-
SpringBoot基础篇 (1)
目录
一、快速上手SpringBoot
1.1 SpringBoot入门程序开发
SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化SPring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
步骤:
①:创建新模块,选择Spring Initializr,并配置模块相关基础信息
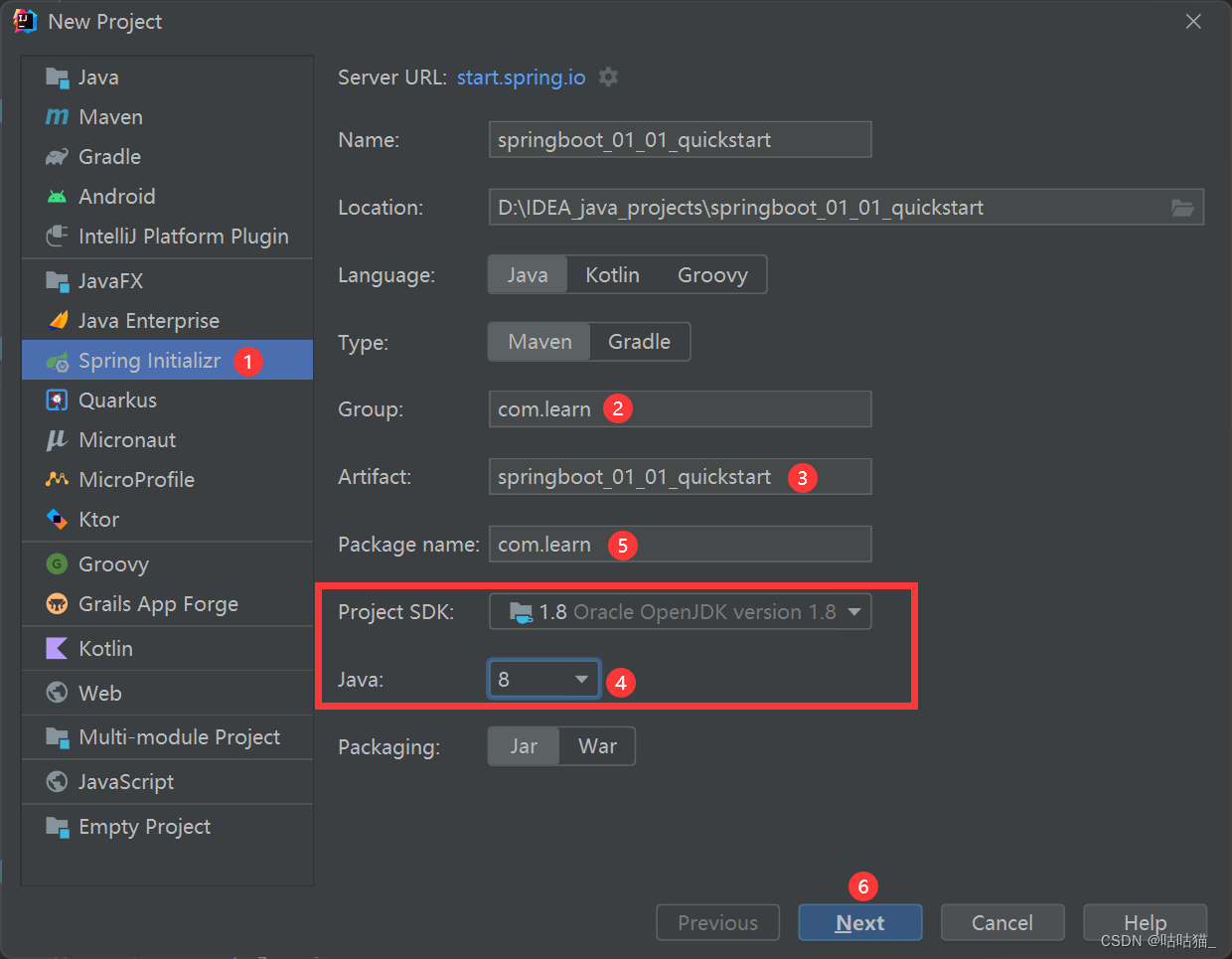
②:选择当前模块需要使用的技术集

