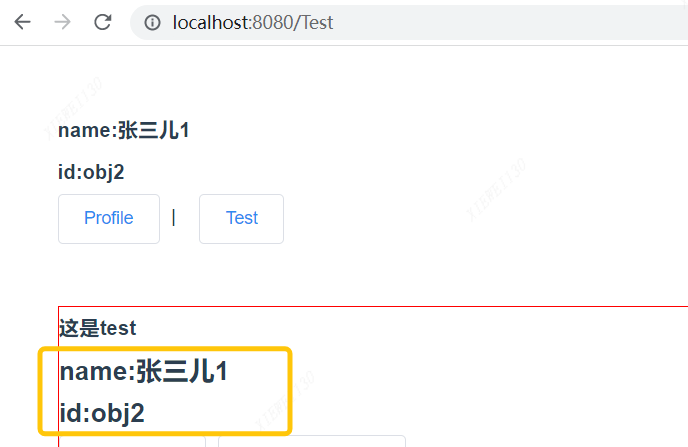
4.4此时 我们在test.vue写一个button按钮改变修改数据
<el-button @click="changeName"><h3>改变name</h3></el-button>然后我们写方法调用 this.$store.commit("AAAA", BBBB);
AAAA就是mutations中要用的方法名,BBBB是参数
- export default {
- data() {
- return {
- name: "new",
- };
- },
- methods: {
- changeName() {
- this.$store.commit("setobjName", this.name);
- },
- },
- };
点击一下,看效果 会发现app.vue, test.vue, profile.vue 三个页面的都改变了,成了new张三儿1,是不是很神奇
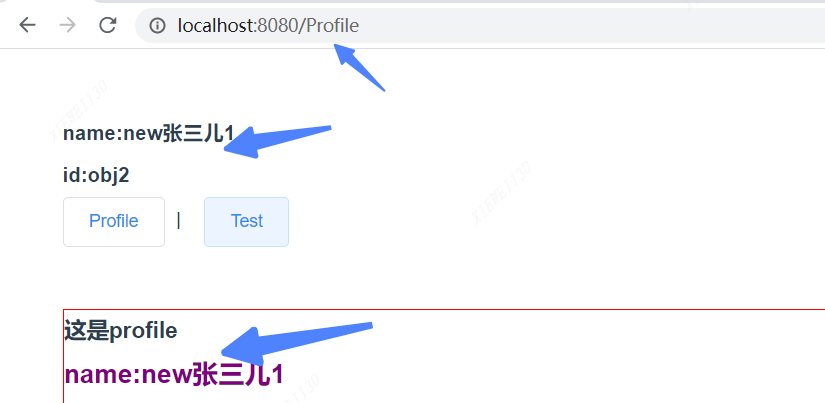
4.5 同样可以使用辅助函数写。我们在profile.vue页面写一个按钮
<el-button @click="changeIdFun"><h3>改变id</h3></el-button>此时我们页面引入辅助函数
import { mapState, mapMutations} from "vuex";然后计算属性获取
- computed: {
- ...mapState(["obj2"]),
- },
我们页面获取数据可以写成这样
- <h2>
- 使用辅助函数
- <div>id:{{ obj2.id }}</div>
- </h2>
- <script>
- //辅助函数
- import { mapState, mapMutations} from "vuex";
- export default {
- name: "Table",
- computed: {
- ...mapState(["obj2"]),
- },
- data() {
- return {
- id: "new",
- };
- },
- methods: {
- //方法2 使用辅助函数提交 和下面注释的效果一样
- ...mapMutations(["setobjId"]),
- changeIdFun() {
- this.setobjId(this.id);
- },
- },
- };
- script>
5 同样异步操作经常是调用接口获取数据需要耗时,我们需要等待,追踪状态
方法asyncSetobjName,隔1秒再修改数据,传递参数Asyncname
方法asyncSetobjId 隔1.2秒再修改数据,传递动态参数
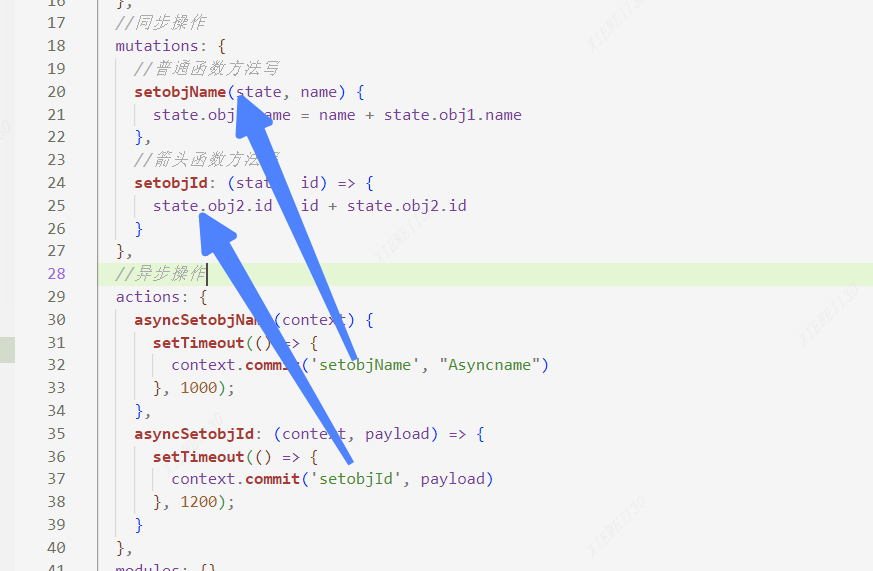
- //异步操作
- actions: {
- asyncSetobjName(context) {
- setTimeout(() => {
- context.commit('setobjName', "Asyncname")
- }, 1000);
- },
- asyncSetobjId: (context, payload) => {
- setTimeout(() => {
- context.commit('setobjId', payload)
- }, 1200);
- }
- },
会发现 context.commit('setobjName', "Asyncname")时候的方法还是mutations里面的同步方法!
