-
linux网络协议栈源码分析 - 传输层(TCP连接的终止)
1、连接终止过程(四处挥手)
1.1、四次挥手
《TCP/IP详解卷 1:协议》“图18-4 连接终止期间报文段的正常交换”如下:
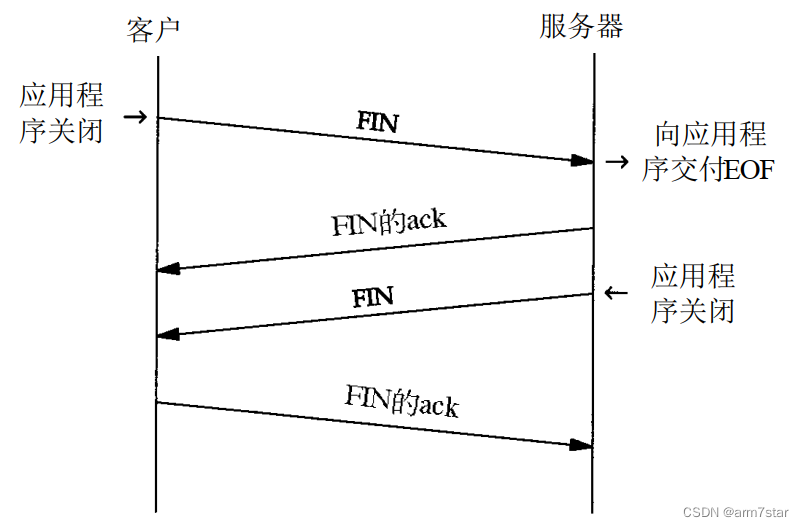
1.2、tcp状态变迁图

2、close系统调用(第一次挥手)
客户端端调用close,发送FIN报文。
2.1、close系统调用
客户端调用close关闭socket,最终调用fput创建一个工作work来执行真正的关闭操作,fput函数代码如下:
- void fput(struct file *file)
- {
- if (atomic_long_dec_and_test(&file->f_count)) {
- struct task_struct *task = current;
- if (likely(!in_interrupt() && !(task->flags & PF_KTHREAD))) {
- init_task_work(&file->f_u.fu_rcuhead, ____fput); // 初始化一个work,work的函数为____fput
- if (!task_work_add(task, &file->f_u.fu_rcuhead, true)) // 添加work task
- return; // 添加成功,返回
- /*
- * After this task has run exit_task_work(),
- * task_work_add() will fail. Fall through to delayed
- * fput to avoid leaking *file.
- */
- }
- if (llist_add(&file->f_u.fu_llist, &delayed_fput_list))
- schedule_delayed_work(&delayed_fput_work, 1);
- }
- }
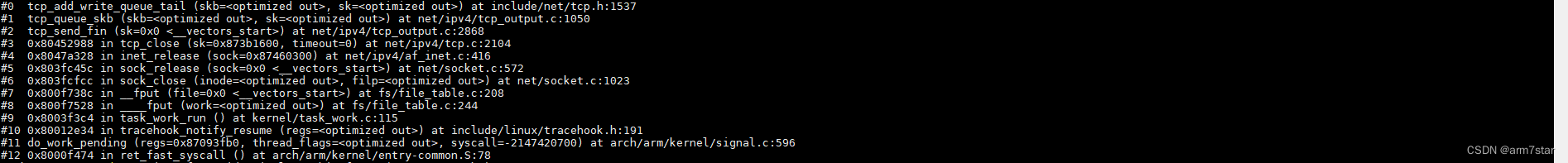
fput函数调用栈:

2.2、tcp_close关闭socket并发送FIN(第一次挥手)
fput系统调用添加一个work task之后,系统调用返回时处理挂起的work,调用____fput,最终调用tcp_close关闭socket。
tcp_close检查各种状态,删除接收队列数据,有数据未接收,直接关闭socket发送RST;正常关闭以及其他需要发送FIN报文的状态,发送FIN,调用sk_stream_wait_close等待关闭socket(某些状态不能立即关闭socket,所以要等待);正常关闭,收到FIN的ACK,进入TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态,c需要启动定时器,避免服务器长时间不调用close,TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态没有数据要发送,不能通过超时重传判断网络异常,另外TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态超时时间太短的话,会直接关闭socket,由timewait控制块替换socket控制块,所以,书籍上的tcp状态转移图与linux内核实现不完全相同,TCP_FIN_WAIT2超时时间够长的情况,就能基本完全匹配。
tcp_close函数代码如下:
- void tcp_close(struct sock *sk, long timeout)
- {
- struct sk_buff *skb;
- int data_was_unread = 0;
- int state;
- lock_sock(sk);
- sk->sk_shutdown = SHUTDOWN_MASK; // 关闭读写(SHUTDOWN_MASK = RCV_SHUTDOWN | SEND_SHUTDOWN);读写关闭状态,如果使用epoll等待该socket的话,调用tcp_poll会返回POLLHUP!!!
