-
Vuex详解(五种状态)
文章目录
备注:npm install vuex@next1 .状态管理
1 .1单状态管理


1 . 1 .1单状态管理的代码实现
<template> <h2>{{ counter }}</h2> <button @click="counter + 1">加</button> <button @click="counter - 1">减</button> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { counter: 0, }; }, }; </script> <style> </style>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

1 .2 Vuex的多状态管理
Vue已经帮我们做好了单个界面的状态管理,但是如果是多个界面呢?
- 多个试图都依赖同一个状态(一个状态改了,多个界面需要进行更新)
- 不同界面的Actions都想修改同一个状态(Home.vue需要修改,Profile.vue也需要修改这个状态)
也就是说对于某些状态(状态1/状态2/状态3)来说只属于我们某一个试图,但是也有一些状态(状态a/状态b/状态c)属于多个试图共同想要维护的
- 状态1/状态2/状态3你放在自己的房间中,你自己管理自己用,没问题。
- 但是状态a/状态b/状态c我们希望交给一个大管家来统一帮助我们管理!!!
- 没错,Vuex就是为我们提供这个大管家的工具。
全局单例模式(大管家)
- 我们现在要做的就是将共享的状态抽取出来,交给我们的大管家,统一进行管理。
- 之后,你们每个试图,按照我规定好的规定,进行访问和修改等操作。
- 这就是Vuex背后的基本思想。
图解

1.3 . Store
每一个Vuex应用的核心就是store(仓库):
- store本质上是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态(state);
Vuex和单纯的全局对象有什么区别呢?
- 第一:Vuex的状态存储是响应式的
- 当Vue组件从store中读取状态的时候,若store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会被更新;
- 第二:你不能直接改变store中的状态
改变store中的状态的唯一途径就显示提交(commit) mutation;
- 这样使得我们可以方便的跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够通过一些工具帮助我们更好的管理应用的状态;
使用步骤:
- 创建Store对象;
- 在app中通过插件安装;
创建Store对象=>Vue3import { createStore } from "vuex"; const stort = createStore({ state() { return { counter:0 } }, }); export default stort;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 进行挂载
import vuex from './stort/index'; createApp(App).use(vuex).mount('#app')- 1
- 2
App.vue=>委托给mutations进行处理<template> <div class="id"> <home /> <br> <h2>{{ $store.state.counter }}</h2> <button @click="addClick()">加一</button> <button @click="redClick()">减一</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { // 基本的状态管理实现 methods: { addClick() { // 进行委托给Mutations处理=>委托的是事件不是数据 this.$store.commit("addClick"); }, redClick() { this.$store.commit("redClick"); }, }, }; </script> <style> </style>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2. Vuex的核心概念(
Options API)2 .1 state的使用
概念:
- State是提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到`Store的State中进行存储。
- 如果状态信息是保存到多个Store对象中的,那么之后的管理和维护等都会变得特别困难,所以Vuex也使用了单一状态树(单一数据源Single
Source of Truth)来管理应用层级的全部状态。 - 单一状态树能够让我们最直接的方式找到某个状态的片段,而且在之后的维护和调试过程中,也可以非常方便的管理和维护。
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
State数据访问方式一 :
- 通过this.$store.state.全局数据名称访问
<h3>当前最新Count值为:{{this.$store.state.count}}</h3>- 1
State数据访问方式二 :
- 从vuex中按需导入mapState函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'- 1
- 通过刚才导入的mapState函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件的computed计算属性:
<template> <div> <h3>当前最新Count值为:{{ count }}</h3> <button>-1</button> </div> </template> <script> import { mapState } from "vuex"; export default { computed: { ...mapState(["count"]) //上面的映射等价于 // count(){ // return this.$store.state.user // } //对象写法 // ...mapState(["counte"]) ...mapState({ count: state => state.counte, }) } }; </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
2 .2 Mutation的使用
- 如果果想修改count的值,我们可以直接在组件中对this.$store.state.count进行操作即可
<template> <div> <h3>当前最新Count值为:{{this.$store.state.count}}</h3> <button @click="add">+1</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { methods: { add() { this.$store.state.count++; } } }; </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 测试发现,这可以实现需求,完成+1操作。
- 但是,这种方法在vuex中是严格禁止的
(检测不到数据的变化),那要怎么做呢?这时,就需要使用Mutation了。
利用Mutation用于变更存储在Store中的数据。
注意点:- 通过mutation变更Store数据,不可以直接操作Store中的数据
- 通过这种方式,虽然操作稍微繁琐一些,但可以集中监控所有数据的变化,直接操作Store数据是无法进行监控的
下图通过devtools工具监控
2 .2 .1 Mutation函数基本语法使用
在mutations中定义函数,如下:
mutations: { // 自增 add(state) { state.count++ } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 定义的函数会有一个默认参数state,这个就是存储在Store中的state对象。
2 .2 .1 .1方式一
- 在组件中,通过
this.$store.commit(方法名)完成触发,如下:
mutations: { // 自增 add(state) { state.count++ } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2 .2 .1 .2 方式二
- 在组件中导入mapMutations函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'- 1
- 通过导入的mapMutations函数,将需要的mutations函数映射为当前组件的methods方法:
methods: { ...mapMutations(["increment", "decrement"]), //对象写法 ...mapMutations({ add: "increment" }) },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2 .2 .2 Mutation传递参数
- 在通过mutation更新数据的时候,有时候需携带一些额外的参数,此处,参数被成为mutation的载荷
Payload。- 如果仅有一个参数时,那payload对应的就是这个参数值,

