-
【React源码】(十一)fiber 树渲染
fiber 树渲染
在正式分析
fiber树渲染之前, 再次回顾一下reconciler 运作流程的 4 个阶段:
- 输入阶段: 衔接
react-dom包, 承接fiber更新请求(参考React 应用的启动过程). - 注册调度任务: 与调度中心(
scheduler包)交互, 注册调度任务task, 等待任务回调(参考React 调度原理(scheduler)). - 执行任务回调: 在内存中构造出
fiber树和DOM对象(参考fiber 树构造(初次创建)和 fiber 树构造(对比更新)). - 输出: 与渲染器(
react-dom)交互, 渲染DOM节点.
本节分析其中的第 4 阶段(输出),
fiber树渲染处于reconciler 运作流程这一流水线的最后一环, 或者说前面的步骤都是为了最后一步服务, 所以其重要性不言而喻.前文已经介绍了
fiber树构造, 现在分析fiber树渲染过程, 这个过程, 实际上是对fiber树的进一步处理.fiber 树特点
通过前文
fiber树构造的解读, 可以总结出fiber树的基本特点:- 无论是
首次构造或者是对比更新, 最终都会在内存中生成一棵用于渲染页面的fiber树(即fiberRoot.finishedWork). - 这棵将要被渲染的
fiber树有 2 个特点:- 副作用队列挂载在根节点上(具体来讲是
finishedWork.firstEffect) - 代表最新页面的
DOM对象挂载在fiber树中首个HostComponent类型的节点上(具体来讲DOM对象是挂载在fiber.stateNode属性上)
- 副作用队列挂载在根节点上(具体来讲是
这里再次回顾前文使用过的 2 棵 fiber 树, 可以验证上述特点:
- 初次构造
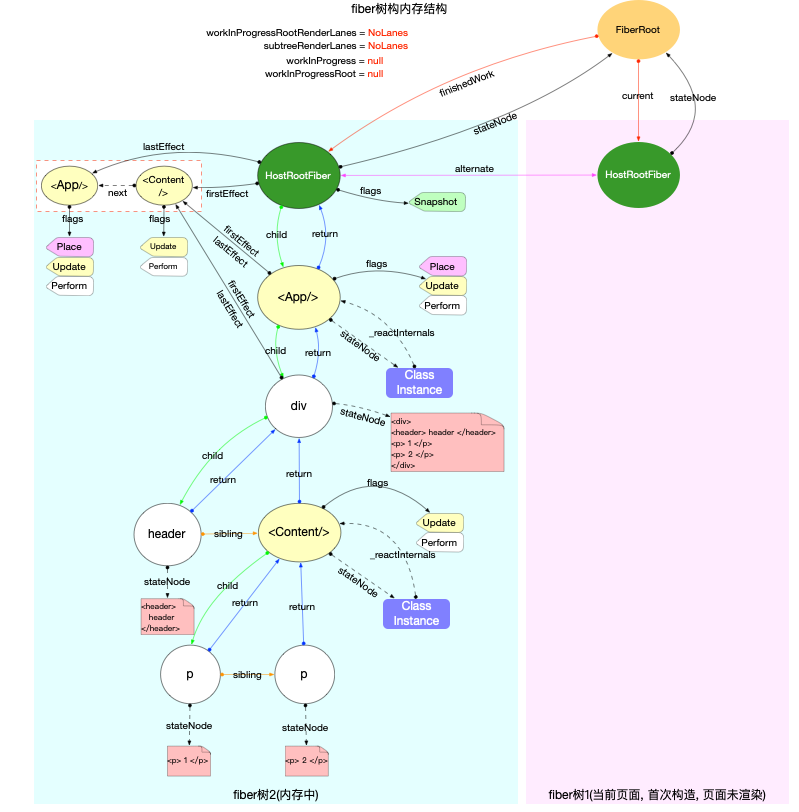
- 对比更新

commitRoot
整个渲染逻辑都在commitRoot 函数中:
- function commitRoot(root) {
- const renderPriorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
- runWithPriority(
- ImmediateSchedulerPriority,
- commitRootImpl.bind(null, root, renderPriorityLevel),
- );
- return null;
- }
在
commitRoot中同时使用到了渲染优先级和调度优先级, 有关优先级的讨论, 在前文已经做出了说明(参考React 中的优先级管理和fiber 树构造(基础准备)#优先级), 本节不再赘述. 最后的实现是通过commitRootImpl函数:- // ... 省略部分无关代码
- function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel) {
- // ============ 渲染前: 准备 ============
- const finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
- const lanes = root.finishedLanes;
- // 清空FiberRoot对象上的属性
- root.finishedWork = null;
- root.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
- root.callbackNode = null;
- if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
- // 重置全局变量
- workInProgressRoot = null;
- workInProgress = null;
- workInProgressRootRenderLanes = NoLanes;
- }
- // 再次更新副作用队列
- let firstEffect;
- if (finishedWork.flags > PerformedWork) {
- // 默认情况下fiber节点的副作用队列是不包括自身的
- // 如果根节点有副作用, 则将根节点添加到副作用队列的末尾
- if (finishedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
- finishedWork.lastEffect.nextEffect = finishedWork;
- firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
- } else {
- firstEffect = finishedWork;
- }
- } else {
- firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
- }
- // ============ 渲染 ============
- let firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect;
- if (firstEffect !== null) {
