-
JDBCUtils的使用和事务
本次博客带领大家学习JDBCUtils的开发、DML和查询语句的使用、事务的介绍。
封装JDBCUtils
- 说明:在jdbc操作中,获取连接和释放资源是经常使用到,可以将其封装JDBC连接的工具类JDBCUtils。
//这是一个工具类,完成mysql的连接和关闭资源 public class JDBCUtils { private static String user; private static String password; private static String url; private static String driver; //在static代码块去初始化 static { try { Properties properties= new Properties(); properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properites")); //读取相关的属性值 user = properties.getProperty("user"); password = properties.getProperty("password"); url = properties.getProperty("url"); driver = properties.getProperty("driver"); } catch (IOException e) { //1.将编译异常转成 运行异常 //2.这是调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便 throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //连接数据库,返回Connection public static Connection getConnection(){ try { return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //关闭相关资源 /* 1.ResultSet 结果集 2.Statement 或者 PreparedStatement 3.Connection 4.如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入null */ public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement,Connection connection){ //判断是否为null try { if(set !=null){ set.close(); } if (statement != null){ statement.close(); } if (connection != null){ connection.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
JDBCUtils的实际使用
- DML语句的使用:
public void testDML(){ //1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; // 2.组织一个sql String sql = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //3.创建PrepareStatement对象 try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1,"周星驰"); preparedStatement.setInt(2,4); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 查询语句的使用:
public void testSelect(){ //1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; // 2.组织一个sql String sql = "select * from actor"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; //3.创建PrepareStatement对象 try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while(resultSet.next()){ int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String name = resultSet.getString("name"); String sex = resultSet.getString("sex"); Date borndate = resultSet.getDate("borndate"); String phone = resultSet.getString("phone"); System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+borndate+"\t"+phone); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
事务的基本介绍
- JDBC程序中当一个Connection对象创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务的:每次执行一个SQL语句时,如果执行成功,就会向数据库自动提交,而不能回滚。
- JDBC程序中为了让多个SQL语句作为一个整体执行,需要使用事务。
- 调用 Connection 的setAutoCommit(false) 可以取消自动提交事务。
- 在所有的 SQL 语句都成功执行后,调用 Connection 的commit();方法提交事务。
- 在其中某个操作失败或出现异常时,调用 Connection 的rollback();方法回滚事务。
事务的应用实例
-
模拟经典的转账业务
CREATE TABLE account( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', balance DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0) ENGINE = INNODB,CHARACTER SET utf8; SELECT * FROM account; INSERT INTO account VALUES(NULL,'马云',3000); INSERT INTO account VALUES(NULL,'马化腾',10000);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
没有使用事务的方法:导致数据不一致
public void noTransaction(){ //1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; // 2.组织一个sql String sql = "update account set balance = balance -100 where id = 1"; String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance +100 where id = 2"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //3.创建PrepareStatement对象 try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第一条sql int i=1/0; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1); preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第二条sql } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 没有使用事务,结果出错。
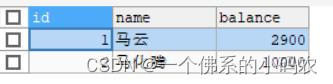
- 使用事务后,数据保持一致!
public void useTransaction(){ //1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; // 2.组织一个sql String sql = "update account set balance = balance -100 where id = 1"; String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance +100 where id = 2"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //3.创建PrepareStatement对象 try { connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //将connection设置为不自动提交 connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启了事务 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第一条sql //int i=1/0; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1); preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第二条sql connection.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) { //这里我们可以进行回滚,即撤销执行的SQL //默认回滚到事务开始的状态。 System.out.println("执行发生了异常,撤销执行的sql"); try { connection.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
-
相关阅读:
基于PHP+MySQL个人信息管理系统的设计与实现
判断JS是否加载完成
Python数据类型:列表的魔法世界
《Effective Java 中文版》读书笔记
Harbor----通过 Harbor 源码进行编译 Harbor
参考线平滑-FemPosDeviation-OSQP
复习四:线性表综合题
【PyTorch】深度学习实践之 RNN基础篇——实现RNN
kafka配置
页面关闭前,如何发送一个可靠请求
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lidong777777/article/details/126752854
