-
基于boost/beast/实现HTTP client,完成从HTTP Server下载文件
一.引言
1.1 内容介绍
为了实现客户端向服务端请求下载文件,本文基于HTTP协议实现了文件下载的客户端(c++基于boost/beast/http库)与服务端(python)程序,并且给出了两种下载方式:
- 客户端直接下载文件,不对文件下载的正确性做判断;
- 客户端对下载的文件做md5运算,并且与server下发的值作比较,以此来判断文件的正确性。
1.2 应用场景
- 文件下载;
- 执行程序在线更新;
- 证书颁发(考虑基于https或websockets协议)。
1.3 boost/beast库介绍
Beast是Boost中关于http(s)/websocket(s)的库,首发于boost 1.66(2016年),是比较新的库,它主要包含了http、websocket协议的解析(反序列化)和封装(序列化)以及关于网络的操作,它以asio为基础,但似乎又想隔离Asio。
http、websocket仅涉及tcp,因此在beast范围内,也仅涉及tcp协议,Beast的网络操作基于Asio,但Beast的一个目标似乎是做一个完整的系统(猜测),因此beast将涉及到的网络数据操作都“重写”的一遍(一些是简单包装,一些是扩展),例如Asio空间被重新命名为net,对std:bind也扩展为bind_handler和bind_front_handler。
beast设计了两套stream,一是用于http的tcp_stream,另一个是用于websocket的stream,它们之间没有直接关系,tcp_stream的相关定义如下:template< class Protocol, class Executor = net::executor,class RatePolicy = unlimited_rate_policy> class basic_stream using tcp_stream = basic_stream< net::ip::tcp, net::executor, unlimited_rate_policy >;- 1
- 2
- 3
从实现上看,beast并没有利用asio中的streambuf,而是采用其中的概念,与buffer类结合,重新写了一大套接收/发送操作,与Asio中类似。
在实现websocket时,beast作者试图体现网络分层的概念,采用get_lowest_layer(),get_next_layer()来获得更下层的实现类,websocket中的stream定义如下:template< class NextLayer, bool deflateSupported> class stream- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
其中deflateSupported是websocket协议扩展,表示是否支持报文压缩,如果定义一个ws流:
websocket::stream< boost::beast::tcp_stream > ws(ioc);- 1
则上面那个ws的next layer就是boost::beast::tcp_stream。同样,beast重新写了一大套接收/发送操作。实际上,在basic_stream的实现代码中也可看到类似layer的身影,但并没有在文档中出现,猜测作者认为还不成熟,暂且在websocket中实验,估计在以后的版本中,网络分层的概念的会被强化。
小结:
-
Beast运用了boost的很多东西,很好地运用了template的特性,但使得学习成本高,看一个东西牵扯其他很多东西,对库的开发者来说,这不是问题,但对普通应用者来说,就是大问题。
-
作为偏向协议解析的库,Beast涉及很多网络操作,反而显得与协议解析部分绑定的较紧,例如: read(stream, buffer, request);
这样的功能感觉上分两步更灵活:read stream into buffer和 parse buffer into request,其中第一步由Asio或其他别的网络库来完成(以目前的实现,如果不采用Asio,真不知如何)。Beast中提供的API,涉及网络及相关的操作不算少数,并且提出了next layer, decorator等概念,目标比较宏大,但却有点偏离协议解析这个最基本的目标。实际的应用中,离不开诸如url encode,querystring parsing等功能,做web服务器应用时,还需要url routing,这些实用的功能,beast反而没有提供,所以有时会迷惑,beast到底定位成什么库呢。 -
TCP数据就是流式数据,无论request还是response都是char序列(流),如果细分,还可以是text流或binary流,接收和发送由网络库负责,接收到时,由request卸载;发送前由response装载,负荷是其他具体类型类(与协议对应)的deserialization /serialization,以上是通常的思路,beast将类型确定提前了,由类型类才能构造出request/response,这种思路是否更好,见仁见智吧,但使用beas写代码时,应该适应这种思路。
-
Beast提供了协议解析的一些新思路,形式的优美与运行的高效之间如何平衡,作为库作者,一般是强调前者,作为项目的作者,则一般强调后者。希望beast能找到一个兼容的方案。
-
Asio已发展了若干版本,从每次boost版本的更新文档中,都可以看到Asio每次不断的努力,beast定位比较宏大,感觉还有很长的路走。
二.基于boost/beast库的http client端代码实现
2.1 仅文件传输
2.1.1 http server端程序
httpserver.py
