-
ResNet网络架构
前言
2015年,何凯明为了降低网络训练难度,解决梯度消失的问题,提出了残差网络(Residual Network,ResNet),在2015年的ImageNet大规模视觉识别竞赛(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge, ILSVRC)中获得了图像分类和物体识别的优胜。
论文地址:Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition网络结构
残差结构
Residual net(残差网络)︰将靠前若干层的某一层数据输出直接跳过多层引入到后面数据层的输入部分。
残差神经单元∶假定某段神经网络的输入是x,期望输出是H(x),如果我们直接将输入x传到输出作为初始结果,那么我们需要学习的目标就是F(x)= H(x) - x,这就是一个残差神经单元,相当于将学习目标改变了,不再是学习一个完整的输出H(x),只是输出和输入的差别H(x) - x,即残差。
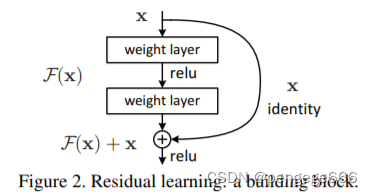
ResNet网络结构
整体架构
下图中展示了 18 层、34 层、50 层、101 层、152 层框架细节
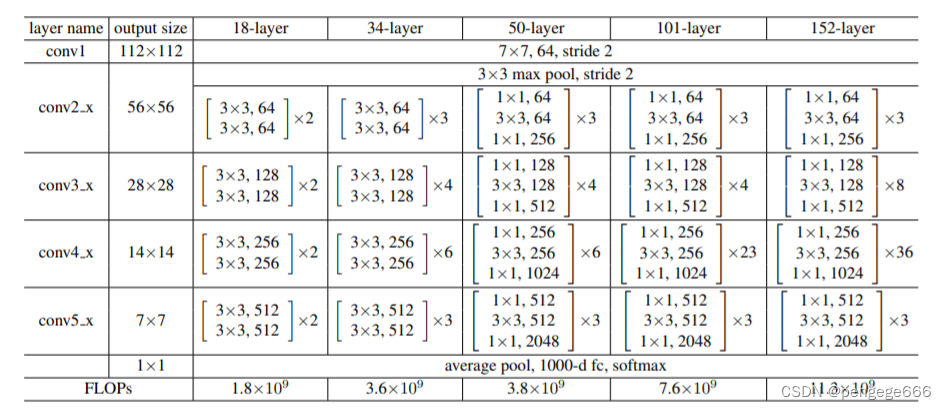
在ResNet类中网络数据的流向:(1)数据进入网络后先经过输入部分(conv1, bn1, relu, maxpool);
(2)然后进入中间卷积部分(layer1, layer2, layer3, layer4);
(3)最后数据经过一个平均池化和全连接层(avgpool, fc)输出得到结果;
具体来说,resnet18和其他res系列网络的差异主要在于layer1~layer4,其他的部件都是相似的。
BottleNeck结构
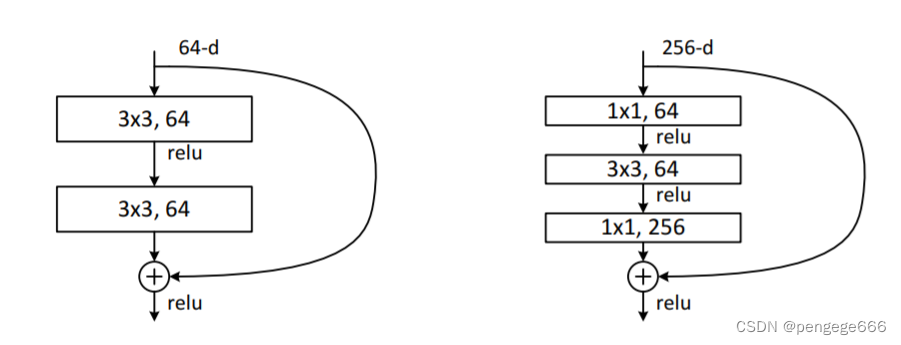
左图是ResNet18/34 BottleNeck
残差结构的主分支是由两层3x3的卷积层组成,而残差结构右侧的连接线是shortcut分支也称捷径分支(注意为了让主分支上的输出矩阵能够与我们捷径分支上的输出矩阵进行相加,必须保证这两个输出特征矩阵有相同的shape)右图是
ResNet50/101/152 BottleNeck
第一个是1x1的卷积层用来压缩channel维度,第二个是3x3的卷积层,第三个是1x1的卷积层用来还原channel维度(注意主分支上第一层卷积层和第二次卷积层所使用的卷积核个数是相同的,第三次是第一层的4倍)代码详解
导库
import argparse import numpy as np import torch import torchvision import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.data as Data import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
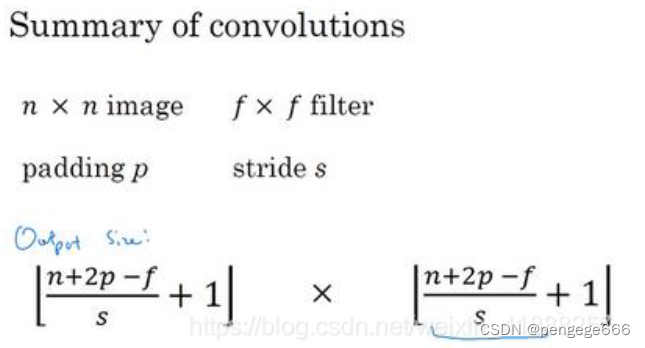
卷积运算
计算公式
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1): """3x3 convolution with padding""" ''' nn.Conv2d 二维卷积的实现 in_planes:输入的四维张量[N, C, H, W]中的C了,即输入张量的channels数 out_planes:期望的四维输出张量的channels数 kernel_size:卷积核的大小 stride:步长 padding:图像填充 ''' return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
残差层
class Bottleneck(nn.Module): expansion = 4 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(Bottleneck, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4) # inplace=True,用输出的数据覆盖输入的数据;节省空间,此时两者共用内存 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x # 先用变量保存初始张量 out = self.conv1(x) print("1:",out.shape) out = self.bn1(out) #作用:卷积层之后总会添加BatchNorm2d进行数据的归一化处理 print("2:",out.shape) out = self.relu(out) print("3:",out.shape) out = self.conv2(out) print("4:",out.shape) out = self.bn2(out) print("5:",out.shape) out = self.relu(out) print("6:",out.shape) out = self.conv3(out) print("7:",out.shape) out = self.bn3(out) print("8:",out.shape) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) print("now:",residual.shape) out += residual print("9:",out.shape) out = self.relu(out) print("10:",out.shape) return out- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
简单查看一下数据流动
net=Bottleneck(256,64) # [N, C, H, W] print(net(torch.rand([1,256,480,480])).shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
ResNet整体框架
class ResNet(nn.Module): ''' ''' def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes, grayscale): self.inplanes = 64 # 判断是否是灰度图 if grayscale: in_dim = 1 else: in_dim = 3 super(ResNet, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_dim, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 最大池化层 self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # 构建每一个阶段 self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]) self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2) self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2) self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2) self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1) self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels m.weight.data.normal_(0, (2. / n)**.5) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.weight.data.fill_(1) m.bias.data.zero_() def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1): downsample = None #保持输出通道数量一致 if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion: downsample = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion), ) layers = [] layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample)) self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion for i in range(1, blocks): layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes)) return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.bn1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.maxpool(x) x = self.layer1(x) x = self.layer2(x) x = self.layer3(x) x = self.layer4(x) # because MNIST is already 1x1 here: # disable avg pooling # x = self.avgpool(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) logits = self.fc(x) probas = F.softmax(logits, dim=1) return logits, probas- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
