-
Java教程之高阶源码分析-ConcurrentHashMap
一、文章导读:
这部分内容让大家读懂ConcurrentHashMap源码的底层实现从而在工作中合理去使用他并且在面试中能做到游刃有余,主要内容如下:
- 核心构造方法
- 核心成员变量
- put方法过程数据的完整过程
- get方法的无锁实现
二、文章讲解内容
JDK8中ConcurrentHashMap的结构是:数组+链表+红黑树。
因为在hash冲突严重的情况下,链表的查询效率是O(n),所以jdk8中改成了单个链表的个数大于8时,数组长度小于64就扩容,数组长度大于等于64,则链表会转换为红黑树,这样以空间换时间,查询效率会变O(nlogn)。
红黑树在Node数组内部存储的不是一个TreeNode对象,而是一个TreeBin对象,TreeBin内部维持着一个红黑树。
在JDK8中ConcurrentHashMap最经点的实现是使用CAS+synchronized+volatile 来保证并发安全
一、JDK7中ConcurrentHashMap的实现
在JDK1.7中ConcurrentHashMap是通过定义多个Segment来实现的分段加锁,一个Segment对应一个数组,如果多线程对同一个数组中的元素进行添加那么多个线程会去竞争同一把锁,他锁的是一个数组,有多少个segment那么就有多少把锁,这个力度还是比较粗的。
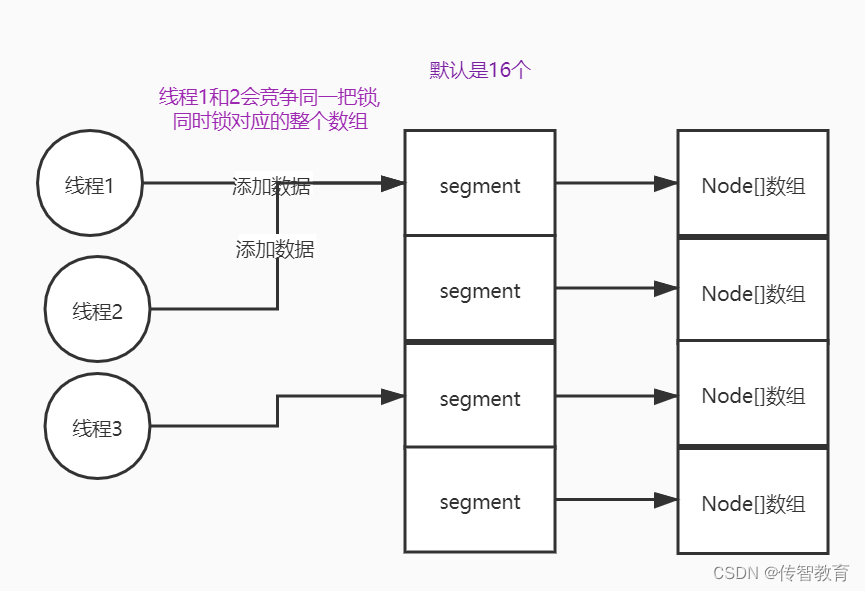
JDK8的实现是下文要重点探讨的内容,同时下文全部都是JDK8的实现。
二、核心构造方法
/** * Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16). 无参构造函数,new一个默认table容量为16的ConcurrentHashMap */ public ConcurrentHashMap() { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
/** * Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size * accommodating the specified number of elements without the need * to dynamically resize. * * @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal * sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of * elements is negative 做了3件事: 1.如果入参<0,抛出异常。 2.如果入参大于最大容量,则使用最大容量(是2的30次方) 3.tableSizeFor方法得到一个大于负载因子入参且最接近2的N次方的数作为容量 4.设置sizeCtl的值等于初始化容量。未对table进行初始化,table的初始化要在第一次put的时候进行。 */ public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1)); this.sizeCtl = cap; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
特别注意:未对table进行初始化,table的初始化要在第一次put的时候进行
三、核心成员变量
// 该字段控制table(也被称作hash桶数组)的初始化和扩容 private transient volatile int sizeCtl; // table最大容量是2的30次方 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // table的默认初始化容量-扩容总是2的n次方 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16; // table的负载因子。当前已使用容量 >= 负载因子*总容量的时候,进行resize扩容 private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 存储数据的数组-注意添加了volatile transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table; // 当桶内链表长度>=8时,会将链表转成红黑树-注意需要和MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY结合起来用 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // table的总容量,要大于64,桶内链表才转换为树形结构,否则当桶内链表长度>=8时会扩容 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 当桶内node小于6时,红黑树会转成链表。 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
四、put存储数据
先从JDK的源码中复制一段上头的代码,如下代码就完成了数据的添加,在添加的时候还完成了数组的初始化、扩容、CAS修改、分段锁的实现,大家大体的对该代码有一个认识即可我们后面会详细的画图分析该过程
