-
mysql中的数据类型
1 概要
注意:本节内容是在
mysql5.5的基础上进行的实验的# 在建数据库的时候选择了以后就不用再选择了(刚才在数据库的时候已经设置了utf8) # 创建表的时候指明字符集 create table temp( id int )character set 'utf8'; show create table temp; # 创建表,指明表中的字段时,可以指明字段的字符集 create table temp1( name varchar(15) character set 'utf8' );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
mysql中的数据类型如下

常见的数据类型如下

2 整数类型
2.1 数据类型介绍
整数类型一共有 5 种,包括 TINYINT、SMALLINT、MEDIUMINT、INT(INTEGER)和 BIGINT。 它们的区别如下表所示:- 1
- 2

首先对整型进行验证
# 2整型数据类型 use test1; create table test_int1( f1 tinyint, f2 smallint, f3 mediumint, f4 integer, f5 bigint ); desc test_int1; insert into test_int1(f1) values (12),(-12),(-128),(127); select * from test_int1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14


当输入如下的时候,会报错(超出范围)–只要超出范围都会报下面的错误(这里的范围指的的-128到127之间)
insert into test_int1(f1) values (128);- 1

2.2 可选属性介绍
整数的可选属性有三个:
2.2.1 M


2.2.2 UNSIGNED

2.2.3 ZEROFILL


2.4 如何选择?

create table test_int2( f1 int, f2 int(5), f3 int(5) zerofill ) insert into test_int2(f1,f2) values (123,123),(123456,123456); select * from test_int2;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9


上面的这种写法是没有意义的
下面的这个f3才是有意义的,但是在8版本以后取消了后面的数字(建议不要这么写了,以后)
create table test_int3( f1 int, f2 int(5), f3 int(5) ZEROFILL # 显示宽度为5.当inserrt的值不足5位时,使用0填充(我的用的5.5好像没有填充,老师用的5.7填充了). 当使用zerofill时,自动会添加unsigned(无符号) ) insert into test_int3(f1,f2) values (123,123),(123456,123456); select * from test_int3; insert into test_int3(f3) values (123),(123456); select * from test_int3;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

超出了之后就会报错
3 浮点类型
3.1 类型介绍
浮点数和定点数类型的特点是可以 处理小数 ,你可以把整数看成小数的一个特例。因此,浮点数和定点
数的使用场景,比整数大多了。 MySQL支持的浮点数类型,分别是
FLOAT(float)、DOUBLE(double)、REAL(real)。- FLOAT 表示单精度浮点数;
- DOUBLE 表示双精度浮点数;

REAL默认就是 DOUBLE。如果你把 SQL 模式设定为启用“ REAL_AS_FLOAT ”,那 么,MySQL 就认为
REAL 是 FLOAT。如果要启用“REAL_AS_FLOAT”,可以通过以下 SQL 语句实现
SET sql_mode = “REAL_AS_FLOAT”;- 1
问题1:为什么浮点数类型的无符号数取值范围,只相当于有符号数取值范围的一半,也就是只相当于有符号数取值范围大于等于零的部分呢?
MySQL 存储浮点数的格式为: 符号(S) 、 尾数(M) 和 阶码(E) 。因此,无论有没有符号,MySQL 的浮
点数都会存储表示符号的部分。因此, 所谓的无符号数取值范围,其实就是有符号数取值范围大于等于
零的部分。(后面mysql不建议这样使用了)
3.2 数据精度说明


CREATE TABLE test_double1( f1 FLOAT, f2 FLOAT(5,2), f3 DOUBLE, f4 DOUBLE(5,2) );DESC test_double1; INSERT INTO test_double1 VALUES(123.456,123.456,123.4567,123.45); #Out of range value for column 'f2' at row 1 INSERT INTO test_double1 VALUES(123.456,1234.456,123.4567,123.45); SELECT * FROM test_double1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
浮点数类型有个缺陷,就是不精准。下面我来重点解释一下为什么 MySQL 的浮点数不够精准。比如,我
们设计一个表,有f1这个字段,插入值分别为0.47,0.44,0.19,我们期待的运行结果是:0.47 + 0.44 + 0.19 =
1.1。而使用sum之后查询:
CREATE TABLE test_double2( f1 DOUBLE ); INSERT INTO test_double2 VALUES(0.47),(0.44),(0.19);- 1
- 2
- 3