③:开发控制器类
- //Rest模式
- @RestController
- @RequestMapping("/books")
- public class BookController {
- @GetMapping
- public String getById(){
- System.out.println("Springboot is running...");
- return "Springboot is running...";
- }
- }
④:运行自动生成的Application类

最简SpringBoot程序所包含的基础文件
- pom.xml文件
- "1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
- <parent>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
- <version>2.7.3version>
- <relativePath/>
- parent>
- <groupId>com.learngroupId>
- <artifactId>springboot_01_01quickstartartifactId>
- <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
- <name>springboot_01_01quickstartname>
- <description>springboot_01_01quickstartdescription>
- <properties>
- <java.version>1.8java.version>
- properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
- dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
- <scope>testscope>
- dependency>
- dependencies>
- <build>
- <plugins>
- <plugin>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
- plugin>
- plugins>
- build>
- project>
- Application类
- @SpringBootApplication
- public class Springboot0101quickstartApplication {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- SpringApplication.run(Springboot0101quickstartApplication.class, args);
- }
- }
- Spring程序与SpringBoot程序对比


1.2 基于SpringBoot官网创建项目
地址:https://start.spring.io/



1.3 基于阿里云创建项目
地址:https://start.aliyun.com
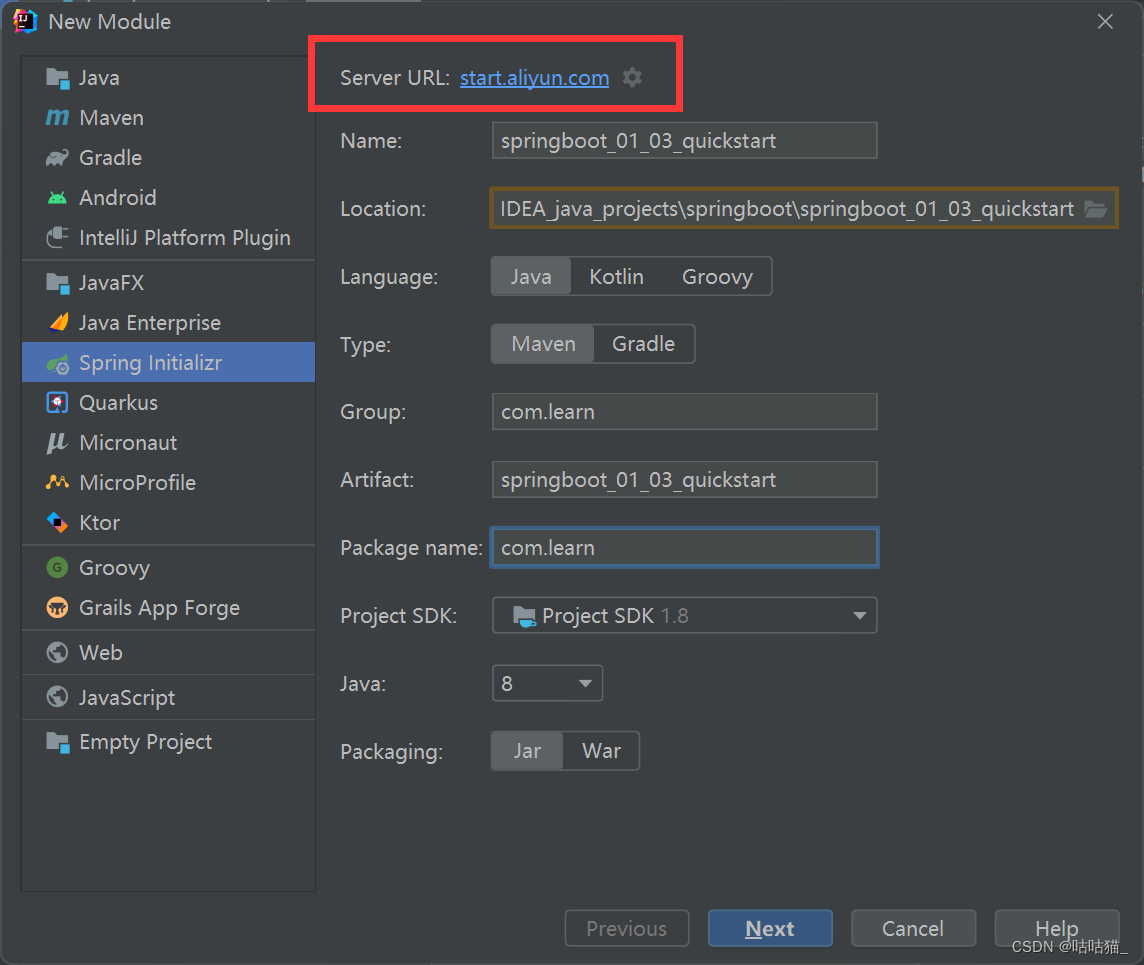



