-
【高阶数据结构】并查集的实现(含压缩路径)及其应用-C++版本
并查集原理
并查集,在一些有N个元素的集合应用问题中,我们通常是在开始时让每个元素构成一个单元素的集合,然后按一定顺序将属于同一组的元素所在的集合合并,其间要反复查找一个元素在哪个集合中
并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合的合并及查询问题。常常在使用中以森林来表示
适合于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-findset)
小例子-编号和人
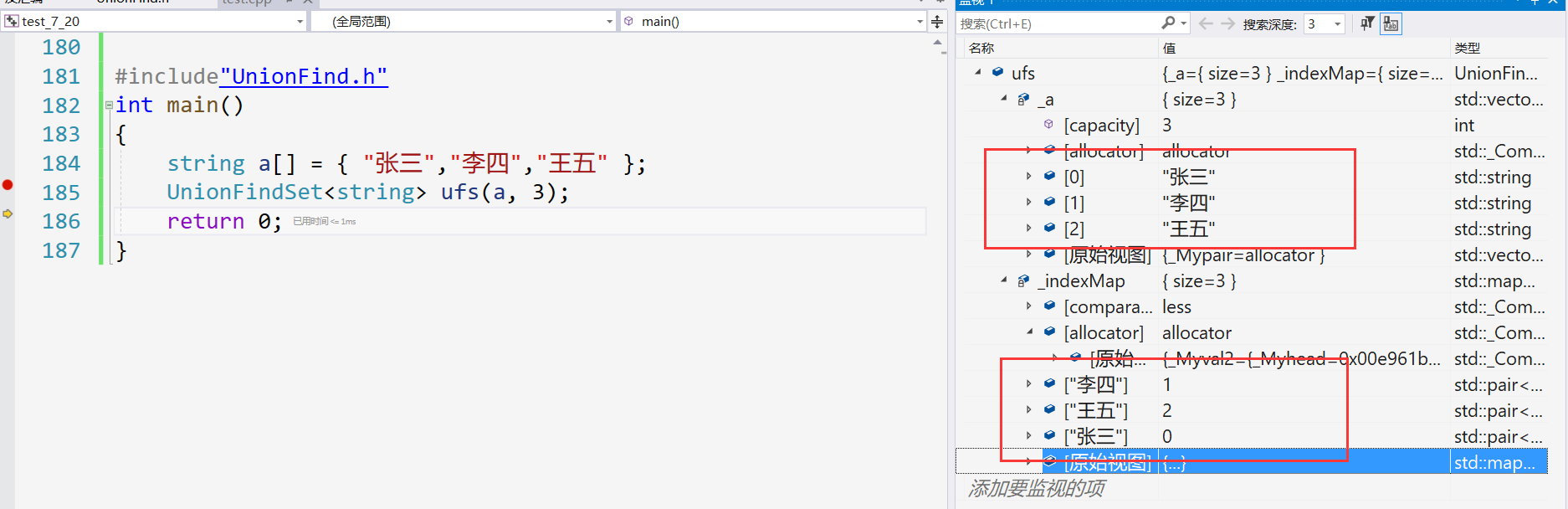
如果我们想让编号和人构成关系, 即可以通过编号找到对应的人,也可以通过人找到对应的编号怎么做?
