-
基于共词分析的中国近代史实体关系图构建(毕业设计:数据处理)
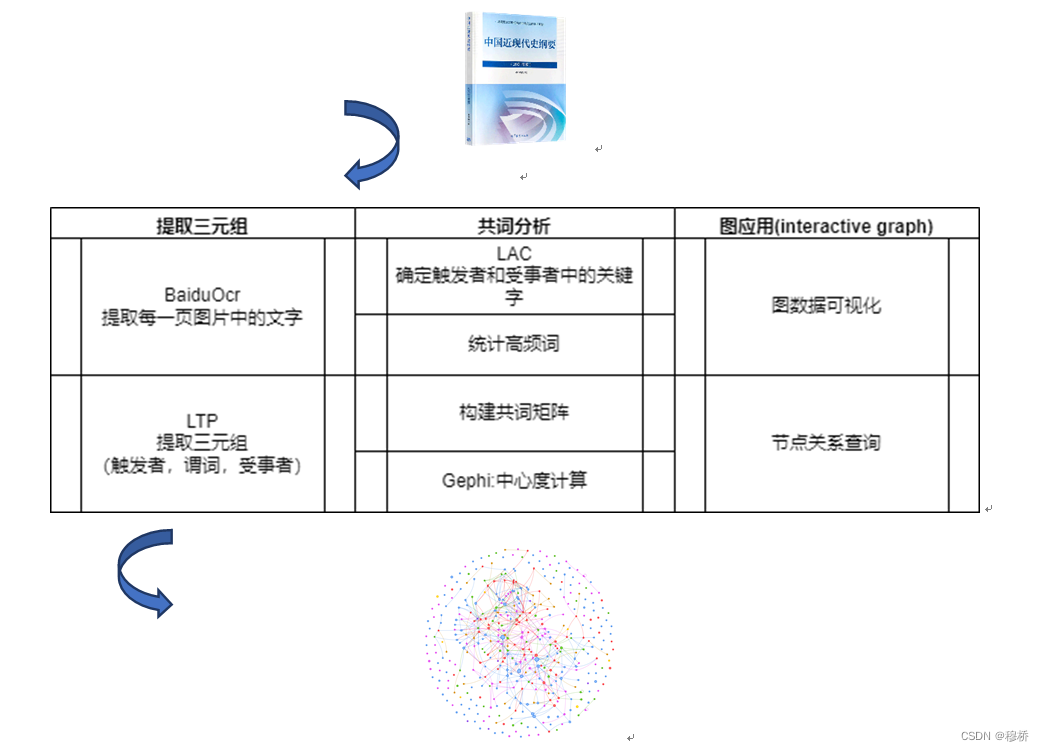
研究方法
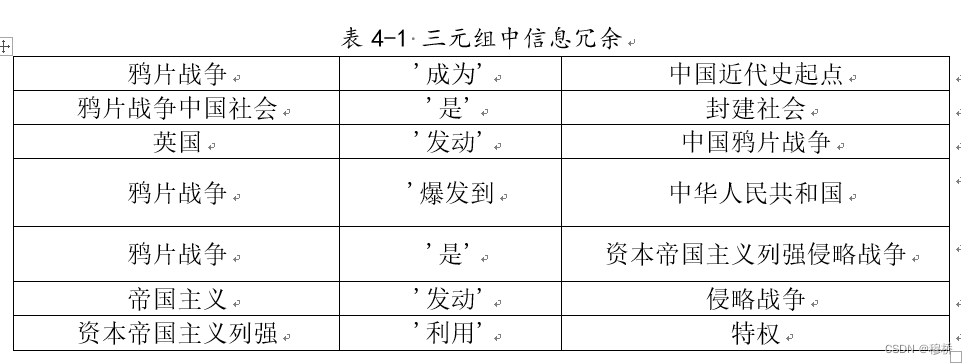
为了体现一些历史人物、地点、事件的关联,需要抽取文本中的重要三元组信息。三元组信息有两种表达形式:实体-关系-实体或实体-属性-性值。对应着两种实体联系。前者称它为实体关系,如李大钊参与五四革命。后者称它实体属性,如林徽因的父亲林长民。对于实体属性值,本文提取了百度词条半结构化数据中的标记链接,不仅抽取实体同时获取了实体与值的属性关系。由谓词连接的实体-关系-实体这类关系使用的则是LTP工具。LTP可以从非结构化文本中直接提取出三元组关系,但它的抽取结果粗糙不能用于构建需要表达精确的历史信息。如下图
研究难点
直接使用LTP抽取三元组主要有两个问题待解决:实体消歧以及共指消解。结合表来说:(鸦片战争中国社会,是,封建社会),中国社会和封建社会是相关概念,(英国,发动,中国鸦片战争)与(鸦片战争,爆发到,中华人民共和国)中信息重复,(鸦片战争,是,资本帝国主义列强侵略战争)更简洁的表达为(鸦片战争,是,侵略战争),(帝国主义,发动,侵略战争),(帝国主义,是,资本主义)。(这有点像数据库里的最优范式了)。
研究方法
为了解决以上问题,本文在使用LTP工具完成粗略的事件抽取后,使用共词分析来确定更重要的三元组,用LAC命名实体识别工具,优化三元组中实体抽取的结果。
工作
OCR从教材图片中提取文字
在网上找了个遍都没有找到中国近代史的完整文本、毕竟还是有版权的,还是自己动手用ocr提取吧
python 提取视频字幕
注意用ocr之前一定要压缩图片#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Jun 12 09:37:38 2018 利用百度api实现图片文本识别 @author: XnCSD """ import glob from os import path import os from aip import AipOcr from PIL import Image def convertimg(picfile, outdir): '''调整图片大小,对于过大的图片进行压缩 picfile: 图片路径 outdir: 图片输出路径 ''' img = Image.open(picfile) width, height = img.size while(width*height > 4000000): # 该数值压缩后的图片大约 两百多k width = width // 2 height = height // 2 new_img=img.resize((width, height),Image.BILINEAR) new_img.save(path.join(outdir,os.path.basename(picfile))) def baiduOCR(picfile, outfile): """利用百度api识别文本,并保存提取的文字 picfile: 图片文件名 outfile: 输出文件 """ filename = path.basename(picfile) APP_ID = '******' # 刚才获取的 ID,下同 API_KEY = '******' SECRECT_KEY = '******' client = AipOcr(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRECT_KEY) i = open(picfile, 'rb') img = i.read() print("正在识别图片:\t" + filename) message = client.basicGeneral(img) # 通用文字识别,每天 50 000 次免费 #message = client.basicAccurate(img) # 通用文字高精度识别,每天 800 次免费 print("识别成功!") i.close(); with open(outfile, 'a+') as fo: fo.writelines("+" * 60 + '\n') fo.writelines("识别图片:\t" + filename + "\n" * 2) fo.writelines("文本内容:\n") # 输出文本内容 for text in message.get('words_result'): fo.writelines(text.get('words') + '\n') fo.writelines('\n'*2) print("文本导出成功!") print() if __name__ == "__main__": outfile = 'export.txt' outdir = 'tmp' if path.exists(outfile): os.remove(outfile) if not path.exists(outdir): os.mkdir(outdir) print("压缩过大的图片...") // 首先对过大的图片进行压缩,以提高识别速度,将压缩的图片保存与临时文件夹中 for picfile in glob.glob("picture/*"): convertimg(picfile, outdir) print("图片识别...") for picfile in glob.glob("tmp/*"): baiduOCR(picfile, outfile) os.remove(picfile) print('图片文本提取结束!文本输出结果位于 %s 文件中。' % outfile) os.removedirs(outdir)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
