-
猿创征文 |【C++】面向对象之微观部分——类的组成(下)
前言
打算做一个C++知识体系的专栏,干货较多,整理较慢,会定期产出,想学习可以关注一下。
承接上文
【C++】面向对象之微观部分——类的组成(上)
【C++】面向对象之微观部分——类的组成(中)一、运算符重载
1.1 运算符重载的意义
运算符重载,就是给运算符赋予一个新的含义,让本来只能处理基本类型运算的运算符,也能处理类对象,如果没有运算符重载,类对象之间是不能直接做运算的。
运算符重载就是为了面向对象而服务的。我们可以自定义缤纷复杂的类型,也可以使用C语言中所定义一系列的运算符进行类对象之间的运算。
1.2 运算符重载形式
运算符重载本质上也是函数重载,我们需要重新定义 operator# (#表示运算符)
返回值 operator 运算符(形式参数) { //运算符重载函数的函数体。 //此函数体内的逻辑荐意与要重载符号的逻辑相匹配。 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
操作数
个数:由重载的运算符本身决定,如:+/-需要两个操作数,++需要一个操作数。
类型:由我们自己定义。
运算符重载函数的调用
左调右参,一般是由左操作数来调用运算数重载的函数,右操作数作为参数。
如s1 = s2<===> 从编译器的角度s1.operator=(s2);。注意:
- 运算符重载的格式是约束好的,虽然逻辑可以自定义,但是我们要尽量保留运算符的含义,不要乱写,如在 + 运算符重载中写减法逻辑。
- 运算符重载可以是成员函数版,也可以全局函数版,但是全局函数访问私有成员不方便,所以一般我们都是用成员函数版。
- 同一个运算符重载函数成员函数版和全局函数版只能实现一个,否则调用时有歧义,会报错。
1.3 =号运算符重载
编译提供一种默认运算符重载函数: = 号运算符重载函数。
也叫 赋值构造函数。
调用时机
两个已经完成初始化的对象之间相互赋值的时候会自动调用拷贝赋值函数。
例:string s1("hello");//有参构造 string s2;//无参构造 s2 = s1;//拷贝赋值- 1
- 2
- 3
----从编译器的角度:
s2.operator=(s1) ;代码示例:
#includeusing namespace std; class Student { private: string name; int age; public: Student(string n, int a):name(n),age(a) { cout<<"有参构造函数"<<endl; } void show() { cout<<"姓名:"<< name <<" 年龄:"<< age << endl; } ~Student() { cout<<"析构函数"<<endl; } Student(const Student& other) { this->name=other.name; this->age=other.age; } //=号运算符重载函数 Student& operator=(const Student& other) { //防止自身给自身赋值 if(this == &other) { return *this; } this->name=other.name; this->age=other.age; cout << "=号运算符重载函数" << endl; return *this;//返回自身的引用是为了级联使用 = 时可以用到 } }; int main() { Student s1("夜猫徐",18); s1.show(); Student s2("张三",20); s2.show(); Student s3("李四",30); s2=s1=s3;//从右向左结合 //需要用到 s1 = s3 函数返回的结果作为 s2 = s1 的参数 //所以需要将 s1 反回来,也就是需要返回自身的引用 s2.show(); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
结果展示:
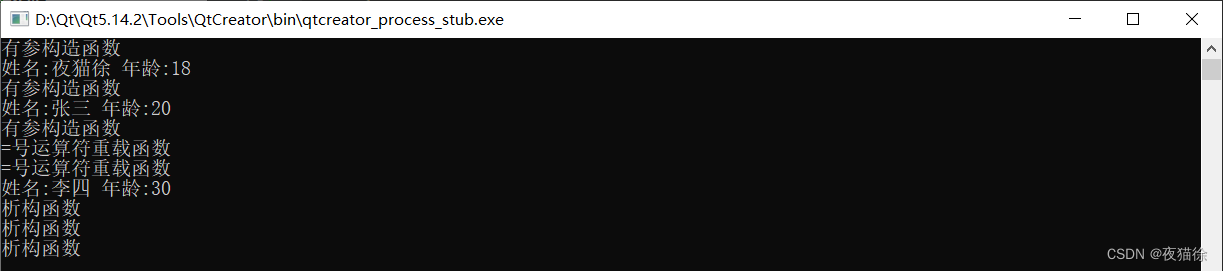
总结:stu1 = stu2 = stu3; <==> stu1.operator=(stu2.operator=(stu3))- 1
运算符重载函数一定必须要有operator修饰。
1.4 编译器自动提供的=号运算符重载中的深浅拷贝的问题
优化代码:
#includeusing namespace std; class Student { private: string name; int age; int *p; public: Student(string n, int a):name(n),age(a),p(new int[20]) { cout<<"有参构造函数"<<endl; } void show() { cout<<"姓名:"<< name <<" 年龄:"<< age << endl; } ~Student() { delete []p; cout<<"析构函数"<<endl; } Student(const Student& other) { this->name=other.name; this->age=other.age; //当类中有属性指针指向堆区,必须将浅拷贝升级为深拷贝 //1.开辟新空间 this->p=new int[20]; //2.拷贝数据 memmove(this->p,other.p,sizeof(int[20])); } //=号运算符重载函数 Student& operator=(const Student& other) { //防止自身给自身赋值 if(this == &other) { return *this; } this->name=other.name; this->age=other.age; if(this->p!=nullptr) { delete []p; this->p=new int[20]; } else { this->p=new int[20]; } memmove(this->p,other.p,sizeof(int[20])); cout << "=号运算符重载函数" << endl; return *this;//返回自身的引用是为了级联使用 = 时可以用到 } }; int main() { Student s1("夜猫徐",18); s1.show(); Student s2("张三",20); s2.show(); Student s3("李四",30); s2=s1=s3;//从右向左结合 //需要用到 s1 = s3 函数返回的结果作为 s2 = s1 的参数 //所以需要将 s1 反回来,也就是需要返回自身的引用 s2.show(); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
结果展示:
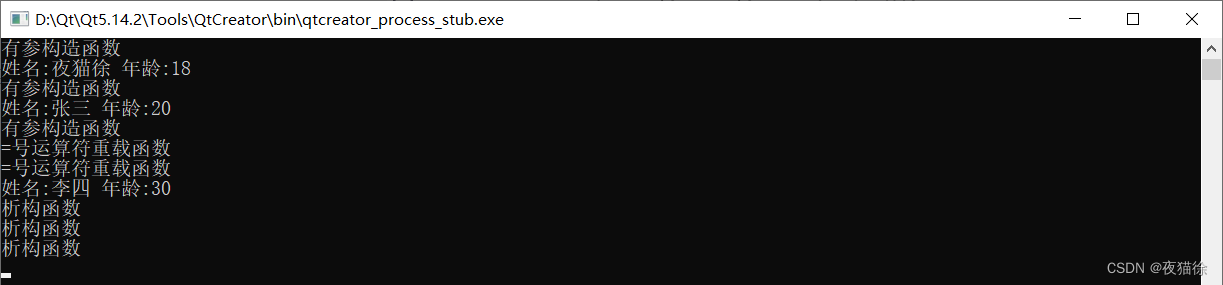
总结:
当类中有属性指针指向堆区,先把指针指向的原空间释放,因为可能开辟过空间了,如果直接拷贝容易出现内存泄漏。
默认的=号运算符重载没有考虑到有属性指针指向堆区这种情况,需要自己写。1.5 常见的运算符重载格式
详细示例看下面1.7,1.8的实战例子。
friend友元,需要在类中声明 全局函数 是类的朋友,就可以访问朋友类中的私有成员。
本文全局函数版的运算符重载会简单提及,在下篇文章会进行详细讲解。本片文章主要使用公有get方法。无法获取类中的私有成员,可以在类中提供公开的get方法或者friend友元在类中声明全局函数。
1.5.1 算数运算符的重载
+ - * / %
表达式:L # R(L 左操作数,# 运算符,R 右操作数)
左操作数:既可以是一个左值,也可以是一个右值。
右操作数:既可以是一个左值,也可以是一个右值。
表达式的结果:只能是右值。成员函数版:
从编译器的角度L.operator#(R);const 类名 operator#(const 类名& R)const;- 1
形参的const修饰的是R,常成员函数的const修饰的是L。
全局函数版:
从编译器的角度operator#(L, R);friend const 类名 operator#(const 类名 &L, const 类名 &R);- 1
代码示例:
//+号运算符重载 const Complex operator+(const Complex& c)const { Complex temp; temp.real=this->real+c.real; temp.vir=this->vir+c.vir; cout << "+号运算符重载" << endl; return temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
1.5.2 关系运算符的重载
> < == != >= <=
成员函数版:
bool operator#(const 类名 &R)const;- 1
全局函数版:
friend const bool operator#(const 类名 &L, const 类名 &R);- 1