template<class T> class UnionFindSet { public: UnionFindSet(const T* a, size_t n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { _a.push_back(a[i]); _indexMap[a[i]] = i; } } private: vector<T> _a; //编号找人 下标对应的就是人名 map<T, int> _indexMap;//人找编号 key:人名 value:编号 }; #include"UnionFind.h" int main() { string a[] = { "张三","李四","王五" }; UnionFindSet<string> ufs(a, 3); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
并查集的实现
#include#include class UnionFindSet { public: UnionFindSet(size_t n); size_t FindRoot(int x); void Union(int x1, int x2); bool Inset(int x1,int x2); size_t SetCount(); private: std::vector<int> _set; }; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
首先我们要知道如下规则:
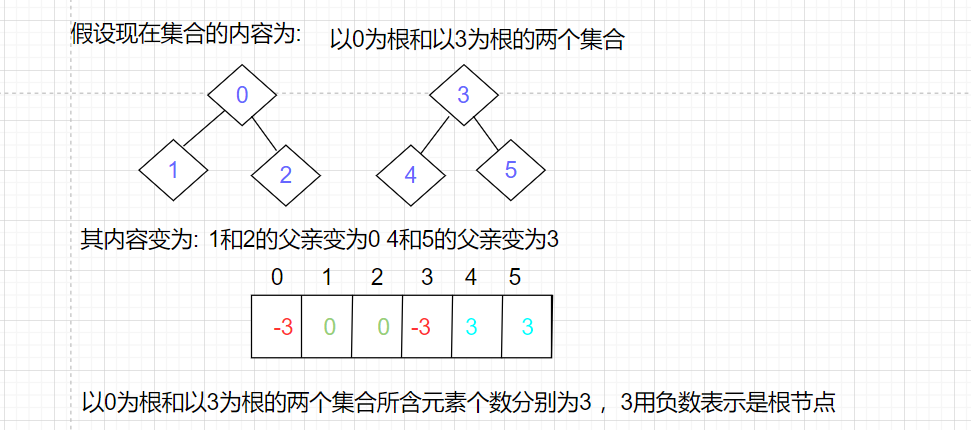
- 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号
- 数组中的值如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数
- 数组中的值如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标
例如:
基本结构
class UnionFindSet { private: std::vector<int> _set; };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
