-
python-opencv 图像处理基础 (九)图像梯度
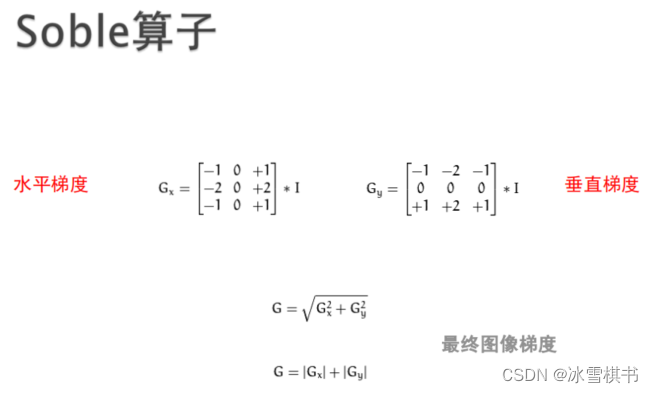
一阶导数与sobel算子
二阶导数与拉普拉斯算子
其它边缘算子—边缘检测、直线检测一阶导数与sobel算子
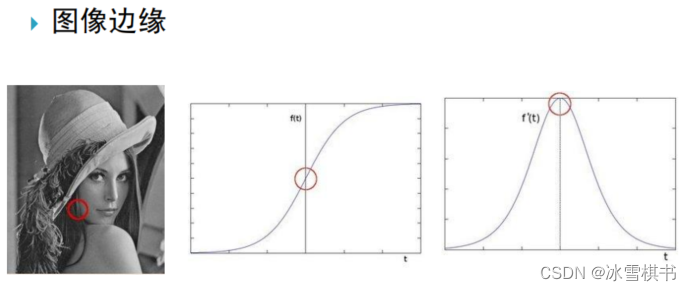
二阶导数和拉普拉斯算子
在二阶导数的时候,最大变化处的值为0即边缘是零值。通过二阶导数计算,依据此理论可以计算图像二阶导数,提取边缘。


import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def lapalian_demo(image): #第一种方法调用算子 #dst = cv.Laplacian(image, cv.CV_32F) #lpls = cv.convertScaleAbs(dst) #第二种方法手动实现 kernel = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [1, -8, 1], [1, 1, 1]])#定义卷积核 8邻域 还可以4邻域 dst = cv.filter2D(image, cv.CV_32F, kernel=kernel) lpls = cv.convertScaleAbs(dst) cv.imshow("lapalian_demo", lpls) def sobel_demo(image): # grad_x = cv.Sobel(image, cv.CV_32F, 1, 0)#32位float浮点数 不能使用8u 加加减减超256了。 # grad_y = cv.Sobel(image, cv.CV_32F, 0, 1) grad_x = cv.Scharr(image, cv.CV_32F, 1, 0) #Scharr边缘增强,对弱边缘梯度提取效果好 grad_y = cv.Scharr(image, cv.CV_32F, 0, 1) gradx = cv.convertScaleAbs(grad_x) grady = cv.convertScaleAbs(grad_y) cv.imshow("gradient-x", gradx) cv.imshow("gradient-y", grady) gradxy = cv.addWeighted(gradx, 0.5, grady, 0.5, 0) cv.imshow("gradient", gradxy) if __name__=='__main__': print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/lena.png") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) #sobel_demo(src) lapalian_demo(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
sobel_demo的result显示:
上下和左右的差异
x和y方向最终结果很好的反应了像素梯度变化差异 scharr 进行边缘增强后的梯度提取,提取弱边缘 ,噪声敏感,需要降噪
scharr 进行边缘增强后的梯度提取,提取弱边缘 ,噪声敏感,需要降噪
 拉普拉斯的结果输出:
拉普拉斯的结果输出:
直接调用算子的结果:

手动卷积实现的结果

其它边缘提取算子
canny边缘提取
canny:边缘检测算法,1986年提出的。
是一个很好的边缘检测器
很常用也很实用的图像处理方法步骤:
高斯模糊--GaussianBlur 为什么:因为canny对边缘噪声敏感 灰度转换--CVTColor 计算梯度--sobel/scharr 非最大信号抑制 高低阈值输出二值图像- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def edge_demo(image): blurred = cv.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 0) gray = cv.cvtColor(blurred, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # X Gradient xgrad = cv.Sobel(gray, cv.CV_16SC1, 1, 0) # Y Gradient ygrad = cv.Sobel(gray, cv.CV_16SC1, 0, 1) #edge #edge_output = cv.Canny(xgrad, ygrad, 50, 150) edge_output = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150) cv.imshow("Canny Edge", edge_output) dst = cv.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=edge_output) cv.imshow("Color Edge", dst) if __name__=='__main__': print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/lena.png") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) edge_demo(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
使用sobel的x和y梯度提取边缘

使用灰度图提取canny边缘:

霍夫直线检测
Hough Line Transform 用来做直线检测
前提条件:边缘检测已经完成
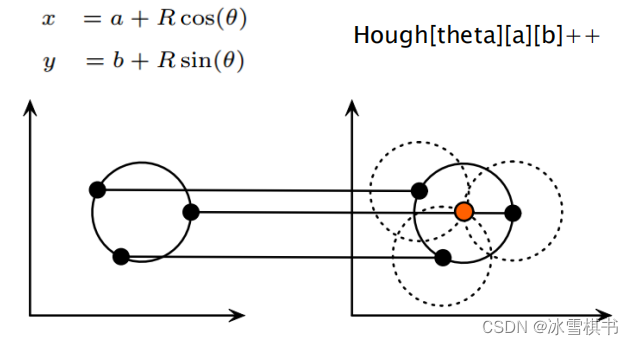
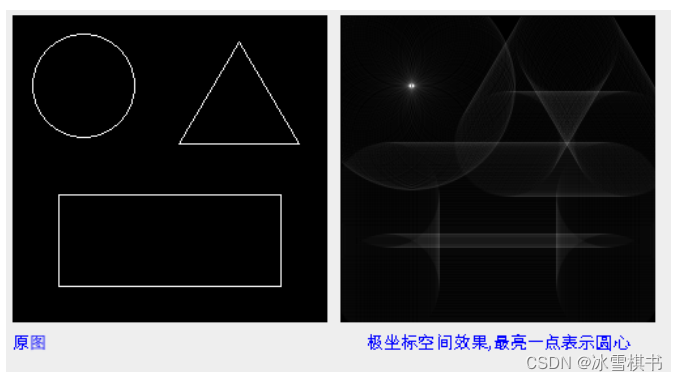
平面空间到极坐标空间转换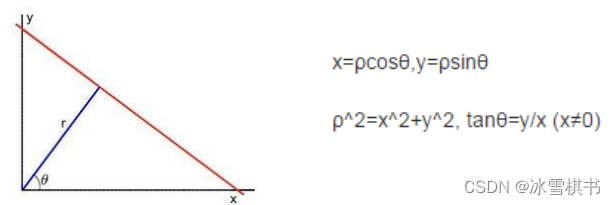
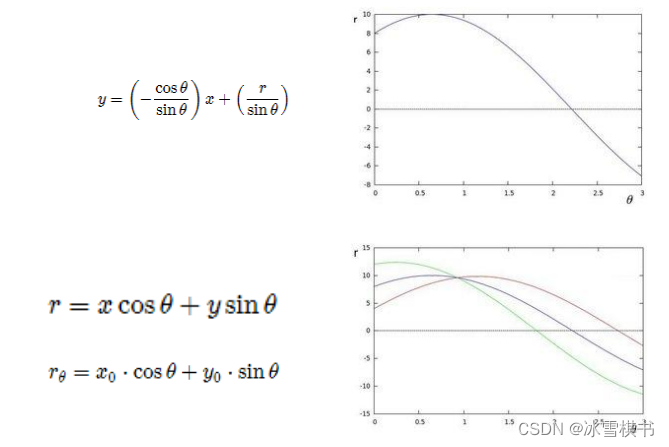
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def line_detection(image): gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) edges = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize=3)#做梯度窗口的大小是3. lines = cv.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 200) #1是半径步长,np.pi/180每次偏转1度, for line in lines: print(type(lines)) rho, theta = line[0] a = np.cos(theta) b = np.sin(theta) x0 = a * rho y0 = b * rho x1 = int(x0+1000*(-b)) y1 = int(y0+1000*(a)) x2 = int(x0-1000*(-b)) y2 = int(y0-1000*(a)) cv.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv.imshow("image-lines", image) def line_detect_possible_demo(image): gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) edges = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize=3) lines = cv.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi/180, 100, minLineLength=50, maxLineGap=10)#常用这个API,会告诉我们线段的开始点和终止点 for line in lines: print(type(line)) x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0] cv.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 2) cv.imshow("line_detect_possible_demo", image) if __name__=='__main__': print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/test.png") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) line_detect_possible_demo(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
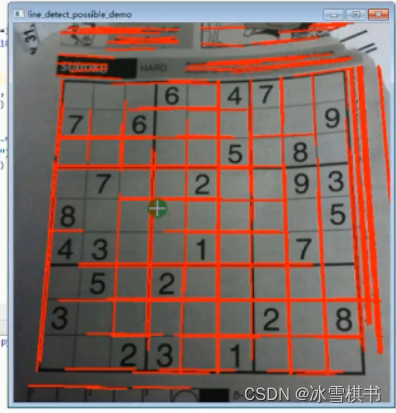
使用HoughLines函数的结果显示:
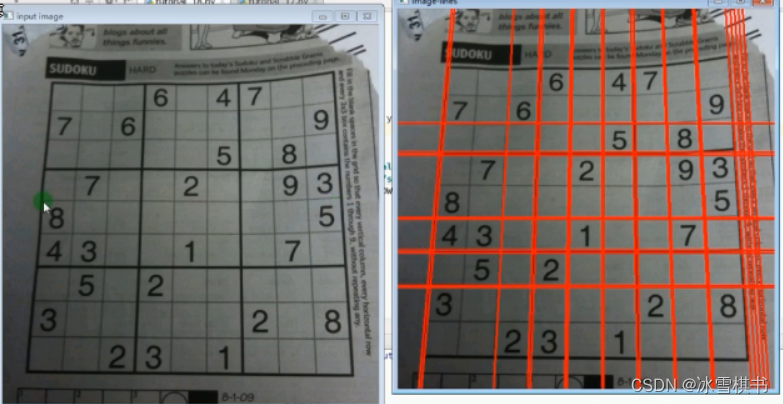
使用HoughLinesP 函数的结果显示:这个API常用。
霍夫圆检测

