-
Spring常见问题解决 - @PathVariable 解析带 / 的参数值报404
Spring常见问题解决 - @PathVariable 解析带 / 的参数值报404
一. @PathVariable 遇到 / 无法解析
Spring的Web开发过程中,我们往往使用@PathVariable注解来获取URL上指定的值。例如:@Controller public class MyController { @GetMapping("/hello/{name}") @ResponseBody public String hello(@PathVariable("name") String name) { return Math.random() + "name: " + name; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
访问对应的路径进行测试:
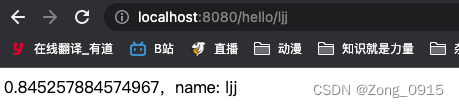
可见,程序自动识别到了我们的name变量,并将其值赋值给了对应的变量,然后输出到页面中。但是,假如我们对这个变量添加一个特殊字符,看看效果会怎么样。1.1 案例复现
第一种:
http://localhost:8080/hello/ljj/,结果如下:
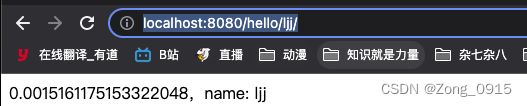
第二种:
http://localhost:8080/hello/ljj/hello,结果如下:
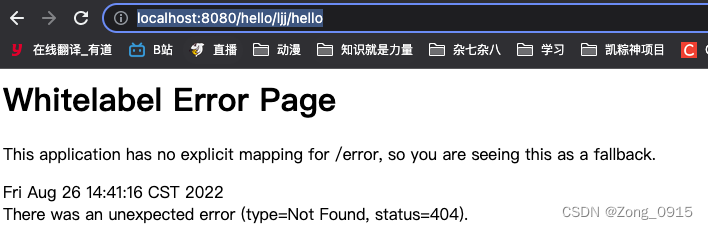
1.2 原理分析
Spring中,对于URL的解析工作,交给AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.lookupHandlerMethod()来完成:public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>(); // 1.根据URL进行精确匹配 List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath); if (directPathMatches != null) { // 做一个缓存记录 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); } if (matches.isEmpty()) { // 遍历所有映射,根据请求来进行模糊匹配 addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request); } if (!matches.isEmpty()) { Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); // 如果匹配结果有多个,那么可以进行筛选 if (matches.size() > 