-
动手学深度学习-深度学习基础
动手学深度学习-深度学习基础
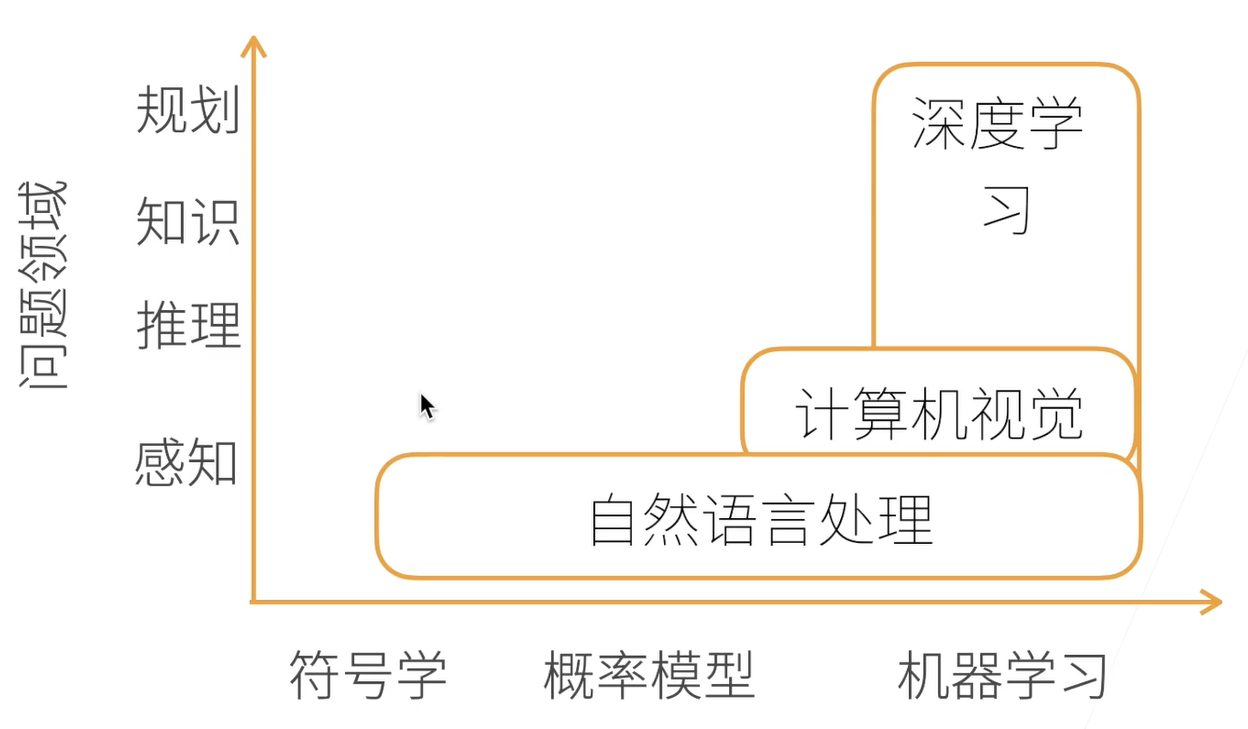
- 深度学习基础:线性神经网络,多层感知机
- 卷积神经网络:LeNet,AlexNet,VGG,Inception,ResNet
- 循环神经网络:RNN,GRU,LSTM,seq2seq
- 注意力机制:Attention,Transformer
- 优化算法:SGD,Momentum,Adam
- 高性能计算:并行,多GPU,分布式
- 计算机视觉:目标检测,语义分割
- 自然语言处理:词嵌入,BERT
1 深度学习介绍
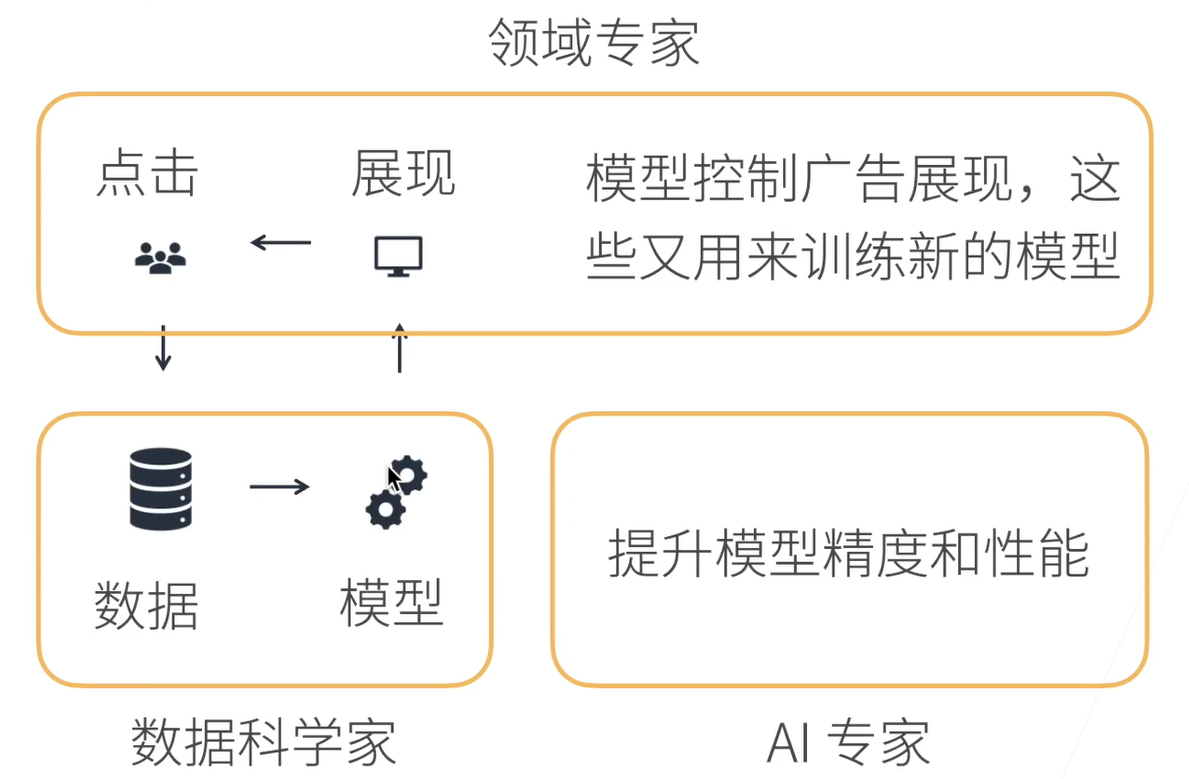
机器学习(Machine Learning)是强大的可以从经验中学习的技术。通过采用观测数据或与环境交互的形式,机器学习算法会积累很多经验,其性能也会逐步提高。
参数(Parameter)可以看作旋钮,我们可以转动旋钮来调整程序的行为。任一调整参数的程序后,称为模型(Model)。通过操作参数而生成的所有不同程序(输入-输出映射)的集合称此为“模型族”。使用数据集来选择参数的元程序被称为学习算法(Learning algorithm)。
2 数据操作+数据预处理
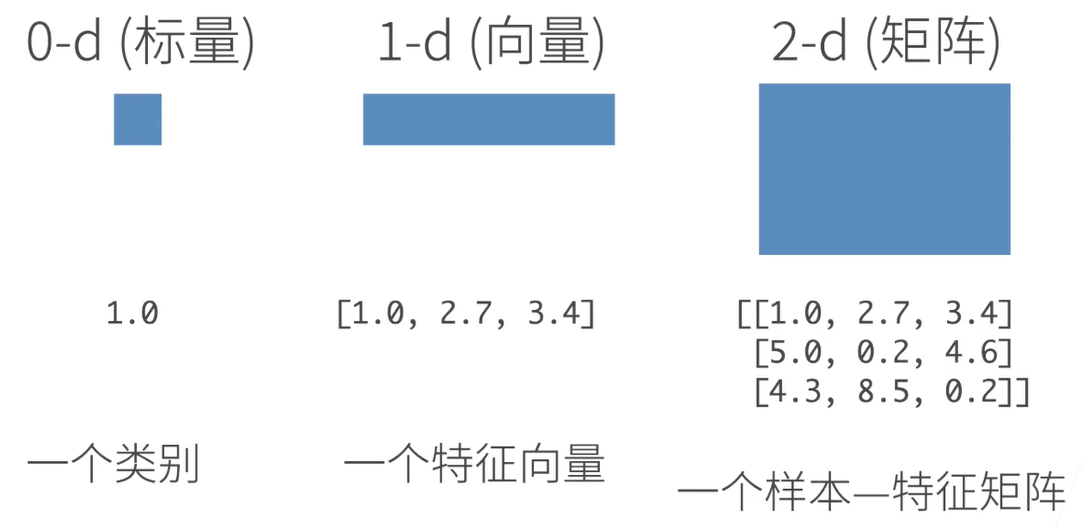
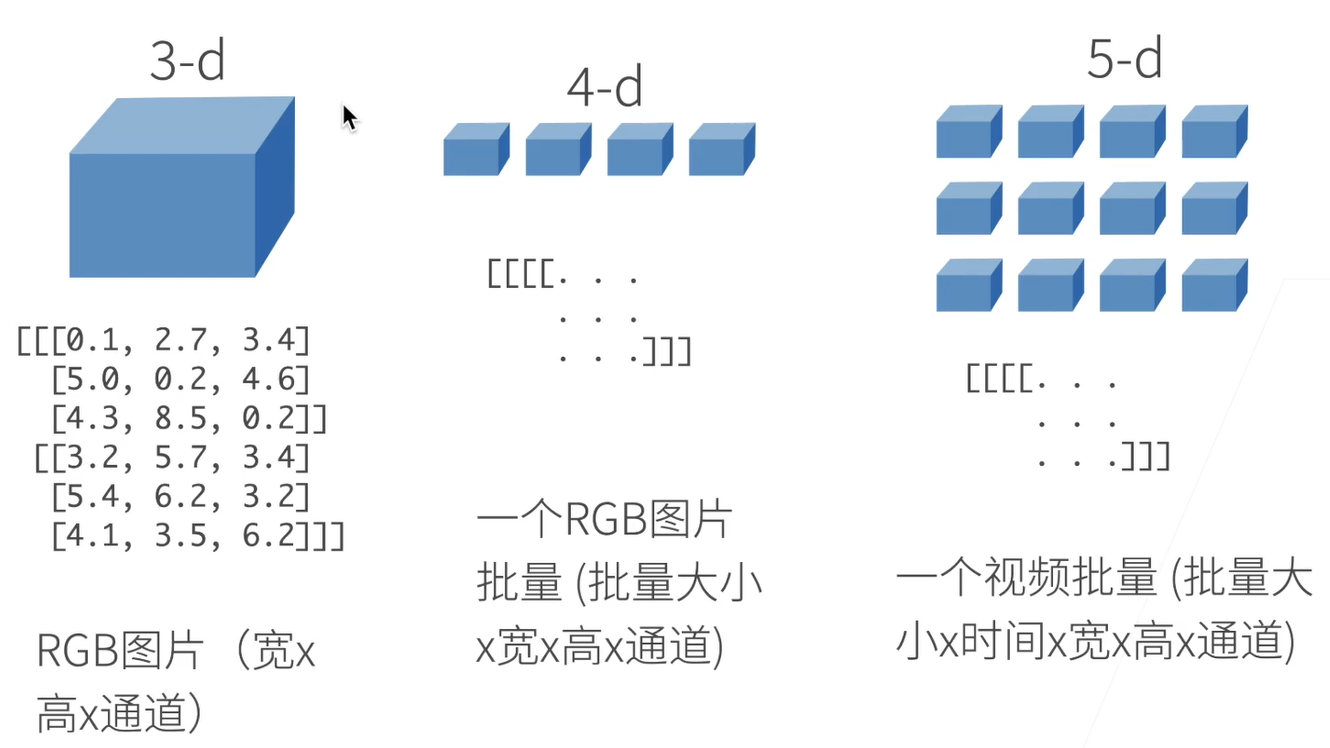
2.1 N维数组
N维数组是机器学习和神经网络的主要数据结构
2.2 创建数组
创建数组需要:形状,每个元素的数据类型和值
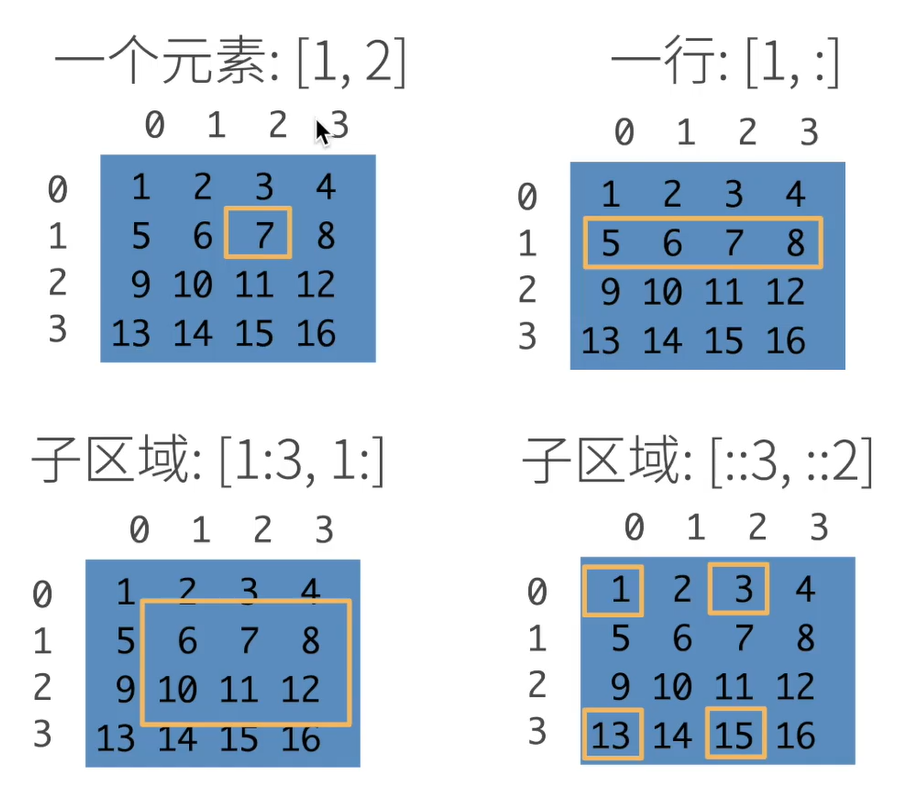
2.3 访问元素
2.4 数据操作
