-
【使用matplotlib】使用函数绘制matplotlib的图片组成元素
1. 使用函数绘制matplotlib的图片组成元素
文章目录
- 1. 使用函数绘制matplotlib的图片组成元素
- 1.1 绘制`matplotlib`图表组成元素的主要函数
- 1.1.1 函数简介
- 1.`linspace` (在固定范围内取均匀分布的数字)
- 2. `plot`(线性图)
- 3.`scattere`(散点图)
- 4. `numpy.random.rand` (生成随机矩阵)
- 5. `xlim`, `ylim` (限制坐标轴的范围)
- 6. `xlabel`, `ylabel` (设置x轴的标签文本)
- 7. `grid`(可以绘制刻度线的网格线)
- 8.`axhline`, `axvline`(绘制平行于x或y轴的水平参考线)
- 9. `axvspan`, `axhspan`(绘制垂直于x或y轴的参考选定区域)
- 10. `annotate`(添加图形内容细节的指向性注释文本)
- 11. `text` 添加图形内容细节的无指向型注释文本
- 12. `title` 添加整个图形内容的标题
- 13. `legend` (标示图形的文本标签图例)
1.1 绘制
matplotlib图表组成元素的主要函数在
matplotlib绘制的图像窗口中,底层是个Figure实例,通常称为画布(包含一些可见和不可见的元素),画布上是图形,图形是
Axes实例,几乎包含了所有matplotlib组成元素,例如坐标轴、刻度、标签、线和标记等。Axes实例有x,y轴属性,即
Axex.xaxis和Axes.yaxis控制x轴和y轴相关元素,如刻度线、刻度标签、可短线定位器和刻度线标签格式器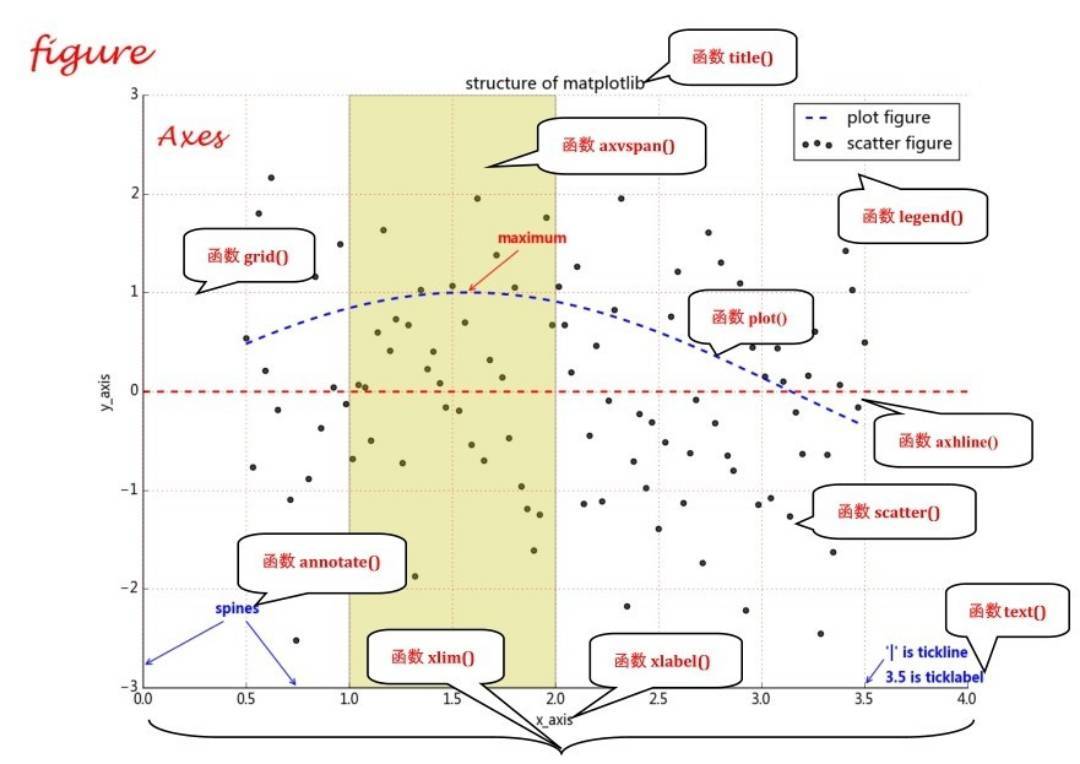
示例:
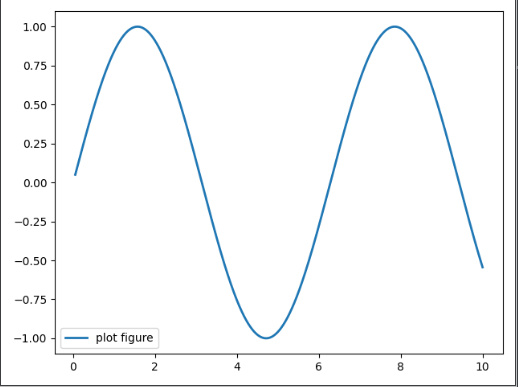
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-", lw=2, label="plot figure") plt.legend() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
代码对应效果
1.1.1 函数简介
1.