- if (sk->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) { // 关闭LISTEN的socket
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE); // 设置为CLOSE
- /* Special case. */
- inet_csk_listen_stop(sk); // 停止监听(具体参考机械工业出版社《Linux内核源码剖析:TCP/IP实现(下册)》"32.3 close传输接口层的实现: tcp_close()")
- goto adjudge_to_death; // 跳转到adjudge_to_death
- }
- /* We need to flush the recv. buffs. We do this only on the
- * descriptor close, not protocol-sourced closes, because the
- * reader process may not have drained the data yet!
- */
- while ((skb = __skb_dequeue(&sk->sk_receive_queue)) != NULL) { // tcp接收队列有数据,则删除接收队列的数据
- u32 len = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq - TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq; // skb报文长度
- if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tcp_flags & TCPHDR_FIN) // FIN报文(FIN报文占一个序号,但是FIN报文没有实际数据)
- len--; // 删除的数据减1(FIN序号不带数据)
- data_was_unread += len; // 删除的没有读的数据总长度
- __kfree_skb(skb); // 释放skb报文
- }
- sk_mem_reclaim(sk); // 回收缓存
- /* If socket has been already reset (e.g. in tcp_reset()) - kill it. */
- if (sk->sk_state == TCP_CLOSE)
- goto adjudge_to_death;
- /* As outlined in RFC 2525, section 2.17, we send a RST here because
- * data was lost. To witness the awful effects of the old behavior of
- * always doing a FIN, run an older 2.1.x kernel or 2.0.x, start a bulk
- * GET in an FTP client, suspend the process, wait for the client to
- * advertise a zero window, then kill -9 the FTP client, wheee...
- * Note: timeout is always zero in such a case.
- */
- if (unlikely(tcp_sk(sk)->repair)) {
- sk->sk_prot->disconnect(sk, 0);
- } else if (data_was_unread) { // 关闭socket的时候,有未接收的数据
- /* Unread data was tossed, zap the connection. */
- NET_INC_STATS_USER(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONCLOSE);
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE); // 直接设置为CLOSE状态
- tcp_send_active_reset(sk, sk->sk_allocation); // 发送RST重置连接
- } else if (sock_flag(sk, SOCK_LINGER) && !sk->sk_lingertime) {
- /* Check zero linger _after_ checking for unread data. */
- sk->sk_prot->disconnect(sk, 0);
- NET_INC_STATS_USER(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONDATA);
- } else if (tcp_close_state(sk)) { // 调用tcp_close_state,从当前状态转换到下一个状态(正常关闭情况下,进入TCP_FIN_WAIT1状态,TCP_FIN_WAIT1需要发送FIN)
- /* We FIN if the application ate all the data before
- * zapping the connection.
- */
- /* RED-PEN. Formally speaking, we have broken TCP state
- * machine. State transitions:
- *
- * TCP_ESTABLISHED -> TCP_FIN_WAIT1
- * TCP_SYN_RECV -> TCP_FIN_WAIT1 (forget it, it's impossible)
- * TCP_CLOSE_WAIT -> TCP_LAST_ACK
- *
- * are legal only when FIN has been sent (i.e. in window),
- * rather than queued out of window. Purists blame.
- *
- * F.e. "RFC state" is ESTABLISHED,
- * if Linux state is FIN-WAIT-1, but FIN is still not sent.
- *
- * The visible declinations are that sometimes
- * we enter time-wait state, when it is not required really
- * (harmless), do not send active resets, when they are
- * required by specs (TCP_ESTABLISHED, TCP_CLOSE_WAIT, when
- * they look as CLOSING or LAST_ACK for Linux)
- * Probably, I missed some more holelets.