- const prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
- executionContext |= CommitContext;
- // 阶段1: dom突变之前
- nextEffect = firstEffect;
- do {
- commitBeforeMutationEffects();
- } while (nextEffect !== null);
- // 阶段2: dom突变, 界面发生改变
- nextEffect = firstEffect;
- do {
- commitMutationEffects(root, renderPriorityLevel);
- } while (nextEffect !== null);
- // 恢复界面状态
- resetAfterCommit(root.containerInfo);
- // 切换current指针
- root.current = finishedWork;
- // 阶段3: layout阶段, 调用生命周期componentDidUpdate和回调函数等
- nextEffect = firstEffect;
- do {
- commitLayoutEffects(root, lanes);
- } while (nextEffect !== null);
- nextEffect = null;
- executionContext = prevExecutionContext;
- }
- // ============ 渲染后: 重置与清理 ============
- if (rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
- // 有被动作用(使用useEffect), 保存一些全局变量
- } else {
- // 分解副作用队列链表, 辅助垃圾回收
- // 如果有被动作用(使用useEffect), 会把分解操作放在flushPassiveEffects函数中
- nextEffect = firstEffect;
- while (nextEffect !== null) {
- const nextNextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
- nextEffect.nextEffect = null;
- if (nextEffect.flags & Deletion) {
- detachFiberAfterEffects(nextEffect);
- }
- nextEffect = nextNextEffect;
- }
- }
- // 重置一些全局变量(省略这部分代码)...
- // 下面代码用于检测是否有新的更新任务
- // 比如在componentDidMount函数中, 再次调用setState()
- // 1. 检测常规(异步)任务, 如果有则会发起异步调度(调度中心`scheduler`只能异步调用)
- ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
- // 2. 检测同步任务, 如果有则主动调用flushSyncCallbackQueue(无需再次等待scheduler调度), 再次进入fiber树构造循环
- flushSyncCallbackQueue();
- return null;
- }
commitRootImpl函数中, 可以根据是否调用渲染, 把整个commitRootImpl分为 3 段(分别是渲染前,渲染,渲染后).渲染前
为接下来正式渲染, 做一些准备工作. 主要包括:
- 设置全局状态(如: 更新
fiberRoot上的属性) - 重置全局变量(如:
workInProgressRoot,workInProgress等) - 再次更新副作用队列: 只针对根节点
fiberRoot.finishedWork- 默认情况下根节点的副作用队列是不包括自身的, 如果根节点有副作用, 则将根节点添加到副作用队列的末尾
- 注意只是延长了副作用队列, 但是
fiberRoot.lastEffect指针并没有改变. 比如首次构造时, 根节点拥有Snapshot标记:

渲染
commitRootImpl函数中, 渲染阶段的主要逻辑是处理副作用队列, 将最新的 DOM 节点(已经在内存中, 只是还没渲染)渲染到界面上.整个渲染过程被分为 3 个函数分布实现:
commitBeforeMutationEffects- dom 变更之前, 处理副作用队列中带有
Snapshot,Passive标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更之前, 处理副作用队列中带有
commitMutationEffects- dom 变更, 界面得到更新. 处理副作用队列中带有
Placement,Update,Deletion,Hydrating标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更, 界面得到更新. 处理副作用队列中带有
commitLayoutEffects- dom 变更后, 处理副作用队列中带有
Update | Callback标记的fiber节点.