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler data = {'result': 'this is a test'} host = ('localhost', 80) # http server监听ip和端口 class Resquest(BaseHTTPRequestHandler): timeout = 5 server_version = "Apache" def do_GET(self): self.send_response(200) self.send_header("Content-type","text/plain") # 设置服务器响应头,返回内容类型为纯文本类型 self.end_headers() file_path = self.path # 获取GET请求的URL print("reuqest file path: ",file_path) with open(file_path, encoding='utf-8') as file_obj: file_contents = file_obj.read().rstrip() # 获取文件内容并存在file_contents中 print("reuqest file contents: \n",file_contents) self.wfile.write(file_contents.encode()) # 里面需要传入二进制数据,用encode()函数转换为二进制数据 print("文件发送完成") # buf = ''' # # #Get page # # # # username:
# password:
# # # # ''' # self.wfile.write(buf.encode()) # 里面需要传入二进制数据,用encode()函数转换为二进制数据 # # 设置响应body,即前端页面要展示的数据 def do_POST(self): path = self.path print(path) # 获取post提交的数据 datas = self.rfile.read(int(self.headers['content-length'])) #固定格式,获取表单提交的数据 # datas = urllib.unquote(datas).decode("utf-8", 'ignore') self.send_response(200) self.send_header("Content-type","text/html") #设置post时服务器的响应头 self.send_header("test","This is post!") self.end_headers() html = '''Post page Post Data:%s
Path:%s ''' %(datas,self.path) self.wfile.write(html.encode()) #提交post数据时,服务器跳转并展示的页面内容 if __name__ == '__main__': server = HTTPServer(host, Resquest) print("Starting http file server, listen at: %s:%s" % host) server.serve_forever()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
2.1.2 http client端程序
mian.cpp
#include#include #include "httpclient.hpp" int main(int argc,char** argv) { std::string http_host_ip = "127.0.0.1"; // http文件服务器ip,host默认是80(可在connect函数中改端口) std::string remote_file_path = "/opt/test.json"; // 远端文件路径 std::string local_file_path = "/opt/http/test.json"; // 本地文件路径 //从remote_file_path下载文件到local_file_path cloud::downloader::download(http_host_ip, remote_file_path, local_file_path); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
httpclient.hpp
#ifndef __HTTPCLIENT_HPP__ #define __HTTPCLIENT_HPP__ #include#include #include #include #include namespace cloud { constexpr const char* HOST = "127.0.0.1"; /** * @brief 1.Http file downloader:Http文件下载器 */ class downloader { private: using string = std::string; using io_context = boost::asio::io_context; using tcp = boost::asio::ip::tcp; static tcp::socket connect(io_context& io, const string& host); public: static void download(const string& host, const string& path, const string& target); }; } // namespace cloud #endif - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
httpclient.cpp
