-
Matlab彩色图像卷积的数学原理及纯手工实现
一、引言
在图像处理中,不论是提取图像边缘特征,还是尺度空间变换,亦或者目前大火的深度学习,图像卷积都是非常重要的基础工作。卷积从整体上说是卷积,从局部上说其实就是内积。卷积不论在数学上还是信号处理中都有非常重要的应用,主要目的是用来做图像滤波、特征提取和多尺度分解等。可以这么说,不会卷积就是不会图像处理。本文给出了图像卷积的数学原理及Matlab手工实现,此外还给出Matlab内部函数imfilter的用法。
二、卷积的数学原理
对于给定的两个一元可积函数f(x)和g(x),其卷积定义为:
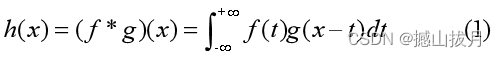
离散化的结果为:
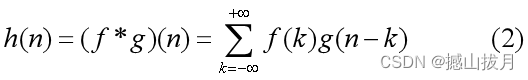
此时,可以称f(x)为滤波器,或者卷积核,g(x)是已知的信号。
推广到二元函数情形,其离散形式的卷积为:
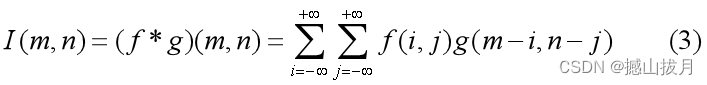
由于数字图像的像素是一个矩阵,所以可以使用上述公式(3)来实现卷积。
通过上述公式,可以发现,当固定(m,n)时,则右端就是内积的表达式了。所以我在前面说卷积的局部就是内积(当然了,这仅仅是我自己的说法,而且这里的局部其实是对固定的点而言,可不是一个局部区域啊)。下图演示了卷积。
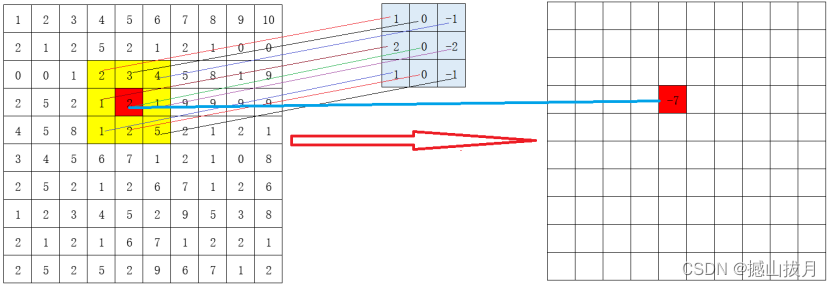
现在想计算红色2处的卷积值,则把中间的3x3卷积核扣到以2为中心的黄色区域,做内积得到-7存放到右侧红色位置。其它位置的卷积也是如此计算。至此,是不是发现了卷积原来如此简单,难怪其在图像处理中具有广泛的应用。
有人可能会问,卷积核都是怎么选取的,我的回答是“看实际需要”,如果是低通滤波,则选取低通滤波器,例如高斯低通滤波器,其作为卷积核可以让图像变得平滑甚至模糊。下图就是利用3x3和5x5高斯卷积核对图像做卷积的结果。

