-
Vue入门(二)
本地存储
webStorage(js本地存储)
1.存储内容大小一般支持5MB左右(不同浏览器可能还不一样)
2.浏览器端通过Window.sessionStorage和Window.localStorage 属性来实现本地存储机制
3.相关API:
🛢.xxxxStorage. setIten( ' key ' , 'value ' );
该方法接受一个键和值作为参数。会把键值对添加到存储中,如果键名存在,则更新其对应的值。
🛢.该方法接受一个键名作为参数。返回键名对应的值.
🛢.xxxxxStorage . removeItem( ' key '):
该方法接受一个键名作为参数,并把该键名从存储中删除.
🛢.xxxxStorage.clear( )
该方法会清空存储中的所有数据。
备注:- SessionStorage存储的内容会随着浏览器窗口关闭而消失。
- LocalStorage存储的内容,需要手动洁除才会消失。
×x××xStorage.getItem( xxxx)如果xxx对应的value获取不到。那么getltem的返回值是null。JSON. parse(null)的结果依然是null.
localStorage
<h2>localStorageh2> <button onclick="saveData()">点我保存一个数据button> <button onclick="getData()">点我读取一个数据button> <button onclick="deleteData()">点我删除一个数据button> <button onclick="deleteAllData()">点我清空数据button> <script> let p = {name:"张三",age:18} function saveData(){ localStorage.setItem('msg',"hello"), localStorage.setItem('msg2',666), localStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p)) } function getData(){ console.log(localStorage.getItem('msg')); console.log(localStorage.getItem('msg2')); const result = localStorage.getItem('person') console.log(JSON.parse(result)); } function deleteData() { localStorage.removeItem('msg2') } function deleteAllData() { localStorage.clear() } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
sessionStorage
<h2>sessionStorageh2> <button onclick="saveData()">点我保存一个数据button> <button onclick="getData()">点我读取一个数据button> <button onclick="deleteData()">点我删除一个数据button> <button onclick="deleteAllData()">点我清空数据button> <script> let p = {name:"张三",age:18} function saveData(){ sessionStorage.setItem('msg',"hello"), sessionStorage.setItem('msg2',666), sessionStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p)) } function getData(){ console.log(sessionStorage.getItem('msg')); console.log(sessionStorage.getItem('msg2')); const result = sessionStorage.getItem('person') console.log(JSON.parse(result)); } function deleteData() { sessionStorage.removeItem('msg2') } function deleteAllData() { sessionStorage.clear() } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
组件的自定义事件
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于子组件==>父组件
⒉.使用场景∶A是父组件,B是子组件,B想给A传数据,那么就要在A中给B绑定自定义事件(事件的回调在A中)。
3.绑定自定义事件:
1.第一种方式。在父组件中:
2.第二种方式,在父组件中:
<Demo ref="dema" /> ------ mounted(){ this.$refs.dema .$on( 'atguigu', this.test) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3.若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用
once修饰符,或$once方法。4.触发自定义事件:
this.$emit("atguigu",数据)5.解绑自定义事件
this.$off('atguigu')6.组件上也可以绑定原生DOM事件,需要使用
native修饰符。7.注意:通过
this.$refs.xxx.$on(' atguigu ',回调)绑定自定义事件时,回调要么配置在methods中,要么用箭头函数,否则this指向会出问题!//触发自定义事件和解绑自定义事件 methods: { sendStudentName(){ // 触发student组件实例对象身上的atguigushijian this.$emit('atguigu',this.name,666,888) // this.$emit('demo') // this.$emit('click') }, unbind(){ this.$off('atguigu') //解绑一个自定义事件 // this.$off(['atguigu','demo']) //解绑多个自定义事件 // this.$off() //解绑所有自定义事件 } },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
//使用ref mounted() { this.$refs.student.$on('atguigu',this.getStudentName)//绑定自定义事件 // this.$refs.student.$once('atguigu',this.getStudentName) },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
全局事件总栈
全局事件总线(GlobalEventBus)
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信。2.安装全局事件总线:
new Vue({ ...... beforeCreate() { Vue.prototype.$bus = this //安装全局事件总线.$bus就是当前应用的vm }, ..... })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
3.使用事件总线:
1.接收数据:A组件想接收数据,则在A组件中给$bus绑定自定义事件,事件的回调留在A组件自身。methods({ demo(data){------} } ..... mounted({ this.$bus.$on('xxxx',this.demo) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.提供数据:
this.$bus.$emit( " xxc" ,数据)
4.最好在beforeDestroy钩子中。用$off去解绑当前组件所用到的事件。消息订阅与发布
消息订阅与发布(pubsub)
1.一种组件间通信的方式。适用与任意组件间通信。