构造函数
最初每个元素各自构成一个集合, 初始状态就是-1,表示size个集合

UnionFindSet(int size) :_set(size, -1)//size个元素都最初初始化为-1 {}- 1
- 2
- 3
查找根节点
返回根节点所在下标
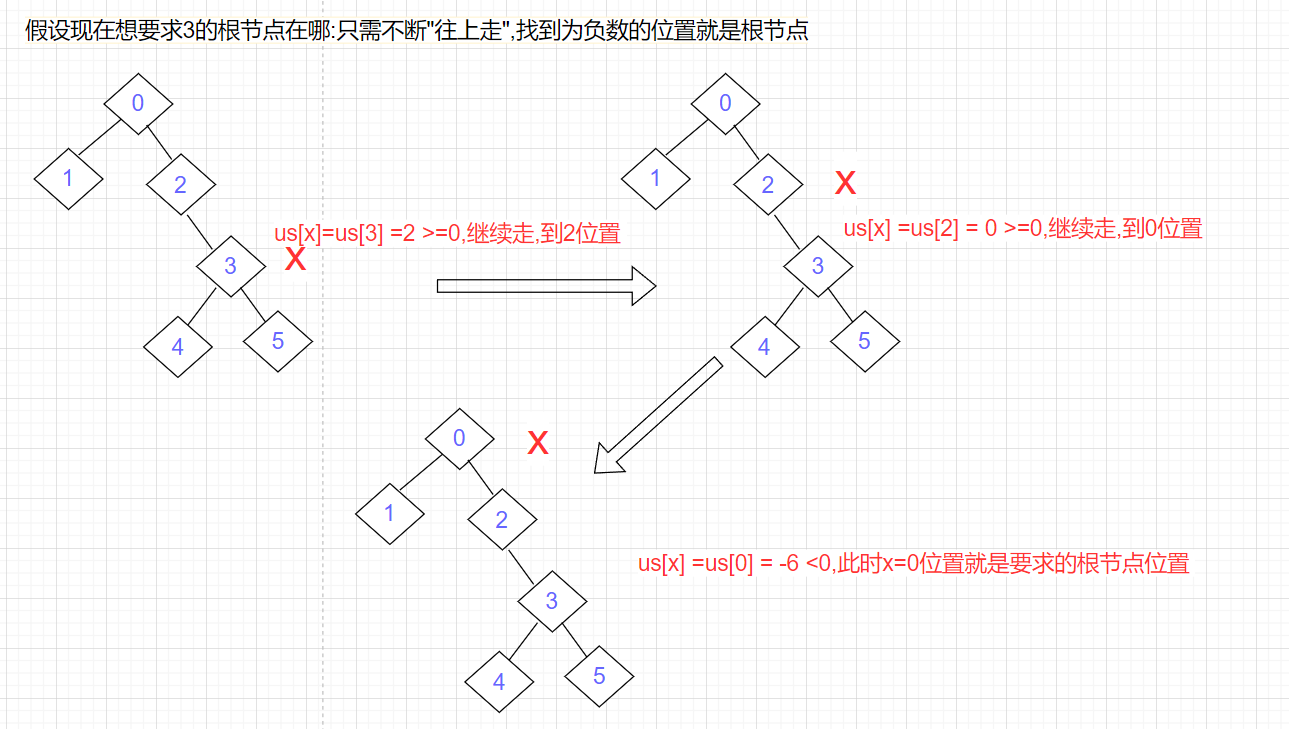
//如果_set[x]是负数,那么x就是某个集合的根 //如果_set[x]不是负数,那么x的父亲节点就是_set[x]值对应的位置 size_t FindRoot(int x) { while (_set[x] >= 0) { x = _set[x]; } //来到这,_set[x] <0, 此时x就是根节点 return x; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
路径压缩技巧
路径压缩实际上是在数据量太大的时候,访问一些数据可能在位于叶子位置,导致访问的效率不高
本质上我们查找的代表节点的时候,可以对该路径上的节点进行路径压缩
注意:最好不要用递归的时候进行路径压缩,因为路径深可能导致栈溢出
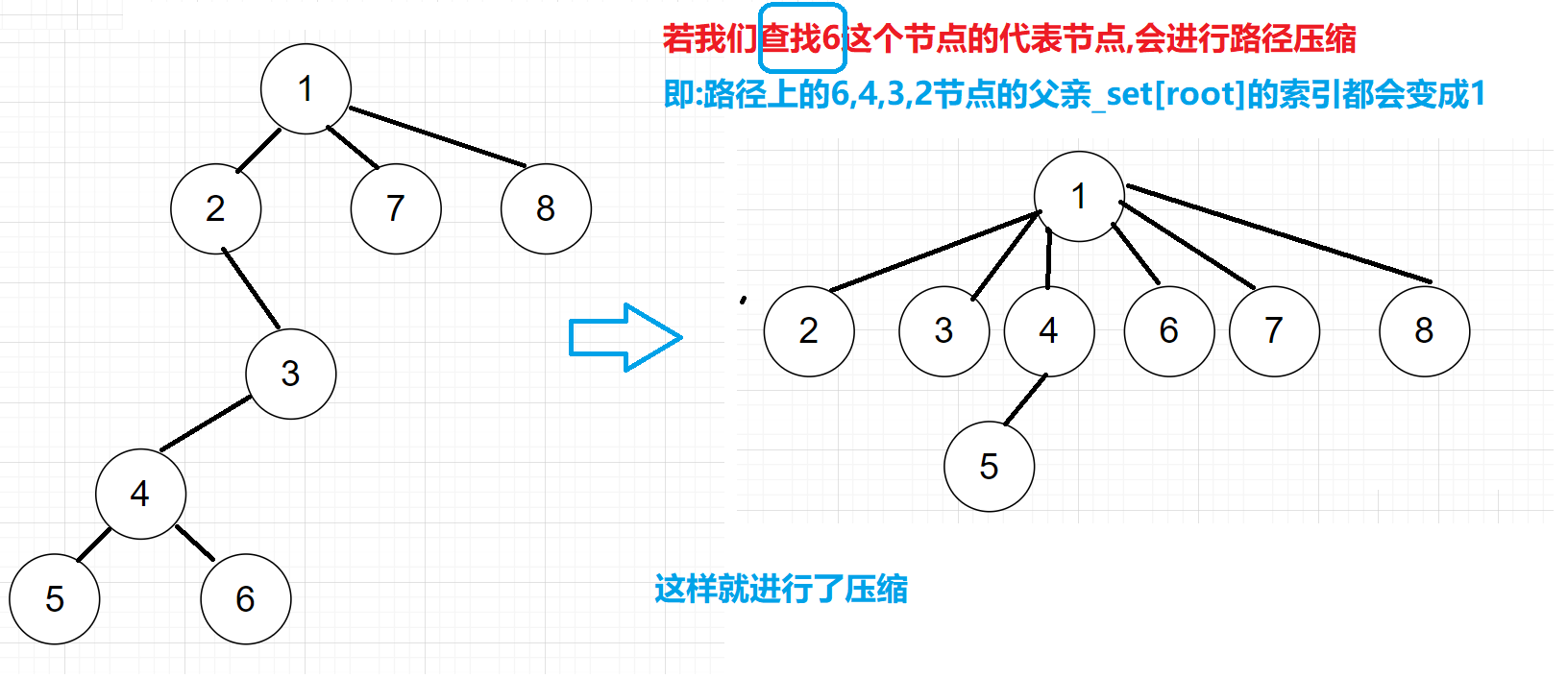
做法:
1)先找到当前路径节点的代表节点
2)然后从当前位置_set[x]开始的节点,沿途的节点的父亲位置都改为代表节点的位置
只需要根据下标关系往上迭代即可x节点的父亲位置就是_set[x]位置
注意:要提前保存x节点的父亲节点位置,因为更改当前位置的父亲节点, 会丢失以前的父亲节点
size_t FindRoot(int x) { int root = x; while (_set[root] >= 0) { root = _set[root]; } //此时root就是x这条路径的头节点(代表节点) //把沿途的节点的父亲都改为root while (_set[x] >= 0) { int parent = _set[x];//先保存x节点的父节点位置 _set[x] = root;//将x节点的父亲位置改为root位置 x = parent;//往上迭代 } return root; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