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include "httpclient.hpp" using namespace std; using json = nlohmann::json; namespace asio = boost::asio; namespace http = boost::beast::http; namespace cloud { /** * @brief Create tcp socket and connect * @param[in] io The asio io context * @param[in] host The server host * @return Return the connected tcp socket */ downloader::tcp::socket downloader::connect(io_context& io, const string& host) { tcp::socket socket(io); tcp::resolver resolver(io); tcp::resolver::query query(host, "80"); asio::connect(socket, resolver.resolve(query)); return socket; } /** * @brief Http file download * @param[in] host The http server's host * @param[in] path The file path on server * @param[in] target Target local file path * @return None */ void downloader::download(const string& host, const string& path, const string& target) { std::cout << "[downloader] download from <" << host + ":" + path << "> to <" << target << ">" <<std::endl; std::cout << "[downloader] try connect to http file server"<<std::endl; asio::io_context io; //与remote file server建立连接,参数为:host==127.0.0.1:80(HTTP port默认为80) tcp::socket socket = downloader::connect(io, host); std::cout << "[downloader] http connect established"<<std::endl; //! Http request send http::request<http::string_body> req(http::verb::get, path, 11); req.set(http::field::host, host); http::write(socket, req); std::cout << "[downloader] Http request send seccess"<<std::endl; // ! Http response get boost::beast::flat_buffer buffer; http::response_parser<http::file_body> res; boost::beast::error_code ec; res.get().body().open(target.c_str(), boost::beast::file_mode::write, ec); res.body_limit(std::numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max()); std::cout << "[downloader] download starting"<<std::endl; http::read(socket, buffer, res); std::cout << "[downloader] file received done"<<std::endl; } } // namespace cloud - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
2.1.3 编译 & 执行
http server端启动:
python3 httpserver.py
http client端编译:
g++ main.cpp httpclient.cpp -lboost_system -lpthread
http client端启动:
./a.out
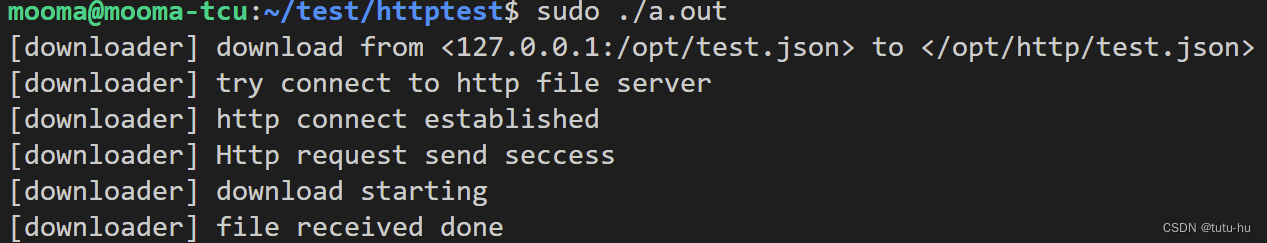
2.1.4 执行结果
http server端:
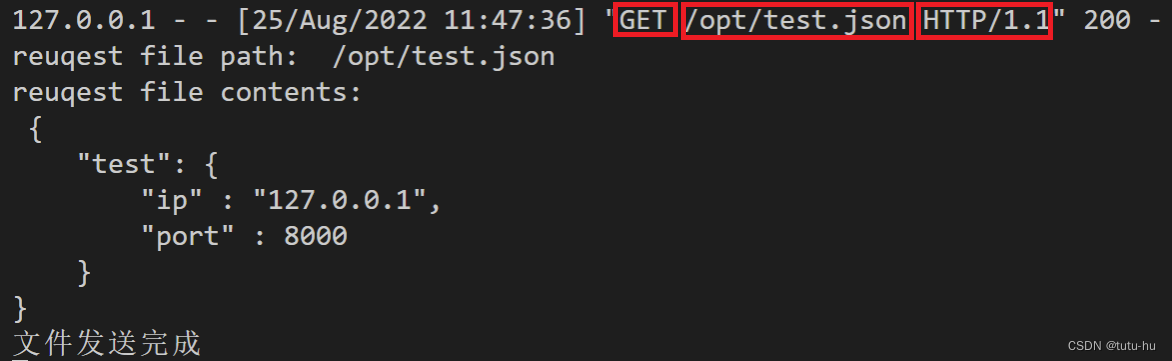
http client端:
2.2 对传输的文件加md5校验
2.2.1 http server端程序
httpserver.py
import hashlib # 导入hash计算库 from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler data = {'result': 'this is a test'} host = ('localhost', 80) # http server监听ip和端口 class Resquest(BaseHTTPRequestHandler): timeout = 5 server_version = "Apache" def do_GET(self): self.send_response(200) self.send_header("Content-type","text/plain") #设置服务器响应头,返回内容类型为纯文本类型 self.end_headers() file_path = self.path # 获取GET的URL print("reuqest file path: ",file_path) with open(file_path, encoding='utf-8') as file_obj: file_contents = file_obj.read().rstrip() # 获取文件内容存在file_contents中 print("reuqest file contents: \n",file_contents) self.wfile.write(file_contents.encode()) # 里面需要传入二进制数据,用encode()函数转换为二进制数据 print("文件发送完成") md5 = hashlib.md5(file_contents.encode()).hexdigest() print("文件的md5值为: ",md5) # buf = ''' # # #Get page # # # # username:
# password:
# # # # ''' # self.wfile.write(buf.encode()) # 里面需要传入二进制数据,用encode()函数转换为二进制数据 # # 设置响应body,即前端页面要展示的数据 def do_POST(self): path = self.path print(path) # 获取post提交的数据 datas = self.rfile.read(int(self.headers['content-length'])) #固定格式,获取表单提交的数据 # datas = urllib.unquote(datas).decode("utf-8", 'ignore') self.send_response(200) self.send_header("Content-type","text/html") #设置post时服务器的响应头 self.send_header("test","This is post!") self.end_headers() html = '''Post page Post Data:%s
Path:%s ''' %(datas,self.path) self.wfile.write(html.encode()) #提交post数据时,服务器跳转并展示的页面内容 if __name__ == '__main__': server = HTTPServer(host, Resquest) print("Starting http file server, listen at: %s:%s" % host) server.serve_forever()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
2.2.2 http client端程序
mian.cpp
#include#include #include "httpclient.hpp" int main(int argc,char** argv) { std::string remote_file_path = "/opt/test.json"; // 远端文件路径 std::string local_file_name = "test.json"; // 本地文件路径 std::string remote_md5 = "adea830c4612bb28229ba238e60441d1"; // 本地文件路径 cloud::download_file(remote_file_path, local_file_name, remote_md5); return 0; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
httpclient.hpp
#ifndef __HTTPCLIENT_HPP__ #define __HTTPCLIENT_HPP__ #include#include #include #include #include namespace cloud { constexpr const char* HOST = "127.0.0.1"; // 远端ip constexpr const char* DOWNLOAD_DIR = "/opt/http/"; // 下载文件存在本地的路径 /** * @brief 1.Http file downloader:Http文件下载器 */ class downloader { private: using string = std::string; using io_context = boost::asio::io_context; using tcp = boost::asio::ip::tcp; static tcp::socket connect(io_context& io, const string& host); public: static void download(const string& host, const string& path, const string& target); static string md5(const string& filepath); }; /** * @brief 2.Helper for file operation:文件操作助手 */ class file_helper { using string = std::string; public: static void move_file(const string& from, const string& to); static void remove_file(const string& path); static string current_exe_path(); }; void download_file(const std::string& remote_path, const std::string& local_file_name, const std::string& md5); } // namespace cloud #endif - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
httpclient.cpp
