-
计算机组成与设计-第五章 memory hierarchy(一)
5.1 Introduction
存储器访问是计算机中最常见的动作。我们希望有无限大的存储空间,并且访问速度很快,但这两者是矛盾的。通常来说,存储器越小,离CPU越近,访问速度会快;存储器越大,离 CPU越远,访问速度越慢。
Memory access有两个局部性(principle of locality):这里直接复制书中的内容
Temporal locality (locality in time): if an item is referenced, it will tend to be referenced again soon.
Spatial locality (locality in space): if an item is referenced, items whose
addresses are close by will tend to be referenced soon
时间局部性通常体现在循环中。
空间局部性的例子有顺序执行的程序,数组等块存储结构。
Cache既利用了空间局部性,也利用了时间局部性。空间局部性是cache中的每一个cache line包含一段地址相邻的数据;时间局部性,缓存在cache中的数据,下次被访问的时候,直接从cache中取。
根据局部性原则,引入了memory hierarchy,如下图
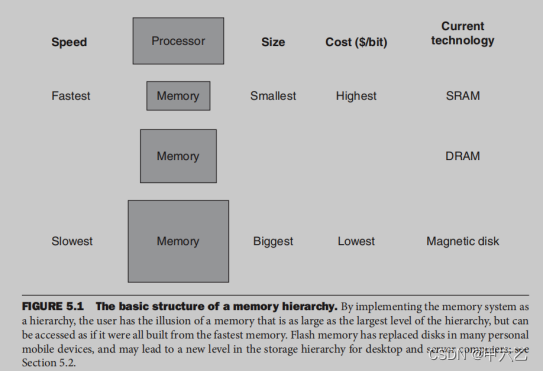
顶层的memory:容量小;速度快;价格贵;存储密度低
底层的memory:容量大;速度慢;价格低;存储密度高
顶层memory中的内容一定包含在底层memory中;通常数据的交换只会发生在相邻的两层memory之间。
hit rate The fraction of memory accesses found in a level of the memory hierarchy.
miss rate The fraction of memory accesses not found in a level of the memory hierarchy.
hit time The time required to access a level of the memory hierarchy, including the time needed to determine whether the access is a hit or a miss.
miss penalty The time required to fetch a block into a level of the memory hierarchy from the lower level, including the time to access the block, transmit it from one level to the other, insert it in the level that experienced
the miss, and then pass the block to the requestor.

5.2 memory technology
SRAM (static random access memory)
每bit由6-8个晶体管组成;读操作不会影响数据,不需要刷新;访问速度快;只要不掉电,数据就不会丢失。
DRAM(dynamic random access memory)
- the value kept in a cell is stored as a charge in a capacitor.
- A single transistor is then used to access this stored charge。 So one transistor per
bit of storage
- must periodically be refreshed
refresh方式:读出来,再写进去。
数据保持时间是几个ms,所以要每隔几个ms要做一次refresh。DDR颗粒可以是每个bank refresh,也可以所有bank一起refresh。
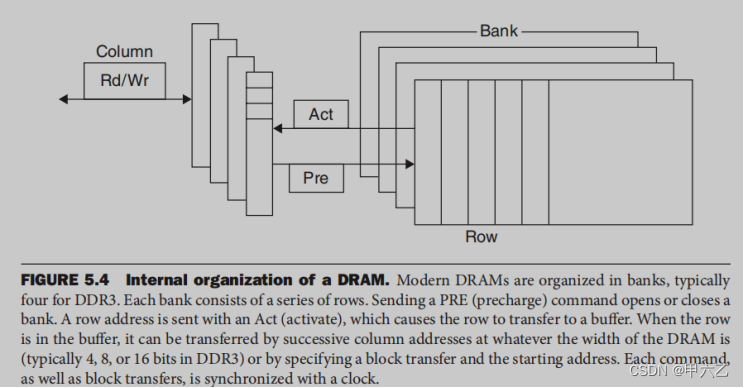
DDR SDRAM。
每个bank都有一个buffer。
Address interleaving:向多个bank发出地址,同时访问多个bank,带宽倍增。
参考:
1. 计算机组成与设计 第五版 ARM版
-
相关阅读:
Gson反序列化List<T>数据返回问题解决方案
Docker Compose
常用的linux命令简要说明以及命令全名理解
JAVA多线程和JUC
AI智慧安防智能监控平台EasyCVR隔天设备录像播放失败是什么原因?该如何解决?
php魔术方法和反序列化漏洞
谈谈 Kubernetes Operator
不妨试试更快更小更灵活Java开发框架Solon
面试突击81:什么是跨域问题?如何解决?
shopee马来西亚和菲律宾站哪个好做?做shopee跨境如何选择站点?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_38037810/article/details/126638169