linspace(在固定范围内取均匀分布的数字)numpy.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None, axis=0)在指定的时间间隔内返回均匀分布的数字。
返回num 个均匀分布的样本,在区间 [ start , stop ] 上计算。
可以选择排除间隔的端点。
np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000)表示在0.05到10之间均匀的取1000个数
2.
plot(线性图)matplotlib.pyplot.plot(*args, scalex=True, scaley=True, data=None, **kwargs)官网地址:https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.plot.html?highlight=plot#matplotlib.pyplot.plot
将 y 与 x绘制为线条和/或标记。
参数介绍:
x, y :array-like or scalar数据点的水平/垂直坐标。 x值是可选的,默认为
range(len(y)).通常,这些参数是一维数组。
它们也可以是标量或二维的(在这种情况下,列表示单独的数据集)。
这些参数不能作为关键字传递。
fmt: str, optional
格式字符串,例如红色圆圈的“ro”。有关格式字符串的完整说明,请参阅注释 部分。
格式字符串只是快速设置基本行属性的缩写。所有这些以及更多也可以通过关键字参数来控制。
此参数不能作为关键字传递。
data :indexable object, optional
带有标签数据的对象。如果给定,请提供要在x和y中 plot 的标签名称 。
plt.plot(x, y, ls="-", lw=2, label="plot figure")x: x轴上的数值y: y轴上的数值ls: 折线图的线条风格(linestyleorls: 填写一下参数{'-', '--', '-.', ':', '', (offset, on-off-seq), ...})Line Styles(线条风格)
character description '-'solid line style(实线样式) '--'dashed line style(虚线样式) '-.'dash-dot line style(点划线样式) ':'dotted line style(虚线样式) ls='-'
ls='--'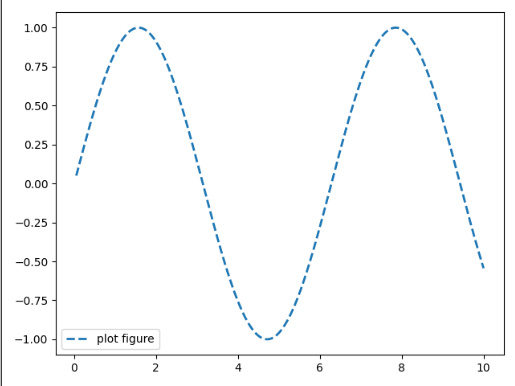
ls='-.'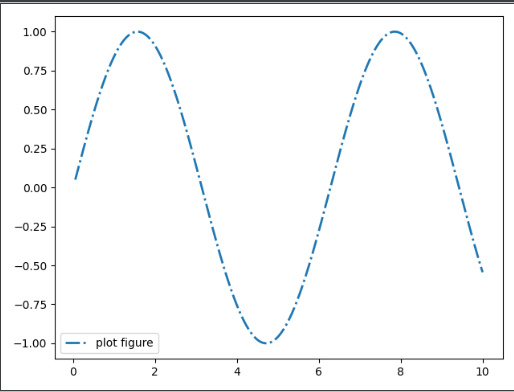
ls=':'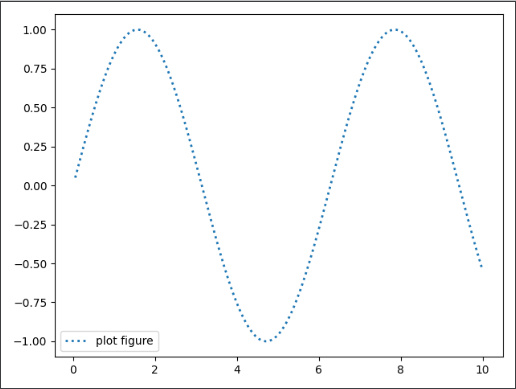
lw: 折线图的线条宽度(linewidthor lw :float类型)label: 标记图形内容的标签文本3.