- dom 变更后, 处理副作用队列中带有
通过上述源码分析, 可以把
commitRootImpl的职责概括为 2 个方面:- 处理副作用队列. (步骤 1,2,3 都会处理, 只是处理节点的标识
fiber.flags不同). - 调用渲染器, 输出最终结果. (在步骤 2:
commitMutationEffects中执行).
所以
commitRootImpl是处理fiberRoot.finishedWork这棵即将被渲染的fiber树, 理论上无需关心这棵fiber树是如何产生的(可以是首次构造产生, 也可以是对比更新产生). 为了清晰简便, 在下文的所有图示都使用初次创建的fiber树结构来进行演示.这 3 个函数处理的对象是
副作用队列和DOM对象.所以无论
fiber树结构有多么复杂, 到了commitRoot阶段, 实际起作用的只有 2 个节点:副作用队列所在节点: 根节点, 即HostRootFiber节点.DOM对象所在节点: 从上至下首个HostComponent类型的fiber节点, 此节点fiber.stateNode实际上指向最新的 DOM 树.
下图为了清晰, 省略了一些无关引用, 只留下
commitRoot阶段实际会用到的fiber节点: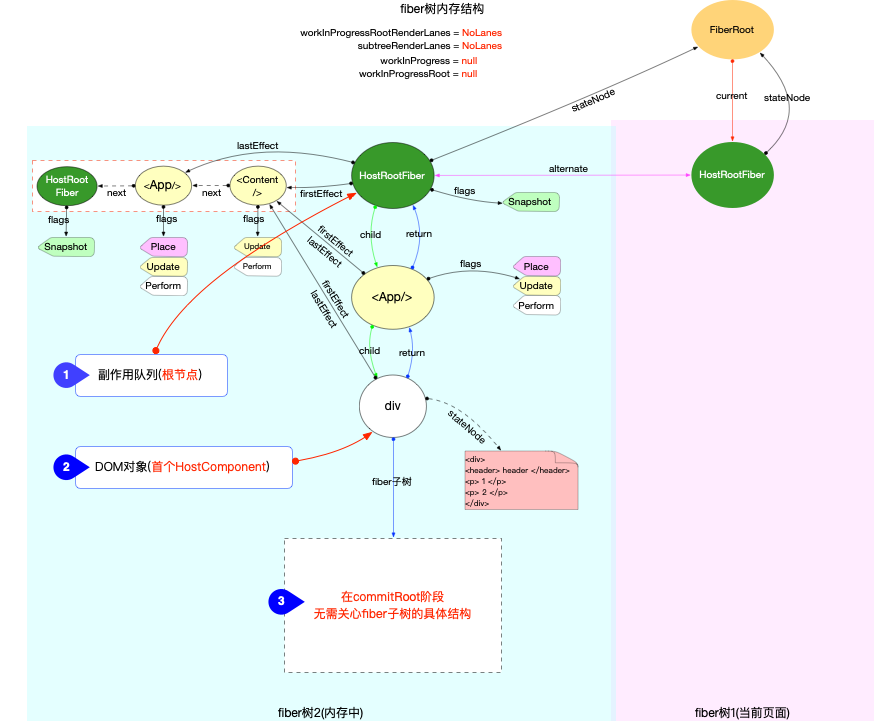
commitBeforeMutationEffects
第一阶段: dom 变更之前, 处理副作用队列中带有
Snapshot,Passive标记的fiber节点.- // ... 省略部分无关代码
- function commitBeforeMutationEffects() {
- while (nextEffect !== null) {
- const current = nextEffect.alternate;
- const flags = nextEffect.flags;
- // 处理`Snapshot`标记
- if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) {
- commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber(current, nextEffect);
- }
- // 处理`Passive`标记
- if ((flags & Passive) !== NoFlags) {
- // Passive标记只在使用了hook, useEffect会出现. 所以此处是针对hook对象的处理
- if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
- rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
- scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
- flushPassiveEffects();
- return null;
- });
- }
- }
- nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
- }
- }
注意:
commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber实际上对应了commitBeforeMutationLifeCycles函数,在导入时进行了重命名- 处理
Snapshot标记
- function commitBeforeMutationLifeCycles(
- current: Fiber | null,
- finishedWork: Fiber,
- ): void {
- switch (finishedWork.tag) {
- case FunctionComponent:
- case ForwardRef:
- case SimpleMemoComponent:
- case Block: {
- return;
- }
- case ClassComponent: {
- if (finishedWork.flags & Snapshot) {
- if (current !== null) {
- const prevProps = current.memoizedProps;
- const prevState = current.memoizedState;
- const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
- const snapshot = instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(
- finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
- ? prevProps
- : resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, prevProps),
- prevState,
- );
- instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate = snapshot;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- case HostRoot: {
- if (supportsMutation) {
- if (finishedWork.flags & Snapshot) {
- const root = finishedWork.stateNode;
- clearContainer(root.containerInfo);