合并集合
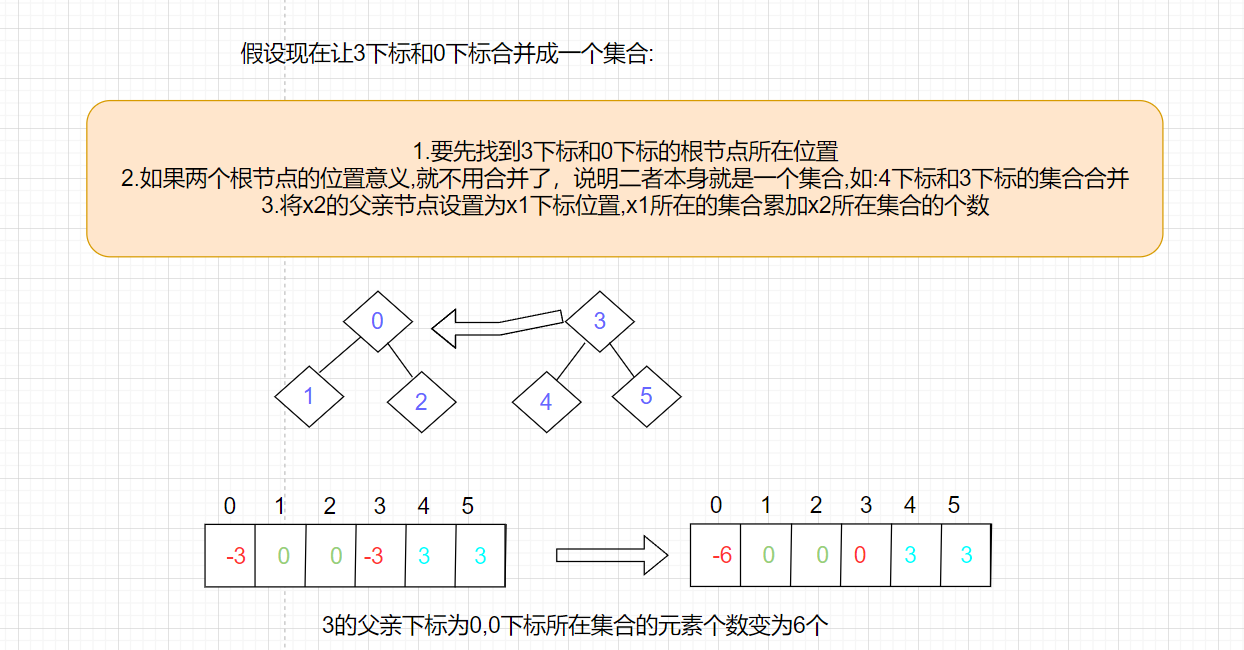
这里选择合并到x2所在的集合合并到x1所在的集合
void Union(int x1, int x2) { //找到x1和x2的代表节点(根节点) size_t root1 = FindRoot(x1); size_t root2 = FindRoot(x2); //两个节点不在一个集合才合并 //把root2合并到root1所在集合 if (root1 != root2) { _set[root1] += _set[root2];//root2所在集合的元素累加到root1所在集合 _set[root2] = root1; //root2的父亲变为root1 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
如果我们希望是小集合合并到大集合呢? 即元素少的集合合并到元素多的集合
路径压缩技巧
两颗树合并的时候,节点少的数往节点多的树合并
目的:为了使节点层数增多的节点相对减少
做法:
1)判断哪颗树的节点更多, 让root1变为是较大的集合, root2往root1合并
如何判断呢? 因为root1和root2是根,_set[root]的值是负数,代表该集合的元素个数, _set[root]值越大,集合元素个数越少
//x1和x2合并 ->本质是代表节点(根节点)合并 void Union(int x1, int x2) { //找到x1和x2的代表节点(根节点) size_t root1 = FindRoot(x1); size_t root2 = FindRoot(x2); //我们让root1的集合是大集合,小集合合并到大集合中 //因为root1和root2是根,所以_set[root]的值为负数,代表集合的元素个数,值越小,元素越多 if (_set[root1] > _set[root2]) //说明root2集合元素多 { ::swap(root1, root2); } //两个节点不在一个集合才合并 if (root1 != root2) { _set[root1] += _set[root2];//root2所在集合的元素累加到root1所在集合 _set[root2] = root1; //root2的父亲变为root1 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