scattere(散点图)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.random.rand(1000) plt.scatter(x, y, label="scatter figure") plt.legend() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
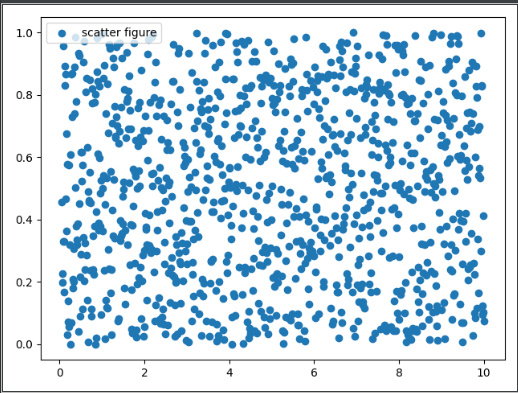
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter(x, y, s=None, c=None, marker=None, cmap=None, norm=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, alpha=None, linewidths=None, *, edgecolors=None, plotnonfinite=False, data=None, **kwargs)官网地址:https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.scatter.html?highlight=scatter#matplotlib.pyplot.scatter
4.
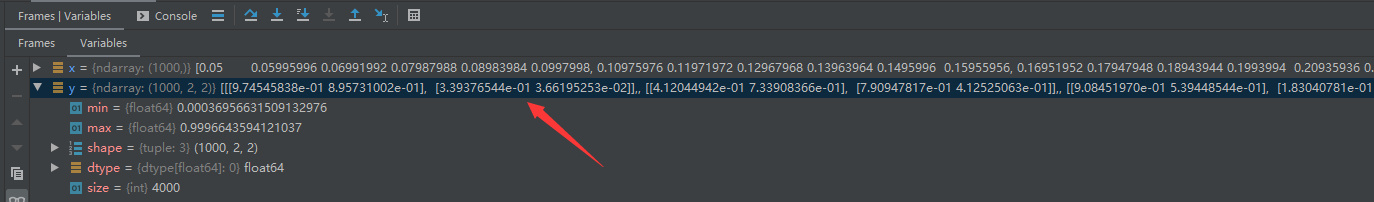
numpy.random.rand(生成随机矩阵)random.rand(d0, d1 , ..., dn)创建一个给定形状的数组,并用 [0, 1) 上均匀分布的随机样本填充它。
参数:
d0, d1, …, dn:int, optionald0表示一维空间的个数d1表示二维空间的个数dn表示n维空间的个数返回实际是个矩阵,每个值返回的[0,1)的随机数
np.random.rand(1000,2,2)的矩阵1000个元素,每个元素内部有2行 2列
5.