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- case HostComponent:
- case HostText:
- case HostPortal:
- case IncompleteClassComponent:
- return;
- }
- }
从源码中可以看到, 与
Snapshot标记相关的类型只有ClassComponent和HostRoot.- 对于
ClassComponent类型节点, 调用了instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期函数 - 对于
HostRoot类型节点, 调用clearContainer清空了容器节点(即div#root这个 dom 节点).
- 处理
Passive标记
Passive标记只会在使用了hook对象的function类型的节点上存在, 后续的执行过程在hook原理章节中详细说明. 此处我们需要了解在commitRoot的第一个阶段, 为了处理hook对象(如useEffect), 通过scheduleCallback单独注册了一个调度任务task, 等待调度中心scheduler处理.注意: 通过调度中心
scheduler调度的任务task均是通过MessageChannel触发, 都是异步执行(可参考React 调度原理(scheduler)).小测试:
- // 以下示例代码中的输出顺序为 1, 3, 4, 2
- function Test() {
- console.log(1);
- useEffect(() => {
- console.log(2);
- });
- console.log(3);
- Promise.resolve(() => {
- console.log(4);
- });
- return <div>testdiv>;
- }
commitMutationEffects
第二阶段: dom 变更, 界面得到更新. 处理副作用队列中带有
ContentReset,Ref,Placement,Update,Deletion,Hydrating标记的fiber节点.- // ...省略部分无关代码
- function commitMutationEffects(
- root: FiberRoot,
- renderPriorityLevel: ReactPriorityLevel,
- ) {
- // 处理Ref
- if (flags & Ref) {
- const current = nextEffect.alternate;
- if (current !== null) {
- // 先清空ref, 在commitRoot的第三阶段(dom变更后), 再重新赋值
- commitDetachRef(current);
- }
- }
- // 处理DOM突变
- while (nextEffect !== null) {
- const flags = nextEffect.flags;
- const primaryFlags = flags & (Placement | Update | Deletion | Hydrating);
- switch (primaryFlags) {
- case Placement: {
- // 新增节点
- commitPlacement(nextEffect);
- nextEffect.flags &= ~Placement; // 注意Placement标记会被清除
- break;
- }
- case PlacementAndUpdate: {
- // Placement
- commitPlacement(nextEffect);
- nextEffect.flags &= ~Placement;
- // Update
- const current = nextEffect.alternate;
- commitWork(current, nextEffect);
- break;
- }
- case Update: {
- // 更新节点
- const current = nextEffect.alternate;
- commitWork(current, nextEffect);
- break;
- }
- case Deletion: {
- // 删除节点
- commitDeletion(root, nextEffect, renderPriorityLevel);
- break;
- }
- }
- nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
- }
- }
处理 DOM 突变:
新增: 函数调用栈commitPlacement->insertOrAppendPlacementNode->appendChild更新: 函数调用栈commitWork->commitUpdate删除: 函数调用栈commitDeletion->removeChild
最终会调用
appendChild, commitUpdate, removeChild这些react-dom包中的函数. 它们是HostConfig协议(源码在 ReactDOMHostConfig.js 中)中规定的标准函数, 在渲染器react-dom包中进行实现. 这些函数就是直接操作 DOM, 所以执行之后, 界面也会得到更新.注意:
commitMutationEffects执行之后, 在commitRootImpl函数中切换当前fiber树(root.current = finishedWork),保证fiberRoot.current指向代表当前界面的fiber树.