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include "httpclient.hpp" using namespace std; using json = nlohmann::json; namespace asio = boost::asio; namespace http = boost::beast::http; namespace cloud { /** * @brief Calculate file md5 * @param[in] filepath The path of file to be calculate * @return Return the md5 string */ string downloader::md5(const string& filepath) { using boost::uuids::detail::md5; constexpr size_t size = 1024 * 1024; char buf[size]; md5 md5; // Loop read file and do md5 update ifstream ifs(filepath, ios::in | ios::binary); while (ifs) { ifs.read(buf, size); md5.process_bytes(buf, ifs.gcount()); } md5::digest_type digest; md5.get_digest(digest); // Convert hex into string string str_digest(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&digest), sizeof(md5::digest_type)); return boost::algorithm::hex_lower(str_digest); } /** * @brief Create tcp socket and connect * @param[in] io The asio io context * @param[in] host The server host * @return Return the connected tcp socket */ downloader::tcp::socket downloader::connect(io_context& io, const string& host) { tcp::socket socket(io); tcp::resolver resolver(io); tcp::resolver::query query(host, "80"); asio::connect(socket, resolver.resolve(query)); return socket; } /** * @brief Http file download * @param[in] host The http server's host * @param[in] path The file path on server * @param[in] target Target local file path * @return None */ void downloader::download(const string& host, const string& path, const string& target) { std::cout << "[downloader] download from <" << host + ":" + path << "> to <" << target << ">" <<std::endl; std::cout << "[downloader] try connect to http file server"<<std::endl; asio::io_context io; //与remote file server建立连接,参数为:host==127.0.0.1:80(HTTP port默认为80) tcp::socket socket = downloader::connect(io, host); std::cout << "[downloader] http connect established"<<std::endl; //! Http request send http::request<http::string_body> req(http::verb::get, path, 11); req.set(http::field::host, host); http::write(socket, req); std::cout << "[downloader] Http request send seccess"<<std::endl; // ! Http response get boost::beast::flat_buffer buffer; http::response_parser<http::file_body> res; boost::beast::error_code ec; res.get().body().open(target.c_str(), boost::beast::file_mode::write, ec); res.body_limit(std::numeric_limits<uint64_t>::max()); std::cout << "[downloader] download starting"<<std::endl; http::read(socket, buffer, res); std::cout << "[downloader] file received done"<<std::endl; } /** * @brief Remove file * @param[in] path The file to be removed */ void file_helper::remove_file(const string& path) { ::remove(path.c_str()); } /** * @brief Move file * @throw std::runtime_error() if @ref ::rename() failed * @param[in] from The file to be move * @param[in] to The target path to be move to */ void file_helper::move_file(const