- * --ANK
- * XXX (TFO) - To start off we don't support SYN+ACK+FIN
- * in a single packet! (May consider it later but will
- * probably need API support or TCP_CORK SYN-ACK until
- * data is written and socket is closed.)
- */
- tcp_send_fin(sk); // 调用tcp_send_fin发送FIN报文(调用tcp_queue_skb将FIN报文缓存到发送队列(如果发送队列还有未确认的数据,那么需要等待其他数据发送完再发送FIN报文,FIN报文虽然不一定有数据(可以附加到最后一个带数据的报文),但是FIN可能丢失,FIN报文需要超时重传),调用__tcp_push_pending_frames发送挂起的报文)
- }
- sk_stream_wait_close(sk, timeout); // 等待socket关闭(查看sk_stream_closing函数,等待TCPF_FIN_WAIT1/TCPF_CLOSING/TCPF_LAST_ACK状态或者超时)
- adjudge_to_death:
- state = sk->sk_state;
- sock_hold(sk);
- sock_orphan(sk); // 设置套接口为孤儿套接口并且设置SOCK_DEAD标志
- /* It is the last release_sock in its life. It will remove backlog. */
- release_sock(sk); // 删除backlog队列并唤醒其他等待socket的线程
- /* Now socket is owned by kernel and we acquire BH lock
- to finish close. No need to check for user refs.
- */
- local_bh_disable();
- bh_lock_sock(sk);
- WARN_ON(sock_owned_by_user(sk));
- percpu_counter_inc(sk->sk_prot->orphan_count);
- /* Have we already been destroyed by a softirq or backlog? */
- if (state != TCP_CLOSE && sk->sk_state == TCP_CLOSE) // socket已经被关闭,跳转到out,不处理
- goto out;
- /* This is a (useful) BSD violating of the RFC. There is a
- * problem with TCP as specified in that the other end could
- * keep a socket open forever with no application left this end.
- * We use a 1 minute timeout (about the same as BSD) then kill
- * our end. If they send after that then tough - BUT: long enough
- * that we won't make the old 4*rto = almost no time - whoops
- * reset mistake.
- *
- * Nope, it was not mistake. It is really desired behaviour
- * f.e. on http servers, when such sockets are useless, but
- * consume significant resources. Let's do it with special
- * linger2 option. --ANK
- */
- if (sk->sk_state == TCP_FIN_WAIT2) { // TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态(已收到FIN的ACK,等待服务器调用close发送FIN)
- struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
- if (tp->linger2 < 0) {
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE);
- tcp_send_active_reset(sk, GFP_ATOMIC);
- NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk),
- LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONLINGER);
- } else {
- const int tmo = tcp_fin_time(sk); // TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态超时时间(本地已经关闭了读写,已经没有任何数据要发送了,如果不启动超时定时器并且服务器不调用close的话,那么TCP_FIN_WAIT2将不会结束)
- if (tmo > TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN) { // 大于60秒,使用TCP_FIN_WAIT2定时器处理TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态,超时之后,tcp_keepalive_timer直接发送RST然后强制关闭socket
- inet_csk_reset_keepalive_timer(sk,
- tmo - TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN);
- } else { // 小于等于60秒
- tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_FIN_WAIT2, tmo); // 调用tcp_time_wait处理,由timewait控制块替代socket控制块(将timewait添加到哈希表,从哈希表删除sk,输入报文将由timewait控制块接收),调用tcp_done将sk状态设置为TCP_CLOSE状态,timewait控制块tw_state处于TCP_TIME_WAIT状态,启动超时定时器,超时之后调用tw_timer_handler释放timewait控制块
- goto out;
- }
- }
- }
- if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE) { // 未处于TCP_CLOSE状态(TCP_FIN_WAIT2等状态,或者等待超时了...)
- sk_mem_reclaim(sk);
- if (tcp_check_oom(sk, 0)) { // 孤儿套接口、发送缓存等超限(具体参考机械工业出版社《Linux内核源码剖析:TCP/IP实现(下册)》P999),不等待服务器,强制关闭socket、发送RST给服务器
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE); // 关闭socket
- tcp_send_active_reset(sk, GFP_ATOMIC); // 发送RST
- NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk),
- LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONMEMORY);
- }
- }
- if (sk->sk_state == TCP_CLOSE) {
- struct request_sock *req = tcp_sk(sk)->fastopen_rsk;
- /* We could get here with a non-NULL req if the socket is
- * aborted (e.g., closed with unread data) before 3WHS
- * finishes.