其他同上。
代码示例:
//>号运算符重载,自定义的规则 bool operator>(const Complex& c)const { if(this->real>c.real&&this->vir>c.vir) { cout << ">号运算符重载" << endl; return true; } cout << ">号运算符重载" << endl; return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
1.5.3 赋值类运算符的重载
= += -= *= /= &= |= ^= …
表达式:L # R
左操作数:只能是左值。
右操作数:既可以是一个左值,也可以是一个右值。
表达式的结果:左操作数自身。成员函数版:
从编译器的角度L.operator#(R)类名 &operator#(const 类名 &R);- 1
全局函数版:
从编译器的角度operator#(L, R);friend 类名 &operator#(类名 &L, const 类名 &R);- 1
代码示例:
//+=运算符重载 Complex& operator+=(const Complex& c) { this->real+=c.real; this->vir=c.vir; cout << "+=号运算符重载" << endl; return *this; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
= 号运算符重载,只能实现成员函数版。
因为编译器给类中提供的特殊的成员函数:拷贝赋值函数就是 = 运算符的重载1.5.4 单目运算符的重载
-(负) !(非) ~(取反)
表达式:#O
操作数:既可以是一个左值,也可以是一个右值。
表达式的结果:是一个右值。成员函数版:
从编译器的角度O.operator#();const 类名 operator#(void)const;- 1
全局函数版:
从编译器的角度operator#(O);代码示例:
friend const 类名 operator#(const 类名 &O);- 1
//-(负号)运算符重载 //他不会和算数运算符的减号重载冲突 //原因是形参列表不同 const Complex operator-()const { Complex temp; temp.vir=-this->vir; temp.real=-this->real; cout << "负号运算符重载" << endl; return temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
1.5.5 自增/自减运算符的重载
++a --a
表达式:#O
操作数:只能是左值。
表达式的结果:只能是左值。成员函数版:
从编译器的角度O.operator#();类名 &operator#(void);- 1
全局函数版:
从编译器的角度operator#(O);friend 类名 &operator#(类名 &O);- 1
代码示例:
//前++运算符重载 Complex& operator++() { this->vir++; this->real++; cout << "前++运算符重载" << endl; return *this; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
a++ a–
表达式:O#
操作数:只能是左值
表达式的结果:是一个右值
成员函数版:
从编译器的角度O.operator#(哑元);
此处的int只起到一个哑元占位用,不用实际传参,是用来区别前++ 和 后++ 的。const 类名 operator#(int);- 1
全局函数版:
从编译器的角度operator#(O,哑元);friend 类名 operator#(类名 &O,int);- 1
代码示例:
//后++运算符重载 const Complex operator++(int) { Complex temp=*this; this->vir++; this->real++; cout << "后+运算符重载" << endl; return temp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
1.5.6 插入>>和提取<<运算符的重载
cin和cout是istream和ostream类的对象namespace std { istream cin; ostream cout; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