import torch # 张量表示一个数值组成的数组,可能有多个维度 x = torch.arange(12) print(x) # tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) # 通过张量的shape属性来访问张量的形状和元素总数 print(x.shape) # torch.Size([12]) print(x.numel()) # 12 # reshape函数改变一个张量的形状而不改变元素数量和元素值 x = x.reshape(3, 4) print(x) ''' tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]]) ''' # 创建全0或者全1的常量 x = torch.zeros((2, 3, 4)) print(x) ''' tensor([[[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]], [[0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0.]]]) ''' x = torch.ones((2, 3, 4)) print(x) ''' tensor([[[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]], [[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]]]) ''' # 通过提供包含数值的Python列表为张量中的每个元素赋值 x = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) print(x) ''' tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) ''' # 将多个张量拼接起来 x = torch.arange(12, dtype=torch.float32).reshape((3, 4)) print(x) ''' tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6., 7.], [ 8., 9., 10., 11.]]) ''' y = torch.tensor([[2.0, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]]) print(y) ''' tensor([[2., 1., 4., 3.], [1., 2., 3., 4.], [4., 3., 2., 1.]]) ''' # 按行拼接 z0 = torch.cat((x, y), dim=0) print(z0) ''' tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6., 7.], [ 8., 9., 10., 11.], [ 2., 1., 4., 3.], [ 1., 2., 3., 4.], [ 4., 3., 2., 1.]]) ''' # 按列拼接 z1 = torch.cat((x, y), dim=1) print(z1) ''' tensor([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 2., 1., 4., 3.], [ 4., 5., 6., 7., 1., 2., 3., 4.], [ 8., 9., 10., 11., 4., 3., 2., 1.]]) ''' # 即使形状不同,仍然可以通过广播机制来执行按元素操作 a = torch.arange(3).reshape((3, 1)) print(a) ''' tensor([[0], [1], [2]]) ''' b = torch.arange(2).reshape((1, 2)) print(b) ''' tensor([[0, 1]]) ''' print(a + b) ''' tensor([[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3]]) '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
2.5 数据预处理
import os import pandas as pd import torch os.makedirs(os.path.join('.', 'data'), exist_ok=True) data_file = os.path.join('.', 'data', 'house_tiny.csv') with open(data_file, 'w') as f: f.write('NumRooms,Alley,Price\n') f.write('NaN,Pave,127500\n') f.write('2.0,NaN,106000\n') f.write('4.0,NaN,178100\n') f.write('NaN,NaN,140000\n') data = pd.read_csv(data_file) print(data) inputs, outputs = data.iloc[:, 0:2], data.iloc[:, 2] inputs = inputs.fillna(inputs.mean()) print(inputs) ''' NumRooms Alley 0 3.0 Pave 1 2.0 NaN 2 4.0 NaN 3 3.0 NaN ''' print(outputs) ''' 0 127500 1 106000 2 178100 3 140000 ''' # 对于inputs中的类别值或离散值,将NaN视为一个类别 inputs = pd.get_dummies(inputs, dummy_na=True) print(inputs) ''' NumRooms Alley_Pave Alley_nan 0 3.0 1 0 1 2.0 0 1 2 4.0 0 1 3 3.0 0 1 ''' x, y = torch.tensor(inputs.values), torch.tensor(outputs.values) print(x, y) ''' tensor([[3., 1., 0.], [2., 0., 1.], [4., 0., 1.], [3., 0., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64) tensor([127500, 106000, 178100, 140000]) '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
2.6 reshape和view相同
reshape示例
import torch a = torch.arange(12) print(a) ''' tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) ''' b = a.reshape((3, 4)) print(b) ''' tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]]) ''' b[:] = 2 print(a) ''' tensor([2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]) ''' print(b) ''' tensor([[2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2]]) '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
