-
网络编程:select的用法和原理
Linux上的select函数
select函数用于检测在一组socket中是否有事件就绪。这里的事件就绪一般分为三类:
- 读事件就绪
1)在socket内核中,接收缓冲区中的字节数大于或等于低水位标记SO_RCVLOWAT,此时调用recv或read函数可以无阻塞地读取内核文件描述符,并且返回值大于0。
2) TCP连接的对端关闭连接,此时本端调用recv或read函数对socket进行读写操作,recv或read函数会返回0值。
3) 在监听socket上有新的连接请求。
4) 在socket上有未处理的错误。- 写事件就绪
1) 在socket内核中,发送缓冲区中的可用字节数大于或等于低水位标记SO_SNDLOWAT,可以无阻塞地写,并且返回值大于0。
2) socket的写操作被关闭(调用了close或shutdown函数)时,对一个写操作被关闭的socket进行写操作,会触发SIGPIPE信号。
3) socket使用非阻塞connect连接成功或失败时。- 异常事件就绪
在socket上收到带外数据,函数签名如下:
int select(int nfds, fd_set* readfds, fd_set* writefds, fd_set* exceptfds, struct timeval* timeout);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
参数说明:
1) nfds:Linux上的socket也叫fd,将这个参数的值设置未所有需要使用socket函数检测事件的fd中的最大值加1.
2) readfds:需要监听的可读事件的fd集合。
3) writefds:需要监听的可写事件的fd集合。
4) exceptfds:需要监听异常事件的fd集合。
5) timeout:超时时间,即在这个参数设定的事件内检测这些fd的事件,超过这个时间后,select函数将立即返回。
timeval类型结构体,定义如下:struct timeval { long tv_sec; // 秒 long tv_usec; // 微秒 };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
select函数的总超时时间是两个参数的和。
2 3 4参数的类型都是fd_set,这是一个结构体信息,其定义在
/usr/include/sys/select.h中// fd_set字段必须是一个long型数组 typedef long int __fd_mask; #define __NFDBITS (8 * (int) sizeof (__fd_mask)) #define __FD_ELT(d) ((d) / __NFDBITS) #define __FD_MASK(d) ((__fd_mask) 1 << ((d) % __NFDBITS)) // fd_set结构用于select和pselect函数 typedef struct { // __FD_SETSIZE = 1024 // __NFDBITS = 64 __fd_mask __fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / NFDBITS]; #define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->__fd_bits) }fd_set; // fd_set结构体中文件描述符的最大数量 #define FD_SETSIZE __FD_SETSIZE- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
假设未定义宏__USE_XOPEN,整理得:
typedef struct { long int __fds_bits[16]; } fd_set;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
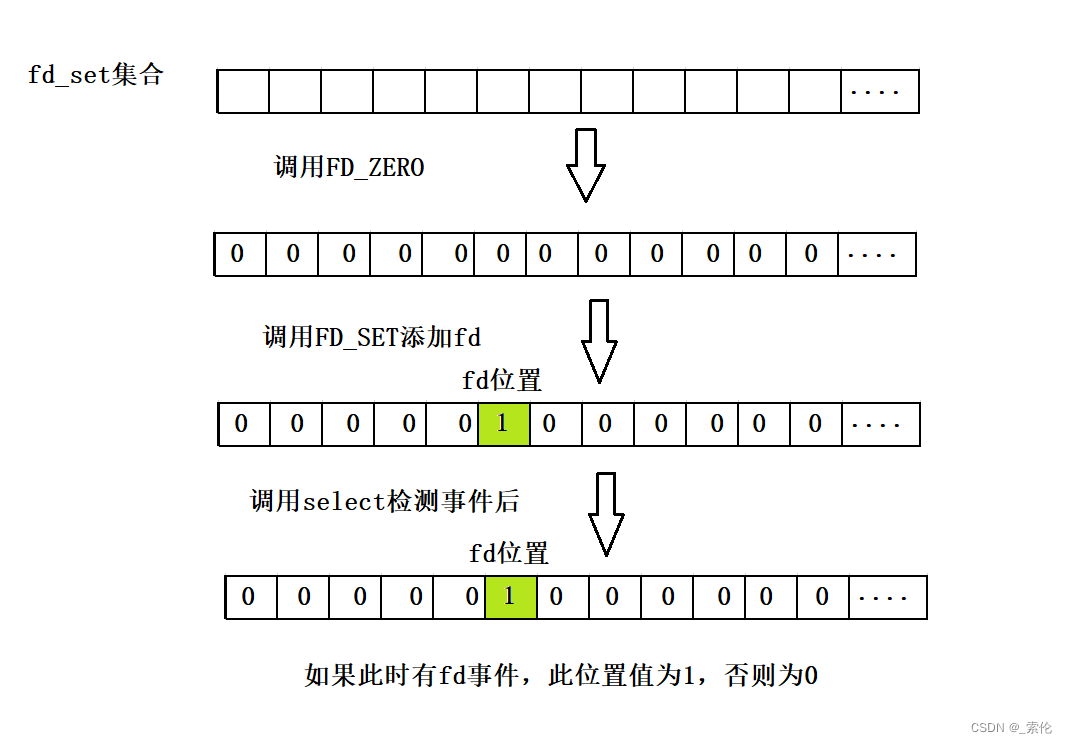
在将一个fd添加到fd_set这个集合中时需要使用FD_SET宏,其定义如下:
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set* set);- 1
实现如下:
#define FD_SET(fd, fdsetp) __FD_SET(fd, fdsetp)- 1
FD_SET又是通过宏__FD_SET实现的,定义如下:
#define __FD_SET(d, set) \ ((void) (__FDS_BITS (set) [__FD_ELT (d)] |= __FD_MASK (d)))- 1
- 2
__FD_MASK和__FD_ELT宏已经给出定义:
#define __FD_ELT(d) ((d) / __NFDBITS) #define __FD_MASK (d) ((__fd_mask) 1 << ((d) % __NFDBITS))- 1