4 定点数类型
4.1 类型介绍
MySQL中的定点数类型只有
DECIMAL(decimal)一种类型。




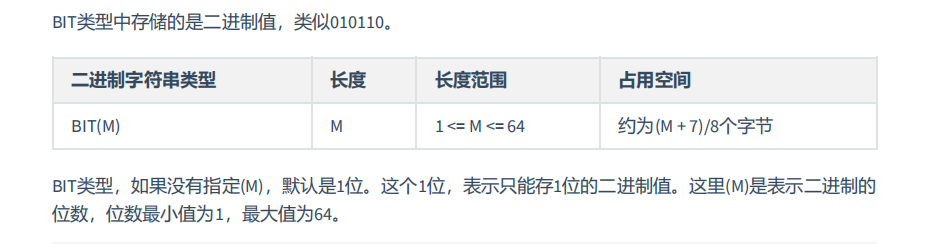
5. 位类型:BIT
(实际开发中用的较少,了解)
#5 位类型: BIT CREATE TABLE teat_bit1( f1 BIT, f2 BIT(5), f3 BIT(64) ); DESC teat_bit1; INSERT INTO teat_bit1(f1) VALUES(0),(1); select * from teat_bit1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

对于f1后面没有指明宽度,就只能存0和1,否者就会报错,默认只有一个比特位

对于f2,可以存的范围最大可以存31



通过其它方式展示

# 此时+0以后,可以以十进制的方式显示数据 SELECT f1+0,f2+0 from teat_bit1;- 1
- 2

6. 日期与时间类型
日期与时间是重要的信息,在我们的系统中,几乎所有的数据表都用得到。原因是客户需要知道数据的
时间标签,从而进行数据查询、统计和处理。
MySQL有多种表示日期和时间的数据类型,不同的版本可能有所差异,MySQL8.0版本支持的日期和时间
类型主要有:YEAR类型、TIME类型、DATE类型、DATETIME类型和TIMESTAMP类型。


可以看到,不同数据类型表示的时间内容不同、取值范围不同,而且占用的字节数也不一样,你要根据
实际需要灵活选取。
为什么时间类型 TIME 的取值范围不是 -23:59:59~23:59:59 呢?原因是 MySQL 设计的 TIME 类型,不光表示一天之内的时间,而且可以用来表示一个时间间隔,这个时间间隔可以超过 24 小时。
6.1 YEAR类型

CREATE TABLE test_year( f1 YEAR, f2 YEAR(4) ); INSERT into test_year(f1) VALUES('2021'),(2022); SELECT * from test_year;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9



2位的情况建议不使用
6.2 DATE类型

例子
CREATE TABLE test_date1( f1 DATE ); INSERT INTO test_date1 VALUES ('2020-10-01'), ('20201001'),(20201001); select * from test_date1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

下面两位的方式了解即可

获取当前系统的时间
INSERT INTO test_date1 VALUES (CURDATE()),(CURRENT_DATE()), (NOW()); SELECT * FROM test_date1;- 1
- 2

6.3 TIME类型

测试
INSERT INTO test_time1 VALUES('2 12:30:29'), ('12:35:29'), ('12:40'), ('2 12:40'),('1 05'), ('45'); SELECT * FROM test_time1;- 1
- 2

INSERT INTO test_time1 VALUES ('123520'), (124011),(1210); SELECT * FROM test_time1;- 1
- 2
- 3

INSERT INTO test_time1 VALUES (NOW()), (CURRENT_TIME()); SELECT * FROM test_time1;- 1
- 2

6.4 DATETIME类型
常用




6.5 TIMESTAMP类型



TIMESTAMP和DATETIME****的区别:


6.6 开发中的经验

7. 文本字符串类型
在实际的项目中,我们还经常遇到一种数据,就是字符串数据。
MySQL中,文本字符串总体上分为 CHAR(char) 、 VARCHAR (varchar)、 TINYTEXT (tinytext)、 TEXT (text)、 MEDIUMTEXT(mediumtext) 、 LONGTEXT(longtext) 、 ENUM (enun)、 SET(set) 等类型。

