-
【收藏系列】MySQL入门总结 ——>看这一篇就够了
目录
3.5、MySQL表的增查改删(CRUD——create、retrieve、update、delete)
1、数据库的操作
1.1、查看当前数据库
show databases;三个注意点:
- SQL里面不区分大小写
- 注意语句要以英文分号;结尾
- 注意database后面有s
1.2、创建数据库
create database [if not exists] 数据库名;两个注意点:
- database后面没有s
- [ ] 中的内容是可选项(可以不写)
1.3、使用数据库
use 数据库名;1.4、删除数据库
drop database 数据库名;
2、常用的数据类型
2.1、数值类型
数据类型 大小(单位:字节) 描述 bit[M] M指定位数,默认为1 二进制数,M范围从1到64,存储数值范围从0到2^M-1 tinyint 1 十分小的数据 smallint 2 较小的数据 int 4 标准的整数 bigint 8 较大的数据 float(M,D) 4 单精度,M指定长度,D指定小数位数(会发生精度丢失) double(M,D) 8 双精度 decimal(M,D) M/D最大值+2 双精度,M指定长度,D表示小数点位数(精确数值) numeric(M/D) M/D最大值+2 双精度,M指定长度,D表示小数点位数(精确数值) 2.2、字符串
数据类型 大小(单位:字节) 描述 char 0-255 字符串固定大小 varchar(SIZE) 0-65535 可变长度字符串 text 0-65535 长文本数据 mediumtext 0-16777215 中等长度文本数据 blob 0-65535 二进制形式的长文本数据 2.3、日期类型
数据类型 大小(单位:字节) 描述 格式 date 4 日期格式 YYYY-MM-DD time 4 HH:MM:SS datetime 8 范围从1000到9999年,不会进行时区的检索及转换 YYYY_MM_DD HH:MM:SS timestamp 4 范围从1970到2038年,自动检索当前时区并进行转换(毫秒数) year 4 年份
3、操作表
3.1、查看当前库中的表
show tables;3.2、创建表
- create table 表名(
- 字段1 类型1,
- 字段2 类型2,
- ...
- );
3.3、查看指定的表的结构
desc 表名;3.4、删除表
drop table 表名;3.5、MySQL表的增查改删(CRUD——create、retrieve、update、delete)
3.5.1、增——create
例:
- create table student (
- id int,
- num int comment '学号',
- name varchar(20),
- );
(1)、单行数据+全列插入
- insert into student values(1,18,'张三');
- insert into student values(2,19,'李四');
(2)、多行数据+指定列插入
insert into student values(3,20,'张三三'),(4,21,'李小四');进阶版新增:
插入查询结果
- insert into 表1 select * from 表2;
- -- 将表2的查询结果复制到表1中
- 通过控制条件,来插入自己想要的数据,并不是一定要全部插入过去
- 查询的结果的列要和插入的表的列相匹配(个数、类型)才可以
3.5.2、查——retrieve
1、全列查询
select * from 表;2、指定列查询
select 字段1,字段2...from 表;3、查询表达式字段
select 字段1+100,字段2+字段3 from 表;4、别名
select 表达式 as 别名 from 表名;5、去重distinct
select distinct 字段 from 表;6、排序order by
select * from 表 order by 排序字段;- -- 降序,加asc
- select * from 表 order by 排序字段 asc;
- -- 升序,默认或者加desc
- select * from 表 order by 排序字段 desc;
7、条件查询
- 比较运算符
- between ... and...