view示例
import torch a = torch.arange(12) print(a) ''' tensor([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) ''' b = a.view((3, 4)) print(b) ''' tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]]) ''' b[:] = 2 print(a) ''' tensor([2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]) ''' print(b) ''' tensor([[2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2], [2, 2, 2, 2]]) '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
3 线性代数
3.1 标量
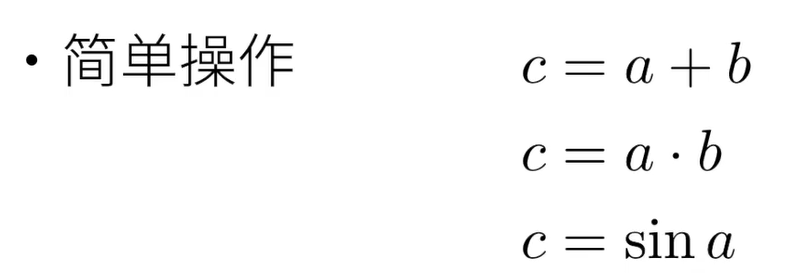
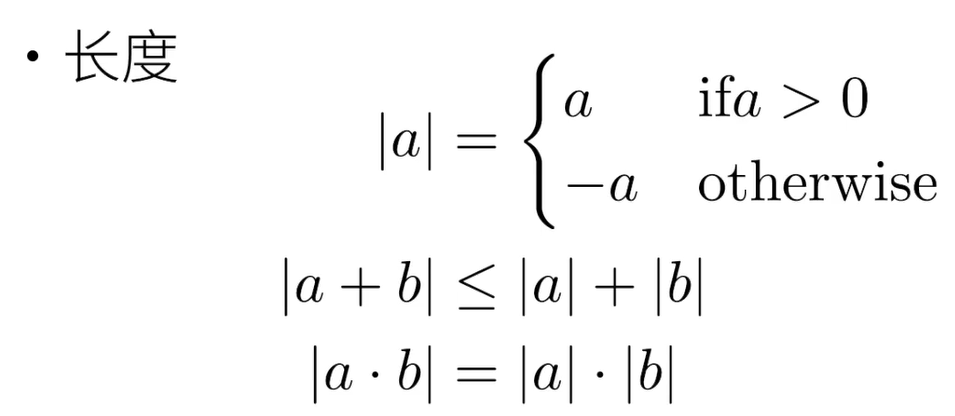
3.2 向量
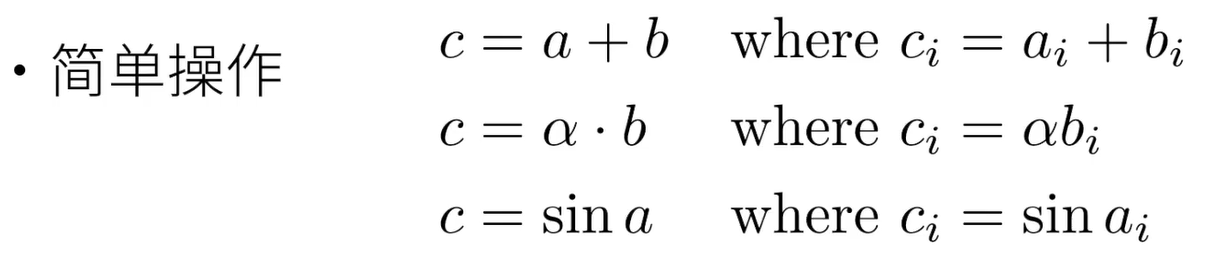
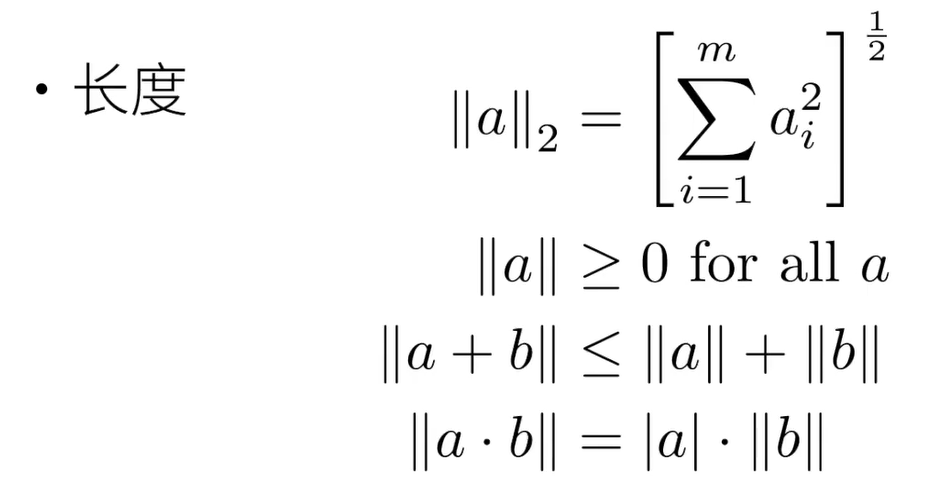
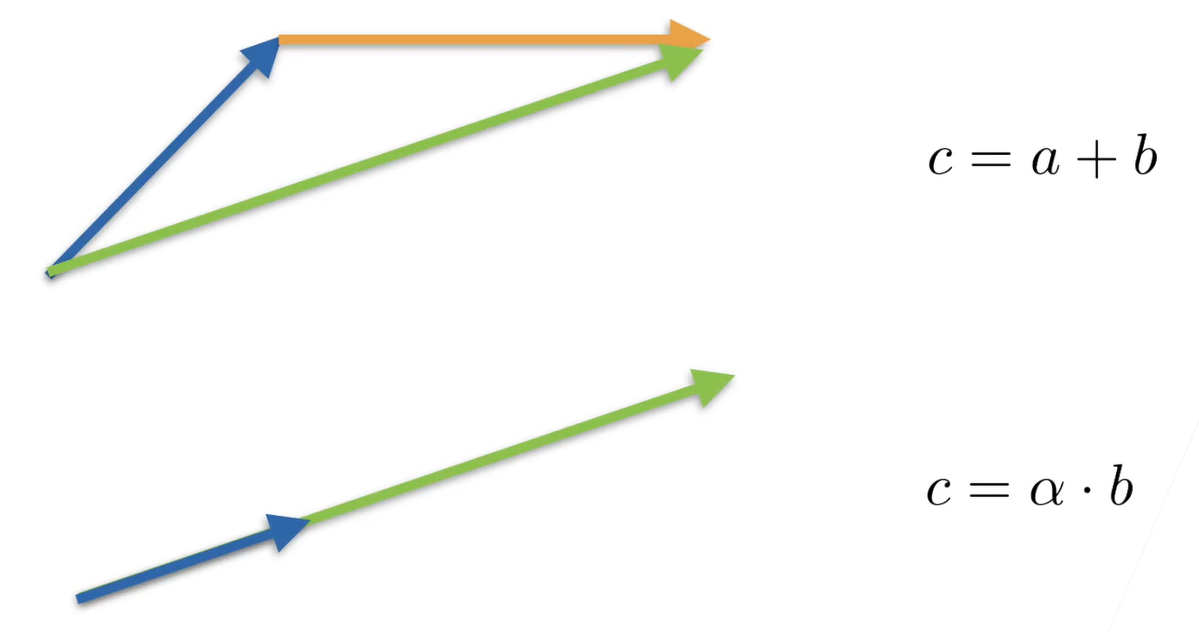
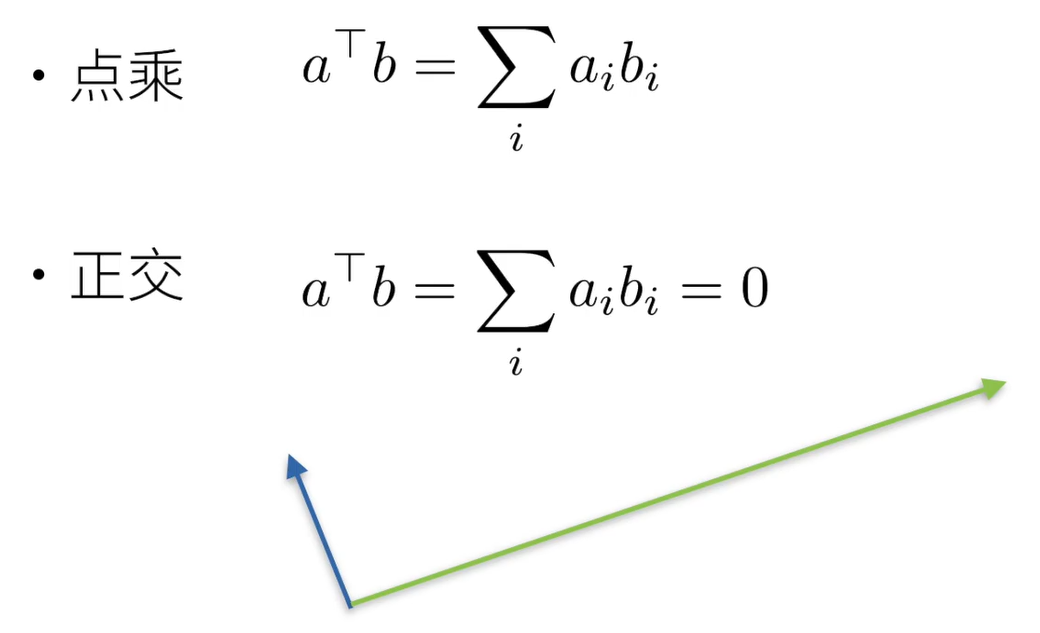
3.3 矩阵