string& from, const string& to) { if (-1 == ::rename(from.c_str(), to.c_str())) throw runtime_error("move file failed <" + string(::strerror(errno)) + ">"); } /** * @brief Get current execute file path * @throw std::runtime_error() if @ref ::readlink() failed * @return Return the path */ string file_helper::current_exe_path() { constexpr size_t size = 512; char buf[size]; auto length = ::readlink("/proc/self/exe", buf, size); if (-1 == length) throw runtime_error("get current execute file path failed"); return string(buf, length); } /** * @brief download file from http server * @throw std::runtime_error() if download failed * @param remote_path The file path on http server:/httpserver/file.txt * @param local_file_name local file name * @param md5 The md5 value from server */ void download_file(const string& remote_path, const std::string& local_file_name, const string& md5) { // 生成local path = DOWNLOAD_DIR + local_file_name string local_path = string(DOWNLOAD_DIR) + local_file_name; try { downloader::download(HOST, remote_path, local_path); // 从remote server下载文件到local path string md5_result = downloader::md5(local_path); // 计算得出的md5 hash值 if (md5_result != md5) { // 计算的hash值与server返回的hash值比较 throw runtime_error("MD5 verification failed.\n\tcalculated: " + md5_result + "\n\tfrom server: " + md5); } std::cout << "MD5 verification successed.\n\tcalculated: " << md5_result << "\n\tfrom server: " << md5 << std::endl; // file_helper::move_file(local_path, file_helper::current_exe_path()); //将当前目录下的可执行文件更新为从http服务端下载的文件 } catch (exception& ex) { file_helper::remove_file(local_path.c_str()); std::cout<<"download_file exception: "<<ex.what()<<std::endl; } } } // namespace cloud - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
2.2.3 编译 & 执行
http server端启动:
python3 httpserver.py
http client端编译:
g++ main.cpp httpclient.cpp -lboost_system -lpthread
http client端启动:
./a.out
2.2.4 执行结果
http server端:
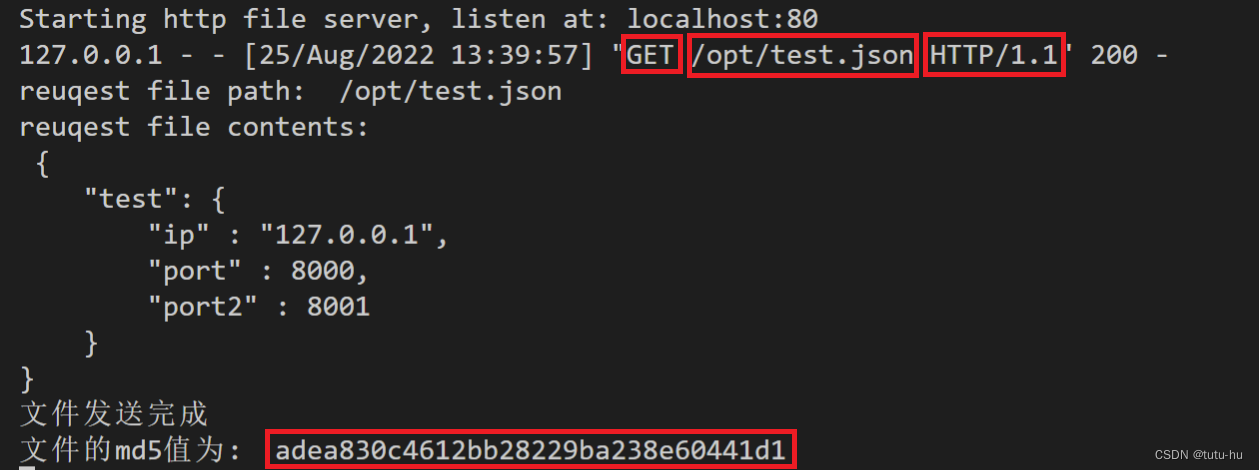
http client端:
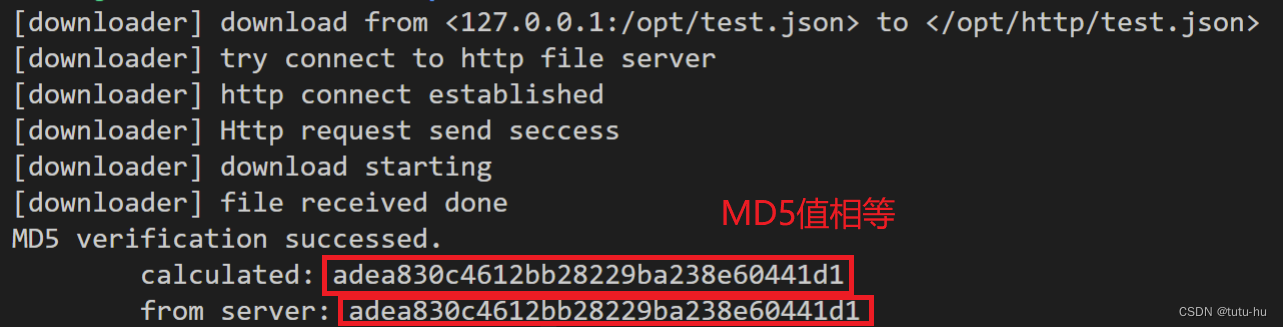
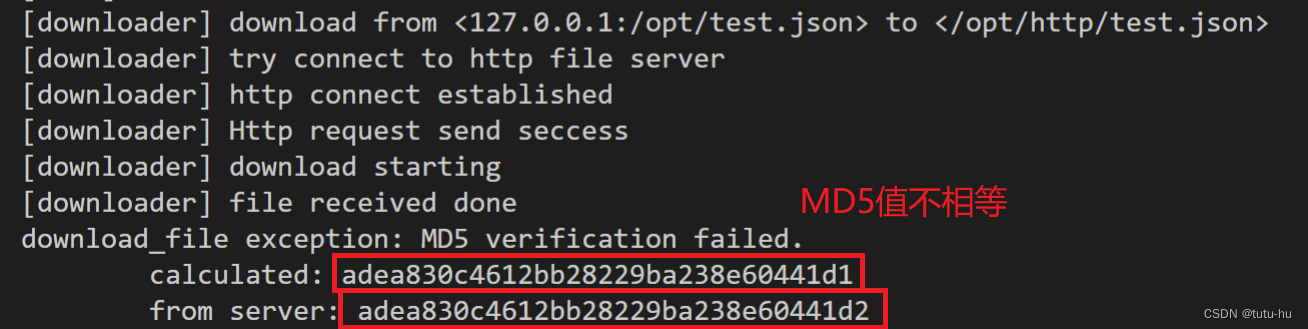
注意:在客户端下载文件,并且从服务端获得该文件的md5哈希值,客户端对于收到的文件计算md5值,当两个md5值相等时,客户端判断收到的文件正确;当两个md5值不相等时,客户端判断收到的文件不正确,则删除该文件(丢弃)!三.总结
在产品大规模线下部署的场景中,常常需要通过云端进行多终端的程序更新,本文给出了基于HTTP协议实现文件下载,可满足程序在线更新的场景需求;结合MQTT协议(可见上一篇文章)可实现批量终端订阅+更新的流程,后续会给出基于FTP协议实现文件下载。
-
相关阅读:
代数曲线和曲面的拓扑研究
【超分:光谱响应函数】
RustDay06------Exercise[71-80]
【小程序专栏】个人及企业资质分别该如何注册小程序
SpringCloud Alibaba - Sentinel 限流规则(案例 + JMeter 测试分析)
docker部署(使用docker-compose)手把手教程
【手写一个SpringBoot简易版框架】
【kubernetes】带你入门k8s中的HPA
VirtualBox配置Centos7双网卡固定IP
addEventListener与useeffect相撞的火花
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42700740/article/details/126467681