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); } /** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */ final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { // 如果key或者value为空,抛出异常 if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // 得到hash值 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); // 用来记录所在table数组中的桶的中链表的个数,后面会用于判断是否链表过长需要转红黑树 int binCount = 0; // for循环,直到put成功插入数据才会跳出 for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { // f=桶头节点 n=table的长度 i=在数组中的哪个下标 fh=头节点的hash值 Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; // 如果table没有初始化 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 初始化table tab = initTable(); // 根据数组长度减1再对hash值取余得到在node数组中位于哪个下标 // 用tabAt获取数组中该下标的元素 // 如果该元素为空 else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { // 直接将put的值包装成Node用tabAt方法放入数组内这个下标的位置中 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } // 如果头结点hash值为-1,则为ForwardingNode结点,说明正再扩容, else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) // 调用hlepTransfer帮助扩容 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); // 否则锁住槽的头节点 else { V oldVal = null; // 锁桶的头节点 synchronized (f) { // 双重锁检测,看在加锁之前,该桶的头节点是不是被改过了 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { // 如果桶的头节点的hash值大于0 if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; // 遍历链表 for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; // 如果遇到节点hash值相同,key相同,看是否需要更新value if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; //如果到链表尾部都没有遇到相同的 if ((e = e.next) == null) { // 就生成Node挂在链表尾部,该Node成为一个新的链尾。 pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } // 如果桶的头节点是个TreeBin else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; // 用红黑树的形式添加节点或者更新相同hash、key的值。 if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { // 如果链表长度>需要树化的阈值 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //调用treeifyBin方法将链表转换为红黑树,而这个方法中会判断数组值是否大于64,如果没有大于64则只扩容 treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) // 如果是修改,不是新增,则返回被修改的原值 return oldVal; break; } } } // 计数器加1,完成新增后,table扩容,就是这里面触发 addCount(1L, binCount); // 新增后,返回Null return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
4.1 高效的hash算法
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); static final int spread(int h) { return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
该算法其实在HashMap中我们就已经重点说过了,他既保存了key值得hash的高16位也保存了低16位,从而让key值在不同的数组中尽可能的散列,从而避免hash冲突。
4.2 数组的初始化
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注意是在循环中判断的table是否为空如果为空则会调用initTable完成数组的默认初始化。
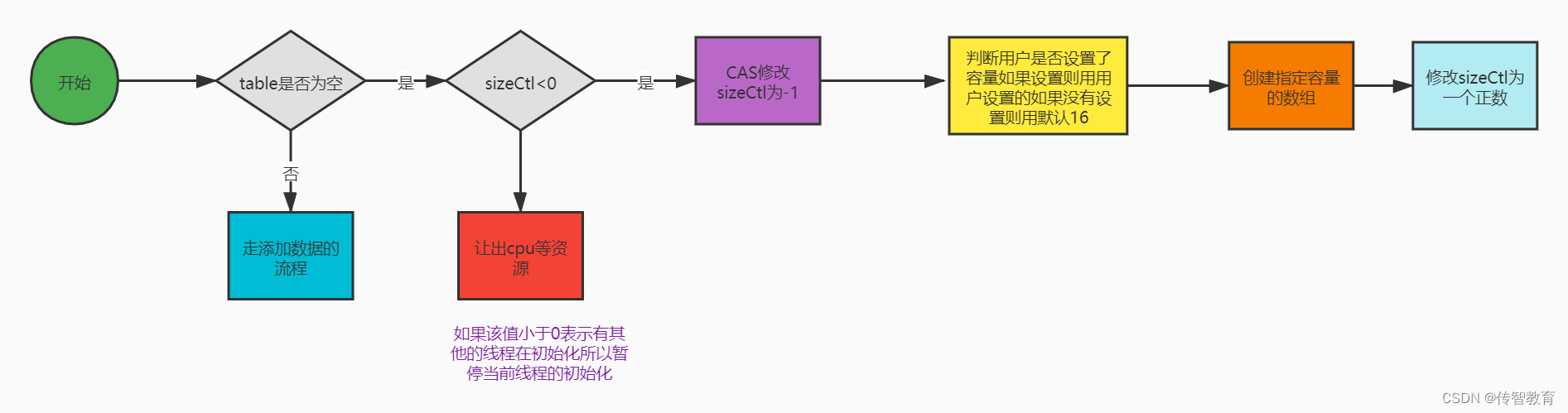
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; table = tab = nt; sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { sizeCtl = sc; } break; } } return tab;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
以上代码做了如下事情:
1.如果table为空,进入while准备开始初始化。
2.将sizeCtl赋值给sc。如果sizeCtl<0,线程等待,小于零时表示有其他线程在执行初始化。
3.如果能将sizeCtl设置为-1,则开始进行初始化操作
4.用户有指定初始化容量,就用用户指定的,否则用默认的16.
