-
拉普拉斯特征映射(Laplacian Eigenmaps, LE)
主要思想
LE将 D D D维特征 X = [ x 1 , x 2 , ⋯ , x N ] ∈ R D × N \mathbf{X}=[\mathbf{x}_1, \mathbf{x}_2, \cdots, \mathbf{x}_N]\in\mathbb{R}^{D\times N} X=[x1,x2,⋯,xN]∈RD×N( x i ∈ R D \mathbf{x}_i\in\mathbb{R}^{D} xi∈RD)映射到 d ( d ≪ D ) d(d\ll D) d(d≪D)维空间中( Y = [ y 1 , y 2 , ⋯ , y N ] ∈ R d × N \mathbf{Y}=[\mathbf{y}_1, \mathbf{y}_2, \cdots, \mathbf{y}_N]\in\mathbb{R}^{d\times N} Y=[y1,y2,⋯,yN]∈Rd×N),使得在降维后的空间中,尽量使在原始空间 X \mathbf{X} X中近的点在新的空间 Y \mathbf{Y} Y中仍然近,远的仍然远。
推导方法
根据原始数据 X \mathbf{X} X构造无向加权图邻接矩阵 W ∈ R N × N \mathbf{W}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times N} W∈RN×N(距离越近的两个点,权重越大),根据此矩阵构造度数矩阵
D = [ ∑ i W 1 , i ∑ i W 2 , i ⋱ ∑ i W N , i ] \mathbf{D}=\left[ ∑iW1,i∑iW2,i⋱∑iWN,i\right] D=⎣ ⎡∑iW1,i∑iW2,i⋱∑iWN,i⎦ ⎤∑iW1,i∑iW2,i⋱∑iWN,i
那么拉普拉斯矩阵 L = D − W \mathbf{L}=\mathbf{D}-\mathbf{W} L=D−W,所以优化目标为
a r g min Y 1 2 ∑ i , j = 1 N W i , j ∥ y i − y j ∥ 2 a r g min Y 1 2 ∑ i , j = 1 N W i , j ( y i − y j ) T ( y i − y j ) a r g min Y 1 2 ∑ i , j = 1 N W i , j ( y i T y i − y i T y j − y j T y i + y j T y j ) a r g min Y ∑ i = 1 N y i T y i ∑ j = 1 N W i , j − ∑ i , j = 1 N W i , j y i T y j a r g min Y t r a c e ( Y D Y T ) − t r a c e ( Y W Y T ) [ t r a c e ( y i T y j ) = t r a c e ( y j y i T ) ] a r g min Y t r a c e ( Y ( D − W ) Y T ) a r g min Y t r a c e ( Y L Y T ) \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i,j=1}^N{\mathbf{W}_{i,j}\parallel \mathbf{y}_i-\mathbf{y}_j\parallel ^2} \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i,j=1}^N{\mathbf{W}_{i,j}\left( \mathbf{y}_i-\mathbf{y}_j \right) ^T\left( \mathbf{y}_i-\mathbf{y}_j \right)} \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i,j=1}^N{\mathbf{W}_{i,j}\left( \mathbf{y}_{i}^{T}\mathbf{y}_i-\mathbf{y}_{i}^{T}\mathbf{y}_j-\mathbf{y}_{j}^{T}\mathbf{y}_i+\mathbf{y}_{j}^{T}\mathbf{y}_j \right)} \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,\sum_{i=1}^N{\mathbf{y}_{i}^{T}\mathbf{y}_i{\color{red} \sum_{j=1}^N{\mathbf{W}_{i,j}}}}-\sum_{i,j=1}^N{\mathbf{W}_{i,j}\mathbf{y}_{i}^{T}\mathbf{y}_j} \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,trace\left( \mathbf{Y}{\color{red} \mathbf{D}}\mathbf{Y}^T \right) -trace\left( \mathbf{YWY}^T \right) \,\, {\color{blue} \left[ trace\left( \mathbf{y}_{i}^{T}\mathbf{y}_j \right) =trace\left( \mathbf{y}_j\mathbf{y}_{i}^{T} \right) \right] } \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,trace\left( \mathbf{Y}{\color{green} \left( \mathbf{D}-\mathbf{W} \right) }\mathbf{Y}^T \right) \\ \mathop {\mathrm{arg} \min} \limits_{\mathbf{Y}}\,\,trace\left( \mathbf{Y}{\color{green} \mathbf{L}}\mathbf{Y}^T \right) \\ Yargmin21i,j=1∑NWi,j∥yi−yj∥2Yargmin21i,j=1∑NWi,j(yi−yj)T(yi−yj)Yargmin21i,j=1∑NWi,j(yiTyi−yiTyj−yjTyi+yjTyj)Yargmini=1∑NyiTyij=1∑NWi,j−i,j=1∑NWi,jyiTyjYargmintrace(YDYT)−trace(YWYT)[trace(yiTyj)=trace(yjyiT)]Yargmintrace(Y(D−W)YT)Yargmintrace(YLYT)
引入约束 Y D Y T = I \mathbf{Y}\mathbf{D}\mathbf{Y}^T=\mathbb{I} YDYT=I(确保尺度大小不变且不会退化到更低维度空间)后的优化目标为
{ a r g min Y t r a c e ( Y L Y T ) s . t . Y D Y T = I ⇔ { a r g min Y t r a c e ( Z D − 1 / 2 L D − 1 / 2 Z T ) s . t . Z Z T = I Y = Z D − 1 / 2 \left\{ argminYtrace(YLYT)s.t.YDYT=I\right. \\ \Leftrightarrow \left\{ argminYtrace(ZD−1/2LD−1/2ZT)s.t.ZZT=IY=ZD−1/2argminYtrace(YLYT)s.t.YDYT=I \right. \\ ⎩ ⎨ ⎧Yargmintrace(YLYT)s.t.YDYT=I⇔⎩ ⎨ ⎧Yargmintrace(ZD−1/2LD−1/2ZT)s.t.ZZT=IY=ZD−1/2argminYtrace(ZD−1/2LD−1/2ZT)s.t.ZZT=IY=ZD−1/2
由上可知,最优值 Y \mathbf{Y} Y为矩阵 D − 1 L \mathbf{D}^{-1}\mathbf{L} D−1L所对应的最小 d d d个特征值对应的特征向量的转置!此外,由于拉普拉斯矩阵 L \mathbf{L} L自身含有特征值为0的全1的特征向量,则相应的 D − 1 L \mathbf{D}^{-1}\mathbf{L} D−1L也有全1的特征向量,这样一来,所有的 y i ∣ i = 1 N \mathbf{y}_i|_{i=1}^{N} yi∣i=1N都有个维度的值为1,所以一般来说不取最小的0特征值对应的特征向量,从倒数第二小的特征值对应的特征向量开始取。
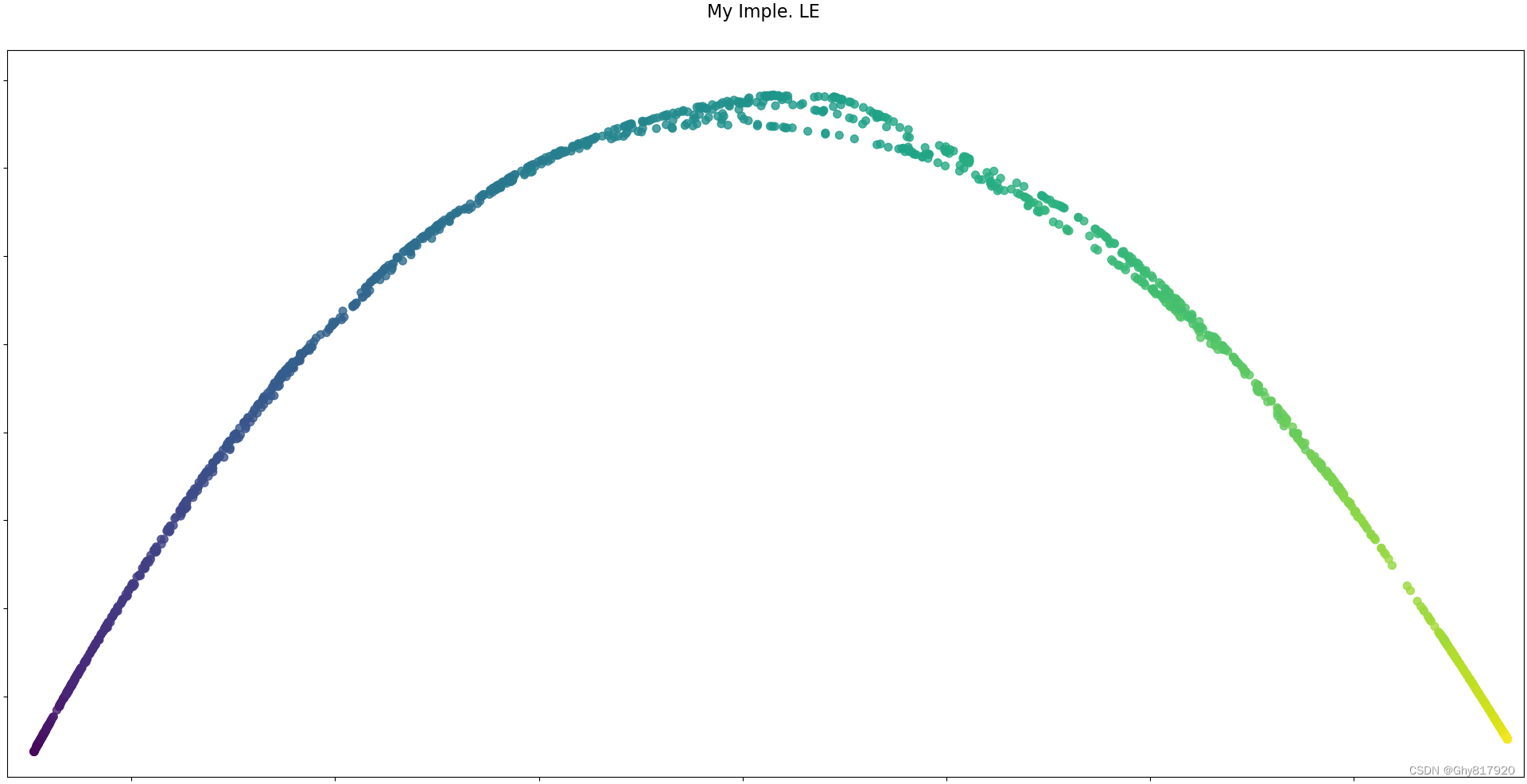
from numpy.random import RandomState import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import ticker # unused but required import for doing 3d projections with matplotlib < 3.2 import mpl_toolkits.mplot3d # noqa: F401 from sklearn import manifold, datasets import numpy as np from scipy.sparse import diags rng = RandomState(0) n_samples = 1500 S_points, S_color = datasets.make_s_curve(n_samples, random_state=rng) def plot_3d(points, points_color, title): x, y, z = points.T fig, ax = plt.subplots( figsize=(6, 6), facecolor="white", tight_layout=True, subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"}, ) fig.suptitle(title, size=16) col = ax.scatter(x, y, z, c=points_color, s=50, alpha=0.8) ax.view_init(azim=-60, elev=9) ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1)) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1)) ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1)) fig.colorbar(col, ax=ax, orientation="horizontal", shrink=0.6, aspect=60, pad=0.01) # plt.show() def plot_2d(points, points_color, title): fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3), facecolor="white", constrained_layout=True) fig.suptitle(title, size=16) add_2d_scatter(ax, points, points_color) # plt.show() def add_2d_scatter(ax, points, points_color, title=None): x, y = points.T ax.scatter(x, y, c=points_color, s=50, alpha=0.8) ax.set_title(title) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.NullFormatter()) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.NullFormatter()) def sklearn_le(): spectral = manifold.SpectralEmbedding( n_components=n_components, n_neighbors=n_neighbors ) S_spectral = spectral.fit_transform(S_points) plot_2d(S_spectral, S_color, "Sklearn LE") def my_le(): # 借助sklearn LE 构造邻接矩阵 偷个懒!! spectral = manifold.SpectralEmbedding( n_components=n_components, n_neighbors=n_neighbors ) W = spectral._get_affinity_matrix(S_points).toarray() D = np.diag(np.sum(W, axis=1)) S = np.diag(1. / np.sum(W, axis=1)) @ (D - W) values, vectors = np.linalg.eig(S) idxs = np.argsort(values) # 除去最小的0特征向量 W = vectors[:,[idxs[i] for i in range(1,3)]] W[:,0] = -W[:,0] #确保与sklearn一样 plot_2d(W, S_color, "My Imple. LE") if __name__ == "__main__": n_neighbors = 12 # neighborhood which is used to recover the locally linear structure n_components = 2 # number of coordinates for the manifold plot_3d(S_points, S_color, "Original S-curve samples") sklearn_le() my_le() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90

-
相关阅读:
在Qt中怎么操作MySQL数据库
1039 到底买不买
Chapter20: Machine Learning for In Silico ADMET Prediction
ps命令介绍及常用操作和参数说明
protable列表实现搜索框
GraalVM java17 Windows打包
Tronapi-波场接口-源码无加密-可二开--附接口文档-基于ThinkPHP5封装-作者详细指导-2022年7月1日08:43:06
项目完成小结 - Django3.x版本 - 开发部署小结 (2)
ADM 架构开发方法概述以及各个阶段的目的和交付物
RUST与Python对比分析
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Ghy817920/article/details/126394919
