-
L59.linux命令每日一练 -- 第九章 Linux进程管理命令 -- killall和pkill
9.5 killall:通过进程名终止进程
9.5.1 命令详解
【命令星级】 ★★★★★
【功能说明】
使用kill命令终止进程还需要先获取进程的pid进程号,这个过程有点繁琐,而使用killall命令就可以直接用“killall 进程名”这种形式终止进程。
【语法格式】
killall [option] [name] killall [选项] [进程名]- 1
- 2
**说明:**在killall命令及后面的选项和进程名里,每个元素之间都至少要有一个空格。
【选项说明】
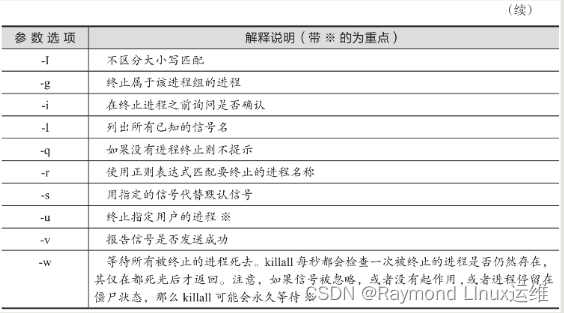
表9-6针对该命令的参数选项进行了说明。
表9-6 killall命令的参数选项及说明

9.5.2 使用范例
**范例9-15:**终止定时任务服务进程的例子。
首先要知道定时任务的进程名是crond,终止该进程的命令如下:
[root@centos7 ~]# killall crond [root@centos7 ~]# killall crond #用killall终止进程可多执行几次。 crond: no process found #等到看到这种结果就证明进场已经死掉了,前提是名称要正确。 [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start crond #这是启动定时任务服务的命令。 [root@centos7 ~]# killall -w crond #使用-w参数,会看到等待几秒后结束命令操作。 [root@centos7 ~]# killall -w crond crond: no process found [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start crond- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
**范例9-16:**终止指定用户的所有进程。
[root@centos7 ~]# killall -u root nginx #这种方式可以终止所有归属于root用户的nginx进程- 1
9.6 pkill:通过进程名终止进程
9.6.1 命令详解
【命令星级】 ★★★★★
【功能说明】
pkill命令可通过进程名终止指定的进程。使用killall终止进程需要连续执行几次,而pkill可以杀死指定进程及其所有子进程。
【语法格式】
pkill [option] [name] pkill [选项] [进程名]- 1
- 2
**说明:**在pkill命令及后面的选项和进程名里,每个元素之间都至少要有一个空格。
【选项说明】
表9-7针对该命令的参数选项进行了说明。
表9-7 pkill命令的参数选项及说明

9.6.2 使用范例
**范例9-17:**通过进场名终止进程。
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl status crond #查看定时任务的运行状态。 ● crond.service - Command Scheduler Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/crond.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-10-27 17:21:21 CST; 10min ago #running,运行。 Main PID: 3775 (crond) CGroup: /system.slice/crond.service └─3775 /usr/sbin/crond -n Oct 27 17:21:21 centos7 systemd[1]: Started Command Scheduler. Oct 27 17:21:21 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (RANDOM_DELAY w...) Oct 27 17:21:22 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (running with i...) Oct 27 17:21:22 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (@reboot jobs w...) Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. [root@centos7 ~]# pkill crond #终止定时任务进程。 [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl status crond ● crond.service - Command Scheduler Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/crond.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) since Tue 2020-10-27 17:31:36 CST; 2s ago #dead,死的。 Process: 3775 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/crond -n $CRONDARGS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 3775 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Oct 27 17:21:21 centos7 systemd[1]: Started Command Scheduler. Oct 27 17:21:21 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (RANDOM_DELAY w...) Oct 27 17:21:22 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (running with i...) Oct 27 17:21:22 centos7 crond[3775]: (CRON) INFO (@reboot jobs w...) Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl start crond- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
**范例9-18:**通过终端名终止进程。
#先在tty1里运行vim /etc/rc.local [root@centos7 ~]# w #第二列TTY就是用户运行的终端。 17:38:27 up 1:23, 2 users, load average: 0.02, 0.02, 0.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root tty1 17:37 11.00s 0.33s 0.29s vim /etc/rc.local #说明:在tty1终端,用户正在编辑/etc/rc.local文件。 root pts/0 10.0.0.1 16:51 3.00s 0.23s 0.00s w [root@centos7 ~]# pkill -t tty1 #使用-t选项杀死指定终端的进程。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
tty1终端的结果如图9-1所示。
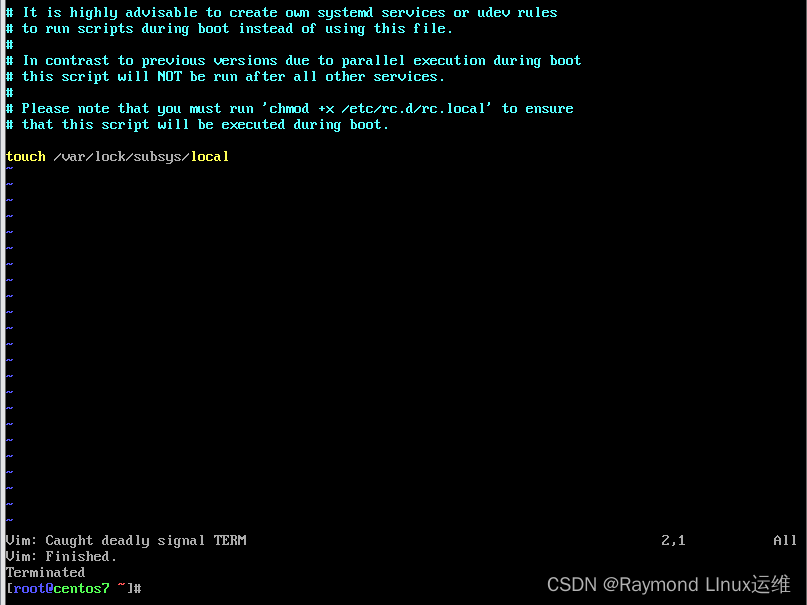
图9-1 根据tty1杀死进程后的终端结果 **范例9-19:**通过用户名终止进程。
#先通过终端用neteagle用户登录并运行top命令。 [root@centos7 ~]# w 17:45:26 up 1:30, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root tty1 17:37 3:10 0.13s 0.13s -bash root pts/0 10.0.0.1 16:51 6.00s 0.24s 0.00s w neteagle pts/1 10.0.0.1 17:44 54.00s 0.28s 0.18s top [root@centos7 ~]# pkill -u neteagle #使用-u选项杀死指定用户的所有进程,最好还是同时再指定进程名去杀,以免误杀服务。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
**说明:**此时,neteagle用户被强制退出了。
-
相关阅读:
用git stash暂存修改
【如何获取数据库表的字段并拼接】
记录keras库中导入函数找不到的问题
【Docker内容大集合】Docker从认识到实践再到底层原理大汇总
4.Spring是如何解决循环依赖的问题的?
工厂仪表定时拍照智能AI算法识别内网部署方案
MapReduce分区、排序、Combiner
「学习笔记」可持久化线段树
猿创征文|Spring MVC学习大总结
从0开始回顾Mysql --- MySQL初体验
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25599925/article/details/126202452