-
C++ 之 perf+火焰图分析与Debug
0. 简介
在遇到一些内存异常的时候,经常这部分的代码是很难去进行分析的,之前作者就专门写过两篇博客(Ubuntu环境下便于调试代码的工具、Valgrind对ROS程序的可视化分析)来介绍性能分析的问题,最近了解到Perf这个神器,这里也展开介绍一下如何使用Perf以及如何去画火焰图。
1. Perf 基础
1.1 Perf 简介
perf是Linux下的一款性能分析工具,能够进行函数级与指令级的热点查找。利用perf剖析程序性能时,需要指定当前测试的性能时间。性能事件是指在处理器或操作系统中发生的,可能影响到程序性能的硬件事件或软件事件
1.2 Perf的安装
ubuntu 18.04:
sudo apt install linux-tools-common linux-tools-4.15.0-106-generic linux-cloud-tools-4.15.0-106-generic- 1
1.3 perf命令简要介绍
perf list
perf list主要是用于列出有哪些可用的event,可以供perf top -e eventname来分析。
perf list [hw|sw|cache|tracepoint|pmu|event_glob],其中perf list hw可以列出 hard ware 的event, sw 是software的event, 其它类似。hw/hardware显示支持的硬件事件相关,如: perf list hardware
sw/software显示支持的软件事件列表: perf list sw
cache/hwcache显示硬件cache相关事件列表: perf list cache
pmu显示支持的PMU事件列表: perf list pmu
tracepoint显示支持的所有tracepoint列表,这个列表就比较庞大: perf list tracepoint$ perf list hw $ perf list sw cpu-clock [Software event] task-clock [Software event] page-faults OR faults [Software event] context-switches OR cs [Software event] cpu-migrations OR migrations [Software event] minor-faults [Software event] major-faults [Software event] alignment-faults [Software event] emulation-faults [Software event] dummy [Software event] $ perf list pmu $ perf list event_glob- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
perf top
perf top的作用是实时显示系统/进程的性能统计信息,上面的
perf list [hw|sw...]可以知道所有的 tracepoint events, 接下来我们就可以使用perf top -e tracepoint-event来专门获得指定的tracepoint的信息。其中常用的常用参数有-e:指定性能事件
-a:显示在所有CPU上的性能统计信息
-C:显示在指定CPU上的性能统计信息
-p:指定进程PID
-t:指定线程TID
-K:隐藏内核统计信息
-U:隐藏用户空间的统计信息
-s:指定待解析的符号信息
‘‐G’ or‘‐‐call‐graph’perf top -e cpu-clock: 查看CPU的使用

perf top -p 28764:查看对应PID的使用
注: p e r f − t o p 需要 r o o t 权限 \color{red}{注: perf -top需要root权限} 注:perf−top需要root权限
perf stat
启动应用程序并分析该程序完整生命周期的性能状况。虽然
perf top也可以指定pid,但是对于perf top而言必须先启动应用才能查看信息。perf stat能够运行指令,并且能完整统计应用整个生命周期的信息。其中默认统计8种event在程序运行过程中的计数,如下所示。也可以使用-e选项来自定义使用的event。task‐clock事件表示目标任务真正占用处理器的时间,单位是毫秒。也称任务执行时间
context-switches是系统发生上下文切换的次数
CPU-migrations是任务从一个处理器迁往另外一个处理器的次数
page-faults是内核发生缺页的次数
cycles是程序消耗的处理器周期数
instructions是指命令执行期间产生的处理器指令数
branches是指程序在执行期间遇到的分支指令数。
branch‐misses是预测错误的分支指令数。
XXX seconds time elapsed系程序持续时间