xlim,ylim(限制坐标轴的范围)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.random.rand(1000) plt.scatter(x, y, label="scatter figure") plt.legend() plt.xlim(0.05, 10) plt.ylim(0, 1) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
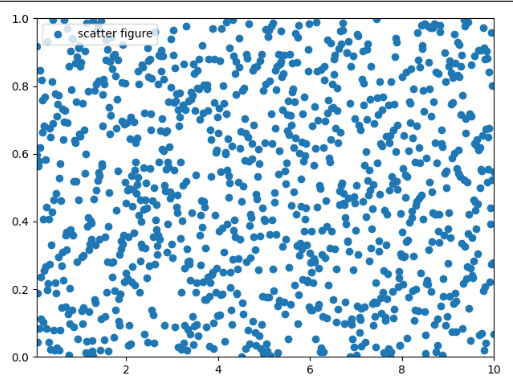
matplotlib.pyplot.xlim(*args, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.xlim.html?highlight=xlim#matplotlib.pyplot.xlim
获取或设置当前坐标区的 显示范围 限制。
可以传入
left,right参数left, right = xlim() # return the current xlim xlim((left, right)) # set the xlim to left, right xlim(left, right) # set the xlim to left, right- 1
- 2
- 3
matplotlib.pyplot.ylim(*args, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.ylim.html?highlight=ylim#matplotlib.pyplot.ylim
与xlim的意义一样
可以传入
bottom,top参数bottom, top = ylim() # return the current ylim ylim((bottom, top)) # set the ylim to bottom, top ylim(bottom, top) # set the ylim to bottom, top- 1
- 2
- 3
6.
xlabel,ylabel(设置x轴的标签文本)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.legend() plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
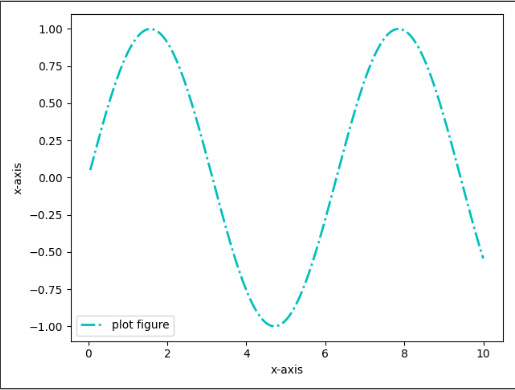
matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel(xlabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None, *, loc=None, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel.html?highlight=xlabel#matplotlib.pyplot.xlabel
参数:
xlabel:str标签的文字描述(不支持中文)
labelpad:float,default:rcParams["axes.labelpad"](default:4.0)轴边界框的点间距,包括刻度和刻度标签。 如果为 None,则保留先前的值。
loc:{'left', 'center', 'right'}, default: rcParams["xaxis.labellocation"] (default:‘center’)标签位置。 这是传递参数 x 和 horizontalalignment 的高级替代方案。
matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel(ylabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None, *, loc=None, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel.html?highlight=ylabel#matplotlib.pyplot.ylabel
参数基本跟
xlabel一致ylabel:str标签的文字描述(不支持中文)
labelpad:float, default: rcParams["axes.labelpad"] (default:4.0)轴边界框的点间距,包括刻度和刻度标签。 如果为 None,则保留先前的值。
loc:{'bottom', 'center', 'top'}, default: rcParams["yaxis.labellocation"] (default: 'center')标签位置。 这是传递参数 y 和 horizontalalignment 的高级替代方案。
7.