- */
- if (req)
- reqsk_fastopen_remove(sk, req, false);
- inet_csk_destroy_sock(sk);
- }
- /* Otherwise, socket is reprieved until protocol close. */
- out:
- bh_unlock_sock(sk);
- local_bh_enable();
- sock_put(sk);
- }
tcp_send_fin函数调用栈:

(调试过程,可以修改/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_fin_timeout,增加tcp_fin_timeout,避免TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态直接关闭socket!!!)
3、服务器收到FIN发送ACK(第二次挥手)
3.1、服务器端收到处理FIN报文
服务器在TCP_ESTABLISHED状态下收到报文调用tcp_rcv_established处理收到的报文,如果收到预期的报文(非乱序的报文),那么调用tcp_data_queue将数据接收到接收队列,并检查该报文是否有FIN标志,如果有,就调用tcp_fin关闭接收(客户端已经关闭了发送,所以客户端也不应该再接收数据了)、状态迁移到TCP_CLOSE_WAIT、删除乱序的数据(FIN之后的乱序数据不接收,这些乱序数据基本上应该就是错误的数据)并唤醒其他等待socket的线程。
tcp_fin函数代码实现:
- static void tcp_fin(struct sock *sk)
- {
- struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
- inet_csk_schedule_ack(sk);
- sk->sk_shutdown |= RCV_SHUTDOWN; // 关闭接收
- sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_DONE);
- switch (sk->sk_state) {
- case TCP_SYN_RECV:
- case TCP_ESTABLISHED:
- /* Move to CLOSE_WAIT */
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSE_WAIT); // 迁移到TCP_CLOSE_WAIT状态,等待调用close
- inet_csk(sk)->icsk_ack.pingpong = 1;
- break;
- case TCP_CLOSE_WAIT:
- case TCP_CLOSING:
- /* Received a retransmission of the FIN, do
- * nothing.
- */
- break;
- case TCP_LAST_ACK:
- /* RFC793: Remain in the LAST-ACK state. */
- break;
- case TCP_FIN_WAIT1:
- /* This case occurs when a simultaneous close
- * happens, we must ack the received FIN and
- * enter the CLOSING state.
- */
- tcp_send_ack(sk);
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_CLOSING);
- break;
- case TCP_FIN_WAIT2:
- /* Received a FIN -- send ACK and enter TIME_WAIT. */
- tcp_send_ack(sk);
- tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_TIME_WAIT, 0);
- break;
- default:
- /* Only TCP_LISTEN and TCP_CLOSE are left, in these
- * cases we should never reach this piece of code.
- */
- pr_err("%s: Impossible, sk->sk_state=%d\n",
- __func__, sk->sk_state);
- break;
- }
- /* It _is_ possible, that we have something out-of-order _after_ FIN.
- * Probably, we should reset in this case. For now drop them.
