-
PostgreSQL数据库统计信息——examine_attribute单列预分析
如下代码所示,如果指定分析的列,这里会对每个列进行预分析。遍历va_cols中的每一列,通过attnameAttNum函数返回该列在该表中的列号,并通过unique_cols集合排除重复的列名,最后通过examine_attribute函数为该列创建VacAttrStats结构体,并设置到vacattrstats指针数据中。
if (va_cols != NIL){ Bitmapset *unique_cols = NULL; ListCell *le; tcnt = 0; vacattrstats = (VacAttrStats **) palloc(list_length(va_cols) *sizeof(VacAttrStats *)); foreach(le, va_cols){ char *col = strVal(lfirst(le)); i = attnameAttNum(onerel, col, false); if (i == InvalidAttrNumber) ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_UNDEFINED_COLUMN),errmsg("column \"%s\" of relation \"%s\" does not exist",col, RelationGetRelationName(onerel)))); if (bms_is_member(i, unique_cols)) ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_COLUMN),errmsg("column \"%s\" of relation \"%s\" appears more than once",col, RelationGetRelationName(onerel)))); unique_cols = bms_add_member(unique_cols, i); vacattrstats[tcnt] = examine_attribute(onerel, i, NULL); if (vacattrstats[tcnt] != NULL) tcnt++; } attr_cnt = tcnt; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
examine_attribute
examine_attribute函数对单个列进行预分析(pre-analysis),首先判别该列是否可分析,如果可以创建并初始化VacAttrStats结构体;否则返回NULL。如果index_expr赋值非空,尝试分析expression index,index_expr时代表列数据的表达式树。该函数经过以下步骤:
- 将pg_attribute系统表中的元组设置到stats->attr中
- 设置stats->attrtypid、stats->attrtypmod、stats->attrcollid字段,根据index_expr或stats->attr对应字段进行设置
- 将pg_type系统表中对应元组设置到stats->attrtype中,设置stats->anl_context和stats->tupattnum
- 初始化stats->statypid、stats->statyplen、stats->statypbyval和stats->statypalign数组
- 调用属性类型特定的分析函数进行分析;对于数组使用array_typanalyze,如果该类型没有对应的分析函数,则采用标准的分析函数std_typanalyze。

static VacAttrStats *examine_attribute(Relation onerel, int attnum, Node *index_expr){ Form_pg_attribute attr = TupleDescAttr(onerel->rd_att, attnum - 1);HeapTuple typtuple; VacAttrStats *stats; int i; bool ok; if (attr->attisdropped) return NULL; /* Never analyze dropped columns */ // 如果该列被drop,则直接返回 if (attr->attstattarget == 0) return NULL; /* Don't analyze column if user has specified not to */ // 如果用户指定不要进行分析,则直接返回 /* Create the VacAttrStats struct. Note that we only have a copy of the fixed fields of the pg_attribute tuple. */ stats = (VacAttrStats *) palloc0(sizeof(VacAttrStats)); stats->attr = (Form_pg_attribute) palloc(ATTRIBUTE_FIXED_PART_SIZE); memcpy(stats->attr, attr, ATTRIBUTE_FIXED_PART_SIZE); // 将pg_attribute系统表中的元组设置到stat->attr中 /* When analyzing an expression index, believe the expression tree's type not the column datatype --- the latter might be the opckeytype storage type of the opclass, which is not interesting for our purposes. (Note: if we did anything with non-expression index columns, we'd need to figure out where to get the correct type info from, but for now that's not a problem.) It's not clear whether anyone will care about the typmod, but we store that too just in case. */ // 在分析表达式索引时,请相信表达式树的类型而不是列数据类型——后者可能是opclass的opckeytype存储类型,这对于我们的目的来说并不有趣。(注意:如果我们对非表达式索引列进行了任何操作,我们需要找出从何处获取正确的类型信息,但目前这不是问题。)不清楚是否有人会关心typmod,但我们也存储它,以防万一。 if (index_expr){ stats->attrtypid = exprType(index_expr); stats->attrtypmod = exprTypmod(index_expr); /* If a collation has been specified for the index column, use that in preference to anything else; but if not, fall back to whatever we can get from the expression. */ // 如果为索引列指定了排序规则,请优先使用该排序规则;但如果不是,我们可以从表达式中得到任何信息 if (OidIsValid(onerel->rd_indcollation[attnum - 1])) stats->attrcollid = onerel->rd_indcollation[attnum - 1]; else stats->attrcollid = exprCollation(index_expr); }else{ stats->attrtypid = attr->atttypid; stats->attrtypmod = attr->atttypmod; stats->attrcollid = attr->attcollation; } typtuple = SearchSysCacheCopy1(TYPEOID, ObjectIdGetDatum(stats->attrtypid)); // 获取pg_type元组 if (!HeapTupleIsValid(typtuple)) elog(ERROR, "cache lookup failed for type %u", stats->attrtypid); stats->attrtype = (Form_pg_type) GETSTRUCT(typtuple); // 将pg_type系统表中对应元组设置到attrtype中 stats->anl_context = anl_context; stats->tupattnum = attnum; /* The fields describing the stats->stavalues[n] element types default to the type of the data being analyzed, but the type-specific typanalyze function can change them if it wants to store something else. */ for (i = 0; i < STATISTIC_NUM_SLOTS; i++) { stats->statypid[i] = stats->attrtypid; stats->statyplen[i] = stats->attrtype->typlen; stats->statypbyval[i] = stats->attrtype->typbyval; stats->statypalign[i] = stats->attrtype->typalign; } /* Call the type-specific typanalyze function. If none is specified, use std_typanalyze(). */ if (OidIsValid(stats->attrtype->typanalyze)) ok = DatumGetBool(OidFunctionCall1(stats->attrtype->typanalyze, PointerGetDatum(stats))); else ok = std_typanalyze(stats); if (!ok || stats->compute_stats == NULL || stats->minrows <= 0){ heap_freetuple(typtuple);pfree(stats->attr);pfree(stats);return NULL; } return stats; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
std_typanalyze
std_typanalyze函数的执行流程如下:首先获取VacAttrStats的attr成员(pg_attribute元组的拷贝),如果attstattarget列为负,则使用GUC default_statistics_target默认值;调用get_sort_group_operators函数获取对应列类型的ltopr、eqopr即小于等于操作符;创建StdAnalyzeData结构体,设置其eqopr、eqfunc、ltoper成员,然后将该结构体设置为VacAttrStats结构体的extra_data成员;决定compute_stats和minrows成员的取值。
bool std_typanalyze(VacAttrStats *stats) { Form_pg_attribute attr = stats->attr; // 使用VacAttrStats的attr成员,是pg_attribute元组的拷贝 Oid ltopr; Oid eqopr; StdAnalyzeData *mystats; /* If the attstattarget column is negative, use the default value. NB: it is okay to scribble on stats->attr since it's a copy */ // 如果attstattarget列为负,则使用默认值。注意:可以改变stats->attr,因为它是一个副本 if (attr->attstattarget < 0) attr->attstattarget = default_statistics_target; // default_statistics_target是一个GUC参数,默认为100 get_sort_group_operators(stats->attrtypid, false, false, false, <opr, &eqopr, NULL, NULL); /* Look for default "<" and "=" operators for column's type */ mystats = (StdAnalyzeData *) palloc(sizeof(StdAnalyzeData)); /* Save the operator info for compute_stats routines */ mystats->eqopr = eqopr; mystats->eqfunc = OidIsValid(eqopr) ? get_opcode(eqopr) : InvalidOid; mystats->ltopr = ltopr; stats->extra_data = mystats; /* Determine which standard statistics algorithm to use */ if (OidIsValid(eqopr) && OidIsValid(ltopr)) { stats->compute_stats = compute_scalar_stats; /* Seems to be a scalar datatype */ stats->minrows = 300 * attr->attstattarget; }else if (OidIsValid(eqopr)){ stats->compute_stats = compute_distinct_stats; /* We can still recognize distinct values */ stats->minrows = 300 * attr->attstattarget; /* Might as well use the same minrows as above */ }else{ stats->compute_stats = compute_trivial_stats; /* Can't do much but the trivial stuff */ stats->minrows = 300 * attr->attstattarget; /* Might as well use the same minrows as above */ } return true; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
