-
算法:(四)链表
4.1 哨兵节点与双指针
哨兵节点的用途:模拟前驱结点,使链表中的每一个节点都有前驱结点,若链表可能产生新的头节点,则可以加入哨兵节点来简化判断。但无法应用到循环链表中。
面试题21:删除倒数第K个节点
题目:如果给定一个链表,请问如何删除链表中倒数第k个节点?假设链表中节点的总数为n,那么1≤ k ≤ n。要求只遍历链表一次。
思路:哨兵节点,双指针
public ListNode removeKthNode(ListNode head, int k){ // 哨兵节点,可用于简化输入的链表为空,或者删除第一个节点这种边界条件的判断 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1); dummy.next = head; // 双指针 ListNode front = dummy; ListNode back = dummy; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){ front = front.next; } while(front.next != null){ front = front.next; back = back.next; } back.next = back.next.next; // 返回dummy.next而不是head,还是为了省去删除第一个节点的判断 return dummy.next; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
面试题22:链表中循环的入口节点
题目:如果一个链表中包含环,那么应该如何找出环的入口节点?从链表的头节点开始顺着next指针方向进入环的第1个节点为环的入口节点。例如下图,节点3是入口节点。
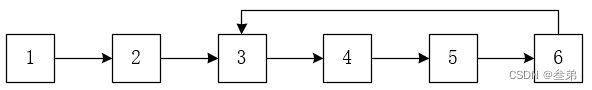
思路:
1.快慢指针判断是否有环,并能返回环中的一个节点
2.环中的一个节点绕环一周,统计环的节点个数k
3.使用双指针,front指针先移动k步,再移动back指针,当两指针相遇则该节点是入口节点
public ListNode getNodeInLoop(ListNode head){ /** * 该方法使用快慢指针,遍历链表 * 判断改链表是否是循环链表 * 若是循环链表,则返回链表中的一个元素 * 若不是循坏链表,则返回null */ if(head == null || head.next == null){ return null; } ListNode slow = head; ListNode fast = slow.next; while(slow!= null && fast != null){ if(slow == fast){ return slow; } // 快慢指针开始为走了第一步后的状态 slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if(fast != null){ fast = fast.next; } } return null; } public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head){ ListNode nodeInLoop = getNodeInLoop(head); if(nodeInLoop == null){ return null; } // 获取循环部分节点的个数 int nodeCount = 1; for(ListNode temp = nodeInLoop.next; temp != nodeInLoop; temp = temp.next){ // 使用for循环而不使用while循环,是为了降低临时变量temp的作用域,减少内存消耗 nodeCount++; } // 双指针获取入口节点 ListNode front = head; ListNode back = head; for(int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++){ front = front.next; } while(front != back){ front = front.next; back = back.next; } return back; } public ListNode detectCyclePro(ListNode head){ /** * 此方法不用获取循环部分的节点个数,根据推导,有以下结论: * ★从相遇点到入环点的距离加上 n-1 圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离★ * 故使用双指针,front指向快慢指针相遇点,back指向表头,二者会在入口节点相遇 */ //获取快慢指针相遇节点,作为front节点 ListNode front = getNodeInLoop(head); if(front == null){ return null; } // back节点指向表头节点 ListNode back = head; while(front != back){ front = front.next; back = back.next; } return back; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
面试题23:两个链表的第1个重合节点
题目:输入两个单向链表,请问如何找出他们的第一个重合节点。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){ /** * 这题方法有三种: * 1. 成环。化为寻找入口节点问题,详见22题。具体做法是遍历任意一个链表,将尾节点与另一个链表的头节点相连,得到一个带环的链表。 * 2. 双栈。由于是单向链表,故重合之后的所有节点都是重合的,所以可以同时遍历两个链表,分别放入一个栈中。然后再出栈,最后一个相同的节点即要找的节点。 * 3. 双指针。先分别遍历两个链表,获取他们节点的个数。然后双指针分别指向各自的头节点。长的链表的指针先走长度之差的步数,保证他们能够同步。 */ // 这是第三种方法 int count1 = countList(head1); int count2 = countList(head2); int delta = Math.abs(count1 - count2); ListNode longer = count1 > count2 ? head1 : head2; ListNode shorter = count1 > count2 ? head2 : head1; for(int i = 0; i < delta; i++){ longer = longer.next; } while(longer != shorter){ longer = longer.next; shorter = shorter.next; } return shorter; } public int countList(ListNode head){ int count = 0; while (head != null){ count++; head = head.next; } return count; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
4.2 反转链表
面试题24:反转链表
题目:定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后的头节点。
思路:三个指针,分别为pre,cur,next
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode next = null; while(cur != null){ next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
面试题25:链表中的数字相加
题目:给定两个表示非负整数的单向链表,请问如何实现这两个整数的相加并且把它们的和仍然用单向链表表示?
