-
#每日一题合集#牛客JZ23-JZ33
为了督促自己每天练一练编程
时间:2022年8月21日-2022年8月31日
网站:https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj/ta?tpId=138.21-JZ23. 链表中环的入口结点

这个题,找环很容易,快慢指针是否相遇即可;主要是找环的入口结点,这个解释可以参考官方题解:

/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* is_cycle(ListNode* head){ if(head == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head; while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){ fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(fast == slow) return slow; } return NULL; } ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { ListNode* slow = is_cycle(pHead); if(slow == NULL) return NULL; ListNode* fast = pHead; while(fast != slow){ fast = fast->next; slow = slow->next; } return slow; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
8.22-JZ24. 反转链表

很简单的链表内部反转,用个tmp指针记录一下下一个即可class Solution { public: ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) { ListNode* cur = pHead; ListNode* pre = NULL; ListNode* tmp = pHead; while(cur != NULL){ tmp = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = tmp; } return pre; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
8.23-JZ25. 合并两个排序的链表
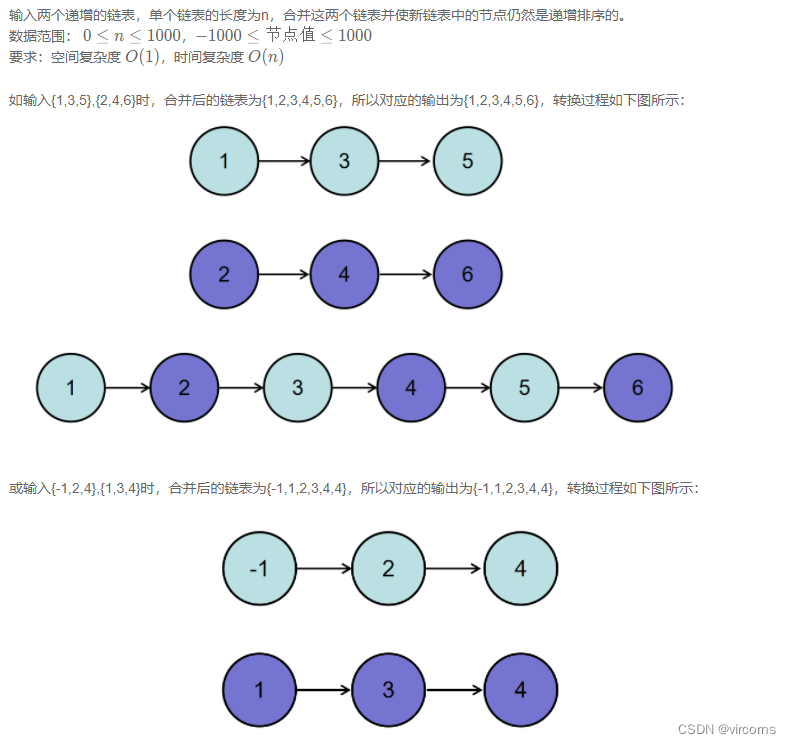
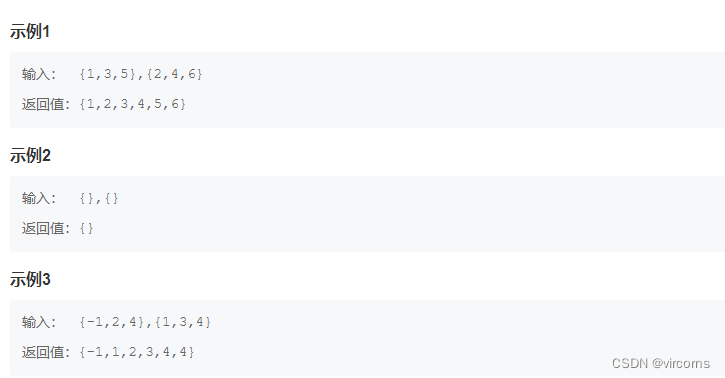