- */
- __skb_queue_purge(&tp->out_of_order_queue); // 删除乱序的队列
- if (tcp_is_sack(tp))
- tcp_sack_reset(&tp->rx_opt);
- sk_mem_reclaim(sk);
- if (!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_DEAD)) {
- sk->sk_state_change(sk); // 调用sk_state_change(正常情况下,sk_state_change函数指针实际指向sock_def_wakeup函数,sk_state_change不是改变socket状态,而是socket状态改变之后的处理函数)
- /* Do not send POLL_HUP for half duplex close. */
- if (sk->sk_shutdown == SHUTDOWN_MASK ||
- sk->sk_state == TCP_CLOSE) // 读写都关闭了或者socket已经关闭了,这种情况下不能读写
- sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_WAITD, POLL_HUP); // 触发POLL_HUP事件
- else
- sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_WAITD, POLL_IN); // 半关闭状态(这里应该是只关闭了读),那么触发POLL_IN事件,socket关闭了读,触发读事件,读socket会返回对应的错误,根据对应的错误就知道socket已经关闭了
- }
- }
tcp_fin函数调用栈:
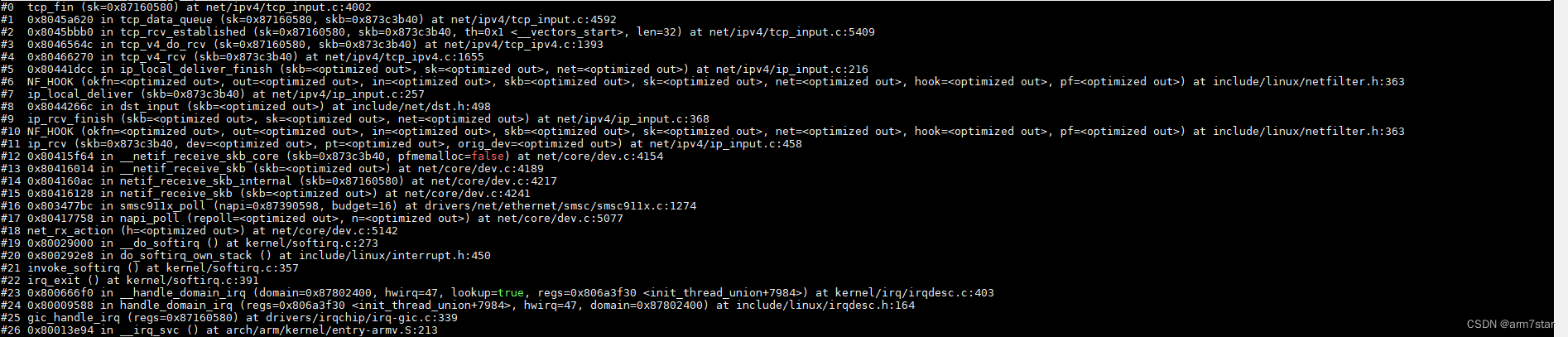
服务器端收到FIN的时候,只关闭了接收,还没关闭发送,服务器端调用tcp_data_snd_check检查是否有数据被确认接收,调用tcp_ack_snd_check检查并发送ACK。
tcp_send_ack函数调用栈:
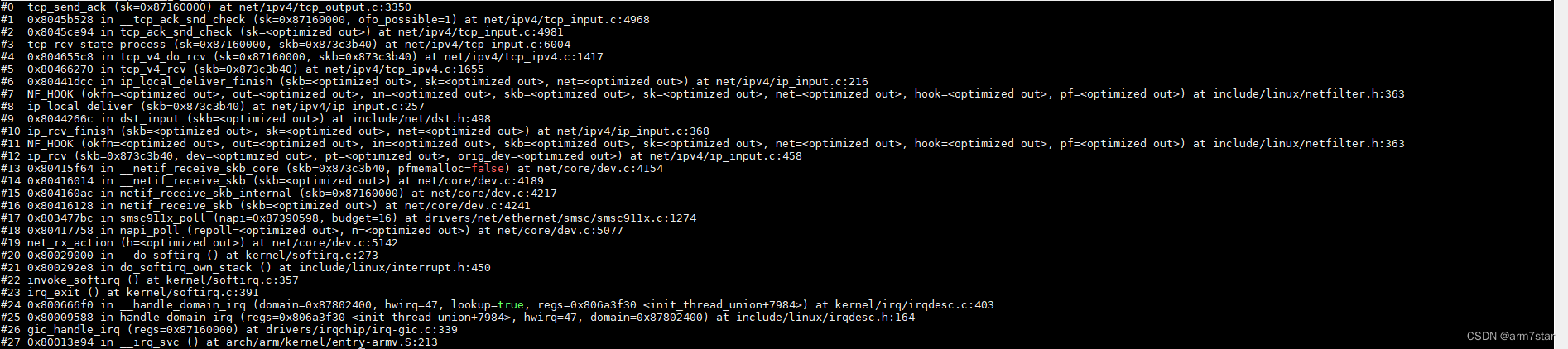
3.2、客户端收到FIN的ACK
阻塞模式,客户端关闭等待socket的时候,收到报文之后,由"用户"处理报文,不在软中断处理;TCP_FIN_WAIT1处理报文的调用栈如下:
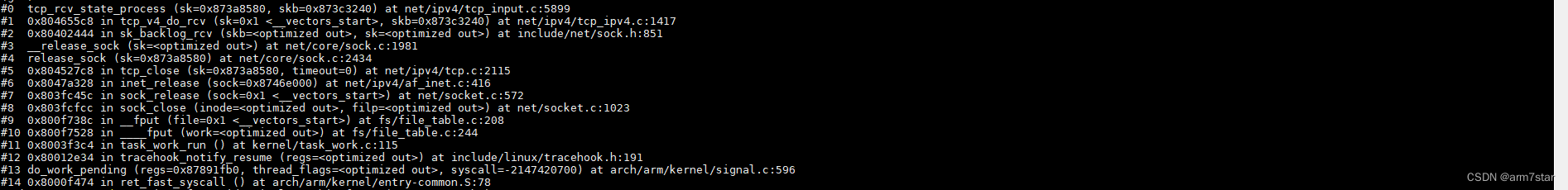
(注意上面的调用栈,接着调用close的函数继续执行,也就是软中断不处理报文)
客户端TCP_FIN_WAIT1状态收到FIN的ACK,迁移到TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态,并启动超时定时器。
tcp_rcv_state_process函数代码如下:
- int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
- {
- struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
- struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
- const struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb);
- struct request_sock *req;
- int queued = 0;
- bool acceptable;
- tp->rx_opt.saw_tstamp = 0;
- switch (sk->sk_state) {
- case TCP_CLOSE:
- goto discard;
- case TCP_LISTEN:
- if (th->ack)
- return 1;
- if (th->rst)
- goto discard;
- if (th->syn) {
- if (th->fin)
- goto discard;
- if (icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request(sk, skb) < 0)
- return 1;
- /* Now we have several options: In theory there is
- * nothing else in the frame. KA9Q has an option to
- * send data with the syn, BSD accepts data with the