思路:反转链表;或者可以用栈来实现
public ListNode addTwoNumber(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){ /** * 反转两个链表进行相加操作 * 需要考虑到进位问题 */ head1 = reverseList(head1); head2 = reverseList(head2); ListNode sumNode = addReverse(head1, head2); sumNode = reverseList(sumNode); return sumNode; } public ListNode addReverse(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){ // 首先建立一个存放结果链表 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode sumNode = dummy; int carry = 0; // 循环遍历链表,同时判断指向两个链表的指针是否走到头了 while(head1 != null || head2 != null){ int sum = (head1 == null ? 0 : head1.val) + (head2 == null ? 0 : head2.val) + carry; carry = sum > 10 ? 1 : 0; sum = sum > 10 ? sum - 10 : sum; ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum); sumNode.next = newNode; sumNode = sumNode.next; head1 = head1 == null ? null : head1.next; head2 = head2 == null ? null : head2.next; } // 最后判断最高位是否需要进位 if(carry > 0){ sumNode.next = new ListNode(carry); } return dummy.next; } public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode next = null; while(cur != null){ next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
面试题26:重排链表
题目:给定一个链表,链表中节点的顺序是L0→L1→L2→…→Ln-1→Ln,请问如何重排链表事节点的顺序变成L0→Ln→L2→Ln-1→L3→Ln-2→…?
思路:将链表一分为二,后半部分进行反转,再使用双指针进行串联。
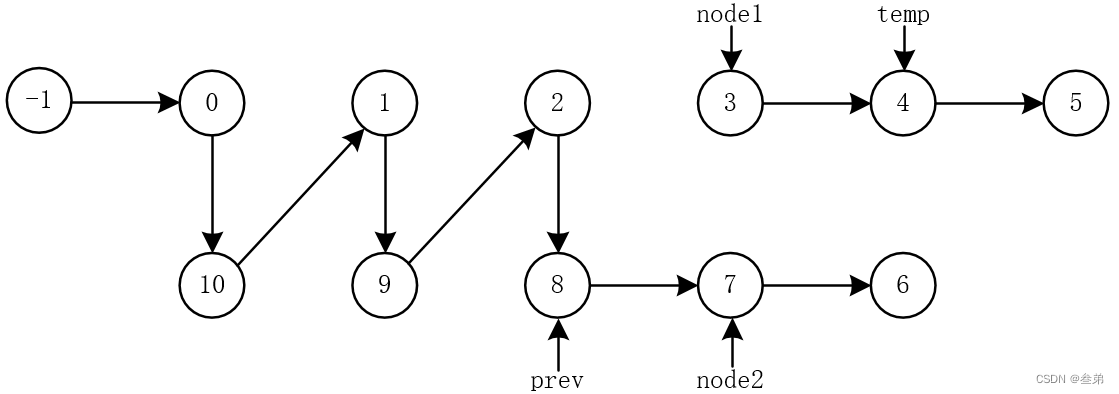
public void recordList(ListNode head){ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy.next = head; ListNode fast = dummy; ListNode slow = dummy; // 快慢指针标准写法 while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; if(fast != null){ fast = fast.next; } } ListNode temp = slow.next; slow.next = null; temp = reverseList(temp); link(head, temp, dummy); } private void link(ListNode node1, ListNode node2, ListNode head){ /** * 将两个链表连接成一个链表 * 需要两个额外的指针,prev指针,指向结果链表当前节点的前一个节点 * temp指针,指向被合入链表的当前节点的下一个节点,用于保存对合入链表的引用 */ ListNode prev = head; // 更改各个指针的指向 while(node1 != null && node2 != null){ ListNode temp = node1.next; prev.next = node1; node1.next = node2; node1 = temp; prev = node2; node2 = node2.next; } // 被合入的链表可能多一个节点 if(node1 != null){ prev.next = node1; } } public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ ListNode next = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } return pre; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
面试题27:回文链表
问题:如何判断一个链表是不是回文?要求解法是时间复杂度是O(n),并且不得使用超过O(1)的辅助空间。如果一个链表是回文,那么链表的节点顺序从前往后和从后往前看都是相同的。