其中左侧图是带有噪声的原始图像,中间图是使用3x3高斯卷积和滤波的结果,右图是使用5x5高斯卷积和滤波的结果,从图中可以看出卷积核模板越大,则去噪效果越好。(到此你又学会了一招,图像的低通滤波可以去噪)三、Matlab纯手工实现图像卷积
1.单通道图像卷积
function convImage = SingleConvolution( image, filter ) %功能: % 单通道图像的卷积运算 %输入参数: % image:扩展后的图像 % filter:滤波器 %输出参数: % imageConv:卷积后的图像 [Height, Width] = size( image ); [mF, nF] = size( filter ); for i = 1 : Height - mF + 1 for j = 1 : Width - nF + 1 localImage = []; localImage = image(i:i+mF-1, j:j+nF-1); convImage(i, j) = sum( sum( localImage .* filter ) ); end end convImage = uint8( convImage ); end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.灰度图像或彩色图像的卷积
function eIm = ImageConlutionFun( image, filter ) imSize = size( image ); dim = numel( imSize ); %图像的维数 if dim == 2 eIm = SingleConvolution( image, filter ); else imR = image( :, :, 1 ); imG = image( :, :, 2 ); imB = image( :, :, 3 ); eImR = SingleConvolution( imR, filter ); eImG = SingleConvolution( imG, filter ); eImB = SingleConvolution( imB, filter ); eIm = cat(3 ,eImR, eImG, eImB );%将三个颜色分量合成彩色图像 end end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
3.灰度图像卷积Demo_1
%利用sobel算子提取图像的边缘特征 clear all clc image = double( imread( 'lena.bmp' ) ); filterY = double( fspecial( 'sobel' ) );%sobel卷积核 filterX = filterY'; imageConvY = ImageConlutionFun( image, filterY ); imageConvX = ImageConlutionFun( image, filterX ); imageConv = max( imageConvY, imageConvX ); figure; imshow( uint8(image) ) figure; imshow( imageConv )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
运行结果如下:

4.灰度图像卷积Demo_2%图像低通滤波 clear all clc image = double( imread( 'lenaNoise.bmp' ) ); filter = double( fspecial( 'gaussian', [5,5], 1 ) );%gaussian卷积核 imageConv = ImageConlutionFun( image, filter ); size( image ) size( imageConv ) figure; imshow( uint8(image) ) figure; imshow( imageConv )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
运行结果如下:

5.彩色图像卷积Demo_3%图像低通滤波 clear all clc image = double( imread( 'cloud.jpg' ) ); filter = double( fspecial( 'gaussian', [7,7], 1 ) );%gaussian卷积核 imageConv = ImageConlutionFun( image, filter ); figure; imshow( uint8(image) ) figure; imshow( imageConv )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
运行结果如下:

说明:从上述运行结果可以看出,卷积之后图像的尺寸比原图像小,这是因为没有做padding造成的,如果在做卷积之前增加一项padding工作,则可以解决此问题,例如demo_3的代码修改为:clear all clc image = double( imread( 'cloud.jpg' ) ); filter = double( fspecial( 'gaussian', [7,7], 1 ) );%gaussian卷积核 [m, n] = size( filter ); im = padarray( image, [floor(m/2), floor(n/2)], 'symmetric' );%图像padding imageConv = ImageConlutionFun( im, filter ); size( image ) size( imageConv ) figure; imshow( uint8(image) ) figure; imshow( imageConv )- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
则运行结果如下:

此时卷积前后图像的尺寸是相同的。四、Matlab卷积函数imfilter
imfilter( Image, filter, boundarymode )
Image:图像像素矩阵
filter:卷积核矩阵
boundarymode:X 边界延拓为X,缺省值为0,其取值有:
Symmetric: 镜像延拓边界
Replicate: 最近邻延拓边界
Circular: 周期延拓边界
例如:clear all clc im = imread( 'cloud.jpg' ); filter = fspecial( 'gaussian' ,[3,3], 1 ); imconv = imfilter( im, filter, 'symmetric' ); figure;imshow(im) figure;imshow(imconv)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
运行结果如下:

-
相关阅读:
Spring | 事件监听器应用与最佳实践
Android入门第38天-使用随鼠标移动的圆点来熟悉onTouchEvent
JSP ssh 校园二手商品拍卖系统myeclipse开发mysql数据库MVC模式java编程网页设计
vscode插件开发
Springboot Vue餐厅在线点餐平台网站java项目
Python数据分析--Numpy常用函数介绍(9)-- 与线性代数有关的模块linalg
如何跳得更高
前端Javascript | 数组值随机选择函数
react 响应式栅格布局
Shell:常见错误总结(一)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/sunnyoldman001/article/details/126514955