- in
- is null
- like
- and
- or
- not
- 分页查询:limit
- -- 条件查询
- select * from 表 where 条件;
- -- 分页查询,从第M条记录开始,查询N条记录
- select * from 表名 limit N offset M;
- select name from student where name like '张%';
- -- NULL和其他值进行运算,结果还是NULL
- select name ,mail from student where mail is null;
- --从s开始,筛选n条结果
- select ... from table_name [where ...] [order by ... ] limit s,n;
- select id,name,math from student order by id limit 3 offset 0;
进阶版查询:
(1、聚合查询
将行和行放到一起进行计算
(1)、聚合函数
函数 说明 count([distinct] expr) 计算查询到的数据的数量(计算行数) sum([distinct] expr) 计算查询到的数据的总和,非数字无意义 avg([distinct] expr) 计算查询到的数据的平均值,非数字无意义 max([distinct] expr) 计算查询到的数据的最大值,非数字无意义 min([distinct] expr) 计算查询到的数据的最小值,非数字无意义 - -- count,统计人数
- select count(*) from student;
- -- sum,统计数学成绩总分
- select sum(math) from student;
- -- avg,求平均总分
- select avg(chinese + math ) 平均总分 from student;
- -- max ,数学最高分
- select max(math) from student;
- -- min,语文最低分
- select min(chinese) from student;
注:如果在求和时,遇到NULL,则直接跳过不参与运算
(2)、分组查询
group by 列名;根据查询结果,进行分组,把值相同的记录,分为一组
然后针对每一组,分别进行聚合
- -- gender->性别——分组(男、女)
- select gender from student group by gender;
- -- 记录男女分别有多少人
- select gender,count(*) from student group by gender;
- -- 查询男女生各自的平均数学成绩
- select gender,avg(math) from student group by gender;
(3)、having 条件筛选
- -- 分组之前条件筛选使用 where
- select gender ,avg(math) from student where name != 'zhangsan' group by gender;
- -- 分组后条件筛选使用having
- select gender,avg(math) from student group by gender having avg(math)>75;
(2、联合查询 ---多表查询
笛卡尔积,其实就是将多个表进行简单的排列组合
如图:
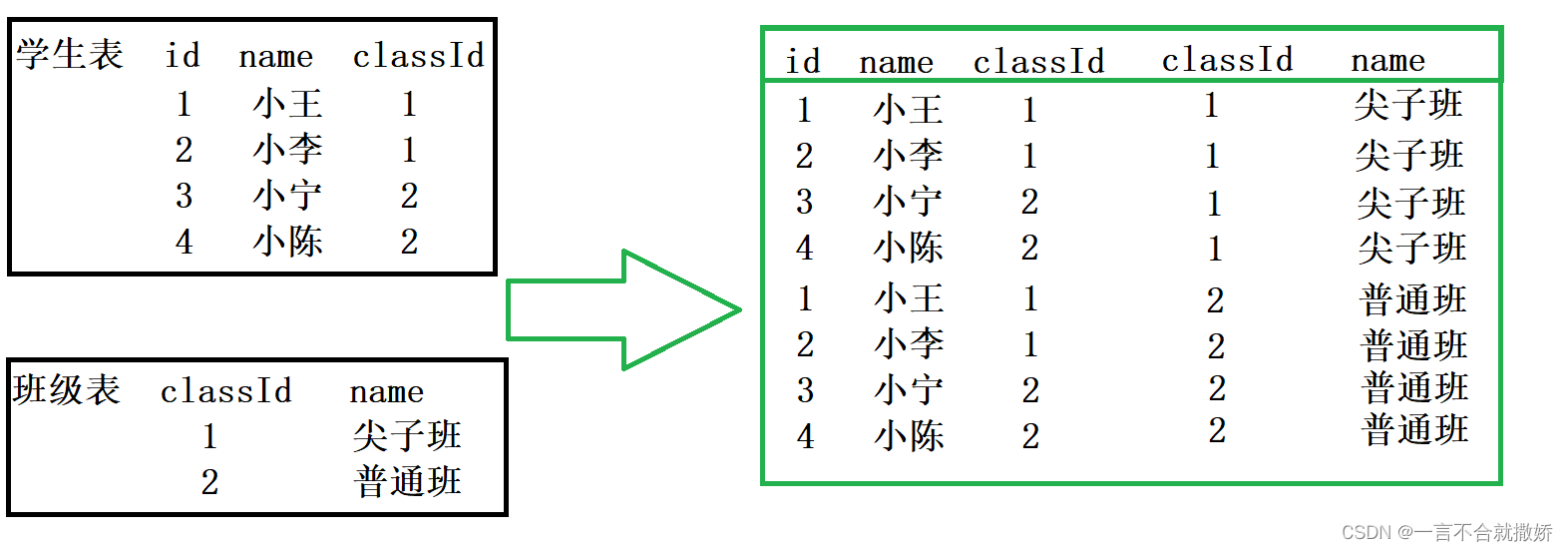
注:当表比较大的时候,多表查询就会非常低效
观察上图,会发现其组合中有很多不合理的数据,因此需要连接条件
联合查询 = 笛卡尔积 + 连接条件 + 其他条件
计算笛卡尔积:
方法一:
- select * from student, class;
- select * from student, class where student.classId = class.classId;
方法二:
- select * from student join class;