求集合个数
遍历_set,查看有多少元素是负数,就代表有多少个根节点, 即有多少个集合
size_t SetCount() { size_t count = 0; for (auto e : _set) { if (e < 0) count++; } return count; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
判断两个元素是否在同一个集合
只需要判断两个元素的代表节点的位置是否相同即可
bool Inset(int x1,int x2) { return FindRoot(x1) == FindRoot(x2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
并查集的应用
省份数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-provinces/
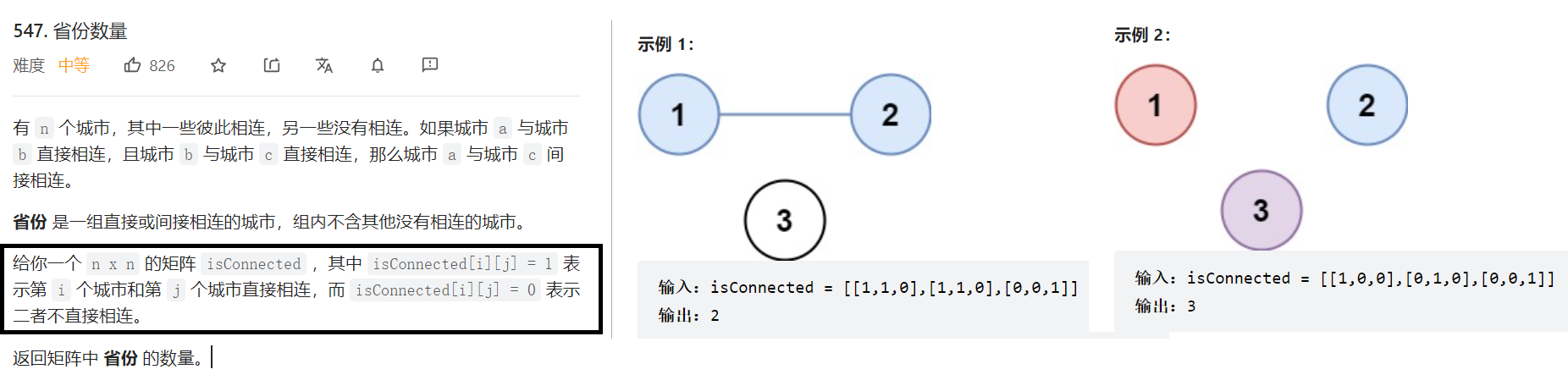
做法:遍历矩阵, 因为n[i][j] =1 表示第i城市和第j个城市相连 -> 所以我们可以把i和j合并到一个集合里面
遍历完成后,返回集合个数
class Solution { public: class UnionSet { public: UnionSet(size_t n = 0) { //最初自己就是一个集合 us.resize(n, -1);//开辟n个空间,初始化为-1 } //查找x对应的根节点下标 int FindRoot(int x) { //下标对应的值为负数的就是根节点 //要保证x下标的合法性 assert(x < us.size()); while (us[x] >= 0) { x = us[x]; } //退出循环时:us[x]<0,此时x下标就是对应的根节点 return x; } //求集合个数->看us中有多少个元素是<0的 int GetSize() { int count = 0; for (auto& x : us) { if (x < 0) count++; } return count; } //小集合合并到大集合 void Union(int x1, int x2) { //要保证x1和x2下标的合法性 assert(x1 < us.size()); assert(x2 < us.size()); //先找到二者对应的根节点所在下标 int root1 = FindRoot(x1); int root2 = FindRoot(x2); //让root1是大集合的根 //因为负数是表示元素个数,us[root1]>us[root2] 表示root2的集合元素个数比root1多 if(us[root1]<us[root2]) { swap(root1,root2); } //如果root1 == root2,说明x1和x2就是在一个集合中,不需要合并 if (root1 != root2) { //将root2所在集合的个数累加到root1中 //root2的父亲的下标变为root1 us[root1] += us[root2]; us[root2] = root1; } } private: vector<int> us; }; int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) { //相连的省份他们都在一个集合里,所以只需要用并查集统计一共有几个集合即可 int n = isConnected.size(); //初始化每一个集合! {0},{1},..... UnionSet us(n); //因为上下对称只需要考察上三角形即可 for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) { for(int j = i+1;j<n;j++) { //当前位置为1,就把j和i位置合并 if(isConnected[i][j] == 1) { us.Union(i,j); } } } //最后返回并查集中有多少个元素 return us.GetSize(); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
当然,我们不必把整个并查集实现出来, 可以采取下面的方式做: 手动控制并查集