int a = 10; cout<<a; //从编译器的角度 cout.operator<<(a)- 1
- 2
对于插入和提取运算符的重载,只能实现 全局函数版,
因为我们无法修改,istream和ostream类提取<<运算符重载的格式:
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &x, const 类名 &y);- 1
代码示例:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& x,Complex& c) { x<<c.getreal()<<"+"<<c.getvir()<<"i"<<endl;//无法获取类中的私密属性,可以在类中提供公开的get方法或者friend友元 cout << "<<运算符重载" << endl; return x;//不返回不能连续输出 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
插入>>运算符重载的格式:
friend istream &operator>>(istream &x, 类名 &y);- 1
代码示例:
istream& operator>>(istream& x,Complex& c) { x>>c.real>>c.vir; cout << ">>运算符重载" << endl; return x; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.6 不可重载的运算符
C++中大多的运算符均可以重载,但有一些是系统定义好的,是禁止重载的。
下面是不可重载的运算符列表:
.(点运算符)通常用于取对象的成员。但是->(箭头运算符)是可以重载的。::(作用域运算符)即类名+域运算符,取成员,不可以重载。.*(成员指针运算符)与->*运算符,也是不可重载的,反正这两个运算符。?:(三目运算符)不可以重载。sizeof不可以重载。#号预处理运算符。
1.7 实战:封装一个复数类 Complex
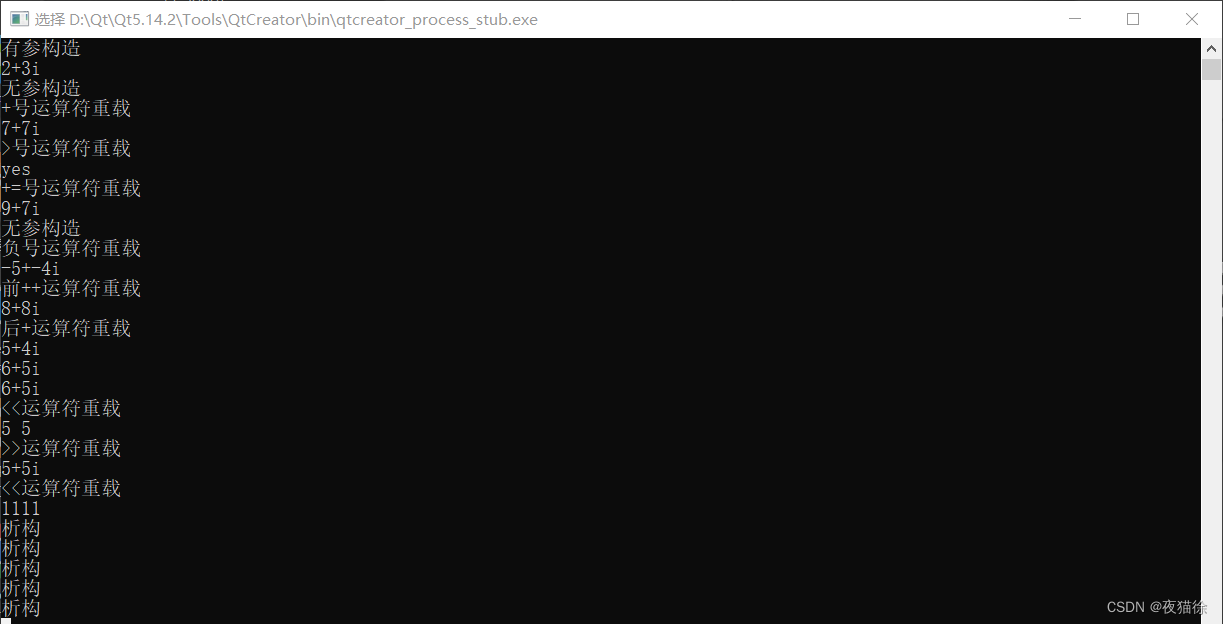
#includeusing namespace std; class Complex//复数类 { private: int real;//实部 int vir;//虚部 public: Complex()//无参构造 { cout << "无参构造" << endl; } Complex(int real,int vir)//有参构造 { this->real=real; this->vir=vir; cout << "有参构造" << endl; } ~Complex()//析构 { cout << "析构" << endl; } void show() { cout << real << "+" << vir <<"i" << endl; } int getreal() { return this->real; } int getvir() { return this->vir; } //+号运算符重载 const Complex operator+(const Complex& c)const { Complex temp; temp.real=this->real+c.real; temp.vir=this->vir+c.vir; cout << "+号运算符重载" << endl; return temp; } //>号运算符重载,自定义的规则 bool operator>(const Complex& c)const { if(this->real>c.real&&this->vir>c.vir) { cout << ">号运算符重载" << endl; return true; } cout << ">号运算符重载" << endl; return false; } //+=运算符重载 Complex& operator+=(const Complex& c) { this->real+=c.real; this->vir=c.vir; cout << "+=号运算符重载" << endl; return *this; } //-(负号)运算符重载 //他不会和算数运算符的减号重载冲突 //原因是形参列表不同 const Complex operator-()const { Complex temp; temp.vir=-this->vir; temp.real=-this->real; cout << "负号运算符重载" << endl; return temp; } //前++运算符重载 Complex& operator++() { this->vir++; this->real++; cout << "前++运算符重载" << endl; return *this; } //后++运算符重载 const Complex operator++(int) { Complex temp=*this; this->vir++; this->real++; cout << "后+运算符重载" << endl; return temp; } friend istream& operator>>(istream& x,Complex& c); }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& x,Complex& c) { x<<c.getreal()<<"+"<<c.getvir()<<"i"<<endl;//无法获取类中的私密属性,可以在类中提供公开的get方法或者friend友元 cout << "<<运算符重载" << endl; return x;//将返回值设计成ostream&/istream& 是为了连续输出 } istream& operator>>(istream& x,Complex& c) { x>>c.real>>c.vir; cout << ">>运算符重载" << endl; return x; } int main() { Complex c1(5, 4); c1.show();//5+4i Complex c2(2, 3); c2.show();//2+3i Complex c3=c1+c2; c3.show();//7+7i cout << (c1>c2?"yes":"no") << endl; c2+=c3; c2.show();//9+7i Complex c5=-c1; c5.show();//-5+-4i ++c3; c3.show();//8+8i Complex c6=c1++; c6.show();//5+4i c1.show();//6+5i cout<<c1;//6+5i cin>>c1; cout<<c1<<1111<<endl; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
结果展示:
1.8 实战:封装一个字符串类 MyString
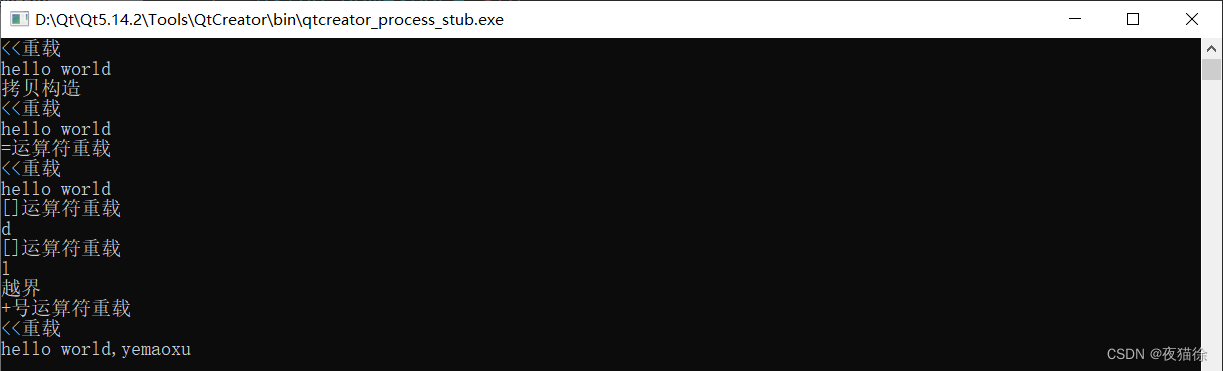
#include#include using namespace std; class my_string { private: char *my_data; public: //无参构造 my_string() { this->my_data=new char[1]; this->my_data[0]='\0'; } //有参构造 my_string(const char *c_str) { //获得字符串长度 int len=strlen(c_str); //开辟空间 this->my_data=new char[len+1]; //拷贝 memmove(this->my_data,c_str,sizeof(char[len])); //加尾0 this->my_data[len]='\0'; } //拷贝构造 my_string(const my_string& other) { cout << "拷贝构造"<< endl; int len=strlen(other.my_data); this->my_data=new char[len+1]; memmove(this->my_data,other.my_data,len); this->my_data[len]='\0'; } //析构 ~my_string() { delete []my_data; my_data=nullptr; } //get方法 char* get() { return this->my_data; } //[]运算符重载 char operator[](int index) { int len=strlen(this->my_data); if(0>index||index>=len) { cout<<"越界"; return -1; } cout << "[]运算符重载"<<endl; return this->my_data[index]; } //=运算符重载 my_string& operator=(const my_string& other) { cout << "=运算符重载"<< endl; if(this==&other) { return *this; } int len=strlen(other.my_data); if(this->my_data!