因为霍夫圆检测对噪声比较敏感,所以首先要对图像做中值滤波。
基于效率考虑,Opencv中实现的霍夫变换圆检测是基于图像梯度的实现,分为两步:- 检测边缘,发现可能的圆心
- 基于第一步的基础上从候选圆心开始计算最佳半径大小
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def detect_circles_demo(image): dst = cv.pyrMeanShiftFiltering(image, 10, 100)#基于边缘保留的滤波 cimage = cv.cvtColor(dst, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) circles = cv.HoughCircles(cimage, cv.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, 20, param1=50, param2=30, minRadius=0, maxRadius=0) circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))#整数 for i in circles[0, :]: cv.circle(image, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 0, 255), 2)#图像,中心点位置,半径,颜色,线宽 cv.circle(image, (i[0], i[1]), 2, (255, 0, 0), 2)#圆心 cv.imshow("circles", image) if __name__=='__main__': print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/coins.jpg") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) detect_circles_demo(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
代码结果显示:

霍夫圆检测的实例
钢管检测:个人总结
轮廓检测
轮廓发现
是基于图像边缘提取的基础寻找对象轮廓的方法。 所以边缘提取的阈值选定会影响最终轮廓发现结果- 1
- 2
API介绍
-findContours发现轮廓 -drawContours绘制轮廓- 1
- 2
API利用梯度来避免阈值烦恼
原图直接找轮廓有噪点:

高斯模糊去噪点dst = cv.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 0):

cv.RETR_TREE 内外轮廓都找(cv2.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE))
 cv.RETR_EXTERNAL找外轮廓cv2.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cv.RETR_EXTERNAL找外轮廓cv2.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)