1) { // ... } request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod); handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); return bestMatch.handlerMethod; } else { // 匹配不上,报错 return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1.2.1 精准匹配
对应的代码:
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);- 1
此时我们的
lookupPath就是我们的URL,例如:
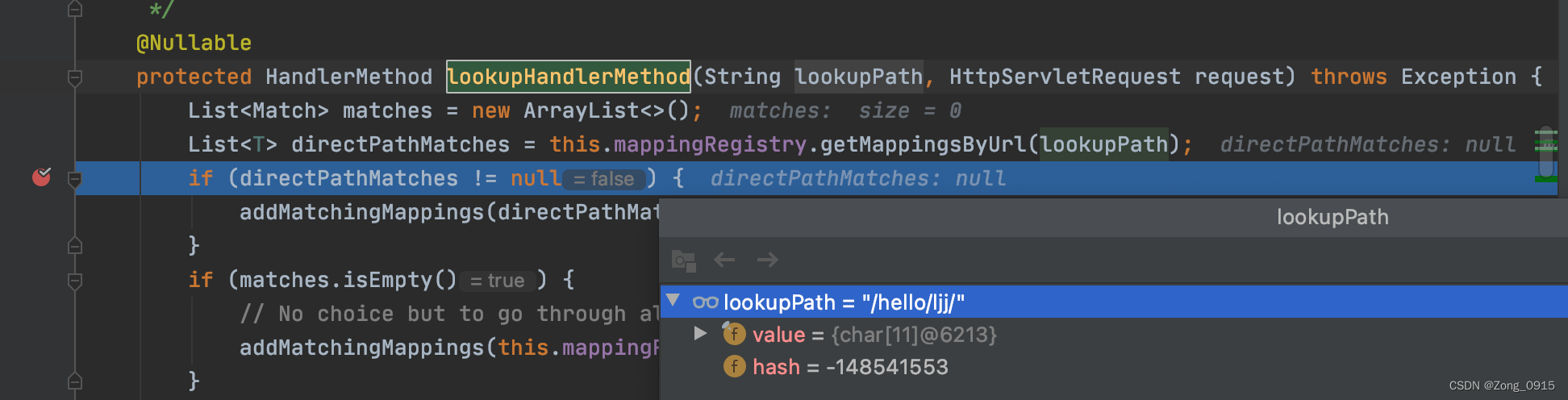
我们跟进去这个函数:@Nullable public List<T> getMappingsByUrl(String urlPath) { return this.urlLookup.get(urlPath); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
此时
this.urlLookup中并没有我们访问的URL路径:
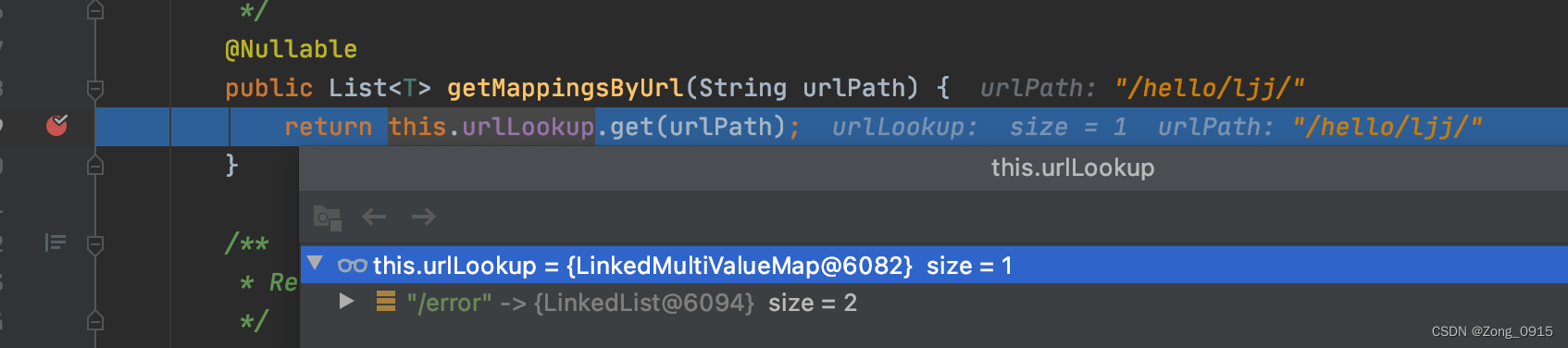
那么此时精确匹配出来的结果就是null,因此根据代码逻辑,需要在进行一次模糊匹配过程。1.2.2 模糊匹配
这段逻辑对应代码:
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);- 1
我们先来看下
getMappings()里面的东西是啥:
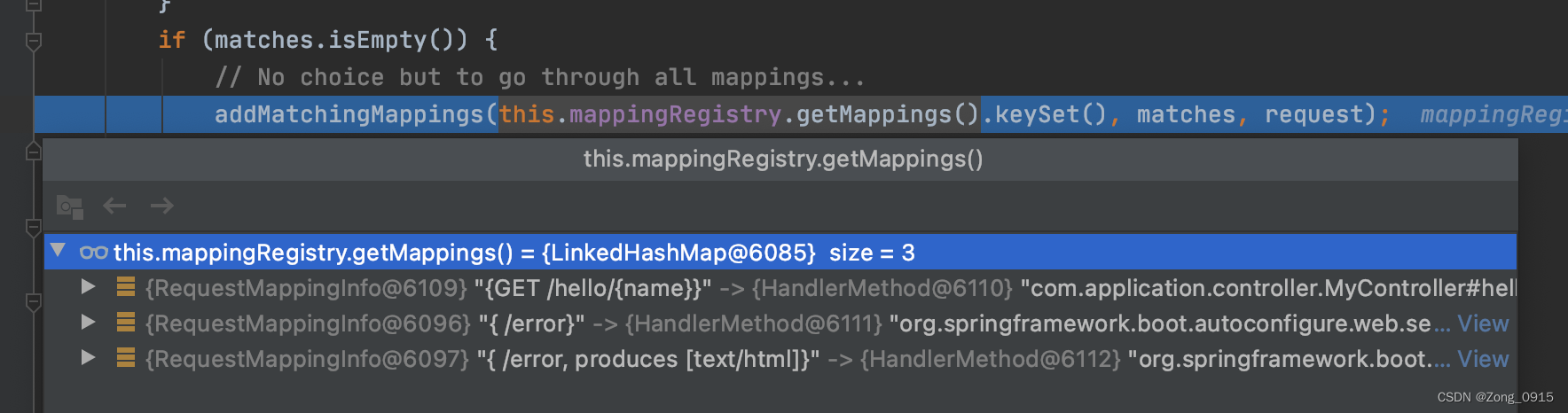
首先明确的是,我们的/hello/{name}已经在待匹配的候选列表中了。那么具体是如何匹配的呢?我们跟进代码:private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) { for (T mapping : mappings) { T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request); if (match != null) { matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping))); } } } public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> { @Override protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) { return