-
密码相关----对称加密,非对称加密
一、发展历史1.1 古典密码学
如凯撒密码、滚筒密码
1.2 近代密码学
如德国Enigma机,被图灵破解
1.3 现代密码学
二、编码算法
不是加密和解密,为了在网络间更方便的传输数据而产生
2.1 base64
由 A-Z、a-z、0-9、+、/ 共64个字符组成,去掉 i I o O + / 即base58
注意:base64以三个字节为一组,如果最后一组不足3个字节,则使用=号补充。
🍎jdk1.8提供的base64类
import org.junit.Test; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.util.Base64; /** * jdk base64测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-02 */ public class jdkBase64Test { @Test public void test01() { String str = "小白一起学编程"; //编码 String encodeStr = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(str.getBytes( StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println(encodeStr); //解码 String decodeStr = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encodeStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)),StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
🍎codec的base64
<dependency> <groupId>commons-codecgroupId> <artifactId>commons-codecartifactId> <version>1.15version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; import org.junit.Test; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; /** * 编解码器base64测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-03 */ public class codecBase64Test { @Test public void test01() { String str = "小白一起学编程"; //编码 String encodeStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println(encodeStr); //解码 String decodeStr = new String(Base64.decodeBase64(encodeStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)),StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
2.2 URL编码
🍎jdk提供的工具
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.net.URLDecoder; import java.net.URLEncoder; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class URLTest { @Test public void test01() throws UnsupportedEncodingException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; //编码 String encode = URLEncoder.encode(str, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); System.out.println(encode); //解码 String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name()); System.out.println(decode); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
三、摘要算法
- 定义
又叫Hash算法、散列函数、数字摘要、消息摘要。它是一种单向算法,用户可以通过hash算法对目标信息生成一段特定长度的唯一hash值,但不能通过这个hash值重新获得目标信息
- 应用场景
密码、信息完整性校验、数字签名
3.1 常见算法
- MD5: Message-Digest Algorithm,结果占 128位 ==> 16个 byte ==>16进制字符串是32个字符
- SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm):安全散列算法
- sha-256 ==> 32byte ==> 16进制字符串64个字符
- 其他如 sha-0, sha-1, sha-512
- MAC(Message Authentication Code):消息认证码,是一种带有秘钥的hash函数
- 其他如MD2,MD4,HAVAL
MD5
jdk原生实现
import org.junit.Test; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.security.MessageDigest; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; /** * jdk md5测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-03 */ public class JdkMd5Test { @Test public void test01() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "MD5"; // 获取消息摘要算法对象 MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm); // 获取原始内容的字节数组 byte[] originalBytes = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 获取摘要结果 byte[] digestBytes = md.digest(originalBytes); //当originalBytes比较大的时候,循环的进行update() // md.update(originalBytes); // md.digest(); //md5占128位->16字节->1字节=8位 可以转为一个16进制 --> 16个16进制的数 //将每个字节转为16进制字符,最终拼接起来即可 String hexStr = convertBytes2HexStr(digestBytes); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); } private String convertBytes2HexStr(byte[] digestBytes) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //循环16个字节 for (byte b : digestBytes) { //获取b的补码的后8位 String hex = Integer.toHexString(((int)b)&0xff); // 15 --> Integer.toHexString(15&0xff) --> 0f // 16 --> Integer.toHexString(16&0xff) if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = "0" +hex; } sb.append(hex); } return sb.toString(); } } //hexStr:2d4c6bc71a670cce33f75b9691488742- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
简单封装
public class HexUtils { /** * 把字节数组转为16进制字符串,如果一个字节转为16进制字符后不足两位,则在前面补0 * * @param digestBytes 字节数组 * @return {@link String} */ public static String convertBytes2HexStr(byte[] digestBytes) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //循环16个字节 for (byte b : digestBytes) { //获取b的补码的后8位 String hex = Integer.toHexString(((int)b)&0xff); // 15 --> Integer.toHexString(15&0xff) --> 0f // 16 --> Integer.toHexString(16&0xff) if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = "0" +hex; } sb.append(hex); } return sb.toString(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.security.MessageDigest; public class MessageDigestUtils { /** * 执行消息摘要 * * @param originalContent 原创字符串 * @param algorithm 算法名称 * @return {@link String} 摘要内容 */ public static String doDigest(String originalContent,String algorithm) { try { // 获取消息摘要算法对象 MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm); // 获取原始内容的字节数组 byte[] originalBytes = originalContent.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 获取摘要结果 byte[] digestBytes = md.digest(originalBytes); //当originalBytes比较大的时候,循环的进行update() // md.update(originalBytes); // md.digest(); //md5占128位->16字节->1字节=8位 可以转为一个16进制 --> 16个16进制的数 //将每个字节转为16进制字符,最终拼接起来即可 return HexUtils.convertBytes2HexStr(digestBytes); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
测试