=nullptr) { delete []my_data; this->my_data=new char[len+1]; } else { this->my_data=new char[len+1]; } memmove(this->my_data,other.my_data,len); this->my_data[len]='\0'; return *this; } //+号运算符重载 my_string& operator+(my_string& other) { cout << "+号运算符重载" << endl; //方法一:通过strcat拼接 //this->my_data=strcat(this->my_data,other.my_data); //方法二: int len=strlen(this->my_data)+strlen(other.my_data); char *temp=new char[len+1]; memmove(temp,this->my_data,strlen(this->my_data)); memmove(temp+strlen(this->my_data),other.my_data,strlen(other.my_data)); temp[len+1]='\0'; delete []my_data; this->my_data=temp; return *this; } }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& x,my_string& s) { cout << "<<重载"<<endl; x<<s.get(); return x; } int main() { my_string s1("hello world"); cout << s1 << endl; my_string s2(s1); cout << s2 << endl; my_string s3; s3=s1; cout << s3 << endl; cout << s3[10] << endl;//d cout << s3[9] << endl;//l cout << s3[11] << endl;//越界 my_string s4(",yemaoxu"); cout << s1+s4 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
结果展示:
二、C++中空类默认提供的函数
1.无参构造函数:
A(void){}- 1
2.析构函数:
~A(void){}- 1
3.拷贝构造函数:
A(const A& ){}- 1
4.=号运算符重载函数(拷贝赋值函数):
A& operator=(const A& ){}- 1
5.取址运算符(一对,一个非const的,一个const的)
-----有争议,跟具体编译器相关,有的生成,有的不生成。A* operator&(); const A* operator&() const;- 1
- 2
三、C++常用设计模式之 Singleton 模式(单例模式)
3.1 设计模式概念
设计模式是软件开发人员在软件开发过程中面临的一般问题的解决方案。这些解决方案是众多前辈经过相当长的一段时间的试验和错误,总结出来的解决某一类问题的一种编码方案。
设计模式是一种设计思想,不依赖于任何语言,也没有固定的代码。
是通过语法的复杂性来提高代码的灵活性的一种套路。3.2 Singleton 模式(单例模式)概念
Singleton 模式是设计模式中最为简单、最为常见、最容易实现,也是最应该熟悉和掌握的模式。
Singleton 模式就是一个类只创建一个唯一的对象,即一次创建多次使用。
通俗讲即为保证一个类有且仅有一个实例,并提供一个该实时全局访问接口。
如:游戏中的背包、windows中的回收站、任务管理器,永远只能打开同一个。单例分为懒汉式和饿汉式。
3.3 实现单例模式的设计思路及步骤
- 如果想有且只有一个实例,就不能让用户可以随便调用为类中构造。因为一旦构造被调用,这个实例就算是产生。所以我们就应该把构造函数私有化。