- 2
fd_set数组定义:
typedef struct { long int __fds_bits[16]; } fd_set;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
long int占8字节,每个字节都有8bit,每个bit都对应一个fd事件状态,0表示无事件,1表示有,数组长度是16,因此一共可以表示8 * 8 * 16 = 1024个fd的状态,这是select函数支持的最大fd数量。
再来看__FD_SET(d, set)的实际操作:
__FD_ELT(d)确定的是某个fd在数组__fds_bits中的下标位置,计算方法将fd与__NFDBITS求商。
__FD_MASK计算对应的fd在对应的bit位置的值,计算方法是先与__NFDBITS求余得到n,然后执行1 << n,即左移n位,然后将值设置到对应的bit上。示例:
若fd值位57,那么__FD_SET(57, set)调用的是
__fds_bits[__FD_ELT(57)] |= __FD_MASK(57),即
__fds_bits[57 / 64] |= (1 << (57 % 64)),
__fds_bits[0] |= (0000 0010 0000 0000 0000…),
在数组下标位0的元素中的第57个bit被置为1。同理,如果需要在fd_set中删除某个fd,即将其对应的bit置为0,使用FD_CLR:
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set* set);- 1
若要将所有fd都清掉,使用宏FD_ZERO:
void FD_ZERO(fd_set* set);- 1
当select返回时,使用FD_ISSET宏判断在某个fd中是否有我们关心的事件:
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set* set);- 1
实际上就是检测对应的bit位是否置位:
#define __FD_ISSET(d, set) \ ((__FD_BITS (set) [__FD_ELT (d)] & __FD_MASK (d)) != 0)- 1
- 2
具体示例
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include // 定义代表无效的fd值 #define INVALID_FD -1 int main(void) { // 1.创建一个监听socket int listenfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (listenfd == INVALID_FD) { std::cout << "create listen socket error." << std::endl; return -1; } // 2.初始化服务器地址 struct sockaddr_in bindaddr; bindaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; bindaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); bindaddr.sin_port = htons(3000); if (bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr*)&bindaddr, sizeof(bindaddr)) == -1) { std::cout << "bind listen socket error." << std::endl; close(listenfd); return -1; } // 3.启动监听 if (listen(listenfd, SOMAXCONN) == -1) { std::cout << "listen error." << std::endl; close(listenfd); return -1; } // 4. 存储客户端socket的数组 std::vector<int> clientfds; int maxfd; while (true) { fd_set readset; FD_ZERO(&readset); // 将监听socket加入待检测的可读事件中 FD_SET(listenfd, &readset); maxfd = listenfd; // 将客户端fd加入待检测的可读事件中 int clientfdslength = clientfds.size(); for (int i = 0; i < clientfdslength; ++i) { if (clientfds[i] != INVALID_FD) { FD_SET(clientfds[i], &readset); if (maxfd < clientfds[i]) maxfd = clientfds[i]; } } timeval tm; tm.tv_sec = 1; tm.tv_usec = 0; // 暂且只检测可读事件,不检测可写和异常事件 int ret = select(maxfd + 1, &readset, NULL, NULL, &tm); if (ret == -1) { // 出错,退出程序 if (errno != EINTR) { break; } } else if (ret == 0) { // select函数超时 continue; } else { // 检测到某个socket有事件 if (FD_ISSET(listenfd, &readset)) { // 监听socket的可读事件,表明有新的连接到来 struct sockaddr_in clientaddr; socklen_t clientaddrlen = sizeof(clientaddr); // 接收客户端连接 int clientfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr*)&clientaddr, &clientaddrlen); if (clientfd == INVALID_FD) { // 接受连接出错,退出程序 break; } // 只接受连接,不调用recv收取任何数据 std::cout << "accept a client connection, fd: " << clientfd << std::endl; clientfds.push_back(clientfd); } else { // 假设对端发来的数据长度不超过63字节 char recvbuf[64]; int clientfdslength = clientfds.size(); for (int i = 0; i < clientfdslength; ++i) { if (clientfds[i] != INVALID_FD && FD_ISSET(clientfds[i], &readset)) { memset(recvbuf, 0, sizeof(recvbuf)); // 非监听socket,接收数据 int length = recv(clientfds[i], recvbuf, 64, 0); if (length <= 0) { // 收取数据出错 std::cout << "recv data error, clientfd: " << clientfds[i] << std::endl; close(clientfds[i]); // 不直接删除该元素,将该位置的元素标记为INVALID_FD clientfds[i] = INVALID_FD; continue; } std::cout << "clientfd: " << clientfds[i] << ", recv data: " << recvbuf << std::endl; } } } } } // 关闭所有的客户端socket int clientfdslength = clientfds.size(); for (int i = 0; i < clientfdslength; ++i) { if (clientfds[i] != INVALID_FD) { close(clientfds[i]); } } // 关闭监听socket close(listenfd); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
使用nc命令模拟客户端
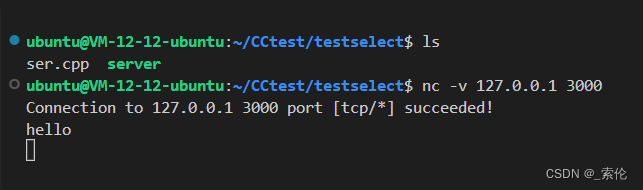
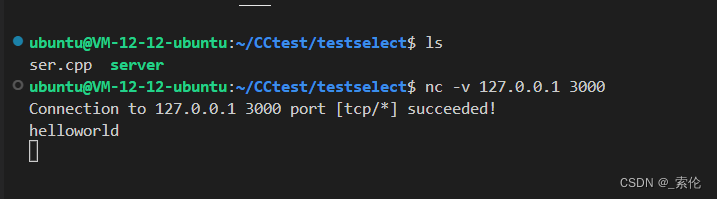
server端显示:
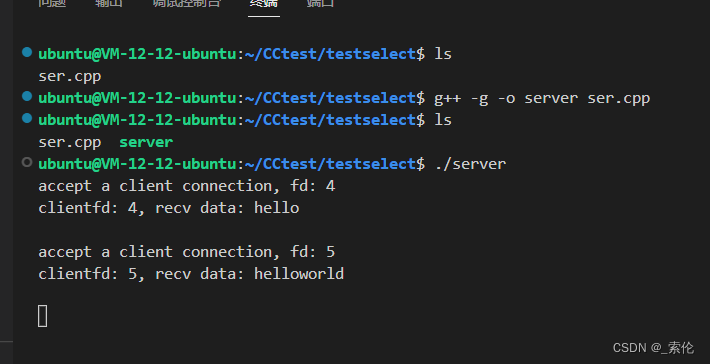
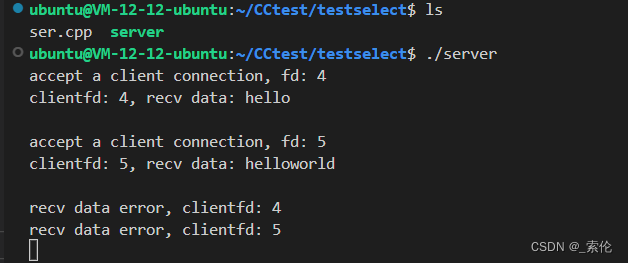
断开客户端连接后,服务端的select函数对每个客户端fd检测时,仍然会触发可读事件,此时对这些fd调用recv函数会返回0(recv函数返回0,表明对端关闭了连接),服务端也关闭这些连接就可以了。
-
相关阅读:
OpenStack常用命令
目标检测YOLO实战应用案例100讲-面向恶劣环境下的多模态 行人识别(续)
heygen模型接口 简单使用 java版
LangChain入门:24.通过Baby AGI实现自动生成和执行任务
容器相关的概念
项目初期如何确定项目的进度计划和资源需求?
机器人中的数值优化(十二)——带约束优化问题简介、LP线性规划
typeScript--[数据定义]
python末尾逗号导致返回结果是一个元组
宇视雷视工勘指导(卡口电警篇)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56257585/article/details/126823648