/** * jdk md5测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-03 */ public class JdkMd5Test { @Test public void test01() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "MD5"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doDigest(str, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); } } //hexStr:2d4c6bc71a670cce33f75b9691488742- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
🍎codec的api调用
codec中byte数组转hex字符串方法
@Test public void test02(){ byte[] bytes = new byte[]{15,16}; System.out.println(Hex.encodeHexString(bytes)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
MD5
@Test public void test04(){ String str = "小白一起学编程"; System.out.println(org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils.md5Hex(str)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
🍎spring中的md5
@Test public void test03(){ String str = "小白一起学编程"; System.out.println(DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
sha256
jdk原生实现
@Test public void test01() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "SHA-256"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doDigest(str, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
codec实现方式
@Test public void test04(){ String str = "小白一起学编程"; System.out.println(DigestUtils.sha256Hex(str)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
sha512
jdk原生实现
@Test public void test01() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "SHA-512"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doDigest(str, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
codec实现
@Test public void test04(){ String str = "小白一起学编程"; System.out.println(DigestUtils.sha512Hex(str)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Mac
jdk中HmacMD5
import javax.crypto.Mac; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class MessageDigestUtils { /** * 执行消息摘要 * * @param originalContent 原创字符串 * @param algorithm 算法名称 * @return {@link String} 摘要内容 */ public static String doMacDigest(String originalContent,String key,String algorithm) { try { // 获取消息摘要算法对象 Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(algorithm); // 获取key对象并初始化mac SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8),algorithm); mac.init(secretKey); // 获取原始内容的字节数组 byte[] originalBytes = originalContent.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 获取到摘要结果 byte[] digestBytes = mac.doFinal(originalBytes); // 把每一个字节转为16进制字符,最终再拼接起来这些16进制字符 return HexUtils.convertBytes2HexStr(digestBytes); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
public class HexUtils { /** * 把字节数组转为16进制字符串,如果一个字节转为16进制字符后不足两位,则在前面补0 * * @param digestBytes 字节数组 * @return {@link String} */ public static String convertBytes2HexStr(byte[] digestBytes) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //循环16个字节 for (byte b : digestBytes) { //获取b的补码的后8位 String hex = Integer.toHexString(((int)b)&0xff); // 15 --> Integer.toHexString(15&0xff) --> 0f // 16 --> Integer.toHexString(16&0xff) if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = "0" +hex; } sb.append(hex); } return sb.toString(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
import org.junit.Test; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; public class JdkMd5Test { /** * jdk HmacMd5 实现方式 * * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException 没有这样算法异常 */ @Test public void test01() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "HmacMD5"; // 指定秘钥,mac摘要和digest算法(md5,sha)不同的地方就是加了盐 String key = "123"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doMacDigest(str,key, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
jdk中HmacSHA256
@Test public void test02() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "HmacSHA256"; // 指定秘钥,mac摘要和digest算法(md5,sha)不同的地方就是加了盐 String key = "123"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doMacDigest(str,key, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
jdk中HmacSHA512
/** * jdk HmacSHA512 实现方式 * * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException 没有这样算法异常 */ @Test public void test03() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String algorithm = "HmacSHA512"; // 指定秘钥,mac摘要和digest算法(md5,sha)不同的地方就是加了盐 String key = "123"; String hexStr = MessageDigestUtils.doMacDigest(str,key, algorithm); System.out.println("hexStr:" + hexStr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
codec中实现方式
@Test public void test04() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { String str = "小白一起学编程"; String key = "123"; //HmacUtils.hmacMd5Hex(); 过时 String hmacMD5HexStr = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_MD5, key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) .hmacHex(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String hmacSHA256HexStr = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_256, key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) .hmacHex(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String hmacSHA512HexStr = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_512, key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) .hmacHex(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println(hmacMD5HexStr); System.out.println(hmacSHA256HexStr); System.out.println(hmacSHA512HexStr); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
四、对称加密
定义:
单秘钥加密。所谓单秘钥,指的是加密和解密的过程中使用相同的秘钥,相比非对称加密,因只有一把秘钥,因而速度更快,更适合加密大文件。
常见算法
- DES:data encryption standard, 已经过时
- AES:Advanced Encryption Standard,替代des
- 其他如:3DES, Blowfish, IDEA,RC4,RC5,RC6
DES加密,只允许密钥是8个字节的。
AES加密,密钥必须是16个字节的.