填充轮廓cv.drawContours(image, contours, i, (0, 0, 255), -1)
 通过canny 获取轮廓:不是想要的结果,根据情况选择,这种硬币的轮廓提取使用二值化提取。
通过canny 获取轮廓:不是想要的结果,根据情况选择,这种硬币的轮廓提取使用二值化提取。 以下示例使用canny获取轮廓效果好:适当调整canny的参数
以下示例使用canny获取轮廓效果好:适当调整canny的参数
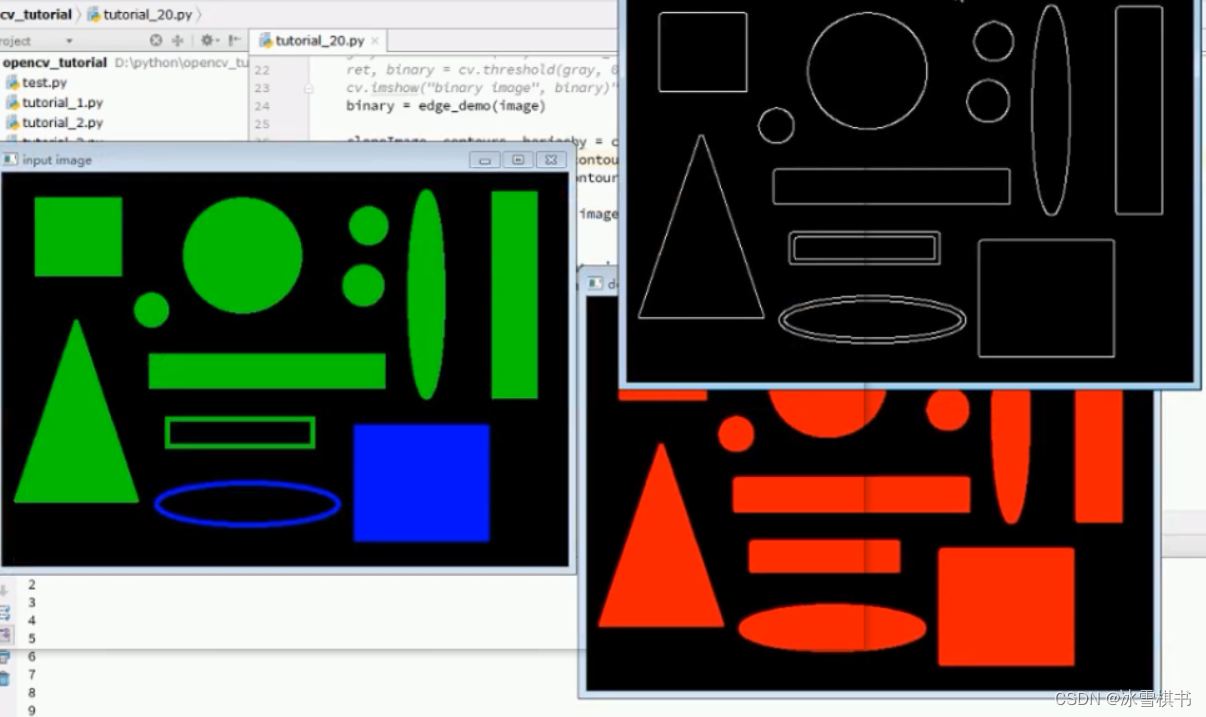
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np def edge_demo(image): blurred = cv.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 0) gray = cv.cvtColor(blurred, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # X Gradient xgrad = cv.Sobel(gray, cv.CV_16SC1, 1, 0) # Y Gradient ygrad = cv.Sobel(gray, cv.CV_16SC1, 0, 1) #edge #edge_output = cv.Canny(xgrad, ygrad, 50, 150) edge_output = cv.Canny(gray, 50, 150) cv.imshow("Canny Edge", edge_output) return edge_output def contours_demo(image): #第一种方法获取二值图像 #dst = cv.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 0)#去除噪点 #gray = cv.cvtColor(dst, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #ret, binary = cv.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY | cv.THRESH_OTSU) #cv.imshow("binary image", binary) #第二种方法通过canny 获取二值图像 binary = edge_demo(image) #cloneImage, contours, heriachy = cv.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) #contours, heriachy = cv.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)#内外的轮廓都找 contours, heriachy = cv.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)#找外面的轮廓 for i, contour in enumerate(contours): #cv.drawContours(image, contours, i, (0, 0, 255), 2)# cv.drawContours(image, contours, i, (0, 0, 255), -1)#轮廓填充 print(i) cv.imshow("detect contours", image) if __name__=='__main__': print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/coins.jpg") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) contours_demo(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
对象测量
- 弧长与面积
轮廓发现
计算每个轮廓的弧长和面积,像素单位 - 多边形拟合
- 几何矩计算