- select & from student join class on student.classId = class.classId;
- -- 查询每个同学所在的班级
- select student.name,class.name from student,class where student.classId = class.classId;
(1)、内连接
- select 字段 from 表1 as 别名1 , 表2 as 别名2 where 连接条件 and 其他条件;
- select 字段 from 表1 as 别名1 [inner] join 表2 as 别名2 on 连接条件 and 其他条件;
例:
select name ,score from student join score on student.id = score.studentId and name = '小王';(2)、外连接
两张表的信息不是完全对应的(如果使用内连接,结果为两张表信息的交集)
- -- 左外连接,表1完全显示
- select 字段 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 连接条件;
- -- 右外连接,表2完全显示
- select 字段 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 连接条件;
(3)、自连接
自连接是指在同一张表连接自身进行查询
思路就是把“行”转成“列”
(4)、子查询
子查询也叫做嵌套查询
- 关键字:[not] in
- 关键字:[not] exists
例:
- select * from score where courseId in (select id from course where name = '语文' or name = '英语');
- select * from score sco where exists (select sco.id from course cou where (name = '语文' or name = '英语' ) and cou.id = sco.courseId);
(5)、合并查询
- -- union:去除重复数据
- select ... from ... where 条件
- union
- select ... from ... where 条件
- -- union all:不去重
- select ... from ... where 条件
- union all
- select ... from ... where 条件
注:使用union和union all 时,前后查询的结果zz寸草心、
vgi`/那么,
、【【y'yu'f'。i集中,字段需要一致
SQL查询中各个关键字的执行先后顺序:
from>on>join>where>group by>with>having>select>distinct>order by>limit
3.5.3、改——update
update 表 set 字段1=value1,字段2=value2... where 条件;3.5.4、删——delete
delete from 表 where 条件;
4、 表的设计
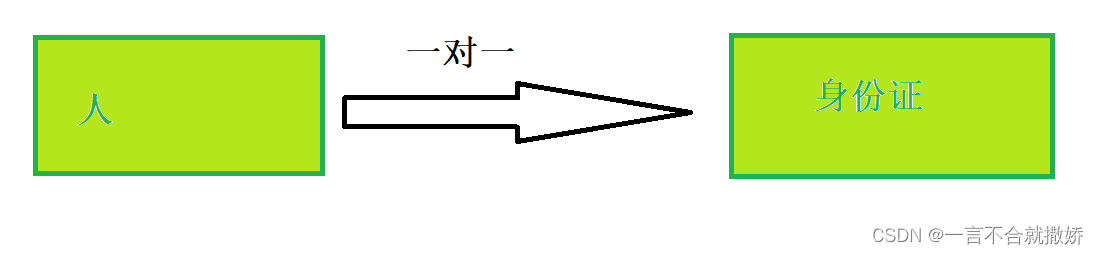
4.1、一对一
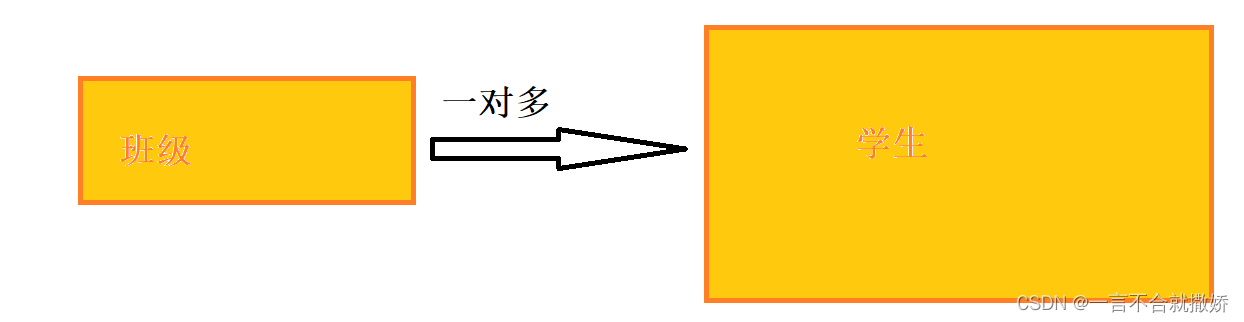
4.2、一对多
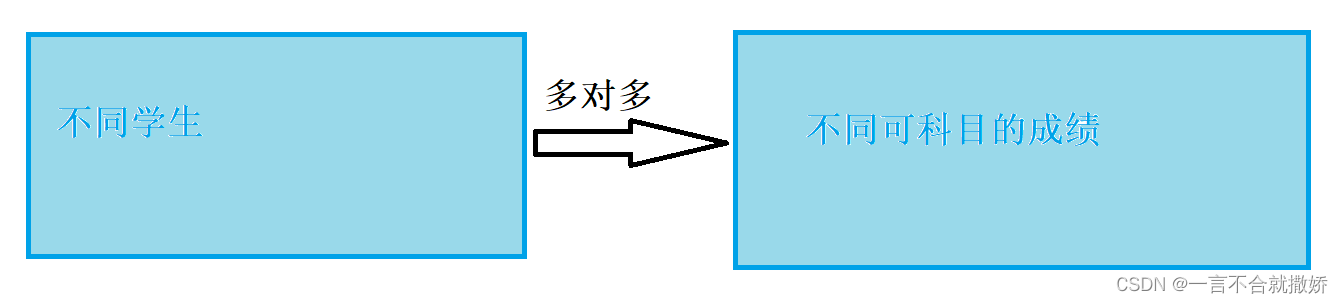
4.3、多对多
5、数据库的字段属性(约束)
unsigned
- 无符号
- 声明该列不能为负数
- 尽量不使用
zerofill
- 0填充的
- 不足为数的用0来填充,如int(3),5则为005
Auto_InCrement
- 通常理解为自增,自动在上一条记录基础上+1
- 通常用来设计唯一的主键,必须是整数类型
- 可定义起始值和步长
- 当前表设置步长(auto_increment=50):只影响当前表