也就是说 key=“12345678”可以,key="123456789"就会报错。
DES
jdk实现DES
import org.apache.commons.net.util.Base64; import org.junit.Test; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class DesTest { private static final String ALGORITHM = "DES"; private static final String KEY = "12345678"; /** * 加密 * * @param text 待加密的内容 * @return {@link String} * @throws Exception 异常 */ private String encrypt(String text) throws Exception { // 获取实例 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); /* 创建加解密的规则 */ SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(KEY.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM); //指定加密模式还是解密模式,秘钥对象 /* 1. 加解密模式 2.秘钥规则 */ cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,secretKey); byte[] encodedBytes = cipher.doFinal(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); /* 加密的字节数组如何展示? 第一种:Base64 第二种:转成16进制字符串 */ return Base64.encodeBase64String(encodedBytes); } /** * 解密 * * @param text 待解密的内容 * @return {@link String} * @throws Exception 异常 */ private String decrypt(String text) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(KEY.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE,secretKey); byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.decodeBase64(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); return new String(decryptedBytes,StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } @Test public void test() throws Exception { String encode = encrypt("小白一起学编程"); System.out.println(encode); String decode = decrypt(encode); System.out.println(decode); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
AES
🍎jdk实现AES
import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class CipherUtils { private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES"; /** * 得到cipher对象 * * @param type 加解密模式 * @param seed 秘钥key * @return {@link Cipher} */ public static Cipher getCipher(int type,String seed) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(seed.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM); cipher.init(type,secretKey); return cipher; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex; import org.junit.Test; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; public class AesTest { @Test public void encrypt() throws Exception { //加密 String text = "小白一起学编程"; Cipher cipher1 = CipherUtils.getCipher(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, "12345678"); byte[] encodedBytes = cipher1.doFinal(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String baseStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(encodedBytes); String hexStr = Hex.encodeHexString(encodedBytes); System.out.println(baseStr); System.out.println(hexStr); //解密 Cipher cipher2 = CipherUtils.getCipher(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, "12345678"); byte[] decodeBytes1 = cipher2.doFinal(Base64.decodeBase64(baseStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); byte[] decodeBytes2 = cipher2.doFinal(Hex.decodeHex(hexStr)); String decodeStr1 = new String(decodeBytes1, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String decodeStr2 = new String(decodeBytes2, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr1); System.out.println(decodeStr2); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
