-
apollo配置中心的client端分析
apollo简介
apollo是携程开源的一款配置中心的产品。什么是配置中心呢?我们在开发的过程中最简单的就是在代码中hard coding,写好之后直接部署到生产环境,但是这样的弊端是每次修改一个简单的配置,就需要重新改代码重新上线,极大的浪费人力。apollo的作用正是在不上线的情况下可以动态实时的修改系统的配置数据。
整体设计

在分析之前,我们需要对apollo的整体架构有一个大概的了解,因为我们下面对各个模块进行简单的介绍。
-
ConfigService
-
- 提供配置获取接口
- 提供配置推送接口
- 服务于Apollo客户端
-
AdminService
-
- 提供配置管理接口
- 提供配置修改发布接口
- 服务于管理界面Portal
-
Client
-
- 为应用获取配置,支持实时更新
- 通过MetaServer获取ConfigService的服务列表
- 使用客户端软负载SLB方式调用ConfigService
-
Portal
-
- 配置管理页面
- 通过MetaServer获取AdminService的服务列表
- 使用客户端软负载SLB方式调用AdminService
辅助模块:
-
Eureka
-
- 用于服务发现和注册
- Config/AdminService注册实例并定期报心跳
- 和ConfigService一起部署
-
MetaServer
-
- Portal通过域名访问MetaServer获取AdminService的地址列表
- Client通过域名访问MetaServer获取ConfigService的地址列表
- 相当于Eureka Proxy
- 和ConfigService一起部署
-
NginxLB
-
- 和域名系统配合,协助Portal访问MetaServer获取AdminService的地址列表
- 和域名系统配合,协助Client访问MetaServer获取ConfigService的地址列表
- 和域名系统配置,协助用户访问Portal进行配置管理。
要点:
- ConfigService是一个独立的微服务,服务于Client进行配置获取。
- Client和ConfigService保持长连接,通过一种推拉结合(push & pull)的模式,在实现配置实时更新的同时,保证配置更新不丢失。
- AdminService是一个独立的微服务,服务于Portal进行配置管理。Portal通过调用AdminService进行配置管理和发布。
- ConfigService和AdminService共享ConfigDB,ConfigDB中存放项目在某个环境中的配置信息。ConfigService/AdminService/ConfigDB三者在每个环境(DEV/FAT/UAT/PRO)中都要部署一份。
- Protal有一个独立的PortalDB,存放用户权限、项目和配置的元数据信息。Protal只需部署一份,它可以管理多套环境。
apollo client分析
上一节我们谈了apollo配置中心的整体架构,但是由于设计的比较全面,不是太好理解,我们通过下面的简化版进行说明:
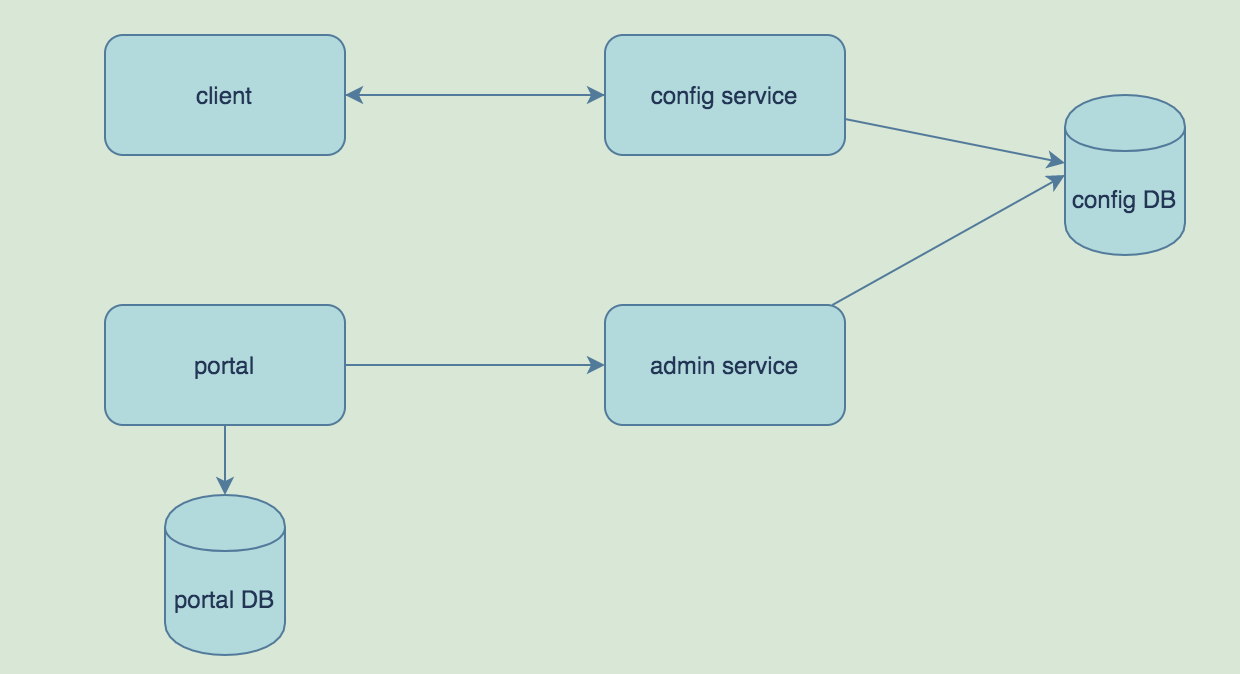
需要配置的数据会通过portal调用admin service将数据存储在DB中。client是我们的业务系统,可以实时的从config service获取最新的配置数据,而在apollo中,获取配置数据有推拉结合的方式。
client分析
客户端总共有四个后台线程
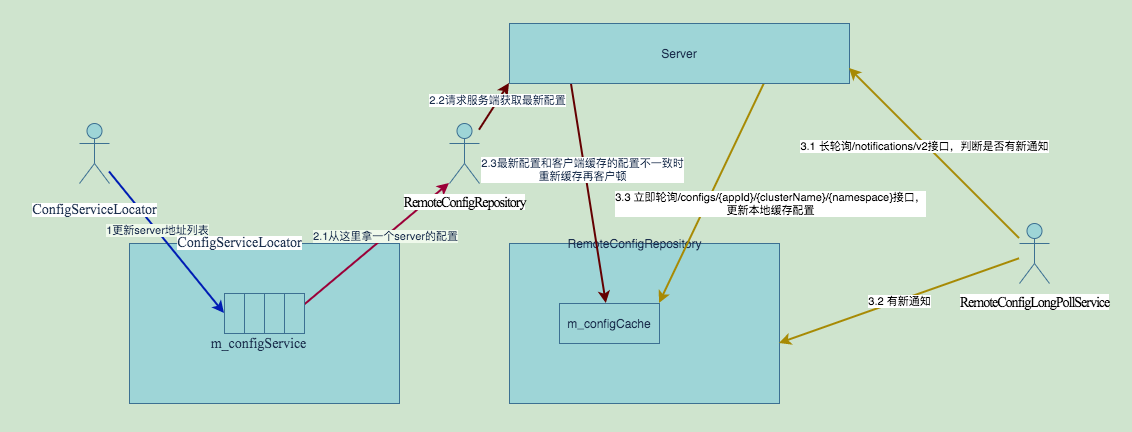
启动流程
- Spring启动
- 调用 ApolloApplicationContextInitializer
- 通过spi方式开始初始化
- ConfigService ->ConfigManager ->ConfigFactory ->Config ->ConfigRepository
- 首次初始化时会同步获取一次资源 RemoteConfigRepository
- 同步调用一次 this.trySync();
- 开启异步定时任务 this.schedulePeriodicRefresh();
- 开启长轮询,及时获取配置调整 this.scheduleLongPollingRefresh();
- 首次初始化时会同步获取一次资源 RemoteConfigRepository
- bean初始化前阶段 - SpringValueProcessor
- 将配置与bean的关系注册到SpringValueRegistry中
- 调用 ApolloApplicationContextInitializer
在springboot项目中,通过@EnableApolloConfig启动apollo client。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Documented @Import({ApolloConfigRegistrar.class}) public @interface EnableApolloConfig { String[] value() default {"application"}; int order() default 2147483647; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
