-
SpringBoot之缓存篇
SpringBoot与缓存
随着时间的积累,应用的使用用户不断增加,数据规模也越来越大,往往数据库查询操作会成为影响用户使用体验的瓶颈,此时使用缓存往往是解决这一问题非常好的手段之一。Spring 3开始提供了强大的基于注解的缓存支持,可以通过注解配置方式低侵入的给原有Spring应用增加缓存功能,提高数据访问性能。在Spring Boot中对于缓存的支持,提供了一系列的自动化配置,使我们可以非常方便的使用缓存。
首先了解下JSR107、Spring缓存抽象等等概念。
一 、Cache缓存的作用
1. JSR107
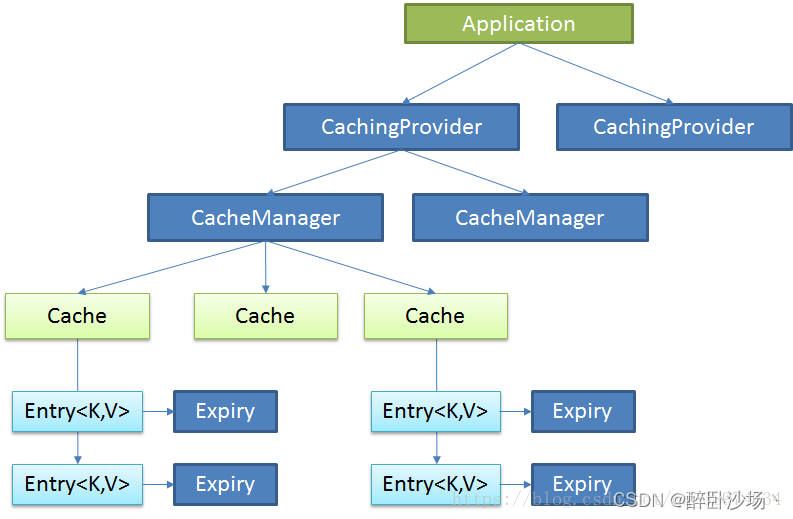
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
-
CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
-
CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
-
Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
-
Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对.
-
Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
2.Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发。
-
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合。
-
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache。
-
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否 已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法 并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
-
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点:
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
二、几个重要概念&缓存注解
概念/注解 作用 Cache 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 CacheManager 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 @Cacheable 可以针对方法和类进行配置,主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
缓存存在,则使用缓存;不存在,则执行方法,并将结果塞入缓存@CacheEvict 清空缓存 @CachePut 保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存。与@Cacheable区别在于是否每次都调用方法,常用于更新 @Caching @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict的组合,定义复杂的缓存规则,在这个组合中只要有@CachePut就一定会调用被注解的方法 @CacheConfig 标注在类上,抽取缓存相关注解的公共配置,可抽取的公共配置有缓存名字、主键生成器等 @EnableCaching 开启基于注解的缓存 keyGenerator 缓存数据时key生成策略 serialize 缓存数据时value序列化策略 说明:
①@Cacheable标注在方法上,表示该方法的结果需要被缓存起来,缓存的键由keyGenerator的策略决定,缓存的值的形式则由serialize序列化策略决定(序列化还是json格式);标注上该注解之后,在缓存时效内再次调用该方法时将不会调用方法本身而是直接从缓存获取结果
②@CachePut也标注在方法上,和@Cacheable相似也会将方法的返回值缓存起来,不同的是标注@CachePut的方法每次都会被调用,而且每次都会将结果缓存起来,适用于对象的更新@Cacheable
主要参数
属性名 描述 示例 cacheNames/value cacheNames和value互为别名。其作用是指定缓存的名字,缓存使用CacheManager管理多个缓存组件Cache,这些Cache组件就是根据这个名字进行区分的。对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache中定义,每个缓存组件Cache都有自己唯一的名字,通过cacheNames或者value属性指定,相当于是将缓存的键值对进行分组,缓存的名字是一个数组,也就是说可以将一个缓存键值对分到多个组里面。 @Cacheable(value=“testCache”) 或者 @Cacheable(cacheNames={“cache1”,“cache2”}) key 缓存数据时的key的值,默认是使用方法参数的值,可以使用SpEL表达式计算key的值 @Cacheable(value=“testCache”,key=“#userName”) keyGenerator 缓存的生成策略,和key二选一,都是生成键的,keyGenerator可自定义 cacheManager 指定缓存管理器(如ConcurrentHashMap、Redis等) cacheResolver 和cacheManager功能一样,和cacheManager二选一 condition 指定缓存的条件(满足什么条件时才缓存),可用SpEL表达式(如#id>0,表示当入参id大于0时才缓存) @Cacheable(value=“testCache”,condition=“#userName.length()>2” unless 否定缓存,即满足unless指定的条件时,方法的结果不进行缓存,使用unless时可以在调用的方法获取到结果之后再进行判断(如#result==null,表示如果结果为null时不缓存) @Cacheable(value=“testCache”,unless=“#result == null”) sync 是否使用异步模式进行缓存;使用异步模式进行缓存时(sync=true):unless条件将不被支持 注:
①既满足condition又满足unless条件的也不进行缓存
②使用异步模式进行缓存时(sync=true):unless条件将不被支持可用的SpEL表达式见下表:
名字 位置 描述 示例 methodName root object 当前被调用的方法名 #root.methodName method root object 当前被调用的方法 #root.method.name target root object 当前被调用的目标对象 #root.target targetClass root object 当前被调用的目标对象类 root.targetClass args root object 当前被调用的方法的参数列表 #root.args[0] caches root object 当前方法调用使用的缓存列表(如@Cacheable(value={“cache1”, “cache2”})),则有两个cache #root.caches[0].name Argument Name evaluation context 当前被调用的方法的参数,可以直接 #参数名,如findArtisan(Artisan artisan),可以通过#artsian.id获得参数;也可以使用#p0或#a0的形式,0代表参数的索引 #iban、#a0、#p0 result evaluation context 方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如"unless","cache put"的表达式,"cache evict"的表达式beforeInvocation=false) #result 详解
这个注解用于修饰方法或者类,当我们访问它修饰的方法时,优先从缓存中获取,若缓存中存在,则直接获取缓存的值;缓存不存在时,则执行方法,并将结果写入缓存。
这个注解,有两个比较核心的设置
/** * 与 cacheNames 效果等价 */ @AliasFor("cacheNames") String[] value() default {}; /** * 与 value 效果等价 */ @AliasFor("value") String[] cacheNames() default {}; /** * 缓存key */ String key() default "";- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
cacheNames 可以理解为缓存 key 的前缀,可以为组件缓存的 key 变量;当 key 不设置时,使用方法参数来初始化,注意 key 为 SpEL 表达式,因此如果要写字符串时,用单引号括起来。
/** * 首先从缓存中查,查到之后,直接返回缓存数据;否则执行方法,并将结果缓存 * * redisKey: cacheNames + key 组合而成 --> 支持SpEL * redisValue: 返回结果 */ @Cacheable(cacheNames = "say", key = "'p_'+ #name") public String sayHello(String name) { return "hello+" + name + "-->" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
如我们传参为 somnus, 那么缓存 key 为
say::somnuscondition参数,这个表示当它设置的条件达成时,才写入缓存。下面这个 case 中,age 为偶数的时候,才走缓存;否则不走缓存。/** * 满足condition条件的才写入缓存 */ @Cacheable(cacheNames = "condition", key = "#age", condition = "#age % 2 == 0") public String setByCondition(int age) { return "condition:" + age + "-->" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
接下来是
unless参数,这个表示它设置的条件不满足时才写入缓存。下面这个 case 中,age 为偶数的时候,不走缓存;否则走缓存。/** * unless, 不满足条件才写入缓存 */ @Cacheable(cacheNames = "unless", key = "#age", unless = "#age % 2 == 0") public String setUnless(int age) { return "unless:" + age + "-->" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
service层代码
第一次查询数据库打印service类方法日志,并把数据保存到Cahce中
第二次传入相同参数不再执行service类方法,不会打印日志,查询的数据直接从缓存中获取
@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired PersonDao personDao; //@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person") //@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id",condition="#id>3") @Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id") public Person queryPersonById(Integer id){ System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工信息"); Person person=new Person(); person.setId(id); return personDao.query(person); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
@CachePut
不管缓存有没有,都将方法的返回结果写入缓存;适用于缓存更新
通俗讲就是:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据 ,即数据库中的数据和缓存都更新!