为了减少三元组抽取中一次的工作量,把一本书的内容放在12个文件中

LTP抽取三元组
LTP 原理介绍
ltp用训练好的模型来完成一些nlp任务,这个工具还挺难下载的,这里附上资源
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1YkGOkU3RShI25DuLuEAvDw
提取码:muqisentence_parser
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os from pyltp import Segmentor, Postagger, Parser, NamedEntityRecognizer, SementicRoleLabeller # pip install pyltp -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple 可以先下载好whl文件 #LTP语言平台:http://ltp.ai/index.html #咱们使用的工具包,pyltp:https://pyltp.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/api.html #LTP附录:https://ltp.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/appendix.html#id3 #安装方法:https://github.com/HIT-SCIR/pyltp class LtpParser: #初始化 def __init__(self): LTP_DIR = "./ltp_data_v3.4.0" # 定义分词器 self.segmentor = Segmentor() self.segmentor.load(os.path.join(LTP_DIR, "cws.model")) # 词性标注 self.postagger = Postagger() self.postagger.load(os.path.join(LTP_DIR, "pos.model")) self.parser = Parser() self.parser.load(os.path.join(LTP_DIR, "parser.model")) self.recognizer = NamedEntityRecognizer() self.recognizer.load(os.path.join(LTP_DIR, "ner.model")) self.labeller = SementicRoleLabeller() self.labeller.load(os.path.join(LTP_DIR, 'pisrl_win.model')) '''语义角色标注''' def format_labelrole(self, words, postags): arcs = self.parser.parse(words, postags) roles = self.labeller.label(words, postags, arcs) roles_dict = {} for role in roles: roles_dict[role.index] = {arg.name:[arg.name,arg.range.start, arg.range.end] for arg in role.arguments} return roles_dict '''句法分析---为句子中的每个词语维护一个保存句法依存儿子节点的字典''' def build_parse_child_dict(self, words, postags, arcs): child_dict_list = [] format_parse_list = [] for index in range(len(words)): child_dict = dict() for arc_index in range(len(arcs)): if arcs[arc_index].head == index+1: #arcs的索引从1开始 arc. head 表示依存弧的父结点的索引。 ROOT 节点的索引是 0 ,第一个词开始的索引依次为1,2,3,···arc. relation 表示依存弧的关系。 if arcs[arc_index].relation in child_dict: child_dict[arcs[arc_index].relation].append(arc_index)#添加 else: child_dict[arcs[arc_index].relation] = []#新建 child_dict[arcs[arc_index].relation].append(arc_index) child_dict_list.append(child_dict)# 每个词对应的依存关系父节点和其关系 rely_id = [arc.head for arc in arcs] # 提取依存父节点id relation = [arc.relation for arc in arcs] # 提取依存关系 heads = ['Root' if id == 0 else words[id - 1] for id in rely_id] # 匹配依存父节点词语 for i in range(len(words)): a = [relation[i], words[i], i, postags[i], heads[i], rely_id[i]-1, postags[rely_id[i]-1]] format_parse_list.append(a) return child_dict_list, format_parse_list '''parser主函数''' def parser_main(self, sentence): words = list(self.segmentor.segment(sentence)) postags = list(self.postagger.postag(words)) arcs = self.parser.parse(words, postags) child_dict_list, format_parse_list = self.build_parse_child_dict(words, postags, arcs) roles_dict = self.format_labelrole(words, postags) return words, postags, child_dict_list, roles_dict, format_parse_list if __name__ == '__main__': parse = LtpParser() #sentence = '我想听一首迪哥的歌' sentence = '奥巴马昨晚在白宫发表了演说' words, postags, child_dict_list, roles_dict, format_parse_list = parse.parser_main(sentence) print(words, len(words)) print(postags, len(postags)) print(child_dict_list, len(child_dict_list)) print(roles_dict) print(format_parse_list, len(format_parse_list))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
triiple_extraction
from sentence_parser import * import re import glob #LTP语言平台:http://ltp.ai/index.html #咱们使用的工具包,pyltp:https://pyltp.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/api.html #LTP附录:https://ltp.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/appendix.html#id3 #安装方法:https://github.com/HIT-SCIR/pyltp class TripleExtractor: def __init__(self): self.parser = LtpParser() '''文章分句处理, 切分长句,冒号,分号,感叹号等做切分标识''' def split_sents(self, content): return [sentence for sentence in re.split(r'[??!!。;;::\n\r]', content) if sentence] '''利用语义角色标注,直接获取主谓宾三元组,基于A0,A1,A2''' def ruler1(self, words, postags, roles_dict, role_index): v = words[role_index] role_info = roles_dict[role_index] if 'A0' in role_info.keys() and 'A1' in role_info.keys(): s = ''.join([words[word_index] for word_index in range(role_info['A0'][1], role_info['A0'][2]+1) if postags[word_index][0] not in ['w', 'u', 'x'] and words[word_index]]) o = ''.join([words[word_index] for word_index in range(role_info['A1'][1], role_info['A1'][2]+1) if postags[word_index][0] not in ['w', 'u', 'x'] and words[word_index]]) if s and o: return '1', [s, v, o] return '4', [] '''三元组抽取主函数''' def ruler2(self, words, postags, child_dict_list, arcs, roles_dict): svos = [] for index in range(len(postags)): tmp = 1 # 先借助语义角色标注的结果,进行三元组抽取 if index in roles_dict: flag, triple = self.ruler1(words, postags, roles_dict, index) if flag == '1': svos.append(triple) tmp = 0 if tmp == 1: # 如果语义角色标记为空,则使用依存句法进行抽取 # if postags[index] == 'v': if postags[index]: # 抽取以谓词为中心的事实三元组 child_dict = child_dict_list[index] # 主谓宾 if 'SBV' in child_dict and 'VOB' in child_dict: r = words[index] e1 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['SBV'][0]) e2 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['VOB'][0]) svos.append([e1, r, e2]) # 定语后置,动宾关系 relation = arcs[index][0] head = arcs[index][2] if relation == 'ATT': if 'VOB' in child_dict: e1 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, head - 1) r = words[index] e2 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['VOB'][0]) temp_string = r + e2 if temp_string == e1[:len(temp_string)]: e1 = e1[len(temp_string):] if temp_string not in e1: svos.append([e1, r, e2]) # 含有介宾关系的主谓动补关系 if 'SBV' in child_dict and 'CMP' in child_dict: e1 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['SBV'][0]) cmp_index = child_dict['CMP'][0] r = words[index] + words[cmp_index] if 'POB' in child_dict_list[cmp_index]: e2 = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict_list[cmp_index]['POB'][0]) svos.append([e1, r, e2]) return svos '''对找出的主语或者宾语进行扩展''' def complete_e(self, words, postags, child_dict_list, word_index): child_dict = child_dict_list[word_index] prefix = '' if 'ATT' in child_dict: for i in range(len(child_dict['ATT'])): prefix += self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['ATT'][i]) postfix = '' if postags[word_index] == 'v': if 'VOB' in child_dict: postfix += self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['VOB'][0]) if 'SBV' in child_dict: prefix = self.complete_e(words, postags, child_dict_list, child_dict['SBV'][0]) + prefix return prefix + words[word_index] + postfix '''程序主控函数''' def triples_main(self, content): sentences = self.split_sents(content) svos = [] for sentence in sentences: words, postags, child_dict_list, roles_dict, arcs = self.parser.parser_main(sentence) svo = self.ruler2(words, postags, child_dict_list, arcs, roles_dict) svos += svo return svos '''测试''' def test(): cnt=0 if os.path.exists("triple_txt"): pass else : os.mkdir("triple_txt") try: for txt in glob.glob("text/*"): with open(txt,encoding="ansi",mode="r") as f: content5=f.read() #content5 = '我购买了一件玩具,孩子非常喜欢这个玩具,但是质量不太好。希望商家能够保障商品质量,不要再出现类似问题。' extractor = TripleExtractor() svos = extractor.triples_main(content5) outfile =os.path.join("triple_txt", os.path.basename(txt)+".txt") with open(outfile,"w",encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(str(svos)) except Exception as e: print(e) test()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