- 如果是多参数的话,那就会以对象的形式传递,此时的payload是一个对象,可以从对象中取出相关的数据。
- 在
mutations中定义函数时,同样可以接收参数,示例如下:
- 在
mutations: { // 自增 add(state) { state.count++ }, // 带参数 addNum(state, payload) { state.count += payload.number } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
App.vue组件调用methods: { add() { // this.$store.state.count++; this.$store.commit("add"); }, addNum() { this.$store.commit("addNum", { number: 10 }); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2 .2 .3Mutation常量类型
- 在mutation中, 我们定义了很多事件类型(也就是其中的方法名称),当项目越来越大时,Vuex管理的状态越来越多,需要更新状态的情况也越来越多,也就意味着Mutation中的方法越来越多。
- 当方法过多,使用者需要花费大量时间精力去记住这些方法,甚至多个文件间来回切换,查看方法名称,也存在拷贝或拼写错误的情况。
解决方案- 创建
mutation-types.js文件,在其中定义常量 - 定义常量时, 可以使用ES2015中的风格, 使用一个常量来作为函数的名称
- 使用处引入文件即可

在store/index.js中引入并使用:
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import * as types from './mutation-type' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0, user: { name: '旺财', age: 12 } }, mutations: { // 自增 [types.ADD_NUM](state) { state.count++ }, }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
在组件中,引入并调用:<script> import { ADD_NUM } from "../store/mutation-type"; export default { methods: { add() { this.$store.commit(ADD_NUM); // this.addAsync(); // this.$store.state.count++; // this.$store.commit("add"); } } }; </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2 .3 Action使用
- Action类似于Mutation,但是是用于处理异步任务的,比如网络请求等
- 如果通过异步操作变更数据,必须通过Action,而不能使用Mutation,但在Action中还是要通过触发Mutation的方式间接变更数据。
参数
context-
在actions中定义的方法,都会有默认值context
-
context是和store对象具有相同方法和属性的对象
-
可以通过context进行commit相关操作,可以获取context.state数据
2 .3 .1 Actons使用方式
注意点-
在 action 中,不能直接修改 state 中的数据
-
必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutation 才行
使用方式一 :- 在index.js中,添加actions及对应的方法:
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, //只有 mutations 中定义的函数,才有权力修改 state 中的数据 mutations: { // 自增 add(state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { addAsync(context) { setTimeout(() => { //在 action 中,不能直接修改 state 中的数据 //必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutation 才行 context.commit('add') }, 1000); } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 在组件中调用:
dispatch派发
<script> export default { methods: { addNumSync(){ // dispatch函数 专门用于触发 Action this.$store.dispatch('addAsync') } } }; </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2 .3 .1 .2 使用方式二
- 在组件中,导入mapActions函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'- 1
- 通过刚才导入的mapActions函数,将需要的actions函数映射为当前组件的methods方法:
<script> import { mapActions } from "vuex"; export default { methods: { ...mapActions(["addAsync"]), add() {Î this.addAsync() }, }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2 .3 .1 .2 使用方式三
- 在导入mapActions后,可以直接将指定方法绑定在@click事件上。
...mapActions(["addAsync"]), --------------------------- <button @click="addAsync">+1(异步)</button>- 1
- 2
- 3
2 .3 .2 Actions携带参数
- 在
index.js的actions中,增加携带参数方法,如下:
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { // 带参数 addNum(state, payload) { state.count += payload.number } }, actions: { addAsyncParams(context, payload) { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('addNum', payload) }, 1000); } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 在组件中,调用如下:
methods: { addNumSyncParams() { this.$store.dispatch("addAsyncParams", { number: 100 }); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2 .3 .3 Actions与Promise结合
Promise经常用于异步操作,在Action中,可以将异步操作放在Promise中,并且在成功或失败后,调用对应的resolve或reject。
- 在store/index.js中,为actions添加异步方法:
actions: { loadUserInfo(context){ return new Promise((resolve)=>{ setTimeout(() => { context.commit('add') resolve() }, 2000); }) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 在组件中调用,如下:
methods: { addPromise() { this.$store.dispatch("loadUserInfo").then(res => { console.log("done"); }); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2 .4 Getters的使用
Getters用于对Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据,类似于Vue中的计算属性Store中数据发生变化,Getters的数据也会跟随变化
2 .4 .1使用方式一
- 在index.js中定义getter
//定义 Getter const store = new Vuex.Store({ state:{ count: 0 }, getters:{ showNum(state){ return '当前Count值为:['+state.count']' } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 在组件中使用:
<h3>{{ this.$store.getters.showNum }}</h3>- 1
2 .4 .2 使用方式二
- 在组件中,导入mapGetters函数
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'- 1
- 通过刚才导入的mapGetters函数,将需要的getters函数映射为当前组件的computed方法:
computed: { ...mapGetters(["showNum"]) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 使用时,直接调用即可:
<h3>{{ showNum }}</h3>- 1
2 .5 Modules使用
- Vues使用单一状态树,意味着很多状态都会交给Vuex来管理
- 当应用变的非常复杂时,Store对象就可能变的相当臃肿
- 为解决这个问题,Vuex允许我们将store分割成模块(Module),并且每个模块拥有自己的State、Mutation、Actions、Getters等
基本使用- 在store目录下,新建文件夹modules,用于存放各个模块的modules文件,此处以moduleA为例。
- 在modules文件夹中,新建moduleA.js,内部各属性state、mutations等都和之前一致,注释详见代码,示例如下:
export default { state: { name: '凤凰于飞' }, actions: { aUpdateName(context) { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('updateName', '旺财') }, 1000); } }, mutations: { updateName(state, payload) { state.name = payload } }, getters: { fullName(state) { return state.name + '王昭君' }, fullName2(state, getters) { // 通过getters调用本组方法 return getters.fullName + ' 礼拜' }, fullName3(state, getters, rootState) { // state代表当前module数据状态,rootState代表根节点数据状态 return getters.fullName2 + rootState.counter } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
注意局部状态通过context.state暴露出来,根节点状态则为context.rootState- 在store/index.js中引用moduleA,如下:
import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" import moduleA from './modules/moduleA' Vue.use(Vuex) const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA } }) export default store- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 这样就通过分模块完成了对状态管理的模块化拆分。
2 .5 .1 访问模块中的数据
- 访问模块中的数据,要加上模块名
获取数据项: {{$store.state.模块名.数据项名}} 获取getters: {{$store.getters['模块名/getters名']}}- 1
- 2


