-
带你畅游 Kubernetes 调度器

kubernetes 调度器,通过 watch 机制来发现集群中新创建且未调度的 pod,通过过滤 node 列表,打分策略,以及各个时机的插件调用机制,选择合适的 node 与之绑定。
一、调度队列
同一时刻会有多个 pod 等待调度,会把等待调度的 pod 放到 activeQ 中(PriorityQueue),然后周期性(1s)的进行调度,对于调度超时( DefaultPodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration 5m)会放入队列中,再次重新调度。
二、单次调度
用下图来说明单个调度的流转逻辑。
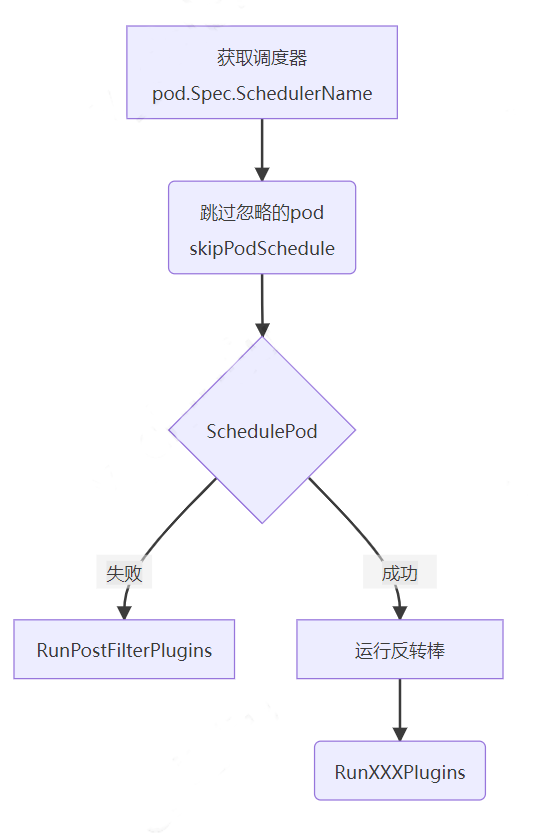
注意:一个集群中可以有多个调度器,所以首先需要根据 pod 中的 spec 参数获取调度器名称
跳过 pod:skipPodSchedule, 过滤调不需要调度的 pod,比如正在删除中的 pod,上个调度周期正在处理中的 pod
筛选 pod:SchedulePod,计算并预选出适合的 node
如果筛选失败,则调用 RunPostFilterPlugins; 如果筛选成功,则调用插件:RunXXXPlugins,开始调用配置的插件列表,从 Reserve 插件到 MultiPoint 依次按照埋点调用。
对于大规模集群,单此调度要遍历所有的 node 么?这是一个值得思考的问题。默认调度器给出的答案是根据集群规模自适应调度数量。
-
对于小规模集群,node 数小于 100, 遍历所有 node。
-
对于大规模集群,node 数大于 100,且配置的百分比小于 100% 时:按照 node 数量的一定百分比遍历,区间范围是 [5,100]。
-
计算公式是
prePercent:=50-numAllNodes/125
percent:=max(5,prePercent)
三、调度过程
调度过程分为 3 个步骤:过滤,打分,筛选,代码步骤如下:
省略非必要代码
// node快照 if err := sched.Cache.UpdateSnapshot(sched.nodeInfoSnapshot); err != nil { return result, err } // 过滤 feasibleNodes, diagnosis, err := sched.findNodesThatFitPod(ctx, fwk, state, pod) if err != nil { return result, err } // 打分 priorityList, err := prioritizeNodes(ctx, sched.Extenders, fwk, state, pod, feasibleNodes) if err != nil { return result, err } // 随机筛选 host, err := selectHost(priorityList)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
(一)过滤
可用的 node 列表:
-
插件过滤:RunPreFilterPlugins 如果插件执行失败,那么返回所有 node 可用,如果插件返回不可调度,则返回失败,终止本次调度。
-
获取 node allNodes,err:=sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos(). 列表()
-
抢占式 pod 的 status 字段中 NominatedNodeName 设置后,会优先抢占同名的 node。
-
allNode 和 preFilter 返回的 node 求交集。
(二)打分
根据优先级选择合适的 node 列表:prioritizeNodes
-
如果没有开启打分插件,返回所有 node list。
-
打分插件逐次调用 RunPreScorePlugins–>RunScorePlugins
(三)筛选
相同优先级列表下,获取 score 最大值的 node,如果存在多个相同分数,则随机一个。
四、插件机制
插件分为了调度和绑定两大类,划分成了多个时机调用,如下图:

(一)插件类型
对于 pod 的调度过程,划分了多个点,每个点调用对应的插件列表,目前支持如下多种类型插件:
// QueueSort is a list of plugins that should be invoked when sorting pods in the scheduling queue. QueueSort PluginSet `json:"queueSort,omitempty"` // PreFilter is a list of plugins that should be invoked at "PreFilter" extension point of the scheduling framework. PreFilter PluginSet `json:"preFilter,omitempty"` // Filter is a list of plugins that should be invoked when filtering out nodes that cannot run the Pod. Filter PluginSet `json:"filter,omitempty"` // PostFilter is a list of plugins that are invoked after filtering phase, but only when no feasible nodes were found for the pod. PostFilter PluginSet `json:"postFilter,omitempty"` // PreScore is a list of plugins that are invoked before scoring. PreScore PluginSet `json:"preScore,omitempty"` // Score is a list of plugins that should be invoked when ranking nodes that have passed the filtering phase. Score PluginSet `json:"score,omitempty"` // Reserve is a list of plugins invoked when reserving/unreserving resources // after a node is assigned to run the pod. Reserve PluginSet `json:"reserve,omitempty"` // Permit is a list of plugins that control binding of a Pod. These plugins can prevent or delay binding of a Pod. Permit PluginSet `json:"permit,omitempty"` // PreBind is a list of plugins that should be invoked before a pod is bound. PreBind PluginSet `json:"preBind,omitempty"` // Bind is a list of plugins that should be invoked at "Bind" extension point of the scheduling framework. // The scheduler call these plugins in order. Scheduler skips the rest of these plugins as soon as one returns success. Bind PluginSet `json:"bind,omitempty"` // PostBind is a list of plugins that should be invoked after a pod is successfully bound. PostBind PluginSet `json:"postBind,omitempty"` // MultiPoint is a simplified config section to enable plugins for all valid extension points. MultiPoint PluginSet `json:"multiPoint,omitempty"`- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
(二)插件列表
默认调度器,实现了多种插件不用特性的插件,目前支持的列表如下, 下面举几个例子说明。
"PrioritySort" : "DefaultBinder" "DefaultPreemption" "ImageLocality" "InterPodAffinity" "NodeAffinity" "NodeName" "NodePorts" "NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" "NodeResourcesFit" "NodeUnschedulable" "NodeVolumeLimits" "AzureDiskLimits" "CinderLimits" "EBSLimits" "GCEPDLimits" "PodTopologySpread" "SelectorSpread" "ServiceAffinity" "TaintToleration" "VolumeBinding" "VolumeRestrictions" "VolumeZone"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
对于打分插件,必须实现如下接口,且每个插件打分范围是 [0, 100]
type ScorePlugin interface { Plugin // Score is called on each filtered node. It must return success and an integer // indicating the rank of the node. All scoring plugins must return success or // the pod will be rejected. Score(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *Status) // ScoreExtensions returns a ScoreExtensions interface if it implements one, or nil if does not. ScoreExtensions() ScoreExtensions }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(三)插件特性
ImageLocality:本地镜像打分插件,计算分数规则如下:
sumScore:=(拥有镜像的 node 数 / node 总数)* 镜像大小
得分:= (总和分数容器数 - 23mb)/(1000mb 3-23mb)
注意:这里不是指单个 containner,而是一个 pod 中的所有 container 的打分之和。为什么范围是 23mb 到 1000mb?可以想一想。
NodeAffinity:node 亲和性和反亲和性,提供了两种策略配置。
-
对于必选策略 RequiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution,如果匹配未成功,则在 PreFilter 阶段返回失败,终止调度。
-
对于首先策略 PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution,如果匹配未成功,则尝试其他 node 也失败,调度器仍然会调度改 pod。亲和性,反亲和性是用来影响打分数值(正负分)weight
逻辑代码如下:
// 亲和性,反亲和性判定判定 if hasPreferredAffinityConstraints || hasPreferredAntiAffinityConstraints { for _, existingPod := range podsToProcess { pl.processExistingPod(state, existingPod, nodeInfo, pod, topoScore) } topoScores[atomic.AddInt32(&index, 1)] = topoScore }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
比如我们业务逻辑中的配置如下图,期望是一个 node 上只调度一个这种 pod,但是配置了首选策略。所以当 node 数小于 pod 数时,是会出现一个 node 上有多个此类 pod,会有一定的影响。