输入文本:content5、输出到triple_text目录下

共词分析确定主题词
共词分析的一般有以下四个步骤如图。首先,确定分析的文本数据;接着提取概念性术语等可以反映文本主题的分析单元,筛选出高频词;下一步统计高频词对的共现频率,构建共词矩阵;最后可视化共词网络,结合节点中心度确定主题词[29]。在实际情况中,根据研究内容的不同,可以将部分过程循环多次[30]。在实验部分,本研究也根据最后实际效果进行了适当的调整。
 为了确定共词网络中节点的影响力,不仅要考虑节点的词频还有考虑节点之间的相互影响[31]。学术界对网络节点影响力进行了深入研究,提出了中介中心度、亲密中心度、特征向量中心度、离心度,谐波亲密中心度等度量方法。文献[32]-[33]评估了各指标的适用性,且提出了在具体网络中选择指标的方法:分析网络中节点度数大的节点与各指标的相关性。
为了确定共词网络中节点的影响力,不仅要考虑节点的词频还有考虑节点之间的相互影响[31]。学术界对网络节点影响力进行了深入研究,提出了中介中心度、亲密中心度、特征向量中心度、离心度,谐波亲密中心度等度量方法。文献[32]-[33]评估了各指标的适用性,且提出了在具体网络中选择指标的方法:分析网络中节点度数大的节点与各指标的相关性。
具体工作
完成三元组预处理工作(包括LAC细化实体和三元组、统计高频实体词、筛选重要的三元组)最后将筛选的三元组构建图谱。初步抽取的三元组关系有7830条,为了减少工作量,本文用LTP抽取的实体上用LAC进一步识别出粒度更小的实体,并用这些实体确定高频词后,直接用在原始的三元组筛选上,在初步选定的三元组上完成三元组的细化。
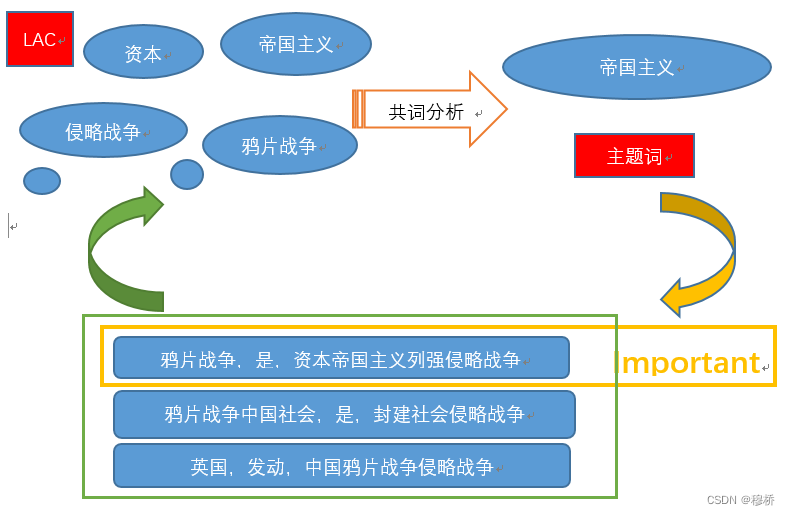
本文使用到了共词分析技术。一般情况下共词分析讨论的基本单元是一篇文档,本文使用的是一个三元组(合理性有待考量)
LAC 实体识别
from collections import Counter import glob import pandas as pd import os import re from LAC import LAC cnt = 0 times = 0 # 统计高频词 if os.path.exists("excel"): pass else : os.mkdir("excel") # 提取中文的函数 f=lambda a:''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', a)) # 命名实体识别工具 lac = LAC(mode='lac') lac_result=lac.run('中国特色社会主义') def co_ner(tmp:str): nlst=["n","ORG","PER","LOC"] lst=[] try: lac_result=lac.run(tmp) for i in range(len(lac_result[0])): w = lac_result[0][i] flag = lac_result[1][i] if flag in nlst or 'n' in flag: lst.append(w) except Exception as e: print(e) if lst != []: return lst else : return [tmp] dic = [] for txt in glob.glob("triple_txt/*"): # if(cnt % 6 == 0): # dic = [] # times = times + 1 with open(txt,encoding='utf-8') as f: content=f.read() lst= content.split("],") for tri in lst: tri.strip(",,[]") dou=tri.split(",") if len(dou)==3: # item=[dou[0].strip("n[]\'\\").strip(),dou[2].strip("n[]\'\\").strip()] tmp1 = ''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', dou[0])) tmp2 = ''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', dou[2])) item = [tmp1, tmp2] for i in item: if i is not None and i != '': i = co_ner(i) dic.extend(i) r=Counter(dic) df=pd.Series(dict(r)) df.to_excel(f"excel/词频_lac.xlsx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
import pandas as pd from LAC import LAC lac=LAC(mode='lac') df = pd.read_excel("excel/词频_lac.xlsx") lst=[] special=["ORG","LOC","PER"] for i in range(df.shape[0]): try: # 去掉小于2 lac_result=lac.run(df.iloc[i,0]) if lac_result[1][0] not in special and len(lac_result[0][0])<=2: continue else : lst.append(df.iloc[i,:]) except Exception as e: print(e) df=pd.DataFrame(lst) df.to_excel("excel/有效词频.xlsx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