同样页面提交时候 this.$store.dispatch("XXXX");
test.vue页面
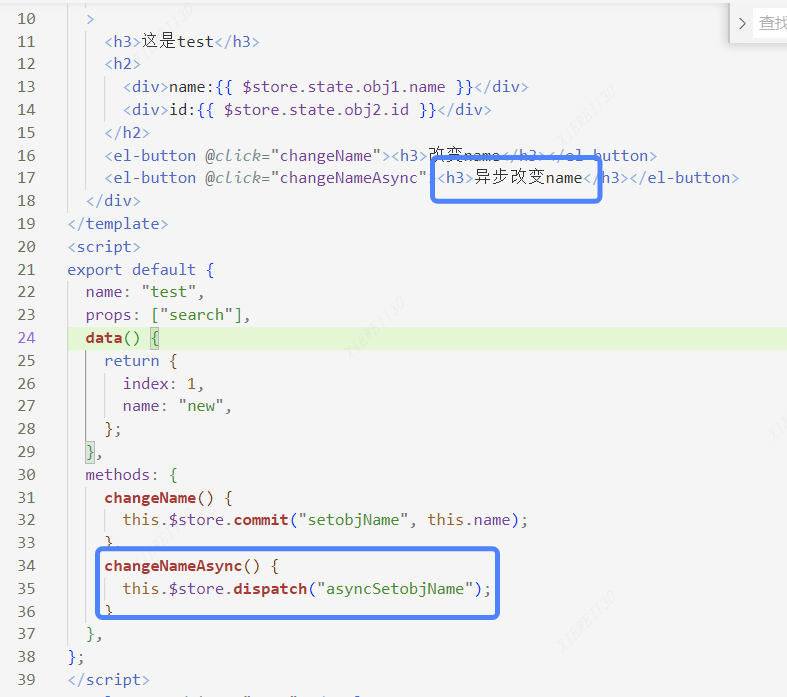
- changeNameAsync() {
- this.$store.dispatch("asyncSetobjName");
- },
也可以使用辅助函数操

使用的详细教程文档结构
使用的详细教程文档结构
使用的详细教程文档结构

1 store.js文档的结构
- import Vue from 'vue'
- import Vuex from 'vuex'
- Vue.use(Vuex)
- export default new Vuex.Store({
- state: {
- //直接使用
- obj1: {
- name: "张三儿1",
- id: "obj1"
- },
- //辅助函数
- obj2: {
- name: "张三儿2",
- id: "obj2"
- }
- },
- //同步操作
- mutations: {
- //普通函数方法写
- setobjName(state, name) {
- state.obj1.name = name + state.obj1.name
- },
- //箭头函数方法写
- setobjId: (state, id) => {
- state.obj2.id = id + state.obj2.id
- }
- },
- //异步操作
- actions: {
- asyncSetobjName(context) {
- setTimeout(() => {
- context.commit('setobjName', "Asyncname")
- }, 1000);
- },
- asyncSetobjId: (context, payload) => {
- setTimeout(() => {
- context.commit('setobjId', payload)
- }, 1200);
- }
- },
- modules: {}
- })
2 路由里面核心代码组件 Home, Test,Profile三个组件页面(也可以不用一下代码。自己写三个路由组件)

- import Vue from 'vue'
- import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
- import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
- import Login from '../views/login.vue'
- import Footer from '../views/footer.vue'
- Vue.use(VueRouter)
- const VueRouterPush = VueRouter.prototype.push
- VueRouter.prototype.push = function push(to) {
- return VueRouterPush.call(this, to).catch(err => err)
- }
- const routes = [{
- path: '/',
- name: 'Home',
- components: {
- default: Home,
- footerName: Footer
- }
- },
- {
- path: '/Login',
- name: 'Login',
- components: {
- default: Login,
- }
- },
- {
- path: '/Test',
- name: 'Test',
- meta: {
- title: "是否有权限",
- transition: "abcd"
- },
- components: {
- default: () => import('../views/Test.vue'),
- footerName: Footer
- },
- props: {
- default: route => {
- return route.query.search
- },
- footerName: {
- footerdata: "正版"
- }
- },
- beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
- if (to.meta.title) {
- console.log('meta后执行', to.meta.title)
- }
- next()
- }
- }, {
- path: '/Profile',
- name: 'Profile',
- components: {
- default: () => import('../views/profile.vue'),
- footerName: Footer
- },
- props: {
- default: true,
- footerName: {
- footerdata: "正版"
- }
- }
- },
- {
- path: '/:all',
- name: 'Router404',
- component: () => import('../views/Router404.vue')
- }
- ]
- const router = new VueRouter({
- mode: 'history',
- base: process.env.BASE_URL,
- routes
- })
- let flag = false;
- let pathName = '';
- router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
- if (to.meta.title) {
- console.log('meta先执行')
- }
- flag = localStorage.getItem('userToken') ? true : false
- if (flag) {
- if (to.name === 'Login') {
- next('/')
- } else if (to.name === 'Home' && pathName) {
- next(pathName)
- } else {
- next()
- }
- } else {
- if (to.name === 'Login') {
- next()
- } else {
- if (to.path === '/Profile') {
- pathName = to.path
- }
- next('/Login')
- }