info.getMatchingCondition(request); } public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) { RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (methods == null) { return null; } ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (params == null) { return null; } HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (headers == null) { return null; } ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (consumes == null) { return null; } ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (produces == null) { return null; } PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request); if (patterns == null) { return null; } RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request); if (custom == null) { return null; } return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns, methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
到这里我们可以看到,具体匹配的时候,会查到当前请求的所有相关信息,例如:请求头、参数、请求类型等。如果有一项不匹配,就直接提前返回
null。当然,还会匹配这个请求的Pattern。以我们的案例http://localhost:8080/hello/ljj/为例:
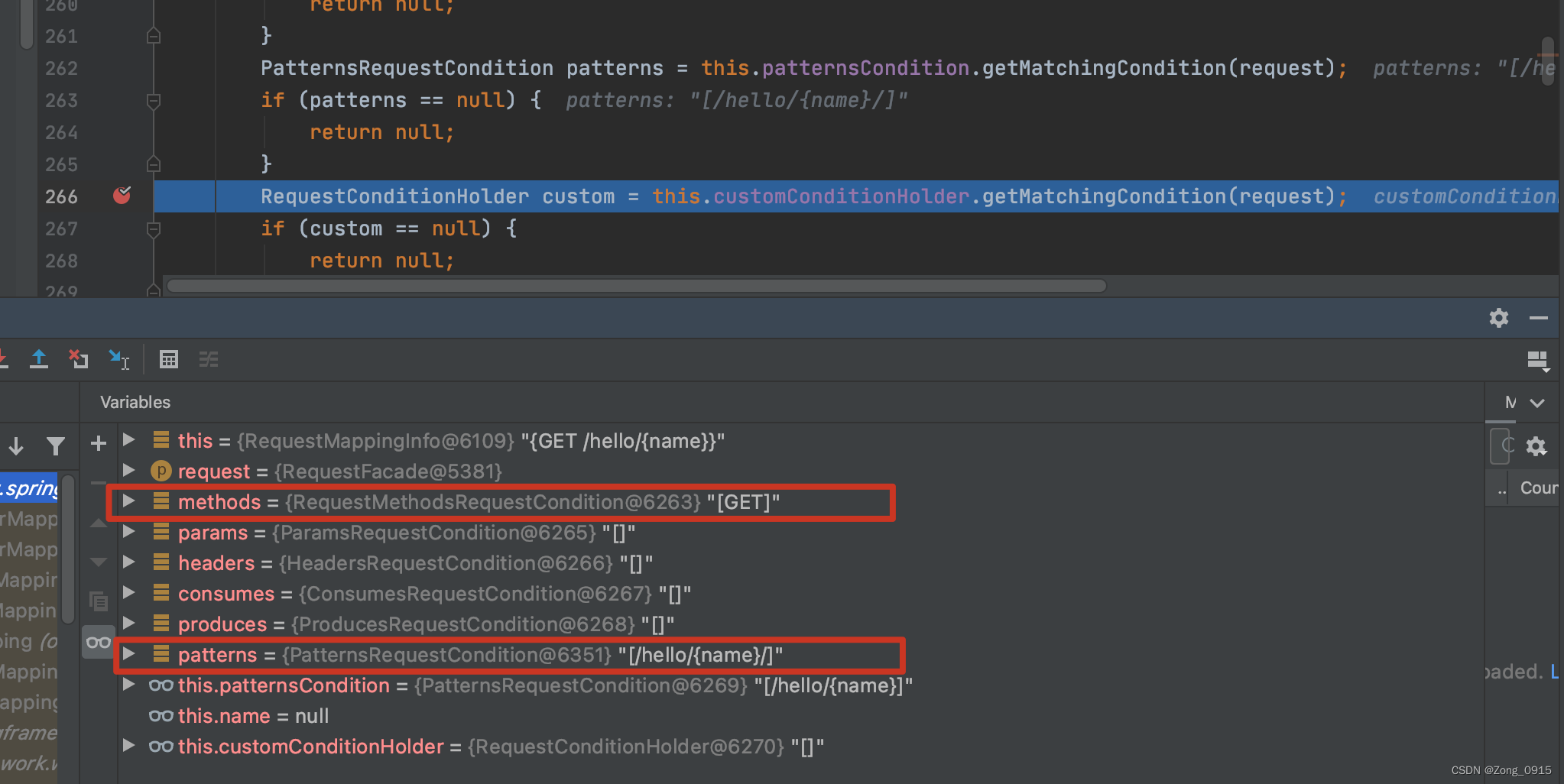
那么也就是说,最终的匹配肯定看的是下述这段代码是否能够成功匹配到:PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);- 1
那么如果我们访问
http://localhost:8080/hello/ljj/hello,将会在patterns的校验上提前返回:
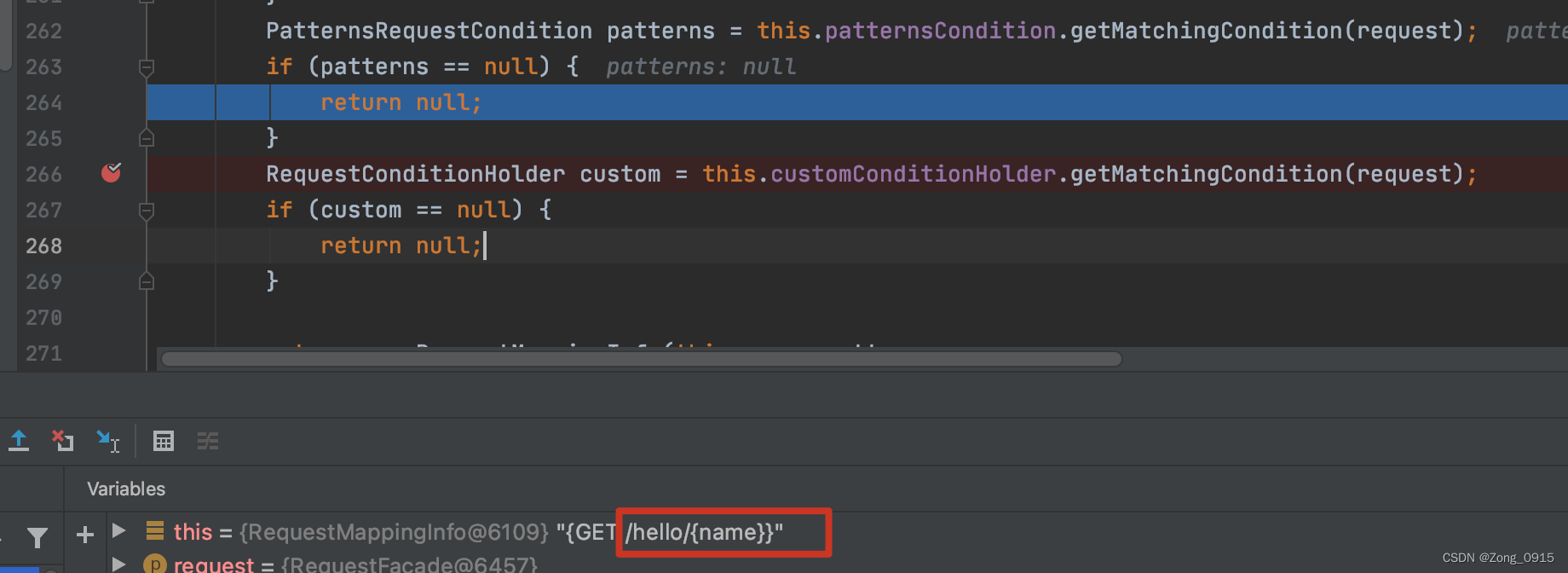
那么为何