- SET @@auto_increment_increment=5;影响所有使用自增的表(全局)
null
- 创建表时,指定某列可以保持为空,不论行中其他列是否已经被填充
- null的精确说法是“无”,而不是空字符或0
create table person ( id int null);not null
- 将一个列定义为not null,将不允许向该列插入null值
create table person( id int not null);unique
- 被赋予unique属性的列将确保所有值都有不同的值,只是null值可以重复
- 使用unique约束,数据库就会自动的给对应的列,创建索引
email varchar(30) unique;default
- default属性确保在没有任何值可用的情况下,赋予某个常量值 (MySQL不允许插入函数或表达式值)
- 该属性无法用于blob或text列
- 如果此列已经指定了null属性,没有指定默认值时,默认值为null,否则默认值将依赖于字段的数据类型
- subscribed enum('0','1') not null default '0';
- name varchar(30) default 'unnknown';
primary key
- primary key 属性用于确保指定行的唯一性
- 指定为主键的列中,值不能重复,也不能为空
- 主键分类:
- 单字段主键——如果输入到数据库中的每行都已经有不可修改的唯一标识符,一般会使用单字段主键(此主键一旦设置不能再修改了)
- 多字段主键——如果记录中任何一个字段都不可能保证唯一性,就可以使用多字段主键。多个字段联合起来确保唯一性
- 对于整数类型的主键,常配搭自增长auto_increment来使用。插入数据对应字段不给值时,使用最大值+1
id int primary key auto_increment;foreign key
- 外键用于关联其他表的主键或唯一键
- foreign key (字段名) references 主表(列)
- 创建学生表student,一个学生对应一个班级,一个班级对应多个学生。使用id为主键,class_id为外键,关联班级表id
-
- create table person (
- id int primary key auto_increment,
- sn int unique,
- name varchar(20) default 'unknown',
- mail varchar(20),
- class_id int,
- -- 当前表的列 另一张表(列)
- foreign key(class_id) references classes(id)
- );
拓展1:每个表,都必须存在以下五个字段
名称 描述 id 主键 version 乐观锁 isDelete 伪删除 gmtCreate 创建时间 gmtUpdate 修改时间 拓展2:分布式系统下,生成唯一ID的算法:(实现方式大同小异),
生成公式=(时间戳 + 机房编号 / 主机编号 + 随机因子) = > 计算哈希值
6、索引
6.1、概念:
索引是一种特殊的文件,包含着对数据表里所有记录的引用指针。可以对表中的一列或多列创建索引, 并指定索引的类型,各类索引有各自的数据结构实现。索引 ,用好理解的话来说, 就是目录6.2、作用
- 索引的效果:索引对于提高数据库的性能有很大帮助,加快查询效率
- 索引的代价:1、空间;2、增删改效率降低
- 索引的核心数据结构:B+树(N叉搜索树)
6.3、使用
创建主键约束(primary key )、唯一约束(unique )、外键约束(foreign key )时,会自动创建对应列的索引。6.3.1、查看索引
show index from 表名;6.3.2、创建索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段名);6.3.3、删除索引
drop index 索引名 on 表名;面试题:
1、索引是干什么的?解决了什么问题?