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head){ /** * 和26题基本一致 * 找到链表的中间节点,将其分为两个链表 * 然后将后半部分反转,然后双指针进行判断 */ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); dummy.next = head; ListNode fast = dummy; ListNode slow = dummy; // 快慢指针标准写法 while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; if(fast != null){ fast = fast.next; } } ListNode temp = slow.next; slow.next = null; temp = reverseList(temp); return equals(head, temp); } private boolean equals(ListNode head1, ListNode head2){ while(head1 != null && head2 != null){ if(head1.val != head2.val){ return false; } head1 = head1.next; head2 = head2.next; } return head1== null || head2 == null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
4.3 双向链表和循环链表
面试题28:展平多级双向链表
题目:在一个多级双向链表中,节点除了有两个指针分别指向前后两个节点,还有一个指针指向它的子链表,并且子链表也是一个双向链表,他的节点也有指向子链表的指针。请将这样的多级双向链表展平成普通的双向链表,即所有节点都没有子链表。
public Node flatten(Node head){ flattenGetTail(head); return head; } public Node flattenGetTail(Node head){ /** * 递归调用 * 递归的出口是该层节点都没有子节点,则返回该层最后一个节点作为尾节点 * 若某一层发现子节点,则将子节点作为参数传入递归方法,获取子节点那一层的尾节点 * 然后将该父层展平 */ Node node = head; Node tail = null; while(node != null){ Node next = node.next; if(node.child != null){ Node child = node.child; // 获取子节点层的尾节点 Node childTail = flattenGetTail(child); // 展平该父层 node.child = null; node.next = child; child.prev = node; childTail.next = next; if (next != null){ next.prev = childTail; } tail = childTail; } else { tail = node; } node = next; } return tail; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
面试题29:排序的循环链表
题目:在一个循环链表中的节点的值递增排序,请设计一个算法在该循环链表中插入节点,并保证插入节点之后的循环链表仍然是排序的。
思路:用cur和next指针记录相邻的两个节点是否满足条件,并用biggest记录cur指针的最大值;若找到满足条件的节点,则直接插入;若未找到满足条件的节点,则插入biggest与next节点之间,此时next节点指向循环链表中最小的节点,即head节点。
public Node insert(Node head, int val){ // 边界条件判断 Node node = new Node(val); if(head == null){ head = node; head.next = head; } else if(head.next == head){ // 似乎不用判断节点为1的情况 head.next = node; node.next = head; } else{ insertCore(head, node); } return head; } private void insertCore(Node head, Node node) { Node cur = head; Node next = head.next; Node biggest = cur; // 若能找到相邻的节点满足node.val >= cur.val && node.val <= next.val,则biggest这个节点是无用节点 // 若插入的节点比最小的节点小,或者比最大的节点大,则保证biggest指向最大的节点 while(!(node.val >= cur.val && node.val <= next.val) && next != head){ cur = next; next = next.next; // 这里必须是小于等于,才能保证biggest与next相邻 if(biggest.val <= node.val){ biggest = node; } } // 判断是否找到符合条件的相邻节点 // 若找到相邻节点,则直接插入,否则插入到biggest和next节点之间,此时next节点指向循环链表中的最小节点 if (node.val >= cur.val && node.val <= next.val){ cur.next = node; node.next = next; } else{ node.next = next; biggest.next = node; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
-
相关阅读:
React入门(上)
文件目录操作——Linux命令核心
C语言获取当前时间
npm yarn 和 pnpm 之间命令的区别
MySql事务
Mysql 5.7开启binlog日志
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError - 解决方法 (-Xmx -Xms)
Java项目(三)-- SSM开发社交网站(4)--实现图书类别和图书分页查询
对一个以“#”结束的字符串
不同相机在不同高度拍的图片resize在同一尺度
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/sd_960614/article/details/126376309