5.生成一个长度为16的Node数组,把引用给table。
6.重新设置sizeCtl=数组长度 - (数组长度 >>>2) 这是忽略符号的移位运算符,可以理解成 n - (n / 2)。
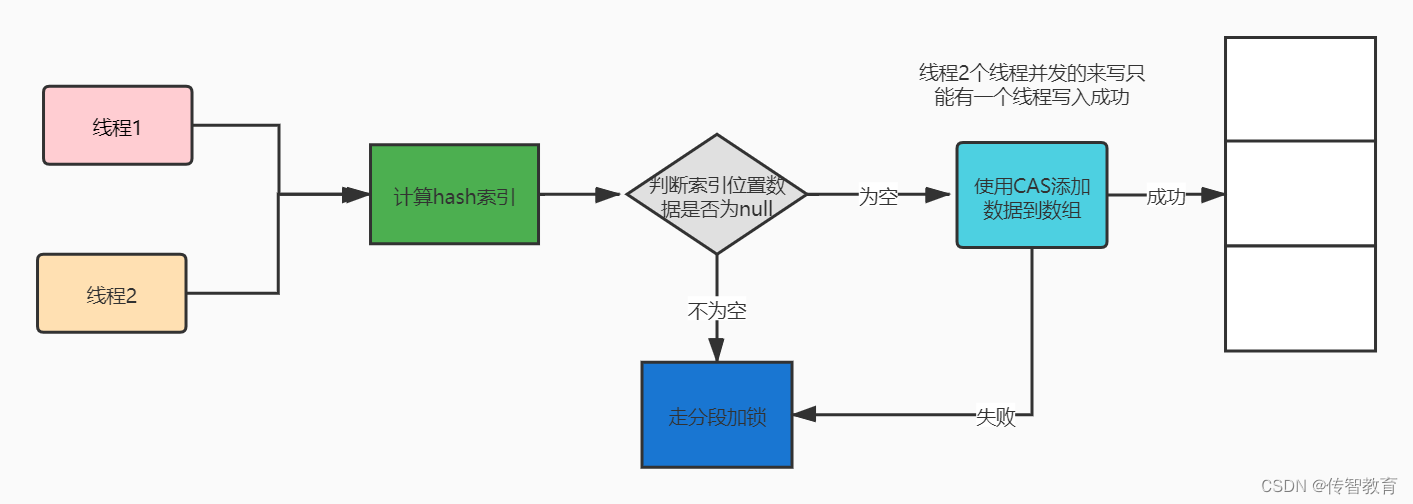
4.3 不冲突的数据添加过程
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin } static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) { return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
高效的寻址算法: (n - 1) & hash这个在我们的HashMap中也是讲过的了就不在赘述。
通过高效的寻址算法得到一个索引并获取该索引的数据如果不为空则调用casTabAt方法进行CAS的原子修改,CAS在Java层面是无锁的所以速度会很快,但是他在硬件层面是有锁的,他会在硬件的拉链散列表中加锁。
如果有多个线程同时hash到了该索引我们的CAS也能保证只有一个线程能添加成功其他的线程其实是走分段加锁的过程。
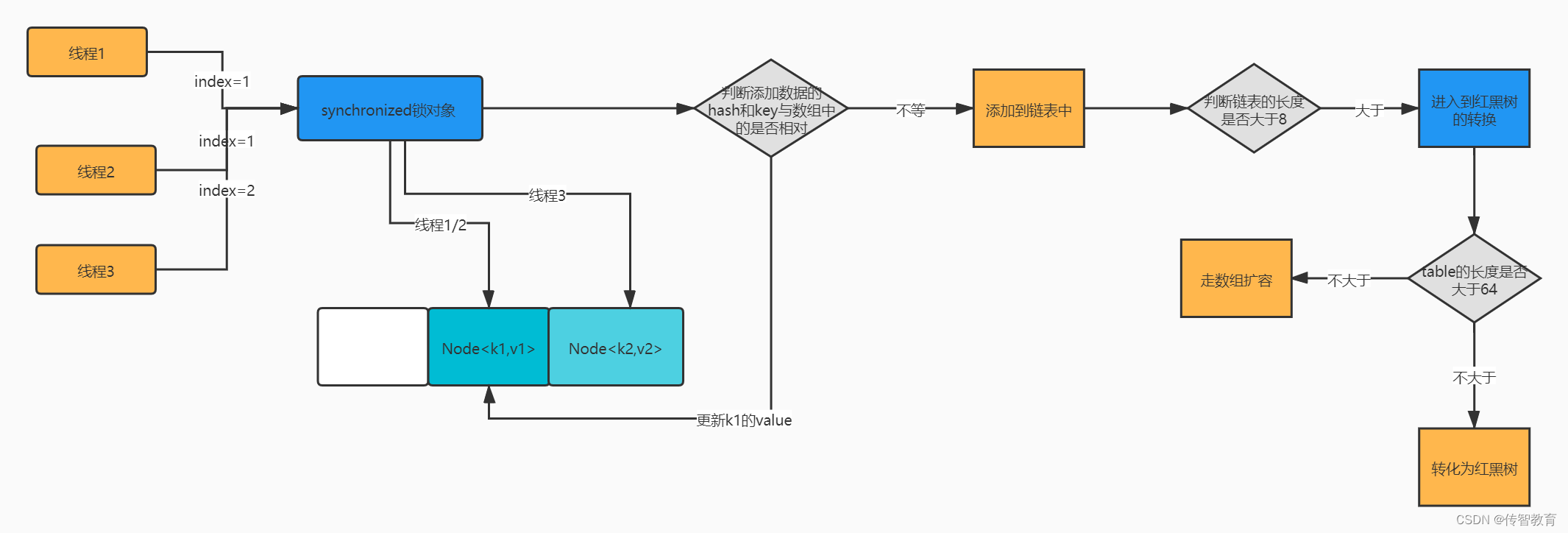
4.4 分段加锁策略
else { V oldVal = null; synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
需要大家特别注意的是synchronized (f)锁了一个f对象,那么这个f对象是什么呢?其实就是我们高效寻址算法的到的一个下标中存储的对象,注意他锁的是我们寻址到的这个对象并没有锁这个数组,所以我们当前的锁一共有多少把呢?就看你的size有多少了默认是16那么就会有16把锁可以来并发的修改,这个其实就是JDK1.8的分段锁拉,他比1.7锁的粒度更细那么并发的效果就会更好。
五、无锁获取