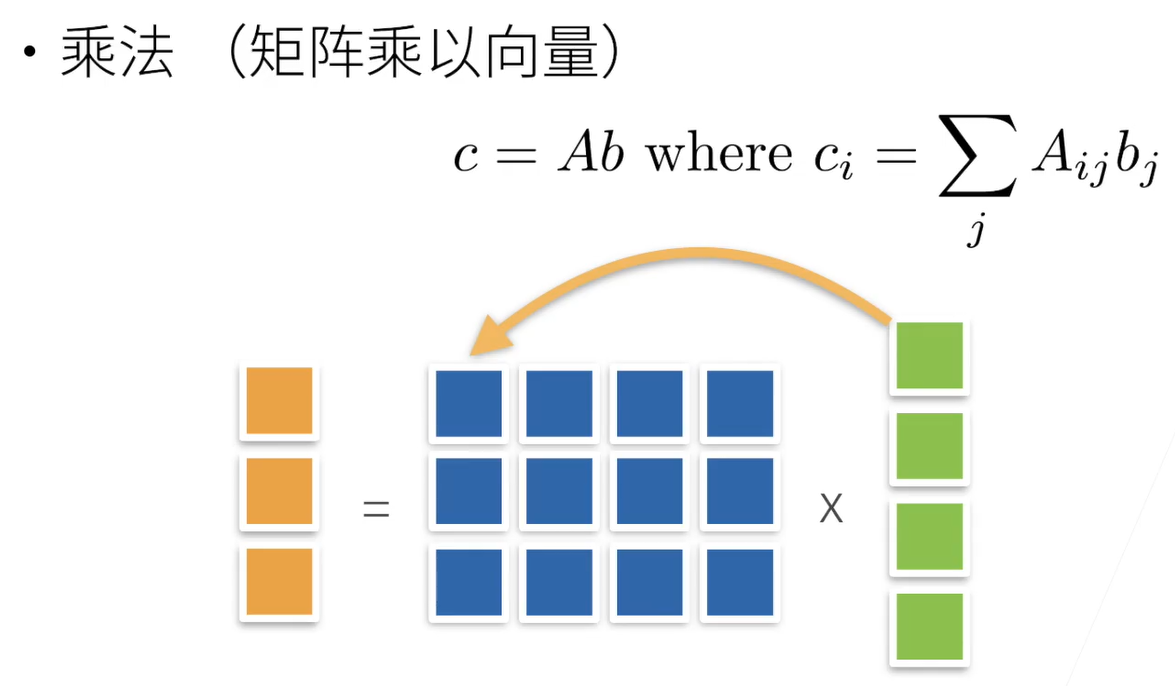



u = torch.tensor([3.0, 4.0]) # L2范数 print(torch.norm(u)) # tensor(5.) # L1范数 print(torch.abs(u).sum()) # tensor(7.)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
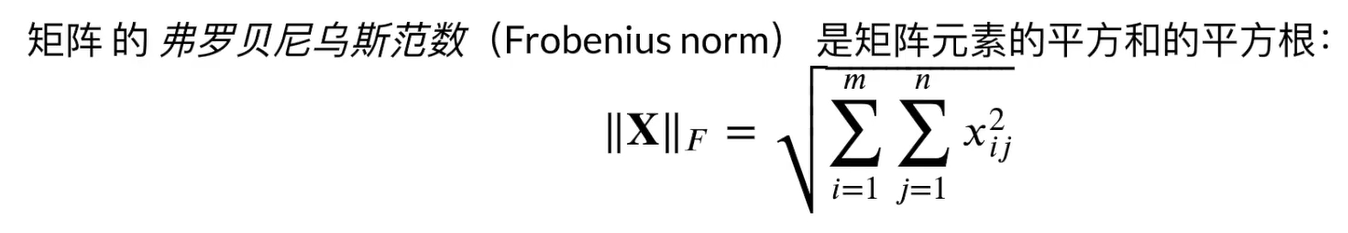
3.4 按特定轴求和
import torch a = torch.ones((2, 5, 4)) print(a.shape) # torch.Size([2, 5, 4]) # 按照第0个维度求和 print(a.sum(axis=0).shape) # torch.Size([5, 4]) # 按照第1个维度求和 print(a.sum(axis=1).shape) # torch.Size([2, 4]) # 按照第2个维度求和 print(a.sum(axis=2).shape) # torch.Size([2, 5]) # 按照第0个维度求和,并且将第0个维度变为1 print(a.sum(axis=0, keepdims=True).shape) # torch.Size([1, 5, 4]) # 按照第1个维度求和,并且将第1个维度变为1 print(a.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True).shape) # torch.Size([2, 1, 4]) # 按照第2个维度求和,并且将第2个维度变为1 print(a.sum(axis=2, keepdims=True).shape) # torch.Size([2, 5, 1])- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