-
访问模块中的mutations/actions:
- 如果
namespaced为true,则需要额外去补充模块名 - 如果
namespaced为false,则不需要额外补充模块名
$store.commit('mutations名') // namespaced为false $store.commit('模块名/mutations名') // namespaced为true- 1
- 2
- 如果
2 .5 .2 利用Modules对项目进行优化
注意如果项目非常复杂,除了分模块划分外,还可以将主模块的actions、mutations、getters等分别独立出去,拆分成单独的js文件,分别通过export导出,然后再index.js中导入使用。- 示例: 分别将主模块的actions、mutations、getters独立成js文件并导出,以actions.js为例,
export default{ aUpdateInfo(context, payload) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('updateInfo') resolve() }, 1000); }) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 在store/index.js中,引入并使用,如下:
import Vue from "vue" import Vuex from "vuex" import mutations from './mutations' import actions from './actions' import getters from './getters' import moduleA from './modules/moduleA' Vue.use(Vuex) const state = { counter: 1000, students: [ { id: 1, name: '旺财', age: 12 }, { id: 2, name: '小强', age: 31 }, { id: 3, name: '大明', age: 45 }, { id: 4, name: '狗蛋', age: 78 } ], info: { name: 'keko' } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, getters, actions, modules: { a: moduleA } }) export default store- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
模块项目图
##2. 6 辅助函数使用汇总如何使用全局state
-
直接使用: this.$store.state.xxx;
-
map辅助函数:
computed: { ...mapState(['xxx']), ...mapState({'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用modules中的state
-
直接使用: this.$store.state.模块名.xxx;
-
map辅助函数:
computed: { ...mapState('模块名', ['xxx']), ...mapState('模块名', {'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用全局getters
-
直接使用:
this.$store.getters.xxx -
map辅助函数:
computed: { ...mapGetters(['xxx']), ...mapGetters({'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用modules中的getters
-
直接使用:
this.$store.getters.模块名.xxx -
map辅助函数:
computed: { ...mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx']), ...mapGetters('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用全局mutations
-
直接使用:
this.$store.commit('mutation名', 参数) -
map辅助函数:
methods: { ...mapMutations(['mutation名']), ...mapMutations({'新名字': 'mutation名'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用modules中的mutations(namespaced:true)
-
直接使用:
this.$store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 参数) -
map辅助函数:
methods: { ...mapMutations('模块名', ['xxx']), ...mapMutations('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用全局actions
-
直接使用:
this.$store.dispatch('action名', 参数) -
map辅助函数:
methods: { ...mapActions(['actions名']), ...mapActions({'新名字': 'actions名'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如何使用modules中的actions(namespaced:true)
-
直接使用:
this.$store.dispatch('模块名/action名', 参数) -
map辅助函数:
methods: { ...mapActions('模块名', ['xxx']), ...mapActions('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'}) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3 .Vuex核心概念(
CPA)注意点setup没有this- 我们知道vue3的setup函数中是没有this的,就算传了context参数,打印出来也没有相关属性
- 但是我们可以直接从vuex 4.X中解构出
useStore方法,就可以在setup中使用vuex的相关函数了
基本使用参考代码<template> <div> <h2>{{ $store.state.count }}</h2> <button @click="plusCount">点击</button> </div> </template> <script> import { useStore } from "vuex"; export default { setup(props, context) { const store = useStore(); // 使用useStore方法 console.log(store); function plusCount() { store.commit("increaseCount"); } return { plusCount }; }, }; </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
3 .1. state的使用
导入函数
import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex' import { computed } from 'vue'- 1
- 2
基本使用setup() { const store = useStore() const sCounter = computed(() => store.state.counter) //必须return return { sCounter, } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
3 .1 .1封装函数的方式使用
创建
useStart.js封装函数import { computed } from 'vue' import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex' export function useState(mapper) { // 拿到store独享 const store = useStore(); // 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function} const storeStateFns = mapState(mapper); // 对数据进行转换 const storeState = {}; // 抽取key进行遍历 Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach((fnKey) => { // 把key给storeStateFns函数=>并绑定this const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({ $store: store }); // 函数给计算属性并赋值给storeState对象 storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn); }); return storeState; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 在组件中进行使用
import { useState } from '../hooks/useState' export default { setup() { const storeState = useState(["counter", "name", "age", "height"]) const storeState2 = useState({ sCounter: state => state.counter, sName: state => state.name }) return { ...storeState, ...storeState2 } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 展示方式
<h2>{{counter}}</h2> <h2>{{name}}</h2>- 1
- 2
3 .2 Getters的基本使用
- 某些属性我们可能需要变化后在使用,这个时候可以使用getters:
(相当于computed属性)


3 .2 .1 getters第二个参数与返回值
-
getters可以接收第二个参数:

-
getters中的函数本身,可以返回一个函数,那么在使用的地方相当于可以调用这个函数:

index.js中state与Getter代码
state() { return { counter: 100, name: "why", age: 18, height: 1.88, books: [ { name: "深入Vuejs", price: 200, count: 3 }, { name: "深入Webpack", price: 240, count: 5 }, { name: "深入React", price: 130, count: 1 }, { name: "深入Node", price: 220, count: 2 }, ], discount: 0.6, banners: [] }; }, getters: { totalPrice(state, getters) { let totalPrice = 0 for (const book of state.books) { totalPrice += book.count * book.price } return totalPrice * getters.currentDiscount }, currentDiscount(state) { return state.discount * 0.9 }, totalPriceCountGreaterN(state, getters) { return function(n) { let totalPrice = 0 for (const book of state.books) { if (book.count > n) { totalPrice += book.count * book.price } } return totalPrice * getters.currentDiscount } },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 组件代码
<h2>总价值: {{ $store.getters.totalPrice }}</h2> <h2>总价值: {{ $store.getters.totalPriceCountGreaterN(1) }}</h2>- 1
- 2
3 .2 .2 封装函数的方式使用
创建useGetters.jsimport { computed } from 'vue' import { mapGetters, useStore } from 'vuex' export function useGetters(mapper) { // 拿到store独享 const store = useStore() // 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function} const storeStateFns = mapGetters(mapper) // 对数据进行转换 const storeState = {} Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => { const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store}) storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn) }) return storeState }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 在组件中的使用
<template> <h2>{{ nameInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ ageInfo }}</h2> <h2>{{ heightInfo }}</h2> </template> import { useGetters } from '../hooks/useGetters' export default { computed: { }, setup() { const storeGetters = useGetters(["nameInfo", "ageInfo", "heightInfo"]) return { ...storeGetters } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3 .Mutation的使用
- 提交载荷(Payload)
- 对象风格的提交方式
- 使用常量替代 Mutation 事件类型
- Mutation 必须是同步函数
- 在组件中提交 Mutation
4 .Action的使用
4 .1Action的异步使用
- 在
index.js中为Actions添加异步方法
getHomeMultidata(context) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then(res => { context.commit("addBannerData", res.data.data.banner.list) resolve({name: "xiazhan", age: 18}) }).catch(err => { reject(err) }) }) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 在组件中使用
setup() { const store = useStore() onMounted(() => { const promise = store.dispatch("getHomeMultidata") promise.then(res => { console.log(res) }).catch(err => { console.log(err) }) }) }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
5 .Mudule的使用
- 由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象,当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿;
- 为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将store 分割成模块(module);
- 每个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块;


5 .1module的命名空间
- 默认情况下,模块内部的action和mutation仍然是注册在全局的命名空间中的:
- 这样使得多个模块能够对同一个action 或mutation 作出响应;
- Getter 同样也默认注册在全局命名空间;
- 如果我们希望模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,可以添加
namespaced: true的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块: - 当模块被注册后,它的所有getter、action 及mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名;
在模块module文件夹中创建
home.jsconst homeModule = { // 指定命名空间 =>局部 namespaced: true, state() { return { homeCounter: 100 } }, getters: { doubleHomeCounter(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) { return state.homeCounter * 2 }, otherGetter(state) { return 100 } }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.homeCounter++ } }, actions: { incrementAction({commit, dispatch, state, rootState, getters, rootGetters}) { commit("increment") commit("increment", null, {root: true}) } } } export default homeModule- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
在入口文件
index.js导入home.jsimport { createStore } from "vuex" import home from './modules/home' import user from './modules/user' const store = createStore({ state() { return { rootCounter: 100 } }, getters: { doubleRootCounter(state) { return state.rootCounter * 2 } }, mutations: { increment(state) { state.rootCounter++ } }, modules: { home, user } }); export default store;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
在组件中访问
home.js'中的counte和action的数据<template> <div> //[查找规则] <h2>{{ $store.getters["home/doubleHomeCounter"] }}</h2> <button @click="homeIncrement">home+1</button> <button @click="homeIncrementAction">home+1</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { methods: { homeIncrement() { this.$store.commit("home/increment") }, homeIncrementAction() { this.$store.dispatch("home/incrementAction") } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
5 .2module修改或派发根组件
- 如果要在action中修改root中的state,可以使用:

参考代码actions: { incrementAction({commit, dispatch, state, rootState, getters, rootGetters}) { commit("increment") commit("increment", null, {root: true}) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
5 .3module的辅助函数
- 方式一:通过完整的模块空间名称来查找;

-方式二: 第一个参数传入模块空间名称,后面写上要使用的属性;

- 方式三:通过createNamespacedHelpers 生成一个模块的辅助函数;