public class ApolloConfigRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { public ApolloConfigRegistrar() { } public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableApolloConfig.class.getName())); String[] namespaces = attributes.getStringArray("value"); int order = (Integer)attributes.getNumber("order"); PropertySourcesProcessor.addNamespaces(Lists.newArrayList(namespaces), order); Map<String, Object> propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues = new HashMap(); propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues.put("order", 0); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class.getName(), PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class, propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesProcessor.class.getName(), PropertySourcesProcessor.class); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class.getName(), ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueProcessor.class.getName(), SpringValueProcessor.class); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class.getName(), SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class); BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class.getName(), ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
enable注解引入了ApolloConfigRegistrar,在该类中注册了多个apollo必须的BeanDefination(后续会被Spring初始化为bean)。主要有PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer、PropertySourcesProcessor、ApolloAnnotationProcessor、SpringValueProcessor、SpringValueDefinitionProcessor、ApolloJsonValueProcessor。
ConfigServiceLocator
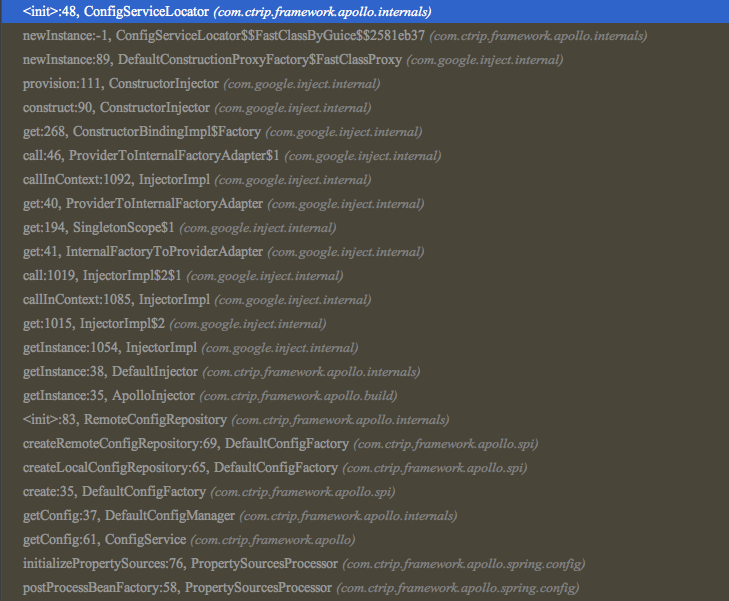
public ConfigServiceLocator() { List<ServiceDTO> initial = Lists.newArrayList(); this.m_configServices = new AtomicReference(initial); this.m_responseType = (new TypeToken<List<ServiceDTO>>() { }).getType(); this.m_httpUtil = (HttpUtil)ApolloInjector.getInstance(HttpUtil.class); this.m_configUtil = (ConfigUtil)ApolloInjector.getInstance(ConfigUtil.class); this.m_executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, ApolloThreadFactory.create("ConfigServiceLocator", true)); this.initConfigServices(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
PropertySourcesProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory作为入口会执行ConfigServiceLocator的初始化,在初始化方法里,会初始化
m_executorService。