主要参数
属性名 描述 示例 cacheNames/value cacheNames和value互为别名。其作用是指定缓存的名字,缓存使用CacheManager管理多个缓存组件Cache,这些Cache组件就是根据这个名字进行区分的。对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache中定义,每个缓存组件Cache都有自己唯一的名字,通过cacheNames或者value属性指定,相当于是将缓存的键值对进行分组,缓存的名字是一个数组,也就是说可以将一个缓存键值对分到多个组里面。 @CachePut(value=“testCache”) 或者 @CachePut(cacheNames={“cache1”,“cache2”}) key 缓存数据时的key的值,默认是使用方法参数的值,可以使用SpEL表达式计算key的值 @CachePut(value=“testCache”,key=“#userName”) keyGenerator 缓存的生成策略,和key二选一,都是生成键的,keyGenerator可自定义 cacheManager 指定缓存管理器(如ConcurrentHashMap、Redis等) cacheResolver 和cacheManager功能一样,和cacheManager二选一 condition 指定缓存的条件(满足什么条件时才缓存),可用SpEL表达式(如#id>0,表示当入参id大于0时才缓存) @CachEvict(value=“testCache”,condition=“#userName.length()>2” unless 否定缓存,即满足unless指定的条件时,方法的结果不进行缓存,使用unless时可以在调用的方法获取到结果之后再进行判断(如#result==null,表示如果结果为null时不缓存) @Cacheable(value=“testCache”,unless=“#result == null”) sync 是否使用异步模式进行缓存;使用异步模式进行缓存时(sync=true):unless条件将不被支持 详解
@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired PersonDao personDao; /** *运行时机: * 1.先调用目标方法 * 2.将目标方法返回的结果缓存起来 * * 测试步骤: * 1.查询1号的个人信息 * 2.以后查询还是之前的结果 * 3.更新1号的个人信息 * 4.查询一号员工返回的结果是什么? * 应该是更新后的员工 * 但只更新了数据库,但没有更新缓存是什么原因? * 5.如何解决缓存和数据库同步更新? * 这样写:@CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#person.id") * @CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#result.id") */ @CachePut(cacheNames = "person",key = "#result.id") public Person updatePerson(Person person){ System.out.println("修改"+person.getId()+"号员工信息"); personDao.update(person); return person; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
@CacheEvict
这个就是我们理解的删除缓存,可以清除缓存中的指定数据或清除缓存中所有数据。
主要参数
属性名 描述 示例 cacheNames/value cacheNames和value互为别名。其作用是指定缓存的名字,缓存使用CacheManager管理多个缓存组件Cache,这些Cache组件就是根据这个名字进行区分的。对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache中定义,每个缓存组件Cache都有自己唯一的名字,通过cacheNames或者value属性指定,相当于是将缓存的键值对进行分组,缓存的名字是一个数组,也就是说可以将一个缓存键值对分到多个组里面。 @CachEvict(value=“testCache”) 或者 @CachEvict(cacheNames={“cache1”,“cache2”}) key 缓存数据时的key的值,默认是使用方法参数的值,可以使用SpEL表达式计算key的值 @CachEvict(value=“testCache”,key=“#userName”) keyGenerator 缓存的生成策略,和key二选一,都是生成键的,keyGenerator可自定义 cacheManager 指定缓存管理器(如ConcurrentHashMap、Redis等) cacheResolver 和cacheManager功能一样,和cacheManager二选一 condition 指定缓存的条件(满足什么条件时才缓存),可用SpEL表达式(如#id>0,表示当入参id大于0时才缓存) @CachEvict(value=“testCache”,condition=“#userName.length()>2”) allEntries 是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false;如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 @CachEvict(value=“testCache”,allEntries=true) beforeInvocation 是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false;如果指定 为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存, 缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 @CachEvict(value=“testCache”,beforeInvocation=true) 详解
清除缓存中的单个数据
/** * 失效缓存 */ @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "say", key = "'p_'+ #name") public String evict(String name) { return "evict+" + name + "-->" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
清除缓存中的所有数据
@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired PersonDao personDao; /** * @CacheEvict:清除缓存 * 1.key:指定要清除缓存中的某条数据 * 2.allEntries=true:删除缓存中的所有数据 * 3.beforeInvocation=false:默认是在方法之后执行清除缓存 * beforeInvocation=true:现在是在方法执行之前执行清除缓存 */ //@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",key = "#id") @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",allEntries=true) public void deletePerson(Integer id){ System.out.println("删除"+id+"号个人信息"); //删除数据库数据的同时删除缓存数据 //personDao.delete(id); /** * beforeInvocation=true * 使用在方法之前执行的好处: * 1.如果方法出现异常,缓存依旧会被删除 */ //int a=1/0; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
也可以使用方法来生成key,格式为
T(类的全类名).方法名(参数列表)@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired private PersonDao personDao; //@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",key = "#id") @CacheEvict(key = "T(org.zpli.service.PersonCacheUtils).generateIdKey(#result.id)") public Person deletePerson(Person person) { System.out.println("删除" + person.getId() + "号个人信息"); //删除数据库数据的同时删除缓存数据 Person deletePerson = personDao.delete(person); return deletePerson; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