- 私有化之后,一个对象也产生不了。所以就应该提供一个公有接口调用私有的构造函数,在这个接口中调用类中的构造函数,并返回一个指向这个对象的指针。但是这个公有的接口是一个普通函数,普通函数的调用还是依赖于对象的,但是对象的构造已经私有化了。为了不依赖某一个对象,所以就必须把这个普通的函数接口提升为不依赖某一个对象的
static的静态成员函数。 - 但是问题又来了,每次调用就会
new一个空间,产生一个实例,这又违背了单例的唯一原则。
所以就应该定义一个指针,把这个指针返回出去。所以就应该把那个new的逻辑在那个静态接口搬出来,但还必须返回一个实例指针。因为静态成员函数只能访问静态属性,所以这个指针的属性就必须升级为静态属性。
因为静态接口只能访问静态属性,又因为类中这个指针是一个静态指针,所以必须在类外完成初始化。类外初始化时,就是指向一个已经开辟好的堆区空间有且只有一份。
3.4 饿汉式
饿汉式:还没有使用该单例对象,该单例对象就已经被加载到内存了,在对象过多时会造成内存浪费。
代码示例:#includeusing namespace std; class Singleton { private: static Singleton *p; Singleton() { cout << "Singleton的构造" << endl; } Singleton(const Singleton& other)=delete;//c++11删除拷贝构造 void operator=(const Singleton& other)=delete;//c++11删除 =号运算符重载 public: static Singleton *get() { return p; } }; Singleton* Singleton::p=new Singleton; int main() { Singleton *s1=Singleton::get(); Singleton *s2=Singleton::get(); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
结果展示:

通过结果可知,地址相同,s1和s2是一个单例。3.5 懒汉式
懒汉式:解决了饿汉式内存浪费问题,但是线程不安全的,可以通过互斥量
mutex.lock()和mutex.unlock()来解决。但是如果new的时候出错返回了异常从而导致了程序终止,没有解锁会导致变成死锁。
所以为了安全我这里使用了智能锁lock_guard出作用域自动解锁。lock(mtx); #include#include using namespace std; mutex mtx;//全局锁 class Singleton { private: static Singleton *p; Singleton() { cout << "Singleton的构造" << endl; } Singleton(const Singleton& other)=delete;//c++11删除拷贝构造 void operator=(const Singleton& other)=delete;//c++11删除 =号运算符重载 public: static Singleton *get() { lock_guard<mutex> lock(mtx);//智能锁 //mtx.lock(); if(p==nullptr) { p=new Singleton; //mtx.unlock(); } return p; } }; Singleton* Singleton::p=nullptr; int main() { Singleton *s1=Singleton::get(); Singleton *s2=Singleton::get(); cout << s1 << endl; cout << s2 << endl; return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
结果展示:

通过结果可知,地址相同,s1和s2是一个单例。 -
相关阅读:
【git】一些容易混淆的操作
5.SpringMVC
pip 清华镜像
华为eNSP实验-三层交换机的不同网段通信(通过OSPF路由方式)
[C++数据结构](33)图,图的遍历,最小生成树,最短路径算法详解
Linux:进程模型和进程管理
Java使用线程池
C++项目——集群聊天服务器项目(六)MySQL模块
【电工基础】电路的基本概念与基本定律
使用Proxyman抓取Android的https请求
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_65835264/article/details/126754191