commitLayoutEffects
第三阶段: dom 变更后, 处理副作用队列中带有
Update, Callback, Ref标记的fiber节点.- // ...省略部分无关代码
- function commitLayoutEffects(root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes) {
- while (nextEffect !== null) {
- const flags = nextEffect.flags;
- // 处理 Update和Callback标记
- if (flags & (Update | Callback)) {
- const current = nextEffect.alternate;
- commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, nextEffect, committedLanes);
- }
- if (flags & Ref) {
- // 重新设置ref
- commitAttachRef(nextEffect);
- }
- nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
- }
- }
- 核心逻辑都在commitLayoutEffectOnFiber->commitLifeCycles函数中.
- // ...省略部分无关代码
- function commitLifeCycles(
- finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
- current: Fiber | null,
- finishedWork: Fiber,
- committedLanes: Lanes,
- ): void {
- switch (finishedWork.tag) {
- case ClassComponent: {
- const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
- if (finishedWork.flags & Update) {
- if (current === null) {
- // 初次渲染: 调用 componentDidMount
- instance.componentDidMount();
- } else {
- const prevProps =
- finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
- ? current.memoizedProps
- : resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, current.memoizedProps);
- const prevState = current.memoizedState;
- // 更新阶段: 调用 componentDidUpdate
- instance.componentDidUpdate(
- prevProps,
- prevState,
- instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate,
- );
- }
- }
- const updateQueue: UpdateQueue<
- *,
- > | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
- if (updateQueue !== null) {
- // 处理update回调函数 如: this.setState({}, callback)
- commitUpdateQueue(finishedWork, updateQueue, instance);
- }
- return;
- }
- case HostComponent: {
- const instance: Instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
- if (current === null && finishedWork.flags & Update) {
- const type = finishedWork.type;
- const props = finishedWork.memoizedProps;
- // 设置focus等原生状态
- commitMount(instance, type, props, finishedWork);
- }
- return;
- }
- }
- }
在
commitLifeCycles函数中:- 对于
ClassComponent节点, 调用生命周期函数componentDidMount或componentDidUpdate, 调用update.callback回调函数. - 对于
HostComponent节点, 如有Update标记, 需要设置一些原生状态(如:focus等)
渲染后
执行完上述步骤之后, 本次渲染任务就已经完成了. 在渲染完成后, 需要做一些重置和清理工作:
-
清除副作用队列
- 由于副作用队列是一个链表, 由于单个
fiber对象的引用关系, 无法被gc回收. - 将链表全部拆开, 当
fiber对象不再使用的时候, 可以被gc回收.