key长度处理
/** * 得到cipher对象 * * @param type 加解密模式 * @param seed 秘钥key * @return {@link Cipher} */ public static Cipher getCipherIgnoreKeyLength(int type,String seed) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 创建keyGenerator对象,可以根据传入的key生成一个指定长度的key KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 初始化secureRandom,并指定生成指定长度key的算法 SecureRandom secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG"); secureRandom.setSeed(seed.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); keyGenerator.init(128,secureRandom); // 通过keyGenerator生成新的秘钥 SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey(); byte[] encoded = secretKey.getEncoded(); SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(encoded, ALGORITHM); cipher.init(type,secretKey); return cipher; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
@Test public void test02() throws Exception { //加密 String text = "小白一起学编程"; Cipher cipher1 = CipherUtils.getCipherIgnoreKeyLength(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef12341234"); byte[] encodedBytes = cipher1.doFinal(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String baseStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(encodedBytes); String hexStr = Hex.encodeHexString(encodedBytes); System.out.println(baseStr); System.out.println(hexStr); //解密 Cipher cipher2 = CipherUtils.getCipherIgnoreKeyLength(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef12341234"); byte[] decodeBytes1 = cipher2.doFinal(Base64.decodeBase64(baseStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); byte[] decodeBytes2 = cipher2.doFinal(Hex.decodeHex(hexStr)); String decodeStr1 = new String(decodeBytes1, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String decodeStr2 = new String(decodeBytes2, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr1); System.out.println(decodeStr2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
分类
- 分组加密,又叫块加密
- 序列加密
块加密常用的加密模式
-
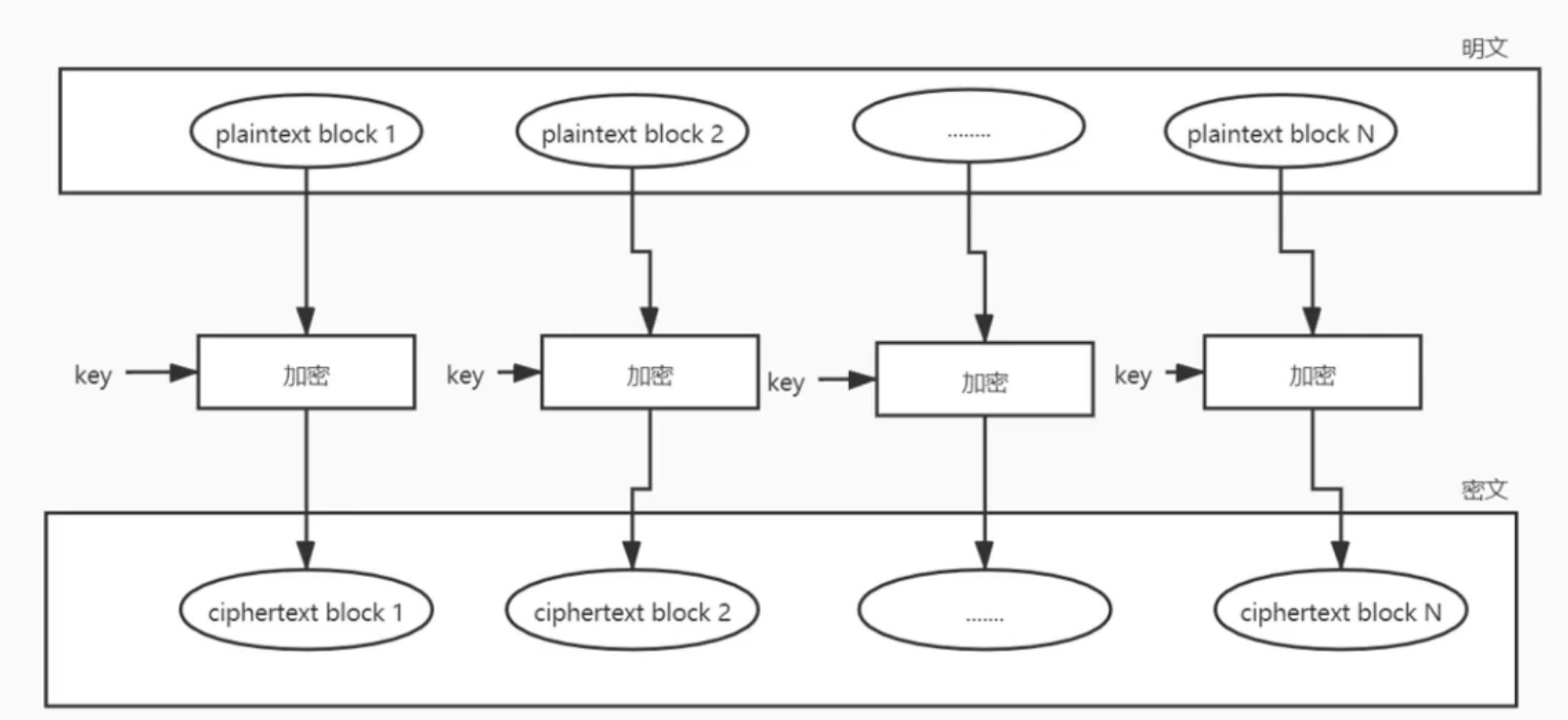
ECB (默认加密模式)
定义:electronic code book, 电码本模式,将整个明文分成若干段相同的小段,然后对每一小段进行加密。
特点:每段之间互不依赖,可以并行处理,同样的明文总是生成同样的密文
-
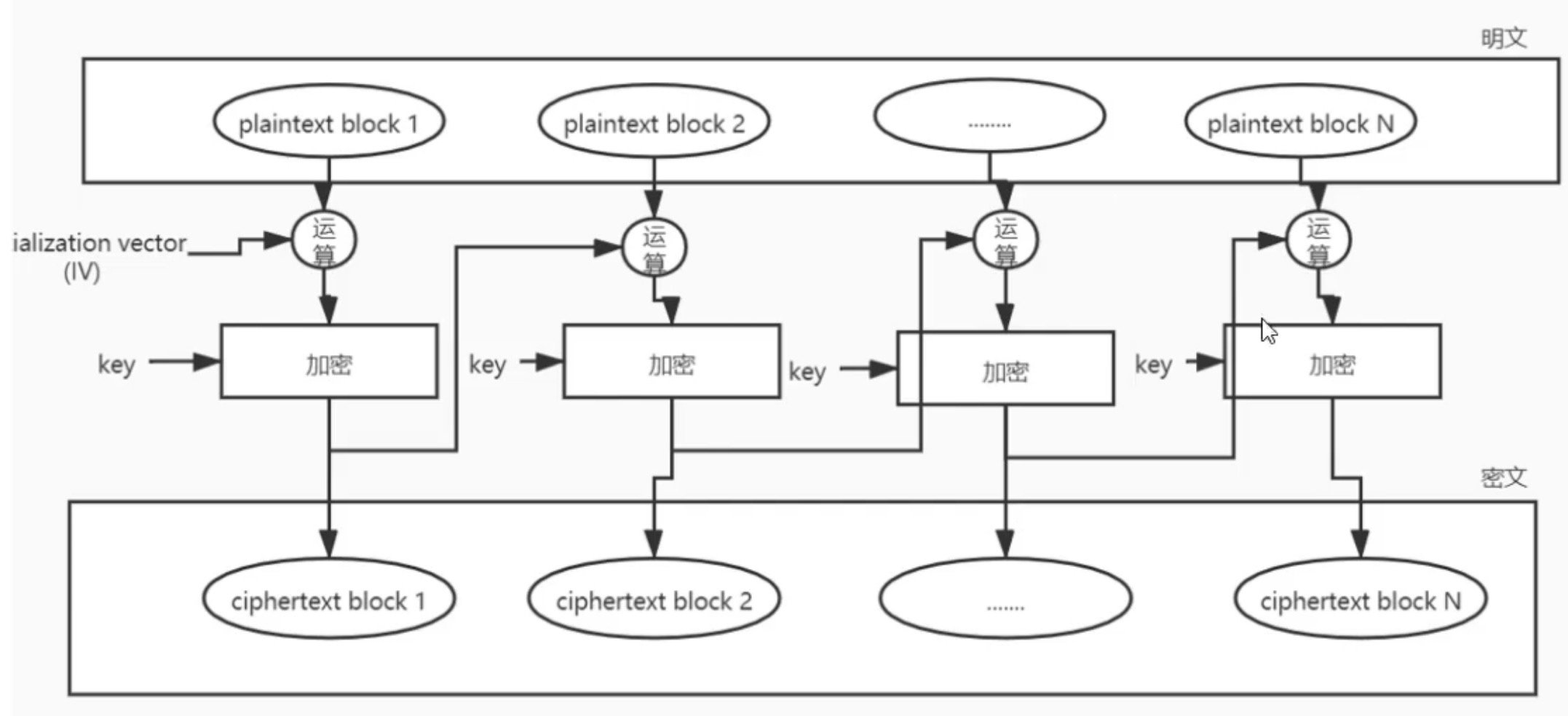
CBC
定义:cipher block chaining,密文分组链模式,所谓链,即密文分组之间像链条一样相互连接在一起。先将明文切分成若干小段,然后每一小段与上一段的密文段(第一个块因没有上一个密文段,使用的是IV)进行运算后,再与密钥进行加密
特点:串行处理;同样的明文每次生成的密文不一样。
private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES"; private static final String ALGORITHM_TYPE_CBC = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"; private static final String ALGORITHM_TYPE_ECB = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding"; /** * 得到cipher对象 * * @param type 加解密模式 * @param seed 秘钥key * @return {@link Cipher} */ public static Cipher getCipherCBC(int type,String seed) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM_TYPE_CBC); SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(seed.