''' 该份代码适合resnet50之后的,resnet18请看实战部分代码 resnet50:layers = [3, 4, 6, 3] resnet101:layers=[3, 4, 23, 3] resnet152:layers=[3, 8, 36, 3] ''' model = ResNet(block=Bottleneck, layers=[3, 4, 6, 3],num_classes=10,grayscale=True) print(model)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
实战
ResNet18识别MNIST数据集
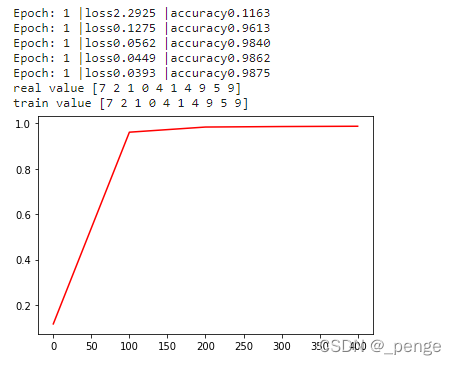
import argparse import numpy as np import torch import torchvision import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.data as Data import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class ResidualBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1): super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__() self.left = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel) ) self.shortcut = nn.Sequential() if stride != 1 or inchannel != outchannel: self.shortcut = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel) ) def forward(self, x): out = self.left(x) out += self.shortcut(x) out = F.relu(out) return out class ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, ResidualBlock, num_classes=10): super(ResNet, self).__init__() self.inchannel = 16 self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(16), nn.ReLU(), ) self.layer1 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 16, 2, stride=1) self.layer2 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 32, 2, stride=2) self.layer3 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 64, 2, stride=2) self.layer4 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 128, 2, stride=2) self.fc = nn.Linear(128, num_classes) def make_layer(self, block, channels, num_blocks, stride): strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) #strides=[1,1] layers = [] for stride in strides: layers.append(block(self.inchannel, channels, stride)) self.inchannel = channels return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): out = self.conv1(x) out = self.layer1(out) out = self.layer2(out) out = self.layer3(out) out = self.layer4(out) out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 4) out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) out = self.fc(out) return out def ResNet18(): return ResNet(ResidualBlock) lr = 0.1 Epoch = 1 Batch_size = 128 # device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") if __name__ == "__main__": train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root='./MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() ) test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root='./MNISt', train=False, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() ) # define train loader train_loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=Batch_size ) test_loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=test_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=Batch_size ) test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_dataset.data, dim=1).type(torch.Tensor) test_y = test_dataset.targets net = ResNet18() # net.to(device) # print(net)#查看网络结构 opt = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) loss_fun = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() a = [] ac_list = [] cnt=1 for epoch in range(Epoch): for i,(x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # cnt+=1 # if cnt>200: # break output = net(x) loss = loss_fun(output, y) opt.zero_grad() loss.backward() opt.step() if i % 100 == 0: a.append(i) test_output = torch.max(net(test_x), dim=1)[1] loss = loss_fun(net(test_x), test_y).item() accuracy = torch.sum(torch.eq(test_y, test_output)).item() / test_y.numpy().size ac_list.append(accuracy) print('Epoch:', Epoch, '|loss%.4f' % loss, '|accuracy%.4f' % accuracy) print('real value', test_y[: 10].numpy()) print('train value', torch.max(net(test_x)[: 10], dim=1)[1].numpy()) plt.plot(a, ac_list, color='r') plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