TaintToleration:污点插件,提供了过滤,预打分,打分,打分标准化(平行扩展到 0 到 100)接口。
污点标记提供了 3 种类型
// 尽可能不调度 TaintEffectPreferNoSchedule TaintEffect = "PreferNoSchedule" // 一定不调度 TaintEffectNoSchedule TaintEffect = "NoSchedule" // 一定不调度且驱逐 TaintEffectNoExecute TaintEffect = "NoExecute"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
比如我们业务中打了污点,那么一般 pod 是不会调度到此 pod 上的。

五、调度器配置
一般情况下,scheduler 会起多副本进行容灾。

{ "name": "BalancedResourceAllocation", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "EvenPodsSpreadPriority", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "InterPodAffinityPriority", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "LeastRequestedPriority", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "NodeAffinityPriority", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "NodePreferAvoidPodsPriority", "weight": 10000 }, { "name": "SelectorSpreadPriority", "weight": 1 }, { "name": "TaintTolerationPriority", "weight": 1 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
六、如何自定义 pod 调度
目前有 2 种常用方法:
(一)扩展模式
实现 type Extender struct 接口,并且在策略文件 scheduler-policy-config 中配置扩展访问方式
"extenders": [{ "urlPrefix": "http://xxx/prefix", "filterVerb": "filter", "weight": 1, "bindVerb": "bind", "enableHttps": false }]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
(二)多调度器
在需要自定义调度的 pod 中,指定 pod 的 spec.schedulerName 为自定义的调度器名称。实现自定义调度器。部署自定义的调度器 deployment。
在新版本 1.19 之后建议扩展自定义调度框架,如下例:
import ( scheduler "k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-scheduler/app" ) func main() { command := scheduler.NewSchedulerCommand( scheduler.WithPlugin("my-plugin", MyPlugin)) if err := command.Execute(); err != nil { fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "%v\n", err) } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
七、总结
在深入 schedule 源码之后,对于调度器有了剖丝抽茧的理解,了解背后的设计初衷。对于高性能,提供了自适应集群规模的调度策略。对于可靠性,kube-scheduler 提供了多副本选主机制,由 master 提供调度功能。对于扩展性,它提供了丰富的扩展接口和时机用,且提供了灵活而实用插件策略配置。
-
-
相关阅读:
浅析 SQL Server 的 CROSS APPLY 和 OUTER APPLY 查询 - 第一部分
这个中秋最潮酷玩法,必须mark!
初学者入门:使用WordPress搭建一个专属自己的博客
Python 基础合集4:Python的数据结构(str、list、tuple、dict、set)
Springboot疫苗预约网站毕业设计-附源码190950
不可不知的 MySQL 升级利器及 5.7 升级到 8.0 的注意事项
java版Spring Cloud+Mybatis+Oauth2+分布式+微服务+实现工程管理系统
【并发编程三】C++进程通信(管道pipe)
blender怎么导入stl格式文件?
Taobao Proxy Purchasing System
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/agonie201218/article/details/126359881