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { if(pHead1 == NULL) return pHead2; if(pHead2 == NULL) return pHead1; ListNode* res = new ListNode(0); ListNode* cur = res; while(pHead1 != NULL && pHead2 != NULL){ if(pHead1->val < pHead2->val){ cur->next = pHead1; pHead1 = pHead1->next; } else{ cur->next = pHead2; pHead2 = pHead2->next; } cur = cur->next; } if(pHead1 != NULL) cur->next = pHead1; if(pHead2 != NULL) cur->next = pHead2; return res->next; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
8.24-JZ26. 树的子结构

因为空树不是任何树的子树,所以要先判断B树是否为空树。
当A树为空,但是B树还有节点的时候,不为子树;但是B树到空节点时可以是子树。
双重遍历:A遍历自己所有的节点当做子树的起点,每次再递归比较是否与B树完全一致/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: bool Judge(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) { if(root1 == NULL && root2 != NULL) return false; if(root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL) return true; if(root1->val != root2->val) return false; return Judge(root1->left, root2->left) && Judge(root1->right, root2->right); } bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) { if(pRoot2 == NULL) return false; if(pRoot1 == NULL && pRoot2 != NULL) return false; if(pRoot1 == NULL || pRoot2 == NULL) return true; bool flag1 = Judge(pRoot1, pRoot2); bool flag2 = HasSubtree(pRoot1->left, pRoot2); bool flag3 = HasSubtree(pRoot1->right, pRoot2); return flag1 || flag2 || flag3; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
8.25-JZ27. 二叉树的镜像