2、索引付出的代价
3、索引背后的数据结构
7、事务
7.1、概念
事务由单独单元的一个或多个SQL语句组成,在这个单元中,每个MySQL语句是相互依赖的。而整个单独单元作为一个不可分割的整体,如果单元中某条SQL语句一旦执行失败或产生错误,整个单元将会回滚。所有受到影响的数据将返回到事物开始以前的状态;如果单元中的所有SQL语句均执行成功,则事务被顺利执行。
即开始事务后执行的所有SQL都是一个整体,一个单元,要么都执行,要么都不执行。这里不执行的意思就row back即回滚,就是回到事务执行前的状态。在不同环境中,都可以有事务。对应在数据库中,就是数据库事务。
7.2、使用
7.2.1、开启事务
start transaction;7.2.2、执行多条SQL语句
7.2.3、回滚或提交:
- -- 全部失败
- rollback;
- --全部成功
- commit;
7.3、事务的特性:
1. 原子性(Atomicity)
原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务的根本所在(事物存在的意义),能够把SQL打包成一个整体,事务中的操作要么 都发生,要么都不发生(如果执行过程中出错,则自动回滚)。
2. 一致性(Consistency)
事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态 ,即事务执行前后,数据处在“一致”的状态(数据能对的上,合情合理)。
3. 隔离性(Isolation)
事务的隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个 事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发 执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
4. 持久性(Durability)
持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是 永久性的,接下来的其他操作和数据库故障不应该对其有任何影 响,即事务的改动都是写到硬盘的,不会随着程序的重启而丢失。7.4、事务的隔离级别
1.read uncommitted:允许读未提交的数据。并发程度最高,隔离性最低,可能存在 脏读/不可重复读/幻读 问题
2.read committed:只能读提交后的数据,相当于写加锁。并发程度降低,隔离性提高,解决了脏读,可能存在 不可重复读/幻读 问题
3.repeatable read:相当于读和写都加锁。并发程度再降低,隔离性再提高,解决了脏读/不可重复读/,可能存在 幻读 问题 (MySQL默认的事务的隔离级别)
4.serializable:严格执行串行化。并发程度最低,隔离性最高,解决了脏读/不可重复读/幻读 问题,效率最低。
注:
脏读: 对于两个事务 T1, T2, T1 读取了已经被 T2 更新但还没有被提交的字段. 之后, 若 T2 回滚, T1读取的内容就是临时且无效的.
不可重复读: 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 更新了该字段. 之后, T1再次读取同一个字段, 值就不同了.
幻读: 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 从一个表中读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 在该表中插入了一些新的行. 之后, 如果 T1 再次读取同一个表, 就会多出几行.
面试题:
1、事务是干什么的(从原子性切入)?
2、事务的其他特性还有啥?
3、隔离性,在并发执行事务下,会有哪些问题,以及如何解决?
4、MySQL的隔离级别有哪些?,和上面的问题如何对应?