2.使用步骤:
(1).安装pubsub:npm i pubsub-js
(2).引入:import pubsub from " pubsub-js"3.使用事件总线:
- 接收数据:A组件想接收数据,则在A组件中订阅消息,订阅的回调留在A组件自身。
- 提供数据: pubsub. publish( " xxxx" ,数据)
- 最好在
beforeDestroy钩子中,用Pubsub .unsubscribe去取消订阅。
methods(){ demo(data){------} } ..... mounted(){ this.pid = pubsub.subscribe( " xxxx " , this.demo) //订阁消息 }, beforeDestroy(){ pubsub.unsubscribe(this.xxxx) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
nextTick
1.语法:
this.$nextTick(回调函数)
2.作用:在下一次DOM更新结束后执行其指定的回调。
3.什么时候用:当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新DOM进行某些操作时,要在nextTIck所指定的回调函数中执行。Vue封装的过度与动画
-
作用:在插入、更新或移除DOM元素时,在合适的时候给元素添加样式类名。
-
图示:
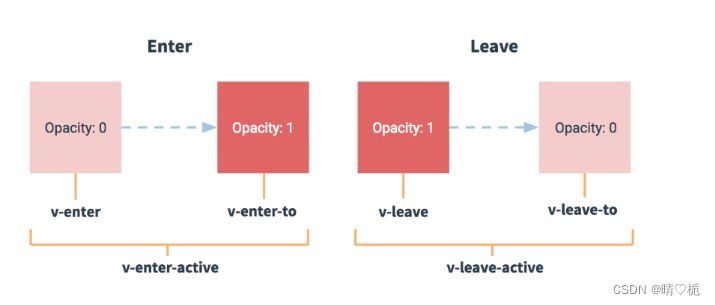
-
写法:
1.准备好样式:
(1)元素进入的样式:
v-enter:进入的起点v-enter-active:进入过程中v-enter-to:进入的终点
(2)元素离开的样式:
v-leave:离开的起点v-leave-active:离开的过程v-leave-to:离开的终点
2.使用
<transition name="hello"> <h1 v-show="isShow">你好啊!</h1> </transition>- 1
- 2
- 3
3.备注:若有多个元素需要过度,则需要使用:
Vue脚手架配置代理
vue脚手架配置代理
方法一
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置:devServer :{ proxy : "http: // localhost:5000" }- 1
- 2
- 3
说明:
1.优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端(8080)即可。
⒉.缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
3.工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器(优先匹配前端资源)方法二
编写vue.config.js配置具体代理规则:module.exports = { devServer: { proxy : { '/api1': {//匹配所有以 '/api1'开头的请求路径 target: 'http://localhost:5000' ,//代理目标的基础路径 changeOrigin: true, pathRewrite: {'^/api1':''} }, '/api2' : {//匹配所有以"/api2'开头的请求路径 target: 'http://localhost: 8081',// 代理目标的基础路径 changeOrigin: true, pathRewrite: {'^/api2':''} } }}} /* changeOrigin设置为true时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为: localhost:5000 changeOrigin设置为false时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为: localhost:8080 changeorigin默认值为true */- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
说明:
1.优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理。2.缺点:配置略微繁唢,请求资源时必须加前缀。
插槽
插槽
1.作用:让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入htm结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于父组件==>子组件。2.分类:默认插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽
3.使用方式:
默认插槽:
🎈父组件中:
<Category/> <div>html结构1</div> </Category>- 1
- 2
- 3
🎈子组件中:
<template> <div> <!--定义插槽--> <slot>插槽默认内容..-</slot> </div> </template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
具名插槽:
🎈父组件中:
<category> <template slot="center"> <div>html结构1</div> </template> <template v-slot:footer> <div>html结构2</div> < /template> </Category>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
🎈子组件中
<template> <div> <slot name="center"></slot> <slot name='footer'></slot> </div> </template>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
作用域插槽:
1.理解:数据在组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。(games数据在Category组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App组件决定)
2.具体编码:
🎈父组件中:<Category> <template scope="scopeData"> <!--生成的是uil列表--> <ul> <li v-for="(i,g) in scopeData.games">{{i}}</li> </ul> </template> </Category> <Category> <template slot-scope="scopeData"> <!--生成的是h4标题--> <h4 v-for="(i,g)" in scopeData.games" : key="g">{{i}}</h4></template> </Category>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
🎈子组件中:
<template> <div> <slot :games="games"></slot> </div> </template> <script> export default{ name:"Category ", data(){ return [ games:{"..","","",} ] } } </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
✨✨希望各位大佬看完之后指正一二
-
相关阅读:
济南软件著作权申请流程
Java类加载器
4个有影响力的绩效管理最佳实践
H3C mstp+vrrp实验 新华三杯拆解
Linux设置开机自启动奇安信可信浏览器,并配置默认页面
node.js云学堂微信小程序学习系统的设计与实现毕业设计源码011735
青骨申报|CSC管理信息平台使用指南
比特币中的符文是什么?
前端路由与vue-router原理
和对手‘打’成一片
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63679126/article/details/126802324