private void schedulePeriodicRefresh() { //启动固定频率的定时任务 this.m_executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate( new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { logger.debug("refresh config services"); Tracer.logEvent("Apollo.MetaService", "periodicRefresh"); tryUpdateConfigServices(); } //这里是间隔的执行时间,默认是5min }, m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(), m_configUtil.getRefreshInterval(), m_configUtil.getRefreshIntervalTimeUnit()); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
private synchronized void updateConfigServices() { //拼接到url http://xxx.config.apollo.xxx.com/services/config?appId=my-server-name&ip=10.xx.xxx.xxx String url = assembleMetaServiceUrl(); HttpRequest request = new HttpRequest(url); int maxRetries = 2; Throwable exception = null; for (int i = 0; i < maxRetries; i++) { Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.MetaService", "getConfigService"); transaction.addData("Url", url); try { //通过http请求,返回的ServiceDTO结构中包含appName、instanceId、homepageUrl HttpResponse<List<ServiceDTO>> response = m_httpClient.doGet(request, m_responseType); transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS); List<ServiceDTO> services = response.getBody(); if (services == null || services.isEmpty()) { logConfigService("Empty response!"); continue; } setConfigServices(services); return; } catch (Throwable ex) { Tracer.logEvent("ApolloConfigException", ExceptionUtil.getDetailMessage(ex)); transaction.setStatus(ex); exception = ex; } finally { transaction.complete(); } try { m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryIntervalTimeUnit().sleep(m_configUtil.getOnErrorRetryInterval()); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { //ignore } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
该方法的主要作用就是定时拉取服务配置
用ApolloInjector做依赖管理
RemoteConfigRepository定时轮询Config Service
RemoteConfigLongPollService ,长轮询Config Service的配置变更通知
/notifications/v2接口
- 一个Namespace对应一个RemoteConfigRepository
- 多个RemoteConfigRepository注册到全局唯一的RemoteConfigLongPollService中
RemoteConfigLongPollService
上面我们介绍过,apollo获取最新配置是通过推拉结合的方式,而推的方式主要是通过长轮询实现的,这个后台线程就是长轮询的实现。大体步骤如下:
- 客户端发起一个Http请求到服务端,设置超时时间为90秒
- 服务端会保持住这个连接60秒
- 如果在60秒内有客户端关心的配置变化,被保持住的客户端请求会立即返回,并告知客户端有配置变化的namespace信息,客户端会据此拉取对应namespace的最新配置
- 如果在60秒内没有客户端关心的配置变化,那么会返回Http状态码304给客户端
- 客户端在收到服务端请求后会立即重新发起连接,回到第一步
