-
Jetson Nano TensorRT C++加速 YOLOV5,集成进qt项目中
tensorrtx C++版本的yolov5 tensorRT加速。 感谢开源大佬的无私奉献。
环境前提:搭建好YOLOv5所需环境,Jetson Nano自带了tensorRT环境。
进入正题,首先是tensorrtx 项目的使用。
简单翻译一下仓库readme。
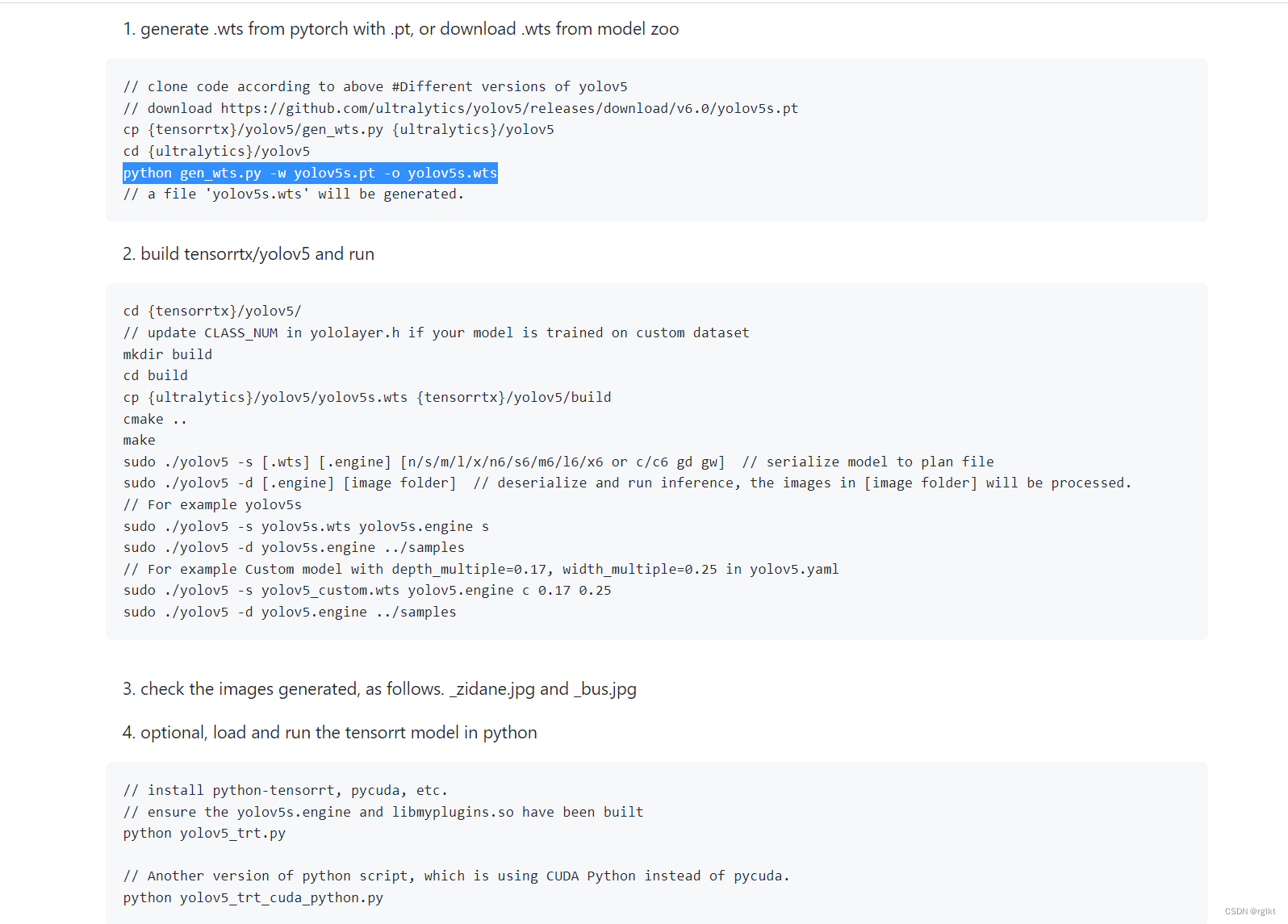
第一步生成后续需要使用到的wts文件。准备好tensorrtx yolov5代码,yolov5官方代码,以及模型权(以官方yolov5s.pt为例),将tensorrtx代码中的gen_wts.py文件复制到yolov5代码文件夹下。使用python3 gen_wts.py -w yolov5s.pt -o yolov5s.wts- 1
- 2
生成.wts文件,注意jetson nano中python是使用的python2.x版本,现在应该都是3.x版本的,所以用python3而不是python。
第二步,使用cmake构建tensorrtx项目并使用。
在tensorrtx yolov5 代码下创建build文件夹,并将第一步生成的wts文件复制到这个文件夹下。进入build文件夹输入以下命令,构建项目
cmake .. make- 1
- 2
生成可执行文件

使用以下命令生成tensorRT引擎文件sudo ./yolov5 -s yolov5s.wts yolov5s.engine s- 1

先准备一下测试用的图片,这里使用yolov5的图片,将tensorrtx yolov5中的samples删除,重新创建一个samples文件夹,并将yolov5以下路径的图片复制到samples文件夹下

(发现这里的cp命令错了,cp到tensorrt的根目录下了,注意复制到samples文件下)使用可执行文件来使用tensorrtx生成的engine文件(记得回到build目录)
sudo ./yolov5 -d yolov5s.engine ../samples- 1

模型没有预热,第一张照片耗时久很正常。

将其集成进qt项目中
首先是qt pro文件,以下是jetson nano环境下的配置文件。简单说明一下,除了opencv,qt,libtorch和tensorrt所需要的库和头文件,还有一个很重要的部分是需要编译.cuda文件,tensorrtx中部分函数是使用cuda进行显卡加速的,因此项目需要配置cuda文件的编译库。
#------------------------------------------------- # # Project created by QtCreator 2022-04-06T13:51:43 # #------------------------------------------------- QT += core gui greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets TARGET = guiTensorRT TEMPLATE = app # The following define makes your compiler emit warnings if you use # any feature of Qt which has been marked as deprecated (the exact warnings # depend on your compiler). Please consult the documentation of the # deprecated API in order to know how to port your code away from it. DEFINES += QT_DEPRECAT/D_WARNINGS # In order to do so, uncomment the following line. # You can also select to disable deprecated APIs only up to a certain version of Qt. #DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0 SOURCES += \ main.cpp \ gui.cpp \ yolov5tr.cpp \ common.cpp HEADERS += \ gui.h \ yolov5tr.h \ common.h # opencv INCLUDEPATH += \ /usr/include/opencv4/opencv2 \ /usr/include/opencv4 \ LIBS += /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libopencv* \ # libtorch #INCLUDEPATH += \ # /home/nvidia/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/include/torch/csrc/api/include \ # /home/nvidia/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/include \ #LIBS += \ # /home/nvidia/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/lib/*.so \ # -L/home/nvidia/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/lib \ # -Wl,--no-as-needed -ltorch_cuda # force to link torch_cuda INCLUDEPATH += \ /usr/local/cuda-10.2/targets/aarch64-linux/include/ \ /usr/local/cuda-10.2/include/ \ /usr/include/aarch64-linux-gnu \ /usr/src/tensorrt/samples/common/ LIBS += \ /usr/local/cuda-10.2/targets/aarch64-linux/lib/*.so \ /usr/local/cuda-10.2/lib64/*.so \ /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/*.so # cannot link opencvlib twice #tensorRT INCLUDEPATH += \ /home/nvidia/Desktop/yolov5-tensorRT LIBS += \ /home/nvidia/Desktop/yolov5-tensorRT/build/*.so \ -L/home/nvidia/Desktop/yolov5-tensorRT/build/ #cuda # yolov5 tensorrt dir HEADERS += \ /home/nvidia/Desktop/yolov5-tensorRT/preprocess.h \ CUDA_SOURCES += \ /home/nvidia/Desktop/yolov5-tensorRT/preprocess.cu CUDA_SDK = "/usr/local/cuda-10.2/" # Path to cuda SDK install CUDA_DIR = "/usr/local/cuda-10.2/" # Path to cuda toolkit install # DO NOT EDIT BEYOND THIS UNLESS YOU KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING.... SYSTEM_NAME = ubuntu # Depending on your system either 'Win32', 'x64', or 'Win64' SYSTEM_TYPE = 64 # '32' or '64', depending on your system CUDA_ARCH = sm_53 # Type of CUDA architecture, for example 'compute_10', 'compute_11', 'sm_10' 'sm_50' # https://blog.csdn.net/lb1244206405/article/details/90718040 NVCC_OPTIONS = --use_fast_math # include paths INCLUDEPATH += $$CUDA_DIR/include # library directories QMAKE_LIBDIR += $$CUDA_DIR/lib64/ CUDA_OBJECTS_DIR = ./ # Add the necessary libraries CUDA_LIBS = -lcuda -lcudart # The following makes sure all path names (which often include spaces) are put between quotation marks CUDA_INC = $$join(INCLUDEPATH,'" -I"','-I"','"') #LIBS += $$join(CUDA_LIBS,'.so ', '', '.so') LIBS += $$CUDA_LIBS # Configuration of the Cuda compiler CONFIG(debug, debug|release) { # Debug mode cuda_d.input = CUDA_SOURCES cuda_d.output = $$CUDA_OBJECTS_DIR/${QMAKE_FILE_BASE}.o cuda_d.commands = $$CUDA_DIR/bin/nvcc -D_DEBUG $$NVCC_OPTIONS $$CUDA_INC $$NVCC_LIBS --machine $$SYSTEM_TYPE -arch=$$CUDA_ARCH -c -o ${QMAKE_FILE_OUT} ${QMAKE_FILE_NAME} cuda_d.dependency_type = TYPE_C QMAKE_EXTRA_COMPILERS += cuda_d } else { # Release mode cuda.input = CUDA_SOURCES cuda.output = $$CUDA_OBJECTS_DIR/${QMAKE_FILE_BASE}.o cuda.commands = $$CUDA_DIR/bin/nvcc $$NVCC_OPTIONS $$CUDA_INC $$NVCC_LIBS --machine $$SYSTEM_TYPE -arch=$$CUDA_ARCH -c -o ${QMAKE_FILE_OUT} ${QMAKE_FILE_NAME} cuda.dependency_type = TYPE_C QMAKE_EXTRA_COMPILERS += cuda }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
然后我根据tensorrtx的yolov5.cpp封装了一个yolov5类,方便项目中使用。加载模型后一直保留在内存中,而无需每次推理图片都重新加载一遍模型。
yolov5tr.h#ifndef YOLOV5TR_H #define YOLOV5TR_H #include#include #include #include "cuda_utils.h" #include "logging.h" #include "yololayer.h" #include "utils.h" #include "calibrator.h" #include "preprocess.h" #include "common.h" using namespace cv; class yolov5TR { private: void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, cudaStream_t& stream, void **buffers, float* output, int batchSize); ICudaEngine* engine = nullptr; IExecutionContext* context = nullptr; IRuntime* runtime = nullptr; float* buffers[2]; uint8_t* img_host = nullptr; uint8_t* img_device = nullptr; cudaStream_t stream; int inputIndex; int outputIndex; std::string engineName; public: yolov5TR(); ~yolov5TR(); yolov5TR(std::string engine_name); std::vector<Yolo::Detection> DoInference(Mat img,clock_t*allTime); }; #endif // YOLOV5TR_H - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
#include "yolov5tr.h" #define USE_FP16 // set USE_INT8 or USE_FP16 or USE_FP32 #define DEVICE 0 // GPU id #define NMS_THRESH 0.5 #define CONF_THRESH 0.1 #define BATCH_SIZE 1 #define MAX_IMAGE_INPUT_SIZE_THRESH 3000 * 3000 // ensure it exceed the maximum size in the input images ! // stuff we know about the network and the input/output blobs static const int INPUT_H = Yolo::INPUT_H; static const int INPUT_W = Yolo::INPUT_W; static const int CLASS_NUM = Yolo::CLASS_NUM; static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = Yolo::MAX_OUTPUT_BBOX_COUNT * sizeof(Yolo::Detection) / sizeof(float) + 1; // we assume the yololayer outputs no more than MAX_OUTPUT_BBOX_COUNT boxes that conf >= 0.1 const char* YOLOv5_INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "data"; const char* YOLOv5_OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "prob"; class Logger : public ILogger { void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override { // suppress info-level messages if (severity <= Severity::kWARNING) std::cout << msg << std::endl; } }; static Logger gLogger; yolov5TR::~yolov5TR(){ // Release stream and buffers cudaStreamDestroy(stream); CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(img_device)); CUDA_CHECK(cudaFreeHost(img_host)); CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex])); CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex])); // Destroy the engine context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); runtime->destroy(); std::cout<<"deleted"<<std::endl; } yolov5TR::yolov5TR(std::string engine_name){ engineName = engine_name; std::ifstream fin(engine_name); std::string cached_engine = ""; while (fin.peek() != EOF){ std::stringstream buffer; buffer << fin.rdbuf(); cached_engine.append(buffer.str()); } fin.close(); runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); assert(runtime != nullptr); this->engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(cached_engine.data(), cached_engine.size()); assert(engine != nullptr); context = engine->createExecutionContext(); assert(context != nullptr); assert(engine->getNbBindings() == 2); inputIndex = engine->getBindingIndex(YOLOv5_INPUT_BLOB_NAME); outputIndex = engine->getBindingIndex(YOLOv5_OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME); assert(inputIndex == 0); assert(outputIndex == 1); //Create GPU buffers on device CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc((void**)&buffers[inputIndex], BATCH_SIZE * 3 * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float))); CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc((void**)&buffers[outputIndex], BATCH_SIZE * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float))); // Create stream CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream)); CUDA_CHECK(cudaMallocHost((void**)&img_host, MAX_IMAGE_INPUT_SIZE_THRESH * 3)); CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc((void**)&img_device, MAX_IMAGE_INPUT_SIZE_THRESH * 3)); } void yolov5TR::doInference(IExecutionContext& context, cudaStream_t& stream, void **buffers, float* output, int batchSize) { // infer on the batch asynchronously, and DMA output back to host context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr); CUDA_CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[1], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream)); cudaStreamSynchronize(stream); } std::vector<Yolo::Detection> yolov5TR::DoInference(Mat img,clock_t*allTime){ float* buffer_idx = (float*)buffers[inputIndex]; size_t size_image = img.cols * img.rows * 3; //copy data to pinned memory memcpy(img_host,img.data,size_image); //copy data to device memory CUDA_CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(img_device,img_host,size_image,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice,stream)); preprocess_kernel_img(img_device, img.cols, img.rows, buffer_idx, INPUT_W, INPUT_H, stream); // Run inference auto start = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); static float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE]; doInference(*context, stream, (void**)buffers, prob, BATCH_SIZE); auto end = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); std::cout << "inference time: " << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count() << "ms" << std::endl; *allTime = *allTime + std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count(); std::vector<std::vector<Yolo::Detection>> batch_res(1); auto& res1 = batch_res[0]; nms(res1, prob, CONF_THRESH, NMS_THRESH); auto& res = batch_res[0]; for (size_t j = 0; j < res.size(); j++) { cv::Rect r = get_rect(img, res[j].bbox); cv::rectangle(img, r, cv::Scalar(0x27, 0xC1, 0x36), 2); cv::putText(img, std::to_string((int)res[j].class_id), cv::Point(r.x, r.y - 1), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1.2, cv::Scalar(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF), 2); } return res; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
本来还有qt部分的代码可以演示的,但是还没有整理完,而且目前手头上暂时没有usb相机,暂且作罢,先将精华部分整理出来。
附录
关于python的tensorrt加速,实际上yolov5官方提供了export.py进行导出。直接使用官方代码就可以导出,并且推理代码也是支持tensorrt进行推理的。甚至backbone魔改后的版本,也是可以进行导出和使用的。
-
相关阅读:
clickhouse单机部署
Android原生实现控件点击弹起效果方案(API28及以上)
tiup cluster import
求职攻略| 硬核公司的硬件笔试题长什么样?先来5道选择题
java计算机毕业设计小型企业员工工资管理系统源码+系统+数据库+lw文档+mybatis+运行部署
Spark RDD惰性计算的自主优化
【Redis技术探索】「高可用架构模式」哨兵(sentinel)模式实现主从故障互切换模式详解
束测后台实操文档2-OpenWrt
js 的 document element 的 querySelectorAll写在for外内速度测试2207302107
java 读取resource下的文件
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/rglkt/article/details/126388102