- 由于副作用队列是一个链表, 由于单个
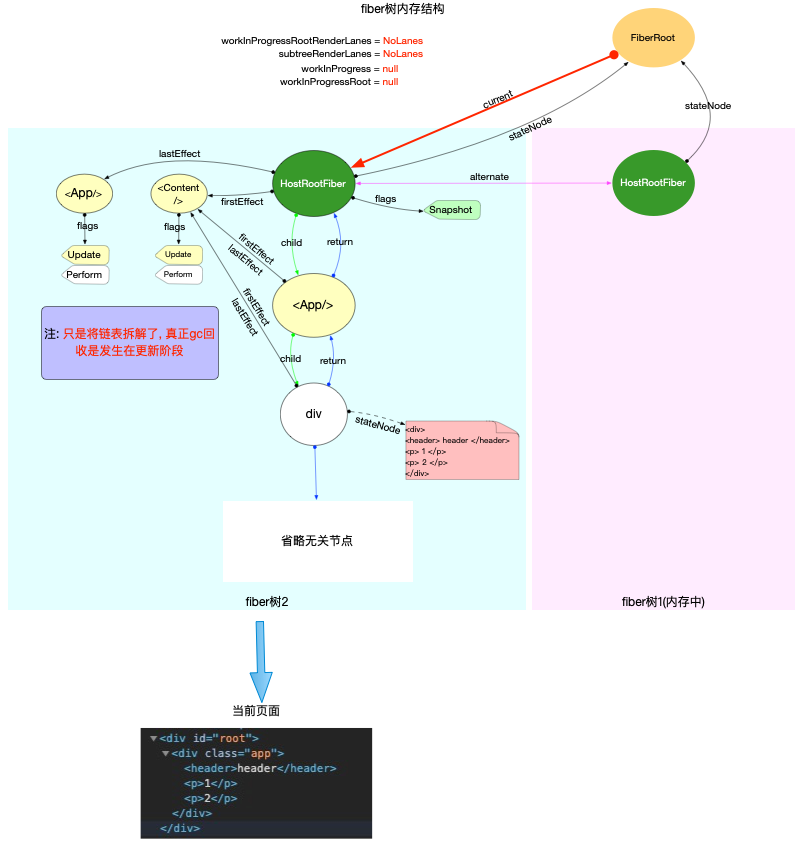
- 检测更新
- 在整个渲染过程中, 有可能产生新的
update(比如在componentDidMount函数中, 再次调用setState()). - 如果是常规(异步)任务, 不用特殊处理, 调用
ensureRootIsScheduled确保任务已经注册到调度中心即可. - 如果是同步任务, 则主动调用
flushSyncCallbackQueue(无需再次等待 scheduler 调度), 再次进入 fiber 树构造循环
- 在整个渲染过程中, 有可能产生新的
- // 清除副作用队列
- if (rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
- // 有被动作用(使用useEffect), 保存一些全局变量
- } else {
- // 分解副作用队列链表, 辅助垃圾回收.
- // 如果有被动作用(使用useEffect), 会把分解操作放在flushPassiveEffects函数中
- nextEffect = firstEffect;
- while (nextEffect !== null) {
- const nextNextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
- nextEffect.nextEffect = null;
- if (nextEffect.flags & Deletion) {
- detachFiberAfterEffects(nextEffect);
- }
- nextEffect = nextNextEffect;
- }
- }
- // 重置一些全局变量(省略这部分代码)...
- // 下面代码用于检测是否有新的更新任务
- // 比如在componentDidMount函数中, 再次调用setState()
- // 1. 检测常规(异步)任务, 如果有则会发起异步调度(调度中心`scheduler`只能异步调用)
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
// 2. 检测同步任务, 如果有则主动调用flushSyncCallbackQueue(无需再次等待scheduler调度), 再次进入fiber树构造循环
flushSyncCallbackQueue();
总结
本节分析了
fiber 树渲染的处理过程, 从宏观上看fiber 树渲染位于reconciler 运作流程中的输出阶段, 是整个reconciler 运作流程的链路中最后一环(从输入到输出). 本节根据源码, 具体从渲染前, 渲染, 渲染后三个方面分解了commitRootImpl函数. 其中最核心的渲染逻辑又分为了 3 个函数, 这 3 个函数共同处理了有副作用fiber节点, 并通过渲染器react-dom把最新的 DOM 对象渲染到界面上. - 输入阶段: 衔接
-
相关阅读:
【06】VirtualService高级流量功能
B站刘二大人-数据集及数据加载 Lecture 8
谈谈Net-SNMP软件
MyBatis完成品牌数据的查询操作
Redis-Sentinel高可用架构学习
Bartende:Mac菜单栏图标管理软件
SCT1270FQAR/TPS61089RNRR
vue常见的keep-alive问题
数学建模--数据预处理
Linux邻居协议 学习笔记 之四 通用邻居项创建、查找、删除等相关的函数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44828588/article/details/126525335