grid(可以绘制刻度线的网格线)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
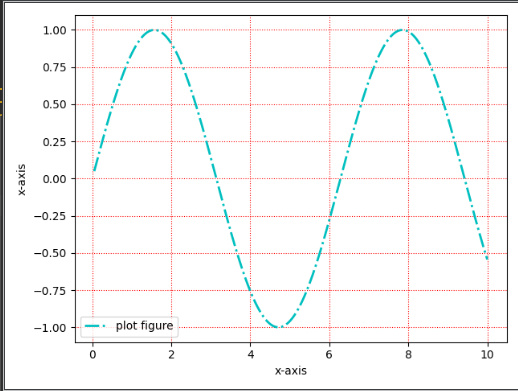
matplotlib.pyplot.grid(visible=None, which='major', axis='both', **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.grid.html?highlight=grid#matplotlib.pyplot.grid
参数:
visible:bool or None, optional(这个参数设置为True或者None没有任何区别,暂不清楚具体意义)是否显示网格线。 如果提供了任何 kwargs,则假定您希望打开网格并且 visible 将设置为 True。
如果 visible 是 None 并且没有 kwargs,这将切换行的可见性。
which:{'major', 'minor', 'both'}, optional应用更改的网格线。
axis:{'both', 'x', 'y'}, optional应用更改的轴。
**kwargs:Line2Dproperties定义网格的线属性, e.g.:
grid(color='r', linestyle='-', linewidth=2)- 1
有效的关键字参数是:
Property Description agg_filtera filter function, which takes a (m, n, 3) float array and a dpi value, and returns a (m, n, 3) array alphascalar or None animatedbool antialiasedor aabool clip_boxBboxclip_onbool clip_pathPatch or (Path, Transform) or None coloror ccolor dash_capstyleCapStyleor {‘butt’, ‘projecting’, ‘round’}dash_joinstyleJoinStyleor {‘miter’, ‘round’, ‘bevel’}dashessequence of floats (on/off ink in points) or (None, None) data(2, N) array or two 1D arrays drawstyleor ds{‘default’, ‘steps’, ‘steps-pre’, ‘steps-mid’, ‘steps-post’}, default: ‘default’ figureFigurefillstyle{‘full’, ‘left’, ‘right’, ‘bottom’, ‘top’, ‘none’} gidstr in_layoutbool labelobject linestyleor ls{‘-’, ‘–’, ‘-.’, ‘:’, ‘’, (offset, on-off-seq), …} linewidthor lwfloat markermarker style string, PathorMarkerStylemarkeredgecoloror meccolor markeredgewidthor mewfloat markerfacecoloror mfccolor markerfacecoloraltor mfcaltcolor markersizeor msfloat markeveryNone or int or (int, int) or slice or list[int] or float or (float, float) or list[bool] path_effectsAbstractPathEffectpickerfloat or callable[[Artist, Event], tuple[bool, dict]] pickradiusfloat rasterizedbool sketch_params(scale: float, length: float, randomness: float) snapbool or None solid_capstyleCapStyleor {‘butt’, ‘projecting’, ‘round’}solid_joinstyleJoinStyleor {‘miter’, ‘round’, ‘bevel’}transformunknown urlstr visiblebool xdata1D array ydata1D array zorderfloat 8.
axhline,axvline(绘制平行于x或y轴的水平参考线)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.axhline(y=0.0, c="r", ls='--', lw=2) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
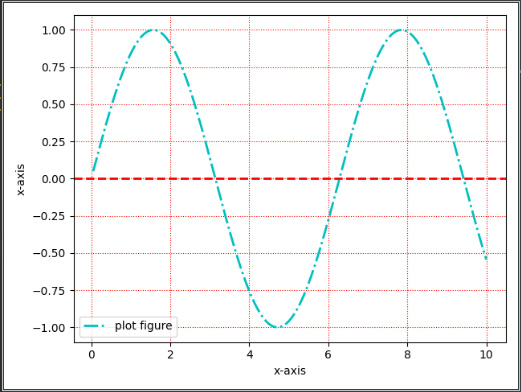
matplotlib.pyplot.axhline(y=0, xmin=0, xmax=1, **kwargs)参数:
y: float, default: 0水平线数据坐标中的 y 位置。
xmin:float, default: 0应该在 0 和 1 之间,0 是绘图的最左侧,1 是绘图的最右侧。(决定画的参考线的左侧起始位置)
xmax:float, default: 1应该在 0 和 1 之间,0 是绘图的最左侧,1 是绘图的最右侧。(决定画的参考线的右侧结束位置)
return: Line2D (返回了2d的线)测试
plt.axhline(y=0.0, c="r", ls='--', lw=2, xmin=0.5)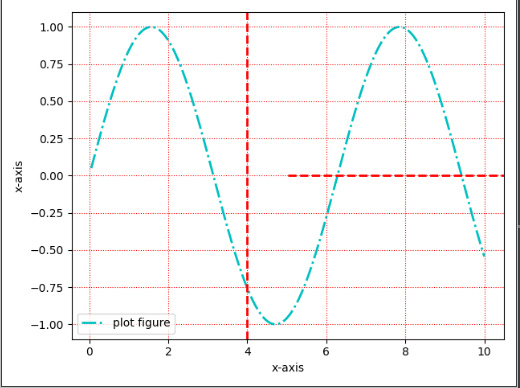
综合示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.axhline(y=0.0, c="r", ls='--', lw=2) plt.axvline(x=4.0, c="r", ls='--', lw=2) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
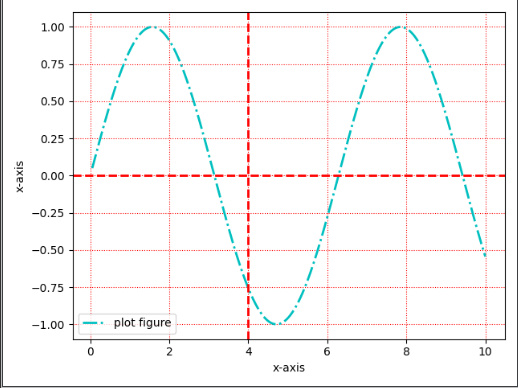
matplotlib.pyplot.axvline(y=0, xmin=0, xmax=1, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.axvline.html?highlight=axvline#matplotlib.pyplot.axvline
参数:
x:float, default: 0x 在垂直线的数据坐标中的位置。
ymin:float, default: 0应该在 0 和 1 之间,0 是图的bottom ,1 是图的top 。
ymax:float, default: 1应该在 0 和 1 之间,0 是图的bottom ,1 是图的top 。
9.
axvspan,axhspan(绘制垂直于x或y轴的参考选定区域)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.axvspan(xmin=4.0, xmax=6.0, facecolor="y", alpha=0.3) plt.axhspan(ymin=0.0, ymax=0.5, facecolor="y", alpha=0.3) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
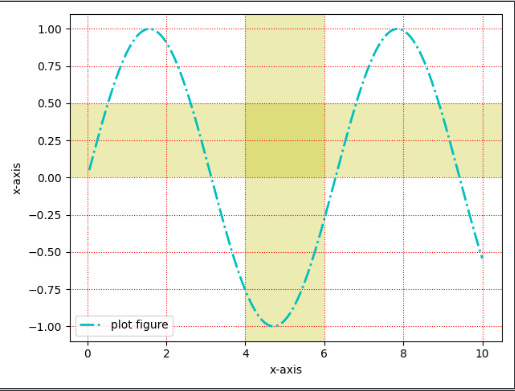
matplotlib.pyplot.axvspan(xmin, xmax, ymin=0, ymax=1, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.axvspan.html?highlight=axvspan#matplotlib.pyplot.axvspan
在轴上添加一个垂直跨度(矩形)。
矩形水平从 xmin 到 xmax,默认情况下,整个 y 轴垂直。 y-span 可以使用ymin(默认值:0)和ymax(默认值:1)以轴为单位进行设置; 例如
ymin = 0.5总是指 y 轴的中间,而不管 [set_ylim](https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_ylim.html #matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_ylim)设置的限制。参数:
xmin:float跨度的下 x 坐标,以数据单位表示。
xmax:float跨度的上 x 坐标,以数据单位表示。
ymin:float, default: 0跨度的下 y 坐标,以 y 轴单位 (0-1) 为单位。
ymax:float, default: 1跨度的上 y 坐标,以 y 轴单位 (0-1) 为单位。
matplotlib.pyplot.axhspan(ymin, ymax, xmin=0, xmax=1, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.axhspan.html?highlight=axhspan#matplotlib.pyplot.axhspan
在轴上添加一个水平跨度(矩形)。
矩形从 ymin 垂直跨越到 ymax,默认情况下,整个 x 轴水平跨越。 x-span 可以使用轴单位的xmin(默认值:0)和xmax(默认值:1)来设置; 例如
xmin = 0.5总是指 x 轴的中间,而不管 [set_xlim](https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xlim.html #matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_xlim) 设置的限制。参数:
ymin:float跨度的下 y 坐标,以数据单位表示。
ymax:float跨度的上 y 坐标,以数据单位表示。
xmin:float, default: 0跨度的下 x 坐标,以 x 轴 (0-1) 为单位。
xmax:float, default: 1跨度的上 x 坐标,以 x 轴 (0-1) 为单位。
10.