- * syn up to the [to be] advertised window and
- * Solaris 2.1 gives you a protocol error. For now
- * we just ignore it, that fits the spec precisely
- * and avoids incompatibilities. It would be nice in
- * future to drop through and process the data.
- *
- * Now that TTCP is starting to be used we ought to
- * queue this data.
- * But, this leaves one open to an easy denial of
- * service attack, and SYN cookies can't defend
- * against this problem. So, we drop the data
- * in the interest of security over speed unless
- * it's still in use.
- */
- kfree_skb(skb);
- return 0;
- }
- goto discard;
- case TCP_SYN_SENT:
- queued = tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(sk, skb, th);
- if (queued >= 0)
- return queued;
- /* Do step6 onward by hand. */
- tcp_urg(sk, skb, th);
- __kfree_skb(skb);
- tcp_data_snd_check(sk);
- return 0;
- }
- req = tp->fastopen_rsk;
- if (req) {
- WARN_ON_ONCE(sk->sk_state != TCP_SYN_RECV &&
- sk->sk_state != TCP_FIN_WAIT1);
- if (!tcp_check_req(sk, skb, req, true))
- goto discard;
- }
- if (!th->ack && !th->rst && !th->syn)
- goto discard;
- if (!tcp_validate_incoming(sk, skb, th, 0))
- return 0;
- /* step 5: check the ACK field */
- acceptable = tcp_ack(sk, skb, FLAG_SLOWPATH |
- FLAG_UPDATE_TS_RECENT) > 0;
- switch (sk->sk_state) {
- case TCP_SYN_RECV:
- if (!acceptable)
- return 1;
- if (!tp->srtt_us)
- tcp_synack_rtt_meas(sk, req);
- /* Once we leave TCP_SYN_RECV, we no longer need req
- * so release it.
- */
- if (req) {
- tp->total_retrans = req->num_retrans;
- reqsk_fastopen_remove(sk, req, false);
- } else {
- /* Make sure socket is routed, for correct metrics. */
- icsk->icsk_af_ops->rebuild_header(sk);
- tcp_init_congestion_control(sk);
- tcp_mtup_init(sk);
- tp->copied_seq = tp->rcv_nxt;
- tcp_init_buffer_space(sk);
- }
- smp_mb();
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);
- sk->sk_state_change(sk);
- /* Note, that this wakeup is only for marginal crossed SYN case.
- * Passively open sockets are not waked up, because
- * sk->sk_sleep == NULL and sk->sk_socket == NULL.