非常简单的递归交换class Solution { public: /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param pRoot TreeNode类 * @return TreeNode类 */ TreeNode* Mirror(TreeNode* pRoot) { // write code here if(pRoot == NULL) return NULL; TreeNode* left = Mirror(pRoot->left); TreeNode* right = Mirror(pRoot->right); pRoot->left = right; pRoot->right = left; return pRoot; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
8.26-JZ28.对称的二叉树


和上一个题思路很像,也是递归判断左右是否一样。class Solution { public: bool Judge(TreeNode* r1, TreeNode* r2){ if(r1 == NULL && r2 == NULL) return true; if(r1 == NULL || r2 == NULL || r1->val != r2->val) return false; return Judge(r1->left, r2->right) && Judge(r1->right, r2->left); } bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) { return Judge(pRoot, pRoot); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
8.27-JZ29. 顺时针打印矩阵
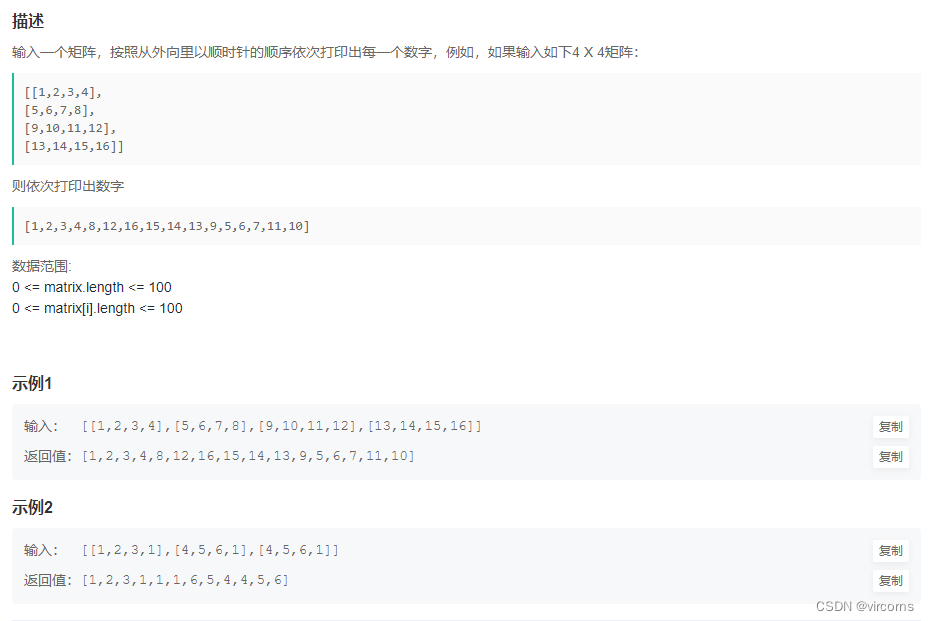
这是一个纯思维题,只要能想到用上下左右来标记判断,上下或左右重合为结束标志。分别对上行、右列、下行、左列进行遍历即可。class Solution { public: vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) { vector<int> res; int n = matrix.size(); if(n == 0) return res; int left = 0, right = matrix[0].size() - 1; int up = 0, down = n - 1; int i; while(left <= right && up <= down){ for(i = left; i <= right; i++) res.push_back(matrix[up][i]); up++; if(up > down) break; for(i = up; i <= down; i++) res.push_back(matrix[i][right]); right--; if(left > right) break; for(i = right; i >= left; i--) res.push_back(matrix[down][i]); down--; if(up > down) break; for(i = down; i >= up; i--) res.push_back(matrix[i][left]); left++; if(left > right) break; } return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
