-
音视频从入门到精通——FFmpeg之av_read_frame函数分析
FFmpeg之av_read_frame函数分析
av_read_frame函数分析
代码
/** * Return the next frame of a stream. * This function returns what is stored in the file, and does not validate * that what is there are valid frames for the decoder. It will split what is * stored in the file into frames and return one for each call. It will not * omit invalid data between valid frames so as to give the decoder the maximum * information possible for decoding. * 返回流的下一帧。 此函数返回文件中存储的内容,并且不验证 即解码器存在有效帧。它会分裂什么 存储在文件中的帧,并为每个调用返回一个帧。不会 省略有效帧之间的无效数据,以便为解码器提供最大值 可以解码的信息。 * * * On success, the returned packet is reference-counted (pkt->buf is set) and * valid indefinitely. The packet must be freed with av_packet_unref() when * it is no longer needed. For video, the packet contains exactly one frame. * For audio, it contains an integer number of frames if each frame has * a known fixed size (e.g. PCM or ADPCM data). If the audio frames have * a variable size (e.g. MPEG audio), then it contains one frame. * * 成功时,返回的数据包被引用计数(pkt->buf被设置),并且 无限期有效。在以下情况下,必须使用av_packet_unref()释放数据包: 它不再需要了。 对于视频,数据包只包含一帧。 对于音频,如果每个帧具有 已知的固定大小(例如PCM或ADPCM数据)。如果音频帧具有: 可变大小(例如MPEG音频),则它包含一个帧。 * pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration are always set to correct * values in AVStream.time_base units (and guessed if the format cannot * provide them). pkt->pts can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if the video format * has B-frames, so it is better to rely on pkt->dts if you do not * decompress the payload. * pkt->pts、pkt->dts和pkt->“持续时间”始终设置为正确 AVStream中的值。time_base units(如果格式不能 提供它们)。如果视频格式为: 具有B帧,因此如果没有,最好依赖pkt->dts 解压缩有效载荷。 * * * @return 0 if OK, < 0 on error or end of file. On error, pkt will be blank * (as if it came from av_packet_alloc()). * * @note pkt will be initialized, so it may be uninitialized, but it must not * contain data that needs to be freed. * * pkt将被初始化,因此它可能未初始化,但不能 包含需要释放的数据。 * */ int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
其中AVFormatContext ,AVPacket 两个参数。
AVFormatContext结构体
AVFormatContext结构体详情
/** * Format I/O context. * New fields can be added to the end with minor version bumps. * Removal, reordering and changes to existing fields require a major * version bump. * sizeof(AVFormatContext) must not be used outside libav*, use * avformat_alloc_context() to create an AVFormatContext. * * Fields can be accessed through AVOptions (av_opt*), * the name string used matches the associated command line parameter name and * can be found in libavformat/options_table.h. * The AVOption/command line parameter names differ in some cases from the C * structure field names for historic reasons or brevity. */ typedef struct AVFormatContext { AVIOContext *pb:输入数据的缓存 unsigned int nb_streams:视音频流的个数 AVStream **streams:视音频流 char filename[1024]:文件名 int64_t duration:时长(单位:微秒us,转换为秒需要除以1000000) int bit_rate:比特率(单位bps,转换为kbps需要除以1000) AVDictionary *metadata:元数据 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