1.4 手动创建项目
①手动导入坐标
- "1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
- <modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
- <groupId>com.learngroupId>
- <artifactId>springboot_01_04_quickstartartifactId>
- <version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
- <parent>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
- <version>2.7.3version>
- <relativePath/>
- parent>
- <properties>
- <maven.compiler.source>8maven.compiler.source>
- <maven.compiler.target>8maven.compiler.target>
- properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
- dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
- <scope>testscope>
- dependency>
- dependencies>
- project>
②手动制作引导类
- package com.learn;
- import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
- import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
- /**
- * @author 咕咕猫
- * @version 1.0
- */
- @SpringBootApplication
- public class Application {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
- }
- }


二、SpringBoot简介
SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发环境
Spring程序缺点
- 依赖配置繁琐
- 配置繁琐
SpringBoot程序优点
- 起步依赖(简化依赖配置)
- 自动配置(简化常用工程相关配置)
- 辅助功能(内置服务器,....)
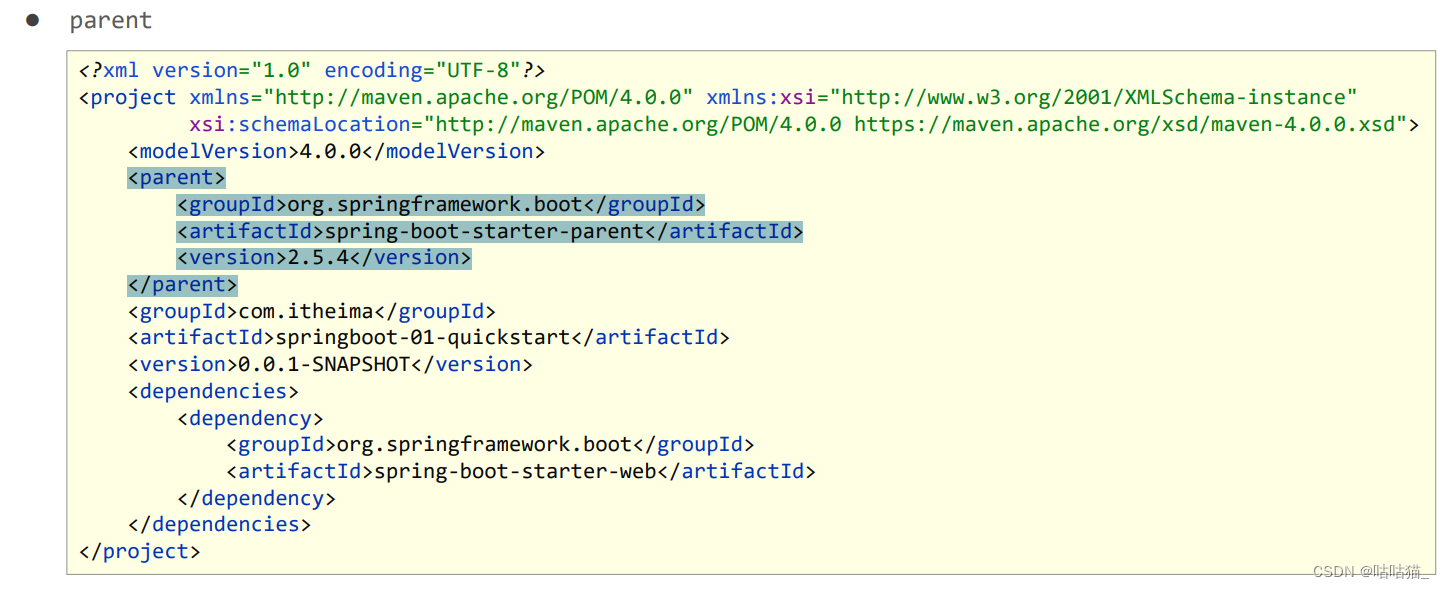
2.1 parent