- }
- })
- export default router
3 App.vue
- <template>
- <div id="app" style="margin: 50px; line-height: 34px; width: 800px">
- <h3>
- <div>name:{{ $store.state.obj1.name }}</div>
- <div>id:{{ $store.state.obj2.id }}</div>
- </h3>
- <el-button> <router-link to="/Profile">Profile</router-link></el-button> 丨
- <el-button> <router-link to="/Test">Test</router-link></el-button>
- <router-view v-slot="{ Component }">
- <transition :name="route.meta.transition || 'fade'">
- <component :is="Component" />
- </transition>
- </router-view>
- <router-view name="footerName"></router-view>
- </div>
- </template>
4 profile.vue
- <template>
- <div
- style="
- margin-top: 50px;
- line-height: 34px;
- width: 800px;
- border: 1px solid red;
- "
- >
- <h3>这是profile</h3>
- <h2>
- <div>name:{{ $store.state.obj1.name }}</div>
- 使用辅助函数
- <div>id:{{ obj2.id }}</div>
- </h2>
- <el-button @click="changeIdFun"><h3>改变id</h3></el-button>
- <el-button @click="changeIdFunAsync"><h3>异步改变id</h3></el-button>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- //辅助函数
- import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
- export default {
- name: "Table",
- props: ["username", "userid"],
- computed: {
- ...mapState(["obj2"]),
- },
- data() {
- return {
- id: "new",
- idAsync: "idAsync",
- };
- },
- methods: {
- //方法2 使用辅助函数提交 和下面注释的效果一样
- ...mapMutations(["setobjId"]),
- ...mapActions(["asyncSetobjId"]),
- changeIdFun() {
- this.setobjId(this.id);
- },
- //方法1 正常commit提交
- // changeId() {
- // this.$store.commit("setobjId", this.id);
- // },
- changeIdFunAsync() {
- this.asyncSetobjId(this.idAsync, this.idAsync);
- },
- },
- };
- </script>
- <style scoped lang="scss">
- h2 {
- color: purple;
- margin-bottom: 10px;
- }
- h3 {
- font-size: 18px;
- }
- </style>
5 test.vue
- <template>
- <div
- id="app"
- style="
- margin-top: 50px;
- line-height: 34px;
- width: 800px;
- border: 1px solid red;
- "
- >
- <h3>这是test</h3>
- <h2>
- <div>name:{{ $store.state.obj1.name }}</div>
- <div>id:{{ $store.state.obj2.id }}</div>
- </h2>
- <el-button @click="changeName"><h3>改变name</h3></el-button>
- <el-button @click="changeNameAsync"><h3>异步改变name</h3></el-button>
- </div>
- </template>
- <script>
- export default {
- name: "test",
- props: ["search"],
- data() {
- return {
- index: 1,
- name: "new",
- };
- },
- methods: {
- changeName() {
- this.$store.commit("setobjName", this.name);
- },
- changeNameAsync() {
- this.$store.dispatch("asyncSetobjName");
- },
- },
- };
- </script>
下一篇讲解模块化处理,module高级用法
看到这里的给个赞哦 ,码字不容易,半小时多,感谢各位
-
相关阅读:
【专栏】RPC系列(理论)-动态代理
Campus SNS 校园社区后端接口开发(附前端地址)
03-GO语言基础基本数据类型
轻松管理项目依赖:深入了解SBT的依赖管理功能
安装PLC1.9.1其它版本号Python3.6+PCL1.9.1+VS2017+gtkbundle_3.6.4版本
java基于springboot的学生公寓管理系统
一、CSS盒子模型[外边距、内边距、box-sizing、边框、轮廓线]
#ACCV2022还有两周截稿#疫情过后期待相聚澳门,相邀参与亚洲视觉盛会
如何避免系统生成的代码成为负资产?
2台nginx只需配置一台,另外一台直接生效
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jieweiwujie/article/details/126856548
