-
【大话设计模式】策略模式
策略模式定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以相互替换,此模式让算法的变化,不会影响到使用算法的客户。
策略模式是一种定义一系列算法的方法,从概念上看,这些算法完成的都是相同的工作,只是实现不同,它可以以相同的方式调用所有的算法,减少了各种算法类与使用算法类之间的耦合。
策略模式的Strategy类层次为Context定义了一系列可供重用的算法或行为。继承有助于析取出这些算法中的公共功能。
策略模式简化了单元测试,因为每个算法都有自己的类,可以通过自己的接口单独测试。
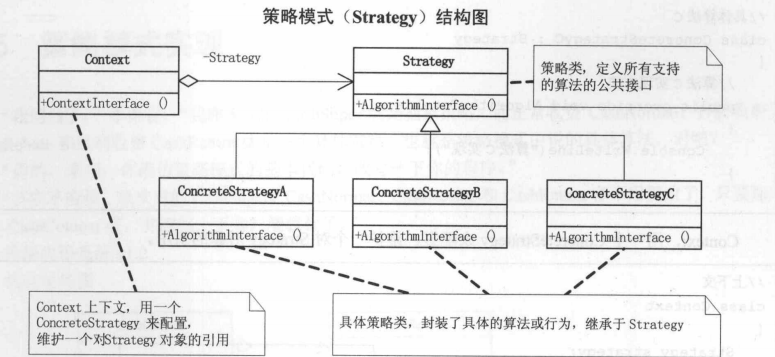
【Strategy类】定义所有支持算法的公共接口
- interface class Strategy:
- void AlgorithmInterface();
【ConcreteStrategy】封装了具体的算法或行为,继承于Strategy
- class ConcreteStrategyA : Strategy
- override void AlgorithmInterface():
- 算法A实现
- class ConcreteStrategyB : Strategy
- override void AlgorithmInterface():
- 算法B实现
- class ConcreteStrategyC : Strategy
- override void AlgorithmInterface():
- 算法C实现
【Context】用一个ConcreteStrategy来配置,维护一个对Strategy对象的引用。
- class Context :
- Strategy strategy;
- public Context(Strategy strategy)
- this.strategy = strategy;
- public void ContextInterface()
- strategy.AlgorithmInterface();
客户端代码:
- static void Main(String[]args)
- Context context;
- context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyA());
- context.ContextInterface();
- context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyB());
- context.ContextInterface();
- context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyC());
- context.ContextInterface();
由于实例化不同,调用算法也不同。
当不同的行为堆砌在一个类中时,就很难避免使用条件语句来选择合适的行为。
将这些行为封装在一个个独立的Strategy 的类中,可以在使用这些行为的类中消除条件语句。
策略模式封装了变化。在实践中,可以封装几乎任何类型的规则,只要在分析过程中需要在不同时间应用不同的业务规则,就可以考虑使用策略模式处理这种变化的可能性。
而策略模式与简单工厂模式结合后,选择具体实现的职责可以由Context来承担,这就最大化地减轻了客户端的职责。
【策略模式和简单工厂结合】
- class Context :
- Strategy strategy;
- public Context(string type):
- switch(type):
- case "A":
- strategy = new ConcreteStrategyA();
- break;
- case "B":
- strategy = new ConcreteStrategyA();
- break;
- case "C":
- strategy = new ConcreteStrategyA();
- break;
- public void ContextInterface()
- strategy.AlgorithmInterface();
简单工厂的应用:将实例化具体策略的过程由客户端转移到Context类中。
客户端:
- Context context;
- context = new Context("A");
- context.ContextInterface();
- context = new Context("B");
- context.ContextInterface();
- context = new Context("C");
- context.ContextInterface();
-
相关阅读:
【# 完美解决 node.js 模块化后报错 ReferenceError: require is not defined】
adb命令大全
计算机毕业设计ssm+vue基本微信小程序的体检预约小程序
Neo4j安装(Docker中安装Neo4j)
AVL树的插入详解
Educational Codeforces Round 130 (Rated for Div. 2) A--C
2022-08-01 C++并发编程(四)
创建一个窗口使用鼠标点击进行画矩形,函数:namedWindow,setMouseCallback
常用类(总结)
字符串截取
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_52043808/article/details/126488933