2.2 starter
一个starter里面包含了若干个依赖信息


2.2.1 starter和parent的区别
starter
- SpringBoot中常见项目名称,定义了当前项目使用的所有依赖坐标,以达到减少依赖配置的目的
parent
- 所有SpringBoot项目要继承的项目,定义了若干个坐标版本号(依赖管理,而非依赖),以达到减少依赖冲突的目的
在实际开发中
- 使用任意坐标是,仅书写GAV中的G和A,V由SpringBoot提供,除非SpringBoot未提供对应版本V
- 如发生坐标错误,再指定Version(要小心版本冲突)
parent和starter解决配置问题
2.3 引导类
- 启动方式
- @SpringBootApplication
- public class Springboot0102QuickstartApplication {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- SpringApplication.run(Springboot0102QuickstartApplication.class, args);
- }
- }
- SpringBoot的引导类是Boot工程的执行入口,运行main方法就可以启动项目
- SpringBoot工程运行后初始化Spring容器,扫描引导类所在包加载Bean

2.4 内嵌tomcat
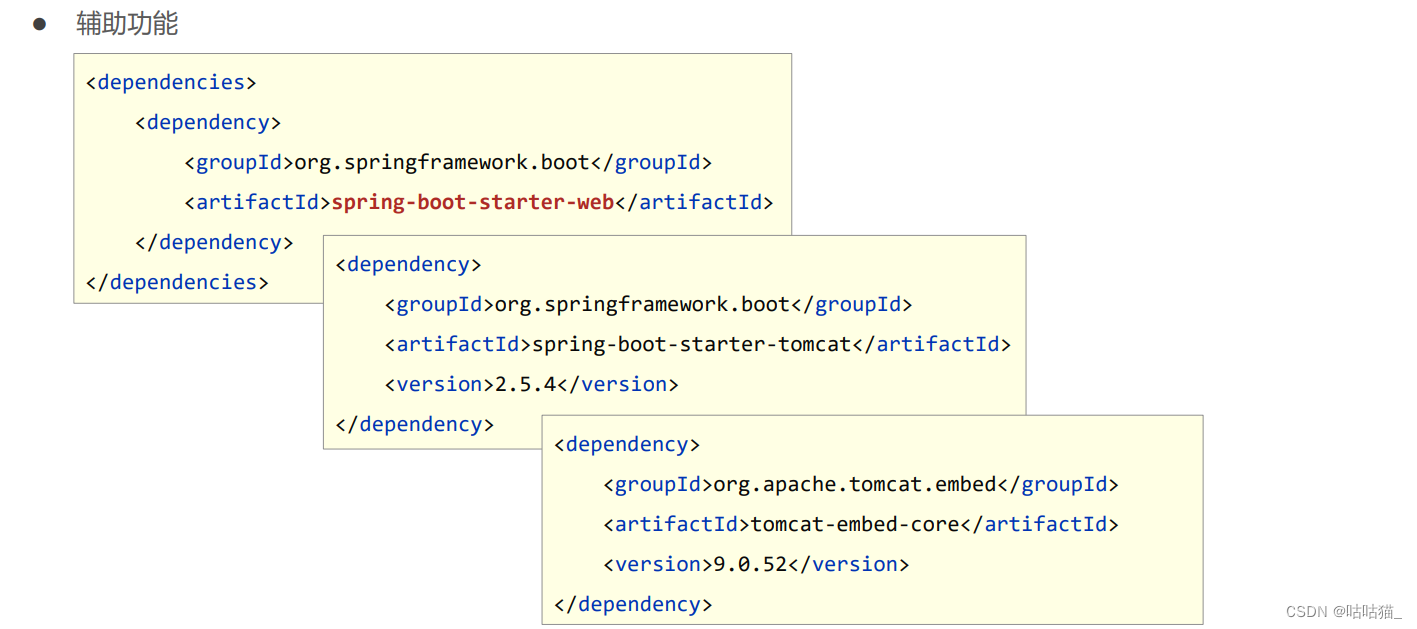
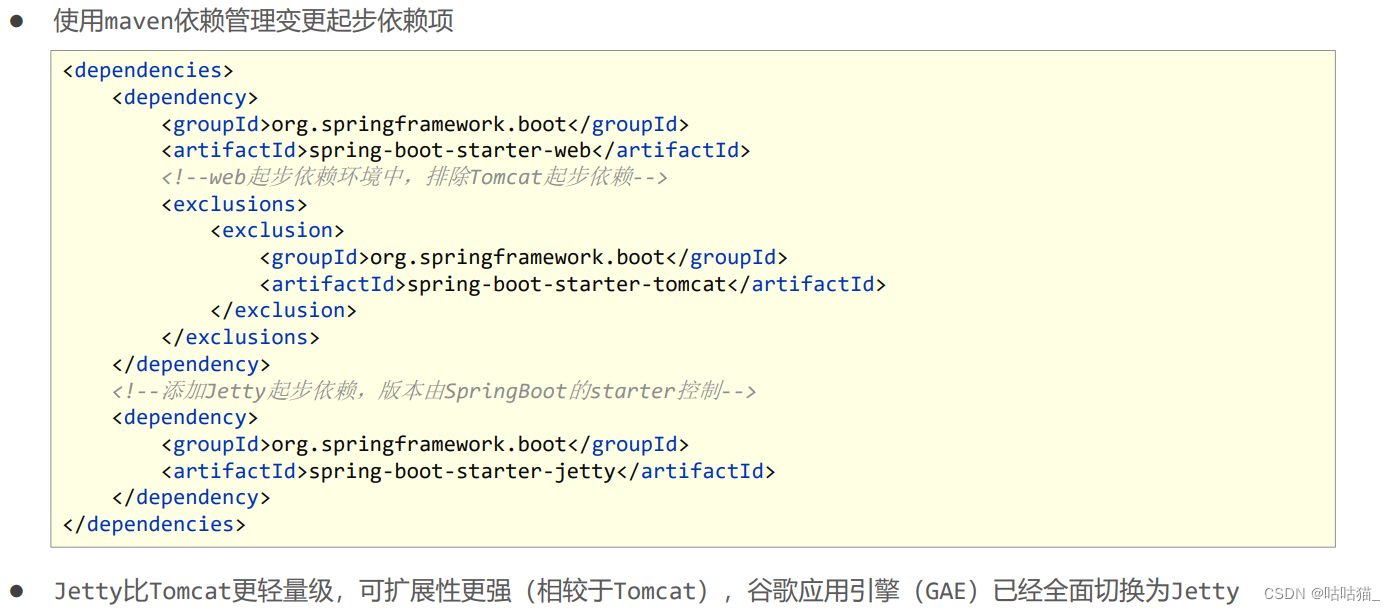