import cv2 as cv import numpy as np #轮廓分析 计算轮廓面积和轮廓几何 #区分不同的几何形状,圆形 四边形等 def measure_object(image): image = cv.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 0) gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #ret, binary = cv.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY | cv.THRESH_OTSU)# ret, binary = cv.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv.THRESH_OTSU)#取反 print("threshold value : %s"%ret) cv.imshow("binary image", binary) dst = cv.cvtColor(binary, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) contours, hireachy = cv.findContours(binary, cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) for i, contour in enumerate(contours): area = cv.contourArea(contour)#求轮廓的面积,得到第几个轮廓的面积 x, y, w, h = cv.boundingRect(contour)#轮廓的外接矩形的大小, rate = min(w, h)/max(w, h) print("rectangle rate : %s"%rate) mm = cv.moments(contour)#得到contour的几何矩 print(type(mm))#dict字典类型 cx = mm['m10']/mm['m00'] cy = mm['m01']/mm['m00'] cv.circle(dst, (np.int(cx), np.int(cy)), 3, (0, 255, 255), -1) cv.rectangle(dst, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 0, 255), 2)#每个轮廓绘制外接矩形 print("contour area %s"%area) approxCurve = cv.approxPolyDP(contour,4, True)#对指定的点集进行逼近 找出轮廓的多边形拟合曲线 print(approxCurve.shape) if approxCurve.shape[0] > 6: cv.drawContours(dst, contours, i, (0, 255, 0), 2) if approxCurve.shape[0] == 4: cv.drawContours(dst, contours, i, (0, 0, 255), 2) if approxCurve.shape[0] == 3: cv.drawContours(dst, contours, i, (255, 0, 0), 2) cv.imshow("measure-contours", dst) print("--------- Python OpenCV Tutorial ---------") src = cv.imread("../opencv-python-img/coins.jpg") cv.namedWindow("input image", cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv.imshow("input image", src) measure_object(src) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllWindows()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
-
相关阅读:
ElasticSearch集群搭建及启动异常的问题
概率论与数理统计(第一章 概率论的基本概念)
Cadence 设计快速入门
Java发起Soap请求
PMP 项目质量管理
Qt SQL:QSqlRelation、QSqlRelationalTableModel、QSqlRelationalDelegate
【HTML】操作表格
Pytorch框架学习记录5——DataLoader的使用
如何优化工业5G网关的网络信号
场景GIT
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/zml194849/article/details/126525333