annotate(添加图形内容细节的指向性注释文本)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-axis") plt.ylabel("x-axis") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.annotate("最大值", xy=(np.pi / 2, 1.0), xytext=((np.pi / 2) + 1.0, 0.8), weight="bold", color="b", arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3", color="b")) plt.show() plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
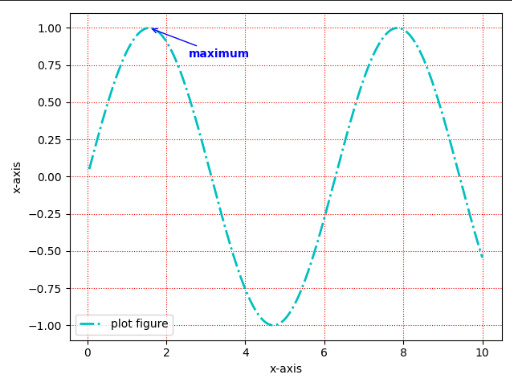
matplotlib.pyplot.annotate(text, xy, *args, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.annotate.html?highlight=annotate#matplotlib.pyplot.annotate
用文本注释点 xy。
在最简单的形式中,文本放置在 xy 处。
可选地,文本可以显示在 xytext 的另一个位置。 然后可以通过定义箭头属性添加从文本指向注释点 xy 的箭头。
参数:
text:str注释的文本。(不支持中文)
xy:(float, float)要注释的点 (x, y)。 坐标系由 xycoords 确定。
xytext:(float, float), default: *xy*放置文本的位置 (x, y)。 坐标系由 textcoords 确定。(主要是标记点的说明)
xycoords: str orArtistorTransformor callable or (float, float), default: ‘data’xy 给出的坐标系。支持以下类型的值:
Value Description ‘figure points’ Points from the lower left of the figure ‘figure pixels’ Pixels from the lower left of the figure ‘figure fraction’ Fraction of figure from lower left ‘subfigure points’ Points from the lower left of the subfigure ‘subfigure pixels’ Pixels from the lower left of the subfigure ‘subfigure fraction’ Fraction of subfigure from lower left ‘axes points’ Points from lower left corner of axes ‘axes pixels’ Pixels from lower left corner of axes ‘axes fraction’ Fraction of axes from lower left ‘data’ Use the coordinate system of the object being annotated (default) ‘polar’ (theta, r) if not native ‘data’ coordinates textcoords: str orArtistorTransformor callable or (float, float), default: value of xycoordsxytext 给出的坐标系。
arrowprops:dict, optional用于在 xy 和 xytext 位置之间绘制
FancyArrowPatch箭头的属性 。 默认为无,即不绘制箭头。由于历史原因,有两种不同的方式来指定箭头,“simple” 和"fancy":
具体的内部参数可以参考文档
11.
text添加图形内容细节的无指向型注释文本import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): # 设置字体为黑体 matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei' # 设置在中文字体是能够正常显示负号(“-”) matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-轴") plt.ylabel("x-轴") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.annotate("最大值", xy=(np.pi / 2, 1.0), xytext=((np.pi / 2) + 1.0, 0.8), weight="bold", color="b", arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3", color="b")) plt.text(3.3, 0.09, "y=sin(x)", weight="bold", color="b") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
matplotlib.pyplot.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, **kwargs)将文本添加到轴。
将文本 s 添加到数据坐标中位置 x、y 的轴上。
参数:
x, y: float放置文本的位置。 默认情况下,这是在数据坐标中。 可以使用 transform 参数更改坐标系。
s: str文本。
fontdict:dict, default: None用于覆盖默认文本属性的字典。 如果 fontdict 为 None,则默认值由
rcParams确定。12.