AVPacket结构体
AVPacket结构体详情
/** * This structure stores compressed data. It is typically exported by demuxers * and then passed as input to decoders, or received as output from encoders and * then passed to muxers. * * For video, it should typically contain one compressed frame. For audio it may * contain several compressed frames. Encoders are allowed to output empty * packets, with no compressed data, containing only side data * (e.g. to update some stream parameters at the end of encoding). * * The semantics of data ownership depends on the buf field. * If it is set, the packet data is dynamically allocated and is * valid indefinitely until a call to av_packet_unref() reduces the * reference count to 0. * * If the buf field is not set av_packet_ref() would make a copy instead * of increasing the reference count. * * The side data is always allocated with av_malloc(), copied by * av_packet_ref() and freed by av_packet_unref(). * * sizeof(AVPacket) being a part of the public ABI is deprecated. once * av_init_packet() is removed, new packets will only be able to be allocated * with av_packet_alloc(), and new fields may be added to the end of the struct * with a minor bump. * * @see av_packet_alloc * @see av_packet_ref * @see av_packet_unref */ typedef struct AVPacket { /** * A reference to the reference-counted buffer where the packet data is * stored. * May be NULL, then the packet data is not reference-counted. */ AVBufferRef *buf; /** * Presentation timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which * the decompressed packet will be presented to the user. * Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file. * pts MUST be larger or equal to dts as presentation cannot happen before * decompression, unless one wants to view hex dumps. Some formats misuse * the terms dts and pts/cts to mean something different. Such timestamps * must be converted to true pts/dts before they are stored in AVPacket. */ int64_t pts; /** * Decompression timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which * the packet is decompressed. * Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file. */ int64_t dts; uint8_t *data; int size; int stream_index; /** * A combination of AV_PKT_FLAG values */ int flags; /** * Additional packet data that can be provided by the container. * Packet can contain several types of side information. */ AVPacketSideData *side_data; int side_data_elems; /** * Duration of this packet in AVStream->time_base units, 0 if unknown. * Equals next_pts - this_pts in presentation order. */ int64_t duration; int64_t pos; ///< byte position in stream, -1 if unknown /** * for some private data of the user */ void *opaque; /** * AVBufferRef for free use by the API user. FFmpeg will never check the * contents of the buffer ref. FFmpeg calls av_buffer_unref() on it when * the packet is unreferenced. av_packet_copy_props() calls create a new * reference with av_buffer_ref() for the target packet's opaque_ref field. * * This is unrelated to the opaque field, although it serves a similar * purpose. */ AVBufferRef *opaque_ref; /** * Time base of the packet's timestamps. * In the future, this field may be set on packets output by encoders or * demuxers, but its value will be by default ignored on input to decoders * or muxers. */ AVRational time_base; } AVPacket;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
AVPacket 几个重要的变量
AVBufferRef *buf;一个指针,指向一个buf空间,这个空间是用来存储引用计数的。用的时候+1,删除的时候-1。 uint8_t *data:压缩编码的数据。 例如对于H.264来说。1个AVPacket的data通常对应一个NAL。 注意:在这里只是对应,而不是一模一样。他们之间有微小的差别:使用FFMPEG类库分离出多媒体文件中的H.264码流 因此在使用FFMPEG进行视音频处理的时候,常常可以将得到的AVPacket的data数据直接写成文件,从而得到视音频的码流文件。 int size:data的大小 int64_t pts:显示时间戳 int64_t dts:解码时间戳 int stream_index:标识该AVPacket所属的视频/音频流。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
DTS、PTS概述
/** * Presentation timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which * the decompressed packet will be presented to the user. * Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file. * pts MUST be larger or equal to dts as presentation cannot happen before * decompression, unless one wants to view hex dumps. Some formats misuse * the terms dts and pts/cts to mean something different. Such timestamps * must be converted to true pts/dts before they are stored in AVPacket. */ int64_t pts;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
PTS(Presentation Time Stamp):即显示时间戳,这个时间戳用来告诉播放器该在什么时候显示这一帧的数据。
/** * Decompression timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; the time at which * the packet is decompressed. * Can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if it is not stored in the file. */ int64_t dts;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
DTS(Decoding Time Stamp):即解码时间戳,这个时间戳的意义在于告诉播放器该在什么时候解码这一帧的数据。
要深入理解PTS,DTS,需要了解一下视频编码的知识。如视频编码之I,P,B帧。
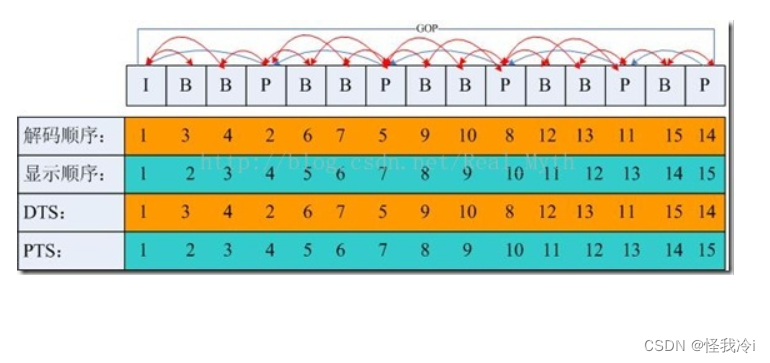
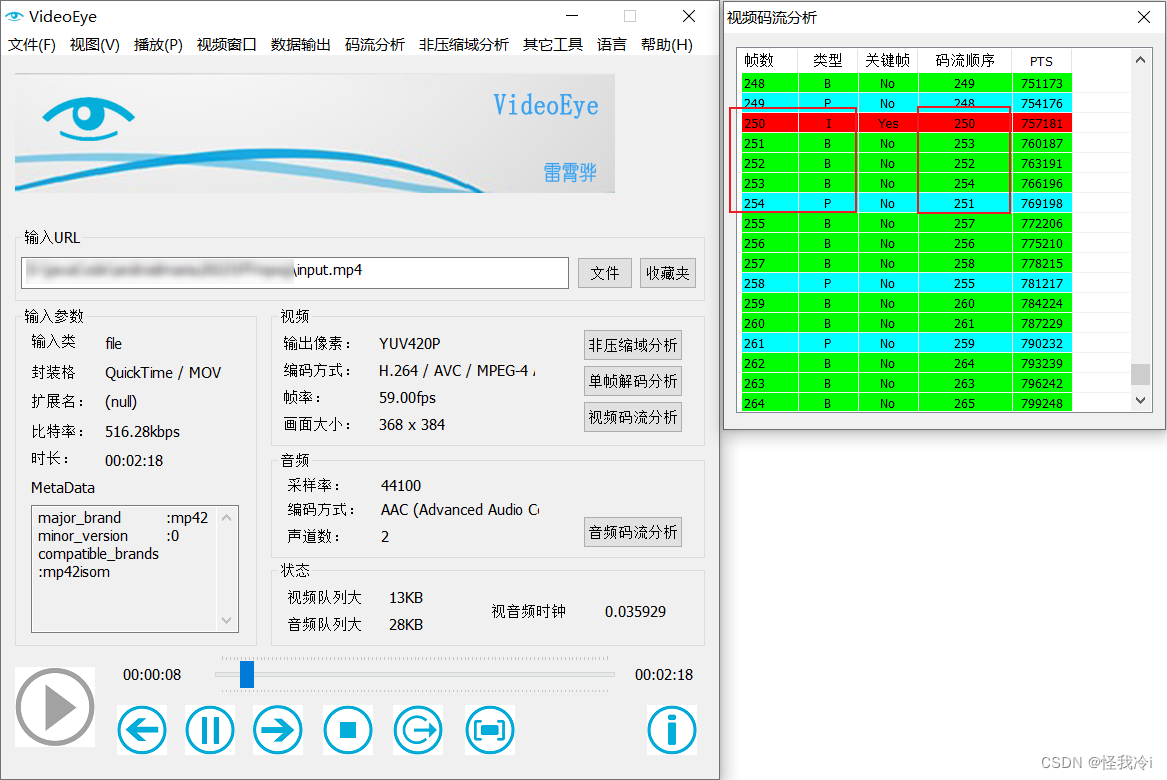
也可以用VideoEye工具分析。
参考
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFrame
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVFormatContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodecContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVIOContext
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVCodec
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVStream
FFMPEG结构体分析:AVPacket -
相关阅读:
Xftp 7过期后下载使用免费版
iOS开发Swift-5-自动布局AutoLayout-摇骰子App
语音信号处理中的“窗函数”
Android Runtime (ART) 和 Dalvik
Leetcode hot 100之双指针(快慢指针、滑动窗口)
Linux:keepalived + ipvsadm
POSTGIS数据库操作
Google Analytics Service account 认证指南
ES6模块化
需要在html中加CSS,怎么加
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/e891377/article/details/126700534