8.28-JZ30. 包含min函数的栈
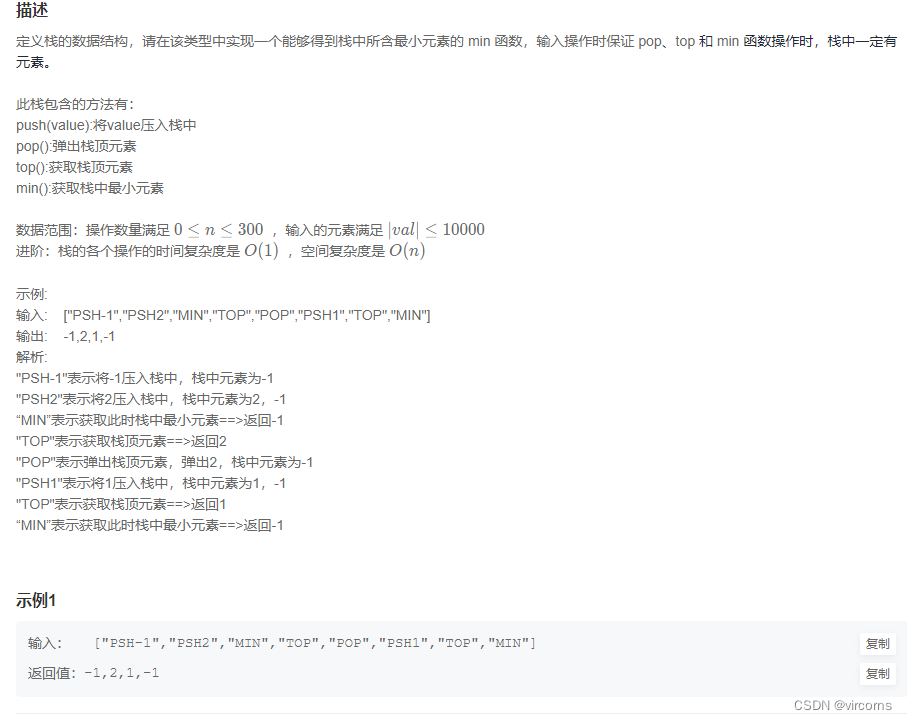
也是比较简单的栈操作,就是用一个栈,每次判断,最小值就存,不是最小值就重复,这样每次栈顶都是现在这个栈的最小值。class Solution { public: stack<int> s; stack<int> m; void push(int value) { s.push(value); if(m.empty() || m.top() > value) m.push(value); else m.push(m.top()); } void pop() { s.pop(); m.pop(); } int top() { return s.top(); } int min() { return m.top(); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
8.29-JZ31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
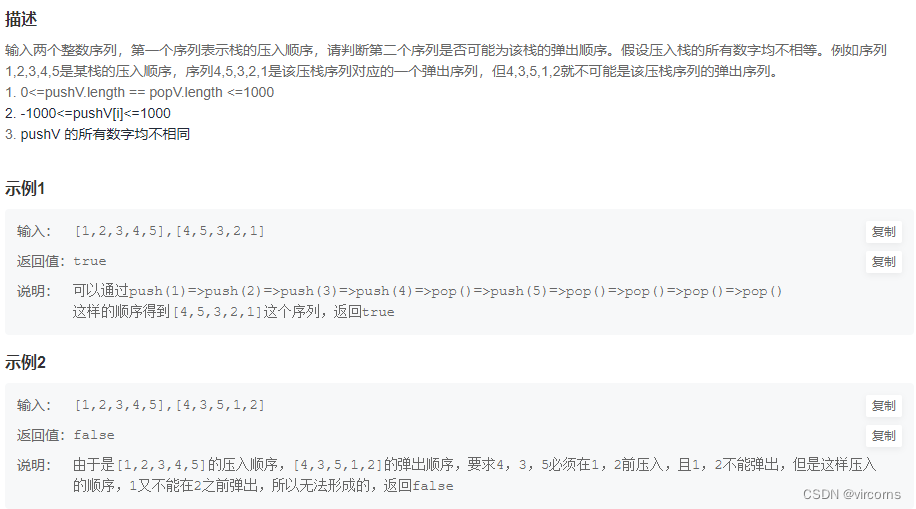
class Solution { public: bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) { stack<int> s; int n = pushV.size(); int i = 0; for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ while(i < n && (s.empty() || s.top() != popV[j])){ s.push(pushV[i]); i++; } if(s.top() == popV[j]) s.pop(); else return false; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
8.30-JZ32.从上往下打印二叉树
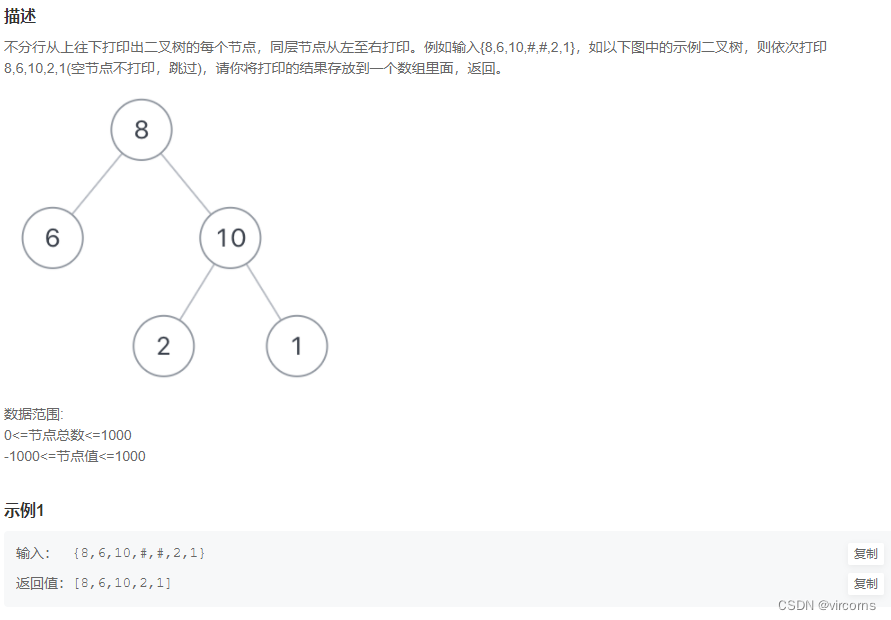
二叉树的层次遍历基础写法了。利用队列遍历节点,如果有左右子节点,就依次放队伍后面;
class Solution { public: vector<int> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> res; if(root == NULL) return res; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); TreeNode* cur; while(!q.empty()){ cur = q.front(); q.pop(); res.push_back(cur->val); if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left); if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right); } return res; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