8、JDBC的基础操作
(1)、创建数据源对象
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();(2)、建立与数据库的连接
由于mySQL是服务器与客户端连接形式的数据库软件, 需要建立客户端与服务器的联系, 但并不是所有数据库软件都是这种形式, 为了通用性, JDBC自带的DataSource类型并没有与服务器建立连接的方法, 所以需要向下转型, 使用MysqlDataSource建立与服务器的连接
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java0909?characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("0410");
- Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
注1:

注2:root指用户名,一般都是root
注3:0410是密码,根据自己设定的填写
(3)、书写sql语句, 并对sql语句进行预处理
- String sql = "insert into student values(1,'小龙')";
- PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //对sql语句进行预处理
(4)、进行sql操作
- //有两个方法
- //executeUpdate 对应插入删除修改语句,返回值表示这次SQL操作影响到的行数
- //executeQuery 对应查询语句
- int n = statement.executeUpdate();
- ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
(5)、释放资源, 先创建的后释放
- statement.close();
- connection.close();
基本的增删改查举例:
(1)、增:
- public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
- DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
- //数据库的位置
- //1、创建数据源对象
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java0909?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("0410");
- //2、让代码和数据库服务器建立连接
- Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
- //System.out.println(connection);
- //【用户输入】
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入要插入的学号:");
- int id = scanner.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入要插入的姓名:");
- String name = scanner.next();
- //3、构造要执行的SQL语句
- String sql = "insert into student values(?,?)";
- PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- statement.setInt(1,id);
- statement.setString(2,name);
- System.out.println("statement1"+statement);
- //4、执行 SQL [ 发送请求 & 读取相应】
- int n= statement.executeUpdate();
- System.out.println("n="+n);
- //5、完成之后,释放相关资源
- statement.close();
- connection.close();
- }
(2)、删
- public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
- //1、创建数据库
- DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java0909?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("0410");
- //2、连接数据库
- Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
- //3、构造SQL语句
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入要删除的学号:");
- int id = scanner.nextInt();
- String sql = "delete from student where id = ?";
- PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- statement.setInt(1,id);
- //4、执行SQL
- int n = statement.executeUpdate();
- System.out.println("n="+n);
- //5、释放资源
- statement.close();
- connection.close();
- }
(3)、改
- public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
- //1、创建数据源
- DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java0909?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("0410");
- //2、和数据库建立连接
- Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
- //3、构造SQL语句
- Scanner scanner= new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入要修改的同学学号:");
- int id = scanner.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入要将同学的名字修改为:");
- String name = scanner.next();
- String sql = "update student set name = ? where id = ?";
- PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- statement.setInt(2,id);
- statement.setString(1,name);
- //4、执行SQL
- int n = statement.executeUpdate();
- System.out.println("n="+ n);
- //释放资源
- statement.close();
- connection.close();
- }
(4)、查
- public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
- //1、创建数据库
- DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java0909?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
- ((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("0410");
- //2、建立连接
- Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
- //3、构造SQL
- String sql = "select * from student where id =?";
- PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- System.out.println("请输入要查询的学号:");
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- int id = scanner.nextInt();
- statement.setInt(1,id);
- //4、执行SQL
- // 查询语句要使用executeQuery来完成
- // 返回的结果是ResultSet 结果集 ,里面是一个表,这样的数据结构
- //一个表里有很多行,每一行有很多列
- ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
- //5、遍历结果集合
- while (resultSet.next()) {
- //每次循环,就能够获取到resultSet中的一行,进一步的就可以拿到每一列
- id = resultSet.getInt("id");
- String name = resultSet.getString("name");
- System.out.println("id= "+ id+" name="+ name);
- }
- //6、释放资源
- resultSet.close();
- statement.close();
- connection.close();
- }
下期见!!!
-
相关阅读:
02 【nodejs开发环境安装】
version GLIBC 2.14 not found问题处理
【Pytorch with fastai】第 11 章 :使用 fastai 的中级 API 进行数据处理
金属压块液压打包机比例阀放大器
解决splice改变原数组的BUG
DNS协议隧道(1)
【Azure 应用服务】Azure Function 启用 Managed Identity后, Powershell Funciton出现 ERROR: ManagedIdentityCredential authentication failed
CentOS8迁移tencentOS实践
每日汇评:黄金正在期待鲍威尔的讲话以获取新的方向动力
SQL Server 2012下载和安装配置详细教程手册
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/LYJbao/article/details/126539040