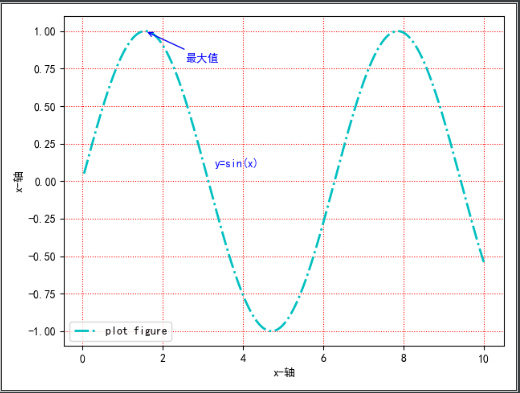
title添加整个图形内容的标题import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): # 设置字体为黑体 matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei' # 设置在中文字体是能够正常显示负号(“-”) matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-轴") plt.ylabel("y-轴") plt.legend() plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.annotate("最大值", xy=(np.pi / 2, 1.0), xytext=((np.pi / 2) + 1.0, 0.8), weight="bold", color="b", arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3", color="b")) plt.text(3.3, 0.09, "y=sin(x)", weight="bold", color="b") plt.title("y=sin(x)") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
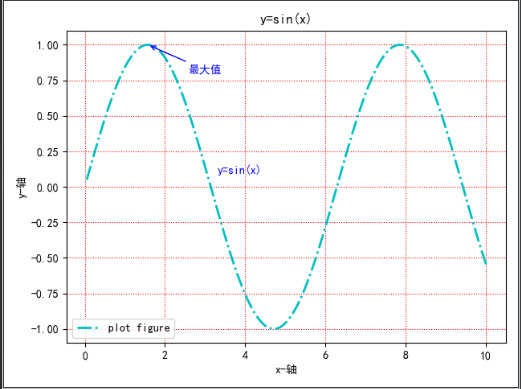
matplotlib.pyplot.title(label, fontdict=None, loc=None, pad=None, *, y=None, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.title.html?highlight=title#matplotlib.pyplot.title
13.
legend(标示图形的文本标签图例)import matplotlib import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def test(): # 设置字体为黑体 matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei' # 设置在中文字体是能够正常显示负号(“-”) matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False x = np.linspace(0.05, 10, 1000) y = np.sin(x) plt.plot(x, y, ls="-.", lw=2, c="c", label="plot figure") plt.xlabel("x-轴") plt.ylabel("y-轴") plt.legend(loc="upper left") plt.grid(linestyle=":", color="r") plt.annotate("最大值", xy=(np.pi / 2, 1.0), xytext=((np.pi / 2) + 1.0, 0.8), weight="bold", color="b", arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3", color="b")) plt.text(3.3, 0.09, "y=sin(x)", weight="bold", color="b") plt.title("y=sin(x)") plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
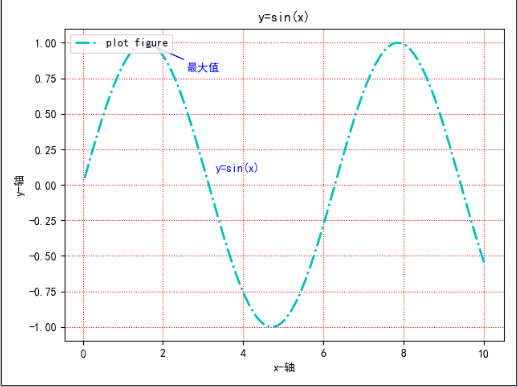
matplotlib.pyplot.legend(*args, **kwargs)https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.legend.html?highlight=legend#matplotlib.pyplot.legend
-
相关阅读:
针对icon报错
力扣labuladong——一刷day10
详解AUTOSAR:AUTOSAR方法论(理论篇—3)
Greenplum-数据导入导出
华为OD机试真题【不含 101 的数】
5年测试经验要个20K不过分吧,谁料面试官三个问题把我打发走了···
2022年9月8号Java的23设计模式学习(课时一)单例模式
【菜狗学前端】uniapp(vue3|微信小程序)实现外卖点餐的左右联动功能
软考-入侵检测技术原理与应用
怎样在线修剪音频文件了?【免费,无须注册】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/myt2000/article/details/126360067