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM); //iv向量 IvParameterSpec ivParameterSpec = new IvParameterSpec("1234123412341236".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); cipher.init(type,secretKey,ivParameterSpec); return cipher; } /** * 得到cipher对象 * * @param type 加解密模式 * @param seed 秘钥key * @return {@link Cipher} */ public static Cipher getCipherECB(int type,String seed) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM_TYPE_ECB); SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(seed.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM); cipher.init(type,secretKey); return cipher; } @Test public void test03() throws Exception { //加密 String text = "小白一起学编程"; Cipher cipher1 = CipherUtils.getCipherCBC(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef"); byte[] encodedBytes = cipher1.doFinal(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String baseStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(encodedBytes); String hexStr = Hex.encodeHexString(encodedBytes); System.out.println(baseStr); System.out.println(hexStr); //解密 Cipher cipher2 = CipherUtils.getCipherCBC(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef"); byte[] decodeBytes1 = cipher2.doFinal(Base64.decodeBase64(baseStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); byte[] decodeBytes2 = cipher2.doFinal(Hex.decodeHex(hexStr)); String decodeStr1 = new String(decodeBytes1, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String decodeStr2 = new String(decodeBytes2, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr1); System.out.println(decodeStr2); } @Test public void test04() throws Exception { //加密 String text = "小白一起学编程"; Cipher cipher1 = CipherUtils.getCipherECB(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef"); byte[] encodedBytes = cipher1.doFinal(text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); String baseStr = Base64.encodeBase64String(encodedBytes); String hexStr = Hex.encodeHexString(encodedBytes); System.out.println(baseStr); System.out.println(hexStr); //解密 Cipher cipher2 = CipherUtils.getCipherECB(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, "0123456789abcdef"); byte[] decodeBytes1 = cipher2.doFinal(Base64.decodeBase64(baseStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); byte[] decodeBytes2 = cipher2.doFinal(Hex.decodeHex(hexStr)); String decodeStr1 = new String(decodeBytes1, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String decodeStr2 = new String(decodeBytes2, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println(decodeStr1); System.out.println(decodeStr2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
块加密常用的填充模式
为什么要有?对于固定的加密算法,每个块有固定大小(BlockSize),比如8个byte,明文分块后,加密前需要保证对最后一块的大小为8个byte,如果不够则使用特定数据进行填充
-
NoPadding: 不自动填充
des时要求原文必须是8个字节的整数倍,aes时是16个字节的整数倍
-
PKCS5Padding(限制了块大小为8个byte的PKCS7Padding) /PKCS7Padding
PKCS:Public-Key Cryptography Standards,公钥密码学标准
五、非对称加密
定义
加密和解密使用的是两个不同的秘钥(public key 和 private key)公钥可以给任何人,私钥总是自己保留。