任务执行时间/任务持续时间大于1,那可以肯定是多核引起的$ sudo perf stat cp -r ~/test test.bak Performance counter stats for 'cp -r /home/test test.bak': 268.941065 task-clock (msec) # 0.688 CPUs utilized 764 context-switches # 0.003 M/sec 0 cpu-migrations # 0.000 K/sec 158 page-faults # 0.587 K/sec <not supported> cycles <not supported> instructions <not supported> branches <not supported> branch-misses 0.390780362 seconds time elapsed- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
参数设置:
-e:选择性能事件
-i:禁止子任务继承父任务的性能计数器。
-r:重复执行 n 次目标程序,并给出性能指标在n 次执行中的变化范围。
-n:仅输出目标程序的执行时间,而不开启任何性能计数器。
-a:指定全部cpu
-C:指定某个cpu
-A:将给出每个处理器上相应的信息。
-p:指定待分析的进程id
-t:指定待分析的线程idperf record&perf report
使用
perf record和perf report命令来进行更详细的分析:perf stat命令只能记录event发生的次数,perf record在此基础之上可以记录event发生时详细的数据(比如IP、堆栈等等)。可以自定义需要记录的event,可以自定义记录数据的格式。
perf record可以记录一段时间内系统/进程的性能时间,具体参数为:-e:选择性能事件
-p:待分析进程的id
-t:待分析线程的id
-a:分析整个系统的性能
-C:只采集指定CPU数据
-c:事件的采样周期
-o:指定输出文件,默认为perf.data
-A:以append的方式写输出文件
-f:以OverWrite的方式写输出文件
-g:记录函数间的调用关系
-F:采样评率,采样频率建议在4000以内,避免造成太多开销perf report可以读取perf record生成的数据文件,并显示分析数据参数-i:输入的数据文件
-v:显示每个符号的地址
-d :只显示指定dos的符号
-C:只显示指定comm的信息(Comm. 触发事件的进程名)
-S:只考虑指定符号
-U:只显示已解析的符号
-g[type,min,order]:显示调用关系,具体等同于perf top命令中的-g
-c:只显示指定cpu采样信息
-M:以指定汇编指令风格显示 –source:以汇编和source的形式进行显示
-p:用指定正则表达式过滤调用函数性能调优时,我们通常需要分析查找到程序百分比高的热点代码片段,这便需要使用
perf record记录单个函数级别的统计信息,并使用perf report来显示统计结果;首先我们用以下命令模拟出CPU利用率暴涨的现象:
$ cat /dev/zero > /dev/null- 1
然后我们看到 CPU 1 的 %system 飙升到95%:
$ sar -P ALL -u 2 2 08:21:16 PM CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle 08:21:18 PM all 2.25 0.00 48.25 0.00 0.00 49.50 08:21:18 PM 0 0.50 0.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 98.51 08:21:18 PM 1 4.02 0.00 95.98 0.00 0.00 0.00- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
现在我们用 perf 工具采样:
$ perf record -a -e cycles -o cycle.perf -g sleep 10 [ perf record: Woken up 18 times to write data ] [ perf record: Captured and wrote 4.953 MB cycle.perf (~216405 samples) ]- 1
- 2
- 3
把采样的数据生成报告:
# perf report -i cycle.perf | more ... # Samples: 40K of event 'cycles' # Event count (approx.): 18491174032 # # Overhead Command Shared Object Symbol # ........ ............... .............................. ................ # 75.65% cat [kernel.kallsyms] [k] __clear_user | --- __clear_user | |--99.56%-- read_zero | vfs_read | sys_read | system_call_fastpath | __GI___libc_read --0.44%-- [...] 2.34% cat [kernel.kallsyms] [k] system_call | --- system_call | |--56.72%-- __write_nocancel | --43.28%-- __GI___libc_read ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
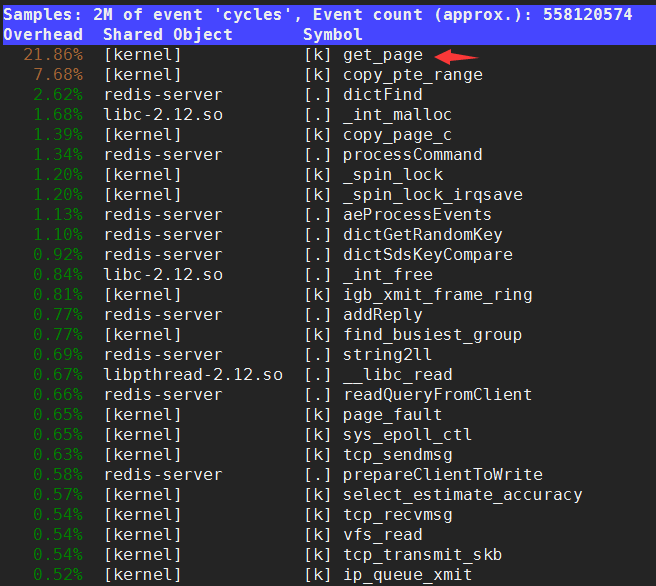
我们很清楚地看到,CPU利用率有75%来自 cat 进程 的 sys_read 系统调用,perf 甚至精确地告诉了我们是消耗在 read_zero 这个 kernel routine 上。
值得说明的是
perf record默认只使用了1种eventcpu-clock,cpu-clock使用的是高精度定时器来进行定时采样。perf record默认数据输出文件为perf.data。2. 火焰图
2.1 火焰图简介
火焰图(Flame Graph)是由Linux性能优化大师Brendan Gregg发明的,Flame Graph以一个全局的视野来看待时间分布,它从底部往顶部,列出所有可能的调用栈。其他的呈现方法,一般只能列出单一的调用栈或者非层次化的时间分布。
2.2 火焰图含义:
-
y 轴表示调用栈, 每一层都是一个函数. 调用栈越深, 火焰就越高, 顶部就是正在执行的函数, 下方都是它的父函数.
-
x 轴表示抽样数, 如果一个函数在 x 轴占据的宽度越宽, 就表示它被抽到的次数多, 即执行的时间长. 注意, x 轴不代表时间, 而是所有的调用栈合并后, 按字母顺序排列的。
-
火焰图就是看顶层的哪个函数占据的宽度最大. 只要有 “平顶”(plateaus), 就表示该函数可能存在性能问题。
-
颜色没有特殊含义, 因为火焰图表示的是 CPU 的繁忙程度, 所以一般选择暖色调.
2.3 火焰图安装
安装FlameGraph
wget https://github.com/brendangregg/FlameGraph/archive/master.zip unzip master.zip sudo mv FlameGraph-master/ /opt/FlameGraph- 1
- 2
- 3
添加到bashrc环境变量
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/FlameGraph- 1
查找程序的pid
$ ps -aux|grep vins nobody 2233 0.2 0.0 19208 4000 pts/37 S 15:35 0:10 /home/name/vins core /tmp client-core-puux8w0hdr7y5kdq9u12qqz7s7cgw5- 1
- 2
- 3
火焰图生成脚本
#!/bin/sh if [ $# -lt 1 ]; then echo 'input pid' exit 1 fi rm -f perf.* perf record -F 99 -p $1 -g -o in-fb.data -- sleep 60 # 首先使用99HZ的采样频率,对pid为$1的进程进行采样,采样输出到in-fb.data中,采样时长为60秒 perf script -i in-fb.data &> perf.unfold stackcollapse-perf.pl perf.unfold &> perf.folded flamegraph.pl perf.folded > perf.svg- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
然后启动bash文件并传入pid
sh fire.sh 2233- 1
…详情请参照古月居
-
相关阅读:
DAO:Web3 的必要组件
数据中台项目前期总结
【Axios学习 二】一文通透Axios跨域和封装
parallels desktop 19密钥分享 附PD虚拟机安装教程 支持M/intel
系统部署常用操作_查看硬盘大小_查看内存情况_查看某个端口是否被占用_telnet_远程scp复制拉取---Linux运维工作笔记055
PHP 接入 Apple 登录对 identityToken 验证
Python Flask Web开发一:环境搭建
3. hdfs概述与高可用原理
Maven 换源 & Mybatis 开启 Log4j 日志框架
Bean的循环依赖问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lovely_yoshino/article/details/125820272