在setup中的使用
setup() { // {homeCounter: function} const state = useState(["rootCounter"]) const rootGetters = useGetters(["doubleRootCounter"]) const getters = useGetters("home", ["doubleHomeCounter"]) const mutations = mapMutations(["increment"]) const actions = mapActions(["incrementAction"]) return { ...state, ...getters, ...rootGetters, ...mutations, ...actions } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
4 .面试题型
4 .1项目结构
Vuex 并不限制你的代码结构。但是,它规定了一些需要遵守的规则:
- 应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中。
- 提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的。
- 异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面。
只要你遵守以上规则,如何组织代码随你便。如果你的 store 文件太大,只需将 action、mutation 和 getter 分割到单独的文件。
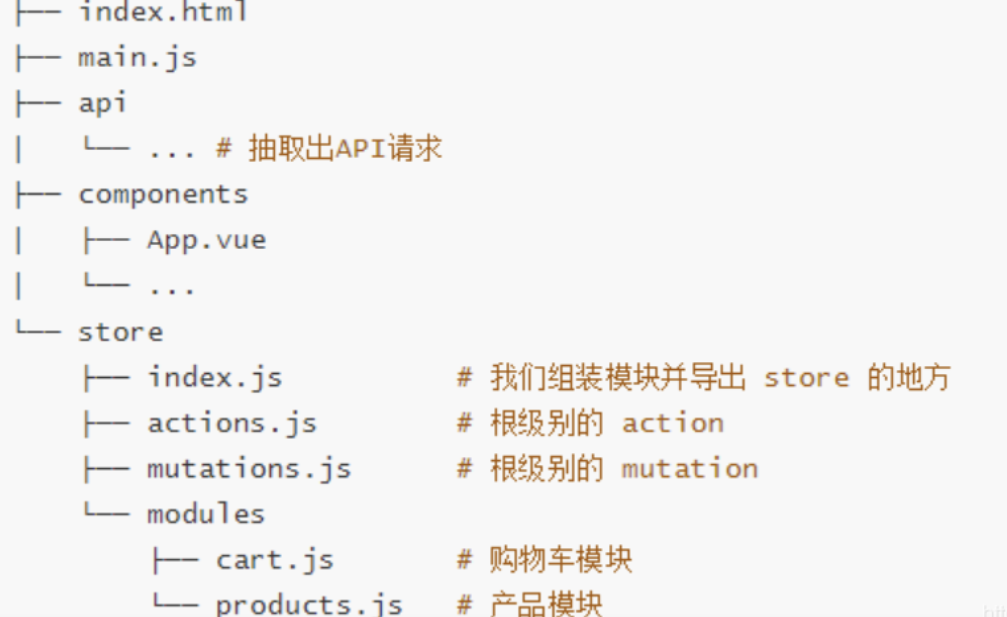
对于大型应用,我们会希望把 Vuex 相关代码分割到模块中。下面是项目结构示例:

4 .2 vuex的五个核心
一、Vuex的五个核心概念:state、getters、mutations、actions、modules
1、state: vuex的基本数据,用来存储变量;
2、getters: 从基本数据(state)派生的数据,相当于state的计算属性;
3、mutations: 提交更新数据的方法,必须是同步的(如果需要异步使用action)。每个mution 都有一个字符串的事件类型(type)和一个回调函数(handler)。
回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state作为第一个参数,提交载荷作为第二个参数。
4、action: 和mution的功能大致相同,不同之处在于①Action提交的是mution,而不是直接变更状态,②Action可以包含任意异步操作。
5、modules: 模块化vuex,可以让每一个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、 getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理。图解

参考: vue中使用vuex(超详细)
vuex基础解析
vuex官网 -
相关阅读:
微服务架构的未来:跨边界的云原生整合
前端面试宝典React篇05 如何设计 React 组件?
模仿快猫猫App实现的微信小程序,前端页面基本完成
深入探索pdfplumber:从PDF中提取信息到实际项目应用【第94篇—pdfplumbe】
吴恩达深度学习笔记——神经网络与深度学习(Neural Networks and Deep Learning)
《WebGIS快速开发教程第四版》重磅更新
在任意位置插入
uni-app--》基于小程序开发的电商平台项目实战(四)
Js判断数据类型的4种⽅式
运放-运算放大器经典应用电路大全-应用电路大全-20种经典电路
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46104934/article/details/126671922