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode()); if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) { if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } else if (eh < 0) return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; while ((e = e.next) != null) { if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
以上代码中的内容几乎我们都讲过了,所以就不在赘述,但是值得一说的是获取的过程中并没有对数组或者某一个Node元素添加锁,获取是无锁的所有性能高。
还有一个问题需要注意的是获取是无锁的那么他如果出现多线程修改或者写入的时候他就有可能会出现可见性的问题,因为每一个线程都有自己的工作内存,那么ConcurrentHashMap是如何解决可见性的问题呢?
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;- 1
从变量的申明中我们可以看到存储数据的table其实是添加了volatile关键字的,所以其他线程修改了以后我们要求其他的线程把数据刷新主内存从而保证数据的可见性。
五、总结:
- JDK1.7 使用分段锁实现
- JDK1.8 使用CAS+synchronized+volatile 的具体实现
- put方法的复杂实现过程
- get方法的无锁实现尤其是volatile关键字的使用
-
相关阅读:
Kubeflow组件和架构
第三节:运算符【java】
【docker】Error response from daemon Container is not running
手摸手系列之批量修改MySQL数据库所有表中某些字段的类型
2.2.3 vim操作合集
智芯微801核心板外设驱动调试经验汇总--每天加一点
js异步与同步
人工智能在教育上的应用2-基于大模型的未来数学教育的情况与实际应用
Docker 安装Kafka
常量池、StringTable(字符串常量池池)和堆内存
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/cz_00001/article/details/126707887