ljj/就可以正常访问呢?我们跟进下getMatchingCondition函数,最终会走到public class PatternsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<PatternsRequestCondition> { private String getMatchingPattern(String pattern, String lookupPath) { // .. if (this.useTrailingSlashMatch) { if (!pattern.endsWith("/") && this.pathMatcher.match(pattern + "/", lookupPath)) { return pattern + "/"; } } return null; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
说白了,
Spring会尝试在URL的末尾加一个/然后在进行匹配,如果能匹配上,在最终返回Pattern时就隐式自动上一个加/。二. 解决
既然
Spring中的URL匹配,是根据Pattern来进行的,那么我们可以使用*去进行匹配。然后手动获取URL,通过split去进行分割取值。 同时要考虑到前缀重复的情况(即name的值依旧包含了相同的前缀)。@Controller public class MyController { private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(); @GetMapping("/hello/**") @ResponseBody public String hello(HttpServletRequest request) { String path = (String) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE); String matchPattern = (String) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE); String res = antPathMatcher.extractPathWithinPattern(matchPattern, path); return Math.random() + ",name: " + res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
结果如下:
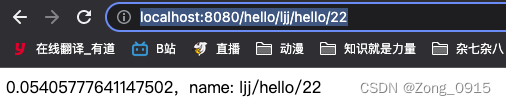
当然,最好的解决方案就是在使用URL上进行动态传承的同时,避免参数值带有/这样的特殊字符。 -
相关阅读:
华为OD机考算法题:TLV解码
MySQL数据库备份
华为机试 - 最长连续子序列
常见vue问题
无序列表 – ul - li
猿创征文| redis基本数据类型
数据科学中的数据库简介
绘画的颜料
Pinia中如何实现数据持久化操作
初识reactor响应式编程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Zong_0915/article/details/126542952