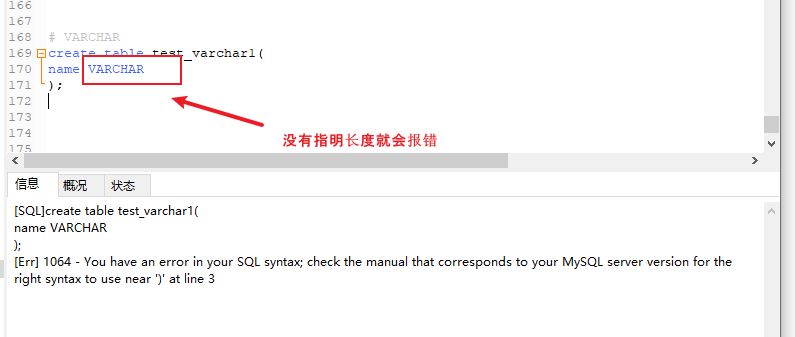
7.1 CHAR与VARCHAR类型
CHAR和VARCHAR类型都可以存储比较短的字符串。



测试
create table test_char1( c1 char, c2 char(5) ); desc test_char1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

char后面没有写的话,默认就是1
create table test_char1( c1 char, c2 char(5) ); desc test_char1; INSERT into test_char1(c1) VALUES('a'); select * from test_char1; INSERT into test_char1(c1) VALUES('ab'); select * from test_char1; INSERT into test_char1(c2) VALUES("小胖"); select * from test_char1; INSERT into test_char1(c2) VALUES('小胖很可爱'); select * from test_char1; INSERT into test_char1(c2) VALUES('小胖很可爱啊'); select * from test_char1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28


这个太长了,会报错,其它的都正常
VARCHAR****类型:

注意




情况2:固定长度.比如适应uuid作为主键,那么char应该更适合.因为它固定长度,varchar动态根据
长度的特性就消失了,而且还要占个长度的信息

7.2 TEXT类型
在MySQL中,TEXT用来保存文本类型的字符串,总共包含4种类型,分别为TINYTEXT、TEXT、
MEDIUMTEXT 和 LONGTEXT 类型。
在向TEXT类型的字段保存和查询数据时,系统自动按照实际长度存储,不需要预先定义长度。这一点和VARCHAR类型相同。
每种TEXT类型保存的数据长度和所占用的存储空间不同,如下:

由于实际存储的长度不确定,MySQL不允许 TEXT 类型的字段做主键。遇到这种情况,你只能采用CHAR(M),或者 VARCHAR(M)。
举例:
创建数据表:


8. ENUM类型

9. SET类型

10.二进制字符串类型(了解)




11. JSON 类型

CREATE table test_json( js json );- 1
- 2
- 3

12. 空间类型(了解)



13. 小结及选择建议
在定义数类型的时候,如果确定是
整数,就用int;如果是小数,一定用定点数类型DECIMAL;如果是日期于时间,就用DATETIME.这样做的好处是,首先确保你的系统不会因为数据类型定义出错.不过,凡事都有两面性,可靠性好.并意为着高效.比如,TXT虽然使用方便,但是效率不如char(M)和varchar(M)

662440985766)]
11. JSON 类型
[外链图片转存中…(img-iTYQijuv-1662440985767)]
CREATE table test_json( js json );- 1
- 2
- 3
[外链图片转存中…(img-Bf4TwwsG-1662440985769)]
12. 空间类型(了解)
[外链图片转存中…(img-DzZizvwa-1662440985771)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-b90hjbWV-1662440985772)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-qYu8Czth-1662440985773)]
13. 小结及选择建议
在定义数类型的时候,如果确定是
整数,就用int;如果是小数,一定用定点数类型DECIMAL;如果是日期于时间,就用DATETIME.这样做的好处是,首先确保你的系统不会因为数据类型定义出错.不过,凡事都有两面性,可靠性好.并意为着高效.比如,TXT虽然使用方便,但是效率不如char(M)和varchar(M)
[外链图片转存中…(img-l4GXDXTj-1662440985775)]
-
相关阅读:
神经网络解决实际问题,神经网络常见问题
持续测试简介
ELK 基础原理 文档 (二)
uniapp轮播图闪烁卡屏解决办法很简单
【Go】fatal error: concurrent map writes 问题记录
JNI查漏补缺
Github Action Flask 应用CI/CD样例
AI绘图:GPT4技术的艺术化呈现与无限可能
不得不会的MySQL数据库知识点(二)
唯众中职人工智能专业解决方案
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47994845/article/details/126723002