- */
- if (sk->sk_socket)
- sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_IO, POLL_OUT);
- tp->snd_una = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->ack_seq;
- tp->snd_wnd = ntohs(th->window) << tp->rx_opt.snd_wscale;
- tcp_init_wl(tp, TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq);
- if (tp->rx_opt.tstamp_ok)
- tp->advmss -= TCPOLEN_TSTAMP_ALIGNED;
- if (req) {
- /* Re-arm the timer because data may have been sent out.
- * This is similar to the regular data transmission case
- * when new data has just been ack'ed.
- *
- * (TFO) - we could try to be more aggressive and
- * retransmitting any data sooner based on when they
- * are sent out.
- */
- tcp_rearm_rto(sk);
- } else
- tcp_init_metrics(sk);
- tcp_update_pacing_rate(sk);
- /* Prevent spurious tcp_cwnd_restart() on first data packet */
- tp->lsndtime = tcp_time_stamp;
- tcp_initialize_rcv_mss(sk);
- tcp_fast_path_on(tp);
- break;
- case TCP_FIN_WAIT1: { // TCP_FIN_WAIT1状态收到报文
- struct dst_entry *dst;
- int tmo;
- /* If we enter the TCP_FIN_WAIT1 state and we are a
- * Fast Open socket and this is the first acceptable
- * ACK we have received, this would have acknowledged
- * our SYNACK so stop the SYNACK timer.
- */
- if (req) {
- /* Return RST if ack_seq is invalid.
- * Note that RFC793 only says to generate a
- * DUPACK for it but for TCP Fast Open it seems
- * better to treat this case like TCP_SYN_RECV
- * above.
- */
- if (!acceptable)
- return 1;
- /* We no longer need the request sock. */
- reqsk_fastopen_remove(sk, req, false);
- tcp_rearm_rto(sk);
- }
- if (tp->snd_una != tp->write_seq) // TCP_FIN_WAIT1收到ACK不并一定是对FIN的确认,发送FIN的时候并没有检查发送队列,发送队列有数据的时候,FIN报文可能还在排队,FIN的序号应该是tp->write_seq - 1,如果FIN被确认,那么tp->snd_una就应该等于tp->write_seq(下一个发送的序号)
- break; // FIN还没发送
- tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_FIN_WAIT2); // tp->snd_una == tp->write_seq表示FIN已经被确认了,迁移到TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态
- sk->sk_shutdown |= SEND_SHUTDOWN; // 关闭发送
- dst = __sk_dst_get(sk);
- if (dst)
- dst_confirm(dst);
- if (!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_DEAD)) {
- /* Wake up lingering close() */
- sk->sk_state_change(sk);
- break;
- }
- if (tp->linger2 < 0 ||
- (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq != TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq &&
- after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq - th->fin, tp->rcv_nxt))) {
- tcp_done(sk);
- NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONDATA);
- return 1;
- }
- tmo = tcp_fin_time(sk); // 计算TCP_FIN_WAIT2超时时间(与调用tcp_close一样)
- if (tmo > TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN) {
- inet_csk_reset_keepalive_timer(sk, tmo - TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN);
- } else if (th->fin || sock_owned_by_user(sk)) {
- /* Bad case. We could lose such FIN otherwise.
- * It is not a big problem, but it looks confusing
- * and not so rare event. We still can lose it now,
- * if it spins in bh_lock_sock(), but it is really
- * marginal case.
- */
- inet_csk_reset_keepalive_timer(sk, tmo); // 与调用tcp_close一样
- } else {
- tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_FIN_WAIT2, tmo); // 与调用tcp_close一样
- goto discard;
- }
- break;
- }
- case TCP_CLOSING:
- if (tp->snd_una == tp->write_seq) {
- tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_TIME_WAIT, 0);
- goto discard;
- }
- break;
- case TCP_LAST_ACK:
- if (tp->snd_una == tp->write_seq) {
- tcp_update_metrics(sk);
- tcp_done(sk);
- goto discard;
- }
- break;
- }
- /* step 6: check the URG bit */
- tcp_urg(sk, skb, th);
- /* step 7: process the segment text */
- switch (sk->sk_state) {
- case TCP_CLOSE_WAIT:
- case TCP_CLOSING:
- case TCP_LAST_ACK:
- if (!before(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq, tp->rcv_nxt))
- break;
- case TCP_FIN_WAIT1:
- case TCP_FIN_WAIT2:
- /* RFC 793 says to queue data in these states,
- * RFC 1122 says we MUST send a reset.