2.4.1 内置服务器
- tomcat(默认) apache出品,粉丝多,应用面广,负载了若干较重的组件
- jetty 更轻量级,但负载性能远不及tomcat
- undertow undertow,负载性能勉强跑赢tomcat
总结:
- SpringBoot先加载所有的自动配置类,xxxxAutoConfiguration
- 每个自动配置类按照条件进行生效,默认都会绑定配置文件指定的值。xxxxProperties里面拿。xxxxProperties和配置文件进行了帮i的那个
- 生效的配置类就会给容器中装配很多组件
- 只要容器中有这些组件,相当于这些功能就有了
- 定制化配置
◇用户直接自己@Bean替换底层的组件
◇用户去看这个组件是获取的配置文件什么值就去修改
xxxxAutoConfiguration----->组件----->xxxxProperties里面拿值----->application.properties
三、简单功能分析
3.1 静态资源访问
3.1.1 静态资源目录
只要静态资源放在当前项目的这几个类路径下:called /static(or /public or /resources or /META-INF/resources)
访问路径:当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
原理:静态映射/**
请求一进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理,不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应404页面。
可以改变默认的静态资源路径
- spring:
- mvc:
- static-path-pattern: /res/**
- resources:
- static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
3.1.2 静态资源访问前缀
默认无前缀
- spring:
- mvc:
- static-path-pattern: /res/**
当前项目 + static-path-pattern + 静态资源名 = 静态资源文件夹下找
3.1.3 webjar
自动映射 /webjars/**
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
- <artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
- <version>3.5.1</version>
- </dependency>
访问地址:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js 后面地址要按照依赖里面的包路径
3.2 欢迎页支持
- 静态资源路径下 index.html
◇ 可以配置静态资源路径
◇ 但是不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
- spring:
- # mvc:
- # static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致welcome page功能失效
- resources:
- static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
- controller能处理 /index
3.3 自定义Favicon
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可
- spring:
- # mvc:
- # static-path-pattern: /res/** 这个会导致 Favicon 功能失效
四、请求参数处理
4.1 请求映射原理

SpringMVC功能分析从org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet--->doDispatch()
- protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
- HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
- HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
- boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
- WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
- try {
- ModelAndView mv = null;
- Exception dispatchException = null;
- try {
- processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
- multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
- // 找到当前请求使用哪个Handler(Controller的方法)处理
- mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
- //HandlerMapping:处理器映射。/xxx->>xxxx

RequestMappintHandlerMapping:保存了所有@RequestMapping和handler的映射规则
所有的请求映射都阻碍HandlerMappint中
- SpringBoot自动配置欢迎页的WelcomePageHandlerMapping。访问 / 能访问到index.html
- SpringBoot自动配置了默认的Request MappingHandlerMapping
- 请求进来,挨个尝试所有的HandlerMapping看是否有请求信息
◇ 如果有就找到这个请求对应的handler
◇ 如果没有就是下一个HandlerMapping
- 我们需要一些自定义的映射处理,也可以自己给容器中放HandlerMapping。自定义HandlerMapping
- protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
- if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
- for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
- HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
- if (handler != null) {
- return handler;
- }
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
-
相关阅读:
Redis学习笔记17:基于spring data redis及lua脚本批处理scan指令查询永久有效的key
el-select的el-option添加操作按钮插槽后实现勾选与按钮操作分离
洛谷 中位数
使用dispatchEvent解决重叠元素响应事件问题
leetcode每日一题30
【ZYNQ-嵌入式】zynq学习笔记(二)—— GIPO的硬件配置和软件配置
基于ssm操作系统课程网站
一级消防工程师证书价值下降,前景茫然?
【电商】管理后台--采购管理(执行层)
计算机毕业设计(附源码)python知识付费运营管理系统
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61843013/article/details/126600143