import argparse import numpy as np import torch import torchvision import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.data as Data import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from PIL import Image import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class ResidualBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, inchannel, outchannel, stride=1): super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__() self.left = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Conv2d(outchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel) ) self.shortcut = nn.Sequential() if stride != 1 or inchannel != outchannel: self.shortcut = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(inchannel, outchannel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannel) ) def forward(self, x): out = self.left(x) out += self.shortcut(x) out = F.relu(out) return out class ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, ResidualBlock, num_classes=10): super(ResNet, self).__init__() self.inchannel = 16 self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(16), nn.ReLU(), ) self.layer1 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 16, 2, stride=1) self.layer2 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 32, 2, stride=2) self.layer3 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 64, 2, stride=2) self.layer4 = self.make_layer(ResidualBlock, 128, 2, stride=2) self.fc = nn.Linear(128, num_classes) def make_layer(self, block, channels, num_blocks, stride): strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) #strides=[1,1] layers = [] for stride in strides: layers.append(block(self.inchannel, channels, stride)) self.inchannel = channels return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): out = self.conv1(x) out = self.layer1(out) out = self.layer2(out) out = self.layer3(out) out = self.layer4(out) out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 4) out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) out = self.fc(out) return out def ResNet18(): return ResNet(ResidualBlock) lr = 0.1 Epoch = 1 Batch_size = 20 if __name__ == "__main__": train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root='./MNIST', train=True, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() ) test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root='./MNISt', train=False, download=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() ) # define train loader train_loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=Batch_size ) test_loader = Data.DataLoader( dataset=test_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=Batch_size ) net=ResNet18() print(len(test_loader)) PATH ="./my_net.pth" net.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH)) test_correct = 0 test_total = 0 net.eval() for x, y in test_loader: y_pred = net(x) y_pred = torch.argmax(y_pred, dim=1) test_correct += (y_pred==y).sum().item() test_total += y.size(0) epoch_test_acc = test_correct / test_total print(epoch_test_acc)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
测试结果:

参考文献
ResNet及其变种的结构梳理、有效性分析与代码解读(PyTorch)
深度学习原理与框架-卷积网络细节-网络设计技巧 1. 3个3 * 3替换7 * 7卷积核 2. 1 * 1 和 3 * 3 替换 3 * 3卷积核
ResNet网络详解及Pytorch代码实现
-
相关阅读:
美国家安全局等发布安全部署人工智能系统指南
Node.js中的Buffer和Stream
ESP8266-Arduino网络编程实例-远程固件升级
Vue脚手架搭建及说明
Kubernetes(24):数据存储-高级存储PV和PVC
设计模式- 建造者模式(Builder Pattern)结构|原理|优缺点|场景|示例
消息队列MQ核心原理全面总结(11大必会原理)
csdn关注打开文章,自动取关脚本(设置为仅粉丝查看的文章)
JavaScript 49 JavaScript 作用域
C#里氏替换
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42888638/article/details/121843903