compute_stats的取值:如果列数据类型支持默认的等于(eqopr equals operator)和小于(ltopr less than operator),那么这个列应该是数值scalar类型,应该可以使用compute_scalar_stats进行分析。如果列数据类型仅仅支持等于运算符,可以使用compute_distinct_stats函数进行唯一值的分析。如果列数据类型不支持上述运算,那么只能使用compute_trivial_stats进行分析了。
minrows的取值:minrows的选择基于《直方图构造的随机抽样:多少足够?》Surajit Chaudhuri、Rajeev Motwani和Vivek Narasayya,1998年ACM SIGMOD数据管理国际会议记录,第436-447页。定理5的推论1表示,对于表大小n、直方图大小k、箱大小f中的最大相对误差和误差概率γ,最小随机样本大小为 r = 4 ∗ k ∗ l n ( 2 ∗ n / g a m m a ) / f 2 r = 4 * k * ln(2*n/gamma) / f^2 r=4∗k∗ln(2∗n/gamma)/f2。我们以f = 0.5, γ = 0.01,n = 10^6,使用前面的公式可以算出 r = 305.82 ∗ k r = 305.82 * k r=305.82∗k。注意,由于对数函数,对n的依赖性非常弱;即使在n=10^12的情况下,300k样本也会给出<=0.66的仓大小误差,概率为0.99。所以不需要对n进行缩放,这是一件好事,因为我们在这一点上不一定知道。The following choice of minrows is based on the paper “Random sampling for histogram construction: how much is enough?” by Surajit Chaudhuri, Rajeev Motwani and Vivek Narasayya, in Proceedings of ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, 1998, Pages 436-447. Their Corollary 1 to Theorem 5 says that for table size n, histogram size k, maximum relative error in bin size f, and error probability gamma, the minimum random sample size is r = 4 ∗ k ∗ l n ( 2 ∗ n / g a m m a ) / f 2 r = 4 * k * ln(2*n/gamma) / f^2 r=4∗k∗ln(2∗n/gamma)/f2, Taking f = 0.5, gamma = 0.01, n = 10^6 rows, we obtain r = 305.82 ∗ k r = 305.82 * k r=305.82∗k. Note that because of the log function, the dependence on n is quite weak; even at n = 10^12, a 300k sample gives <= 0.66 bin size error with probability 0.99. So there’s no real need to scale for n, which is a good thing because we don’t necessarily know it at this point.
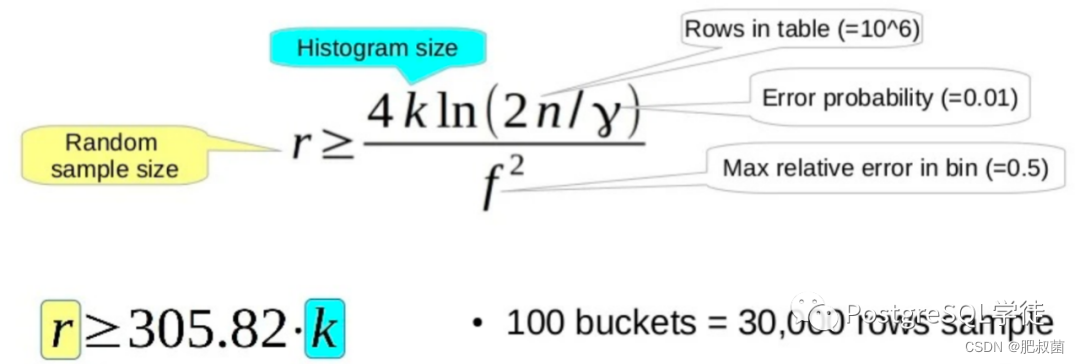
这里的k指代的是直方图采集桶的数量, 其实就是attr->attstattarget,默认情况下使用guc default_statistics_target参数,也就是100。因此采集样本大小为30000行。如下为经过examine_attribute单列预分析流程处理后的VacAttrStats结构体:
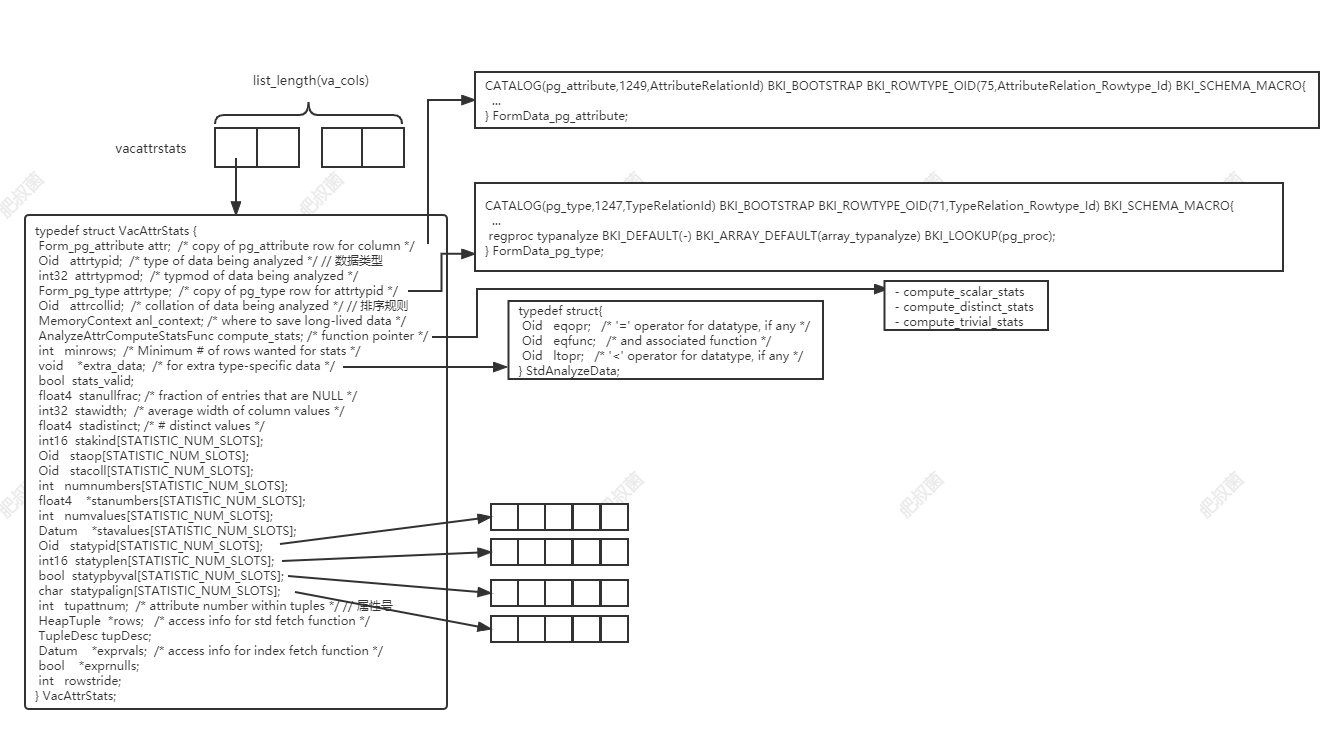
-
相关阅读:
自建Elasticsearch 集群的规划和常见问题
从代码逻辑到场景实战,百度高级工程师带你解密PP-ChatOCR!
SwiftUI 教程之如何呈现不同高度的sheet, 新的视图修改器使工作变得容易。
【Proteus仿真】基于stm32的数码管时钟
交叉编译器环境配置与boa嵌入式web服务器移植问题
云存储架构——打造安全的企业级数据流转平台技术方案
你还只知道404?来看HTTP状态码详解
看完这篇 教你玩转渗透测试靶机vulnhub——FunBox11(Scriptkiddie)
J2EE从入门到入土05.XML配置文件
Java反序列化基础篇-JDK动态代理
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/asmartkiller/article/details/126679628