package org.zpli.service; /** * created at 2023/3/9 16:52 * * @author somnuszpli */ public class PersonCacheUtils { public static String generateIdKey(String id) { return "p_" + id; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
@Caching
在实际的工作中,经常会遇到一个数据变动,更新多个缓存的场景,对于这个场景,可以通过
@Caching来实现/** * caching实现组合,添加缓存,并失效其他的缓存 */ @Caching(cacheable = @Cacheable(cacheNames = "caching", key = "#age"), evict = @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "t4", key = "#age")) public String caching(int age) { return "caching: " + age + "-->" + UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
上面这个就是组合操作
- 从
caching::age缓存取数据,不存在时执行方法并写入缓存; - 失效缓存
t4::age
@Service public class PersonService { @Autowired PersonDao personDao; /** * @Caching是 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合 * 以下注解的含义: * 1.当使用指定名字查询数据库后,数据保存到缓存 * 2.现在使用id、age就会直接查询缓存,而不是查询数据库 */ @Caching( cacheable = {@Cacheable(value = "person",key="#name")}, put={ @CachePut(value = "person",key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(value = "person",key = "#result.age") } ) public Person queryPersonByName(String name){ System.out.println("查询的姓名:"+name); return personDao.queryByName(name); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
三、使用缓存
第一步: 导入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
第二步: @EnableCaching开启缓存
@SpringBootApplication @EnableCaching public class SpringbootCacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第三步: 使用缓存注解
四、缓存工作原理
1、自动配置类:CacheAutoConfiguration,通过CacheAutoConfiguration导入的CacheConfigurationImportSelector会向数组中添加一些缓存的配置类全类名
2、缓存的配置类 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration(默认使用)
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
3、默认生效的配置类:SimpleCacheConfiguration
4、SimpleCacheConfiguration给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager@Configuration @ConditionalOnMissingBean({CacheManager.class}) @Conditional({CacheCondition.class}) class SimpleCacheConfiguration { private final CacheProperties cacheProperties; private final CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker; SimpleCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers customizerInvoker) { this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties; this.customizerInvoker = customizerInvoker; } @Bean public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() { ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager(); List<String> cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames(); if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) { cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames); } return (ConcurrentMapCacheManager)this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
5、通过ConcurrentMapCacheManager可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件:ConcurrentMapCache的作用是数据保存在ConcurrentMap中
6、@Cacheable运行流程:
①方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取(CacheManager先获取相应的缓存,第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建)
②去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用的key默认就是方法的参数:
key默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用的是SimpleKeyGenerator
SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略:
如果没有参数:key = new SimpleKey();
如果有一个参数:key = 参数的值
如果有多个参数:key = new SimpleKey(params);
③没有查到缓存就调用目标方法
④将目标方法返回的结果放进缓存中
总结:@Cacheable标注的方法在执行之前会先检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值为key查询缓存,如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存,以后再来调用时直接使用缓存中的数据。
核心:
1️⃣使用CacheManager(ConcurrentMapCacheManager)按照名字得到Cache(ConcurrentMapCache)组件
2️⃣key使用keyGenerator生成,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator -
-
相关阅读:
类和对象常见题目解法
第3章业务功能开发(用户访问项目)
【PAT甲级】1136 A Delayed Palindrome
风控规则引擎(一):Java 动态脚本
贪心算法-----------------装箱问题
驱动开发:内核读写内存多级偏移
Git和Github的基本用法
Pycharm的安装和使用
【3D目标检测】OpenPCDet自定义数据集训练
上海华清远见
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ToBeMaybe_/article/details/126707473