为什么会出现
对称加解密使用相同的秘钥,但对不同的原始内容加密会采用不同的秘钥,导致秘钥数量巨大,难以维护
对称加密容易破解,非对称不容易破解
常见算法
- RSA
- 其他如:ECC, Diffie-Hellman, EI Gamal, DSA


应用场景
-
加解密
可以使用公钥加密,对应的就是私钥解密;也可以使用私钥加密,对应的就是公钥解密
-
数字签名
-
数字信封
-
数字证书
加解密
package com.zs.codeTest.asymmetric; import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.junit.Test; import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException; import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URLDecoder; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.security.*; import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; /** * rsa测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-03 */ public class RsaTest { private static final String ALGORITHM = "RSA"; private static String publicKeyPath; private static String privateKeyPath; /** * RSA单次最大加密的明文大小 */ private static final int MAX_ENCRYPT_BLOCK = 117; /** * RSA单次最大解密的密文大小 */ private static final int MAX_DECRYPT_BLOCK = 128; static { ClassLoader cl = RsaTest.class.getClassLoader(); publicKeyPath = cl.getResource("rsa.pub").getPath(); privateKeyPath = cl.getResource("rsa.pri").getPath(); } /** * 加密 * * @param originalCount 原始数 * @param key 公钥或私钥 * @return {@link String} base64b编码后的加密内容 */ public String encrypt(String originalCount, Key key) throws Exception { Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key); byte[] bytes = doCodec(cipher, originalCount.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8),MAX_ENCRYPT_BLOCK); return Base64.encodeBase64String(bytes); } /** * 解密 * * @param encryptedStr 加密后的内容 * @param key 公钥或私钥 * @return {@link String} 原始内容 */ public String decrypt(String encryptedStr, Key key) throws Exception { byte[] decodeBase64 = Base64.decodeBase64(encryptedStr); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key); byte[] decryptedBytes = doCodec(cipher, decodeBase64,MAX_DECRYPT_BLOCK); return new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } /** * 执行加密或者解密 * * @param cipher 密码 * @param bytes 字节 * @param maxBlockSize 最大block大小 * @return {@link byte[]} */ private byte[] doCodec(Cipher cipher, byte[] bytes, int maxBlockSize) throws Exception { //字节数组的长度 int inputLen = bytes.length; //偏移量,相当于指针来用 int offset = 0; //分段缓冲数组 byte[] cache; ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //循环变量 int i = 0; //循环分段处理 while ((inputLen - offset) > 0) { //判断处理数据的长度是否需要分段处理 if ((inputLen - offset) > maxBlockSize) { //第三个参数是要处理多长 cache = cipher.doFinal(bytes,offset,maxBlockSize); } else { //不需要分段处理 cache = cipher.doFinal(bytes,offset,inputLen - offset); } //把当前cache的内容存起来 baos.write(cache,0,cache.length); //偏移量的增加 offset = ++i * maxBlockSize; } //加密或解密后的结果 byte[] codecBytes = baos.toByteArray(); baos.close(); return codecBytes; } /** * 获取公钥 * 从生成好的公钥文件rsa.pub(进过base64编码后存储的)中获取公钥对象 * * @return {@link PublicKey} */ private PublicKey getPublicKey() throws Exception { String publicKeyBase64Str = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(publicKeyPath), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); byte[] decodeBase64 = Base64.decodeBase64(publicKeyBase64Str); //公钥的规则就是 x509 X509EncodedKeySpec x509EncodedKeySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(decodeBase64); //生成公钥对象 KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); return keyFactory.generatePublic(x509EncodedKeySpec); } /** * 获取私钥 * 从生成好的私钥文件rsa.pri(进过base64编码后存储的)中获取私钥对象 * * @return {@link PublicKey} */ private PrivateKey getPrivateKey() throws Exception { String privateKeyBase64Str = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File(privateKeyPath), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); byte[] decodeBase64 = Base64.decodeBase64(privateKeyBase64Str); // 私钥的规则就是 PKCS8 PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8EncodedKeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(decodeBase64); //生成公钥对象 KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(ALGORITHM); return keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8EncodedKeySpec); } /** * 生成经过base64编码后的密钥对(公钥/私钥)并存储在文件中 */ private void writeKey2File() throws Exception { KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024); // 通过KeyPair生成器生成KeyPair KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); //生成公钥对象,获取公钥编码值 把对象转成字节数组,转成base64字符串 PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); byte[] publicKeyEncoded = publicKey.getEncoded(); String publicKeyBase64Str = Base64.encodeBase64String(publicKeyEncoded); //生成私钥对象,获取私钥编码值 把对象转成字节数组,转成base64字符串 PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate(); byte[] privateKeyEncoded = privateKey.getEncoded(); String privateKeyBase64Str = Base64.encodeBase64String(privateKeyEncoded); //分别吧公钥字符串和私钥字符串写入文件 FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File(URLDecoder.decode(publicKeyPath, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name())), publicKeyBase64Str,StandardCharsets.UTF_8); FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File(URLDecoder.decode(privateKeyPath, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name())), privateKeyBase64Str,StandardCharsets.UTF_8); } @Test public void testWriteKey2File() throws Exception { writeKey2File(); } @Test public void testRsa() throws Exception { String str = "小白一起学编程"; // 测试 公钥加密 --> 私钥解密 String encryptedStr = encrypt(str, getPublicKey()); System.out.println("公钥加密结果:" + encryptedStr); String decryptedStr = decrypt(encryptedStr, getPrivateKey()); System.out.println("私钥解密结果:" + decryptedStr); // 测试 私钥加密 --> 公钥解密 encryptedStr = encrypt(str, getPrivateKey()); System.out.println("私钥加密结果:" + encryptedStr); decryptedStr = decrypt(encryptedStr, getPublicKey()); System.out.println("公钥解密结果:" + decryptedStr); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
公钥加密结果:nnc5MyIAICAliEa8yyyo7z3h2aurGDXFvuDs0dXaSGvu1YeWNl/4s6p21UaW3nzwGu5GcaEXyh57J0TDSSrmO8V2Mlr2EMWXnvUQ0LhjK/eY89TwXfvGNS75Dx6BWizEPenIBMA4zQGXUJOJWMdIwKCu9MCnkzxPMUW2ZhXBElk=
私钥解密结果:小白一起学编程
私钥加密结果:Ds81AdB/fCP2ULDe70AKTq4zwmofmaWAy6riY98OSeGOkJxrszdclrddnf/fe371py5HZxL+8YC7CzBSidoWqjVkrjJFZ257vpmIq54p6zcmdvrRIDl1qHn7rrttMP3YR+jY9PAx87pG61Fm+jEkS5F+kiM9y6WzQ8fDt7f5nlQ=