建立共词矩阵
共词矩阵是高频词组成的二维矩阵,它的值表示两个高频词共同出现在一个三元组的次数。由于共词范围的缩小,扩大了共词统计的遍历范围,即为三元组.cvs中7830条数据,为了快速地从批量数据中确定是否有词对[node1,node2]的共词关系,分别利用Series.str.contains(node1)、Series.str.contains(node2)在触发者列和受事者列完成全元素的内容查询,当且仅当返回的两个布尔数组在同一index下都为TRUE,[node1,node2]才确定为共词
# co_word_high_freq from collections import Counter import glob import pandas as pd import os import re from ltp import LTP from LAC import LAC lac = LAC(mode='lac') cnt = 0 times = 0 # 统计高频词 """ 分析出实体以免重复 lac 命名实体识别效果不是特别好 根据词性做一个预处理 """ if os.path.exists("excel"): pass else : os.mkdir("excel") # 提取中文的函数 f=lambda a:''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', a)) # 命名实体识别工具 ltp = LTP() ltp.init_dict(path="user_dict.txt", max_window=7) def co_ner(tmp:str): nlst = [ "ORG", "PER", "LOC"] lst=[] try: lac_result = lac.run(tmp) for i in range(len(lac_result[0])): w = lac_result[0][i] flag = lac_result[1][i] if flag in nlst or ('n' in flag ): lst.append(w) except Exception as e: print(e) return lst # seg,hidden = ltp.seg([tmp]) # nre = ltp.ner(hidden) # try: # tag,start,end=nre[0][0] # tmp = "".join(seg[0][start:end + 1]) # except Exception as e: # print(e) # return tmp dic = [] doulist=[] for txt in glob.glob("triple_txt/*"): # if(cnt % 6 == 0): # dic = [] # times = times + 1 with open(txt,encoding='utf-8') as f: content=f.read() lst= content.split("],") for tri in lst: flag = True tri.strip(",,[]") dou=tri.split(",") if len(dou)==3: # item=[dou[0].strip("n[]\'\\").strip(),dou[2].strip("n[]\'\\").strip()] tmp1 = ''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', dou[0])) tmp2 = ''.join(re.findall('[\u4e00-\u9fa5]', dou[2])) item = [tmp1, tmp2] if tmp1 is not None and tmp1 != '': tmp1=co_ner(tmp1) if tmp1!=[]: dic.extend(tmp1) if tmp2 is not None and tmp2 != '': tmp2=co_ner(tmp2) if tmp2!=[]: dic.extend(tmp2) # 都没有的就是没有价值的信息 if(tmp1!=[] or tmp2 !=[]): doulist.append([''.join(tmp1),dou[1].strip(),''.join(tmp2)]) # # r=Counter(dic) # df=pd.Series(dict(r)) # df.to_excel(f"excel/词频_optimize.xlsx") #r = Counter(doulist) df = pd.DataFrame(doulist) df.to_excel(f"excel/三元组.xlsx")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
# co-word_matrix import pandas as pd from collections import Counter import numpy as np triple=pd.read_csv("excel/三元组.csv") node = pd.read_csv("excel/有效词频.csv").iloc[:,0] def judge( node1:str,node2:str): doulst1=pd.Series(triple.iloc[:, 