class Solution { public: int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) { vector<int> ufs(isConnected.size(),-1);//每个元素各为一个集合,初始化为-1 //查找根节点 auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x) //Lamber表达式 { while(ufs[x]>=0) x = ufs[x]; return x; }; //遍历矩阵 for(size_t i = 0;i<isConnected.size();i++) { for(size_t j = 0;j<isConnected[i].size();j++) { if(isConnected[i][j] == 1) { //合并集合 int root1 = findRoot(i); int root2 = findRoot(j); if(root1 != root2) //合并到root1上 { ufs[root1] += ufs[root2]; ufs[root2] = root1; } } } } //统计集合个数 int count = 0; for(auto e:ufs) { if(e<0) count++; } return count; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
等式方程的可满足性
https://leetcode.cn/problems/satisfiability-of-equality-equations/
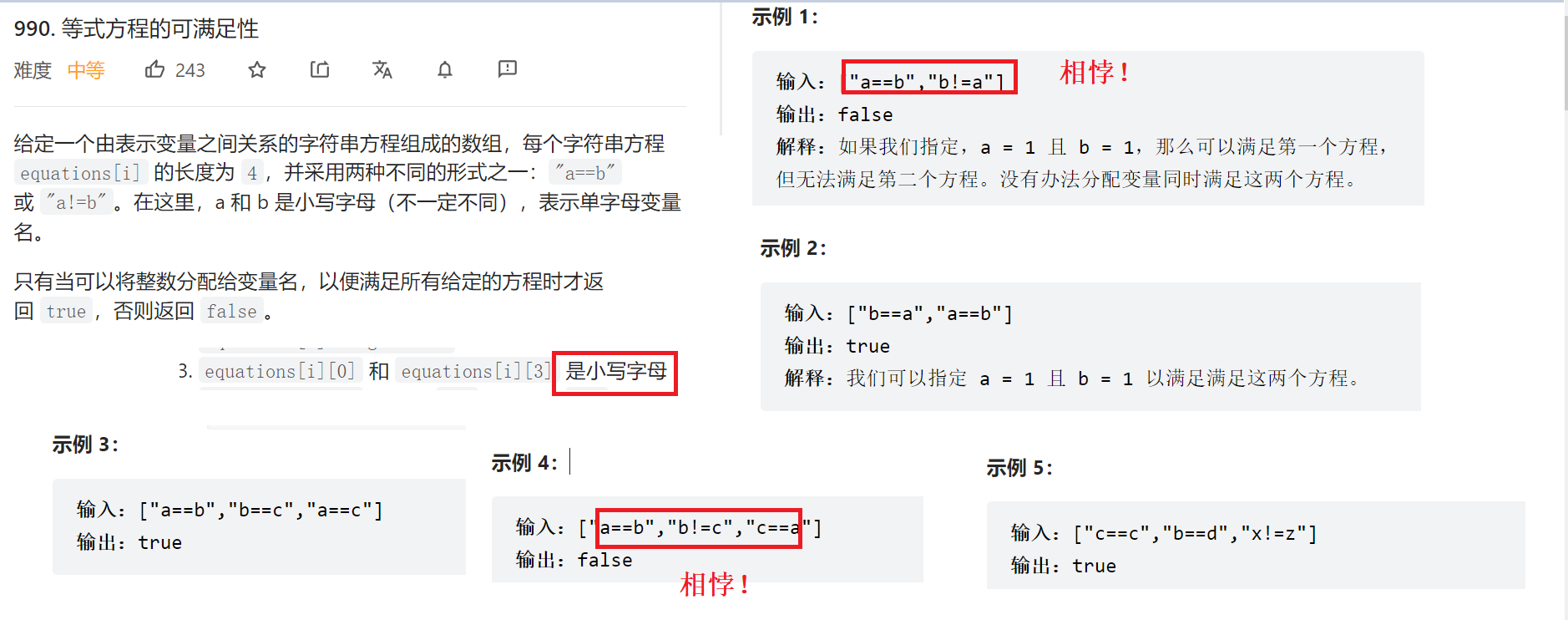
函数参数是:
vector每一个元素是一条长度为4的方程& equations 
怎么做呢? 可以根据str[1]的字符判断这条方程是!= 还是 ==
-
相等的值放到一个集合中, 例如: a ==b b == c,那么a,b,c就在一个集合中!
-
不相等的值不能在一个集合中, 所以当我们遍历到 '!'字符时.判断左右两个字符是否在一个集合,如果在,就是相悖的,返回false!
方法:先遍历一遍字符串,把相等的值放到一个集合,然后再遍历一遍集合,看不相等的值是否在一个集合,如果在,就是相悖的,返回false 因为只有小写字母.所以可以只开辟26个空间进行映射!
等式左侧的字符str[0]映射为:
str[0] - 'a'等式右侧的字符str[3]映射为:str[3] - 'a'
class Solution { public: class UnionSet { public: UnionSet(size_t n = 0) { //最初自己就是一个集合 us.resize(n, -1);//开辟n个空间,初始化为-1 } //查找x对应的根节点下标 int FindRoot(int x) { //下标对应的值为负数的就是根节点 //要保证x下标的合法性 assert(x < us.size()); while (us[x] >= 0) { x = us[x]; } //退出循环时:us[x]<0,此时x下标就是对应的根节点 return x; } //求集合个数->看us中有多少个元素是<0的 int GetSize() { int count = 0; for (auto& x : us) { if (x < 0) count++; } return count; } //将x2合并到x1 void Union(int x1, int x2) { //要保证x1和x2下标的合法性 assert(x1 < us.size()); assert(x2 < us.size()); //先找到二者对应的根节点所在下标 int root1 = FindRoot(x1); int root2 = FindRoot(x2); //如果root1 == root2,说明x1和x2就是在一个集合中,不需要合并 if (root1 != root2) { //将root2所在集合的个数累加到root1中 //root2的父亲的下标变为root1 us[root1] += us[root2]; us[root2] = root1; } } private: vector<int> us; }; //如果两个字符相等,则放入同一个集合之中 //如果两个字符不相等,它们应当在不同的集合中,此时查找它们所在集合的根 //如果相同则说明这两个字符在同一个集合中,返回false。 bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations) { UnionSet us(26);//只有小写字母->开26个空间足矣 //第一遍先把相等的值合并到一个集合 for(auto& str:equations) { if(str[1]=='=') { us.Union(str[0]-'a',str[3]-'a'); } } //第二遍把不相等的值判断在不在一个集合,如果在就逻辑相悖,返回false for(auto& str:equations) { if(str[1]=='!') { if(us.FindRoot(str[0]-'a')==us.FindRoot(str[3]-'a')) { return false; } } } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
当然,我们不必把整个并查集实现出来, 可以采取下面的方式做: 手动控制并查集
class Solution { public: bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations) { vector<int> ufs(26,-1);//只需要开26个空间映射 auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x) { while(ufs[x]>=0) x = ufs[x]; return x; }; //第一遍遍历,把相同的值合并到一个集合 for(auto& str:equations) { if(str[1] == '=') { //合并两个集合 int root1 = findRoot(str[0] -'a');//左字符的映射:str[0] -'a' int root2 = findRoot(str[3] -'a');//右字符的映射:str[3] -'a' if(root1 != root2) { ufs[root1] += ufs[root2]; ufs[root2] = root1; } } } //第二遍遍历,判断不相等的是否在一个集合,如果在,就是相悖,返回false for(auto& str:equations) { if(str[1] == '!') { //合并两个集合 int root1 = findRoot(str[0] -'a');//左字符的映射:str[0] -'a' int root2 = findRoot(str[3] -'a');//右字符的映射:str[3] -'a' if(root1 == root2) //二者在一个集合中,相悖 { return false; } } } return true;//所有等式符合要求 } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
-
相关阅读:
Excel 使用 ctrl + E 快捷键进行数据提取、合并、添加前后缀等操作
Debian安装redis
ElasticSearch索引刷新周期(refresh_interval)
实操教学|如何用Serveless3分钟做好邀请函?
低代码之光!轻量级 GUI 的设计与实现
华为通过FTP 进行文件操作示例
JAVASE语法零基础——static成员和代码块
代码随想录 Day 48| 198. 打家劫舍 |
(后续补充)vue+express、gitee pm2部署轻量服务器
docker0: iptables: No chain/target/match by that name
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/chuxinchangcun/article/details/126681915