- * BSD 4.4 also does reset.
- */
- if (sk->sk_shutdown & RCV_SHUTDOWN) {
- if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq != TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq &&
- after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq - th->fin, tp->rcv_nxt)) {
- NET_INC_STATS_BH(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONDATA);
- tcp_reset(sk);
- return 1;
- }
- }
- /* Fall through */
- case TCP_ESTABLISHED:
- tcp_data_queue(sk, skb);
- queued = 1;
- break;
- }
- /* tcp_data could move socket to TIME-WAIT */
- if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE) {
- tcp_data_snd_check(sk);
- tcp_ack_snd_check(sk);
- }
- if (!queued) {
- discard:
- __kfree_skb(skb);
- }
- return 0;
- }
4、服务器端调用close(第三次挥手)
服务器调用close发送FIN与客户端一样,只不过服务器从TCP_CLOSE_WAIT迁移到TCP_LAST_ACK状态,TCP_LAST_ACK状态不用等待关闭,有不用启动定时器,TCP_LAST_ACK如果FIN没有应答的话,会超时重传,超时重传失败就会关闭socket。
5、客户端收到服务器的FIN并发送ACK(第四次挥手)
客户端收到服务器的FIN报文,与服务器收到FIN报文一样,调用tcp_fin处理FIN,客户端处于TCP_FIN_WAIT2状态,收到FIN就发送ACK并迁移到TCP_TIME_WAIT状态。
客户端处理FIN并发送ACK代码如下:

调用栈:
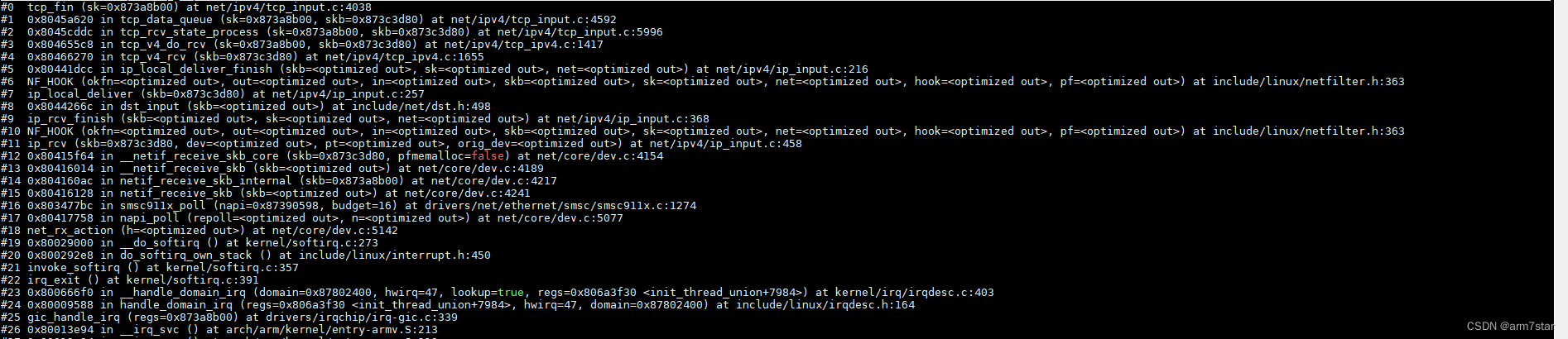
服务器收到FIN的ACK,调用tcp_done关闭socket。
代码如下:

至此,客户端、服务器都已经关闭了socket,更具体细节可以参考机械工业出版社《Linux内核源码剖析:TCP IP实现(下册)》,关闭流程代码基本一致。
-
相关阅读:
Unity热更模块基于 HybridCLR + Addressable
QT object元对象
构建微波和毫米波自动测试系统需要考虑哪些因素?(一)
整理总结提高抖音小店商品转化率的五大策略
Java 进阶:实例详解 Java 虚拟机字节码指令
无法加载文件 C:\Users\haoqi\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\profile.ps1,因为在此系统上禁止运行脚本
Linux服务器的一些优点
git学习
使用mysql语句操作数据库
jQuery学习:显示隐藏 --点击图片显示隐藏
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/arm7star/article/details/126493089