考虑到会有数万客户端向服务端发起长连,在服务端使用了async servlet(Spring DeferredResult)来服务Http Long Polling请求。
//客户端发起请求的代码 RemoteConfigLongPollService: private void doLongPollingRefresh(String appId, String cluster, String dataCenter, String secret) { ServiceDTO lastServiceDto = null; //这就是各while循环 while (!m_longPollingStopped.get() && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { if (!m_longPollRateLimiter.tryAcquire(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { //wait at most 5 seconds try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.ConfigService", "pollNotification"); String url = null; try { if (lastServiceDto == null) { lastServiceDto = this.resolveConfigService(); } url = assembleLongPollRefreshUrl(lastServiceDto.getHomepageUrl(), appId, cluster, dataCenter, m_notifications); logger.debug("Long polling from {}", url); HttpRequest request = new HttpRequest(url); request.setReadTimeout(LONG_POLLING_READ_TIMEOUT); if (!StringUtils.isBlank(secret)) { Map<String, String> headers = Signature.buildHttpHeaders(url, appId, secret); request.setHeaders(headers); } transaction.addData("Url", url); final HttpResponse<List<ApolloConfigNotification>> response = m_httpClient.doGet(request, m_responseType); logger.debug("Long polling response: {}, url: {}", response.getStatusCode(), url); if (response.getStatusCode() == 200 && response.getBody() != null) { updateNotifications(response.getBody()); updateRemoteNotifications(response.getBody()); transaction.addData("Result", response.getBody().toString()); notify(lastServiceDto, response.getBody()); } //try to load balance if (response.getStatusCode() == 304 && ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextBoolean()) { lastServiceDto = null; } m_longPollFailSchedulePolicyInSecond.success(); transaction.addData("StatusCode", response.getStatusCode()); transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS); } catch (Throwable ex) { lastServiceDto = null; Tracer.logEvent("ApolloConfigException", ExceptionUtil.getDetailMessage(ex)); transaction.setStatus(ex); long sleepTimeInSecond = m_longPollFailSchedulePolicyInSecond.fail(); logger.warn( "Long polling failed, will retry in {} seconds. appId: {}, cluster: {}, namespaces: {}, long polling url: {}, reason: {}", sleepTimeInSecond, appId, cluster, assembleNamespaces(), url, ExceptionUtil.getDetailMessage(ex)