公钥解密结果:小白一起学编程注意:秘钥需要先生成到文件中
数字签名
发送方A:
原始内容
① 摘要算法 ==》原始内容摘要 str
②摘要 str ==》A私钥加密 ==》 数字签名。
③发送给 B: 数字签名 + A的公钥
接收方B:
① A公钥解密 数字签名 ==》摘要 str
package com.zs.codeTest.asymmetric; import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.PrivateKey; import java.security.Signature; /** * 签名测试 * * @author zs * @date 2022-09-03 */ public class SignatureTest { // public static final String SIGNTURE_ALGORITHM = "mD5withRSA";//大小写无所谓 public static final String SIGNTURE_ALGORITHM = "sha256withrsa";//大小写无所谓 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String content = "今晚8点,行动!"; byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String sign = sign(contentBytes); System.out.println("签名:" + sign); boolean status = verify(contentBytes,sign); System.out.println("验证结果:\r" + status); } /** * 对信息使用私钥生成数字签名 * * @param data 原始数据 * @return {@link String} */ private static String sign(byte[] data) throws Exception { //获取私钥 PrivateKey privateKey = new RsaTest().getPrivateKey(); //用指定的算法初始化签名对象:进行摘要再进行加密 Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(SIGNTURE_ALGORITHM); signature.initSign(privateKey); signature.update(data); return Hex.encodeHexString(signature.sign()); } /** * 验证数字签名 * * @param data 原始数据 * @param sign 数字签名 * @return boolean */ private static boolean verify(byte[] data, String sign) throws Exception { Signature signature = Signature.getInstance(SIGNTURE_ALGORITHM); signature.initVerify(new RsaTest().getPublicKey()); signature.update(data); return signature.verify(Hex.decodeHex(sign)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
数字信封
对称加密的秘钥分发不安全 ==》 发送方用接收方的公钥 【加密秘钥】 ==》 接收方用私钥解开
注意: 分发秘钥的场景,秘钥会随着每个零件的数据一起发送给接收方
数字证书
Q: 有了数字签名就可以证明发送者的身份了,还有什么问题?
A:B这里存储的A的公钥被换成C的公钥,A发送的信息也换了C的私钥生成的签名。现在需要一种手段,
来证明 B 这里存储的A的公钥,就是A的公钥

涉及的一些概念:
-
ca
certificate authority, 使用pki(public key Infrastructure) 技术的机构,也可自己内部搭建,如使用ejbca.
-
ca 根证书
Q: B 除了存储A的数字证书对应的ca公钥,假设还有N个人给B发信息,难道B都要保存一份他们的数字证书的CA公钥吗?
A:不需要,CA认证中心可以给B一份“根证书”,里面存储的CA公钥可以验证所有CA分中心颁发的数字证书
public class NumberCertificateTest { @Test public void test() throws Exception { CertificateFactory cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509"); //证书是使用jdk自带的keytool工具生成的 String filePath = NumberCertificateTest.class.getClassLoader().getResource("certificate/tomcat.pem").getPath(); FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(filePath); //生成一个证书对象并使用从输入流中读取的数据对他进行初始化 Certificate c = cf.generateCertificate(in); PublicKey publicKey = c.getPublicKey(); //获取到了证书中的公钥 String key = Base64.encodeBase64String(publicKey.getEncoded()); System.out.println(key); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
-
相关阅读:
【unity】安卓环境配置(踩坑整理)
python爬虫requests.get乱码问题
如何通过Express和React处理SSE
Spring AOP如何基于AspectJ XML开发呢?
Java --- SpringMVC配置拦截器
#每日一题合集#牛客JZ54-JZ64
el-table中el-popover失效问题
Bug战场:C++篇
kubernetesr进阶之将容器组调度到指定的节点
『现学现忘』Docker基础 — 31、实现MySQL同步数据
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44235759/article/details/126684144