8.31-JZ33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
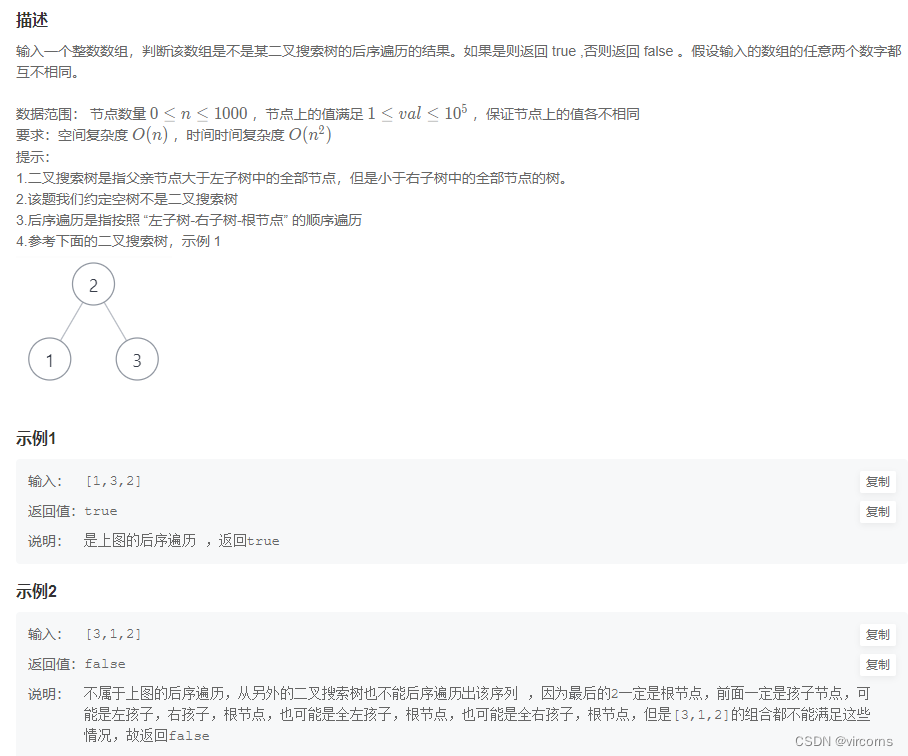
递归最重要的是找到左右子树的分界点,如果他是一个二叉搜索树,那么他的左边一定都比根节点小,那么从0到最后一个比根节点小的都是左子树;同理,从第一个比根节点大的位置到根节点前一个,都是右子树。如果能一直这样划分,说明是二叉搜索树,否则不是。
注意:递归的边界一定要写对,否则会超时class Solution { public: bool Judge(vector<int> sequence,int begin, int end){ int flag = 1; if(begin > end) return true; int left = -1, right = end, root = sequence[end]; for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++){ if(sequence[i] < root){ left = i; } if(flag && sequence[i] > root){ right = i; flag = 0; } } // for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++){ // if(sequence[i] > root){ // right = i; // break; // } // } if(left > right) return false; return Judge(sequence, begin, left) && Judge(sequence, right, end-1); } bool VerifySquenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) { int n = sequence.size(); if(n == 0) return false; return Judge(sequence, 0, n-1); } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
-
相关阅读:
如何使用 edu 邮箱注册 Azure
Java Nacos与Gateway的使用
扩展欧几里得
【Python 零基础入门】常用内置函数 初探
# RocketMQ 实战:模拟电商网站场景综合案例(二)
Rust 基础(五)
数据结构-作业1
Python tests in.....
【Web前端二级导航栏】
基于STM32和阿里云的智能台灯(STM32+ESP8266+MQTT+阿里云+语音模块)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43476037/article/details/126433266