0].values) doulst2=pd.Series(triple.iloc[ :,2].values) try: f = lambda x, y: pd.Series([(tur[0] and tur[1]) for tur in zip(x, y)]) # str fillna 都是series独有 lst 没有的 bol1=doulst1.str.contains(node1) bol2=doulst2.str.contains(node2) bol1=bol1.fillna(False) bol2=bol2.fillna(False) v = f(bol1, bol2) bol10 = doulst1.str.contains(node1) bol20 = doulst2.str.contains(node2) bol10 = bol10.fillna(False) bol20 = bol20.fillna(False) k = f(bol10, bol20) if np.sum(v) != 0 or np.sum(k)!=0: return [node1,node2] except Exception as e: print(e) return None lst=[] for i in range(len(node)): for j in range(len(node)): if(i!=j and j>i ) : k = judge(node[i],node[j]) if k!=None: lst.append(" ".join(k)) r=Counter(lst) df=pd.DataFrame(dict(r),index=[0]) df.to_csv("excel/matrix_pro.csv")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
将边数据和高频词导入Gephi,得到高频共词矩阵构成的网络图

Gephi 计算中心度筛选主题词
计算中心度的指标有多个:亲密中心度、谐波亲密中心度、中介中心度、特征向量中心度。为了确定更优的度量指标,计算词频与各中心度的相关系数。

上表4-2展示了各中心度的指标与词频的相关系数,其中中介中心度的相关系数最大,表示这一变量和词频之间的关系越强,观察词频排在前50的节点中心度曲线图4-6。观察它们与词频之间变化的关系,可以发现其中亲密中心度和谐波亲密中心度的波动和异常点较小,变化趋势更接近词频。综上,将中介中心度作为评估节点影响。

# 有50 个点刻度只要标注其中 5 10 15 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import numpy as np from matplotlib import font_manager import os plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 用来正常显示负号 my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="AdobeHeitiStd-Regular.otf") d=pd.read_excel("excel/node_centrality.xlsx") df=d.sort_values(by="词频", ascending=False) df=df.reset_index(drop=True) # x=df.loc[:50,"Id"] fig,ax=plt.subplots() ax2=ax.twinx() y1=df.loc[0:49,"词频"] x= np.arange(50) y2=df.loc[0:49,"特征向量中心度"] l1,=ax.plot(x,y1,color='b') # c coral deeppink https://finthon.com/matplotlib-color-list/ lawngreen l2,=ax2.plot(x,y2,color='deeppink') ax2.legend([l1, l2], ['词频', '特征向量中心度'],prop=my_font) ax.set_ylabel('词频') ax2.set_ylabel('特征向量中心度') try: plt.savefig("img/特征向量中心度.png") except Exception as e: print(e) # print(df.unique())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
将结果中中介中心度大于0的词作为主题词,并将它的中心度作为权重导入Gephi,根据权重观察各个主题词内容如下图4-7,从图中可以看到统一战线、马克思主义共产、中国特色社会主义等重要字眼。

-
相关阅读:
程序员副业之无货源闲鱼
中小企业数字化思考:数字化转型应该走自己的路
快速排序和归并排序的非递归形式
大二Web课程设计 HTML+CSS制作苹果商城网站 Apple商城 8个页面
高并发扣款,如何保证结果一致性
DP7340——192KHz双声道输入24位AD 转换器
Springboot启动mongoDB报错后禁用mongoDB自动配置
Git如何统计代码行数
2011-2019年各省农村人均受教育年限和村委会个数数据
JS使用正则+replace实现replace All 全部替换的方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46312299/article/details/126641233