4 矩阵计算
4.1 标量导数
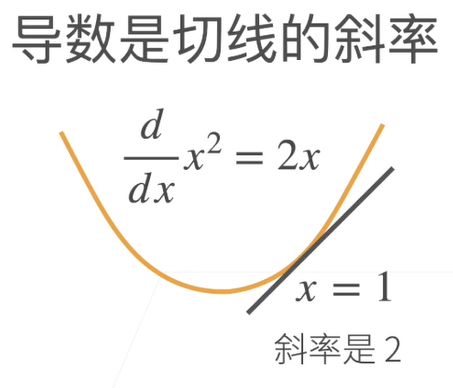
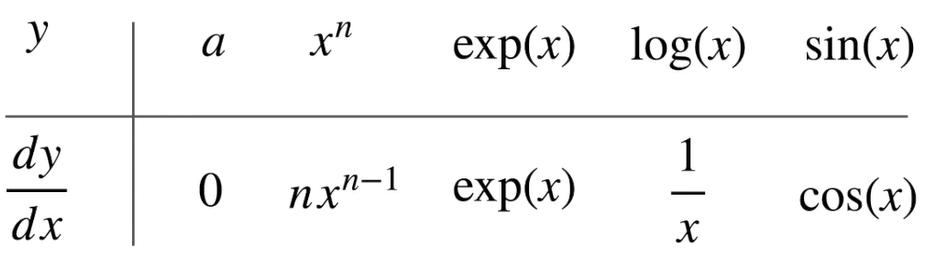
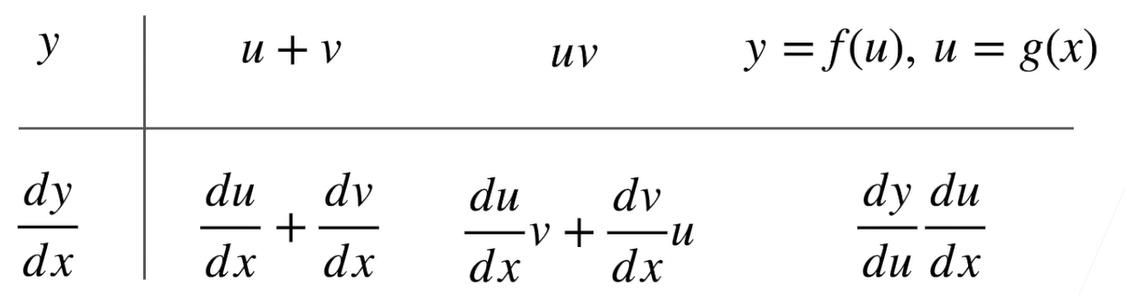
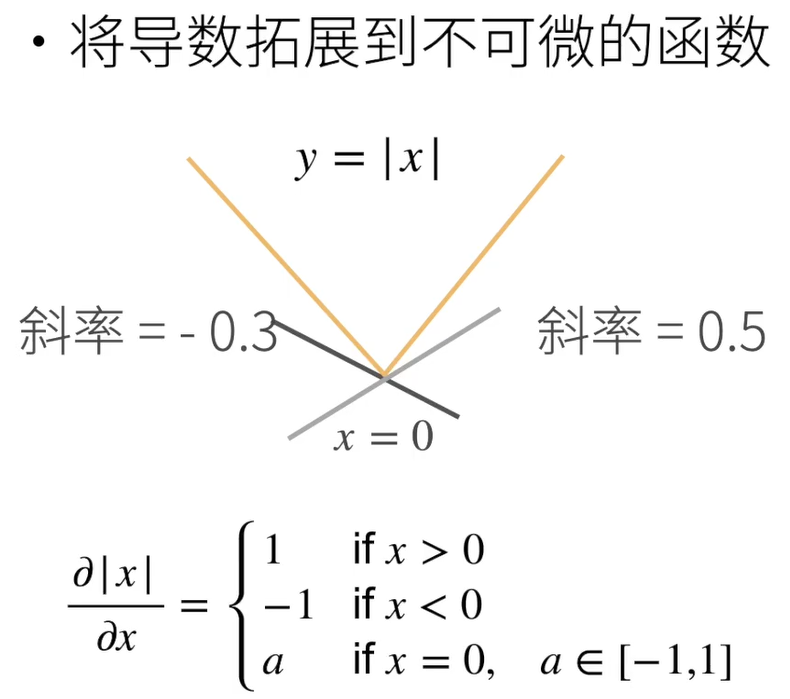
4.2 亚导数
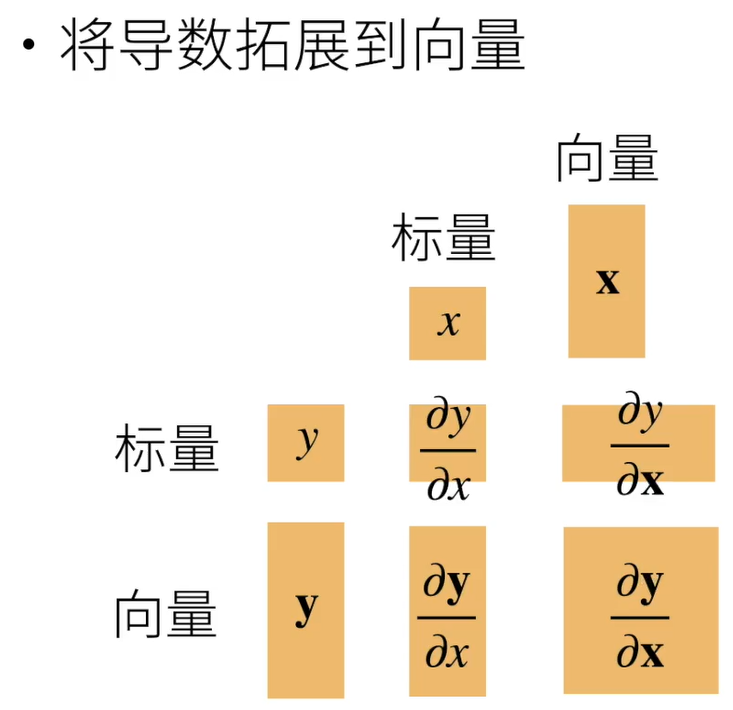
4.3 梯度
5 自动求导
5.1 向量链式法则
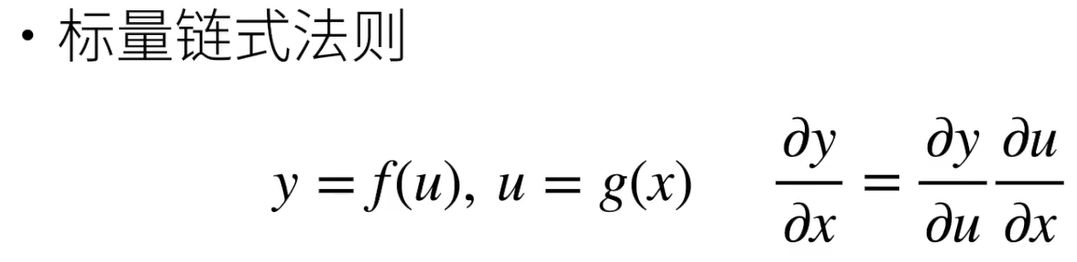
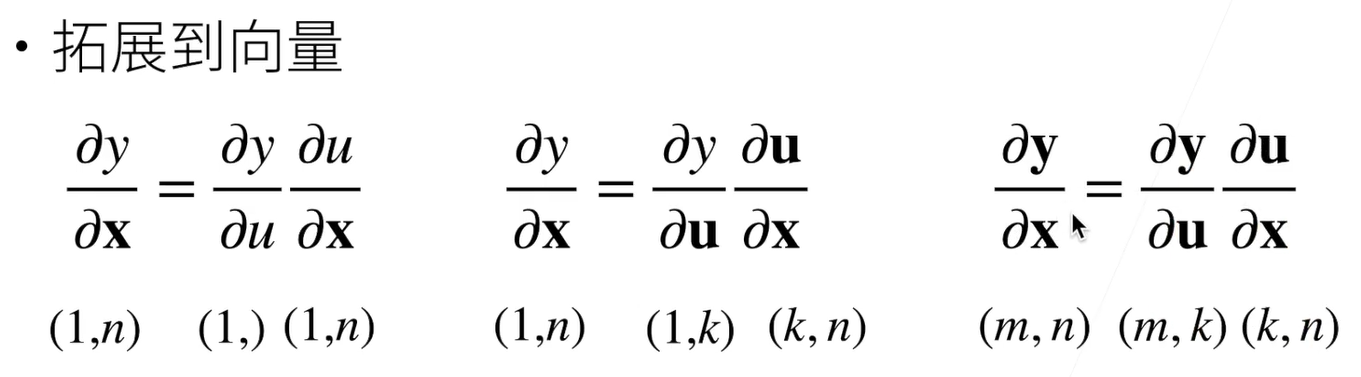
5.2 自动求导

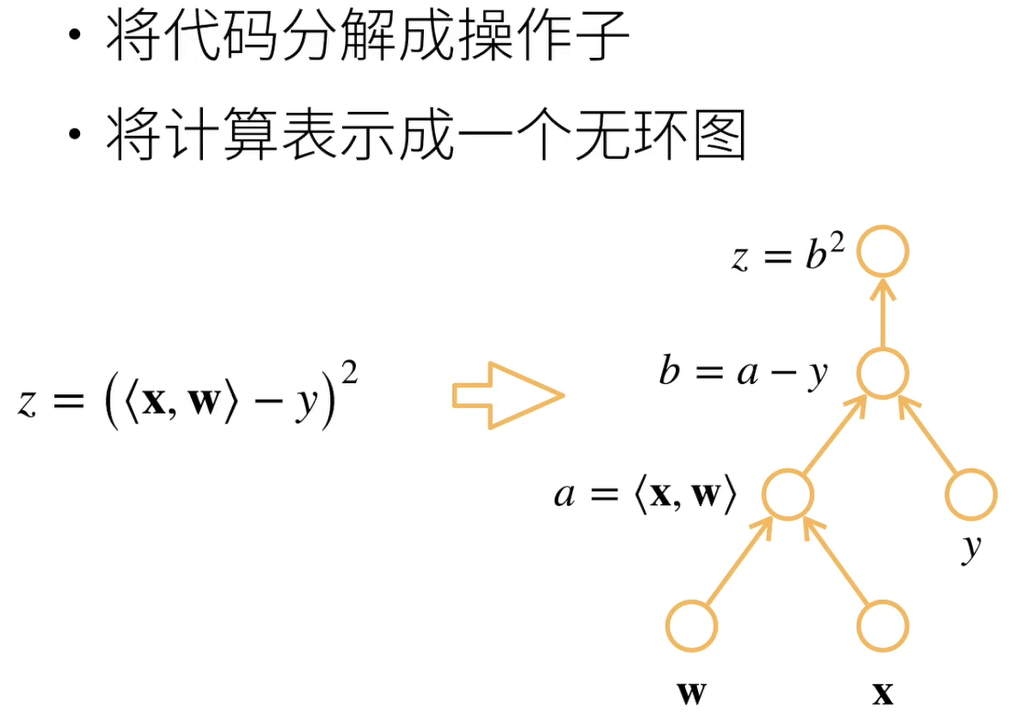
5.3 自动求导的两种模式

-
相关阅读:
java 并行处理任务
Solidity案例详解(四)投票智能合约
五年Java程序员进阶架构师的一些心得以及职业生涯规划
【智能家居入门1之环境信息监测】(STM32、ONENET云平台、微信小程序、HTTP协议)
十四、使用 Vue Router 开发单页应用(2)
Java通过反射机制获取数据类对象的属性及方法
Pytorch入门进行迁移学习实现自行车分类识别:模型迁移训练与效果评估
团队管理|如何提高技术 Leader 的思考技巧?
将项目部署至云服务器的详细过程 以community项目为例
编程随笔-Java | 02.File类常用API
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40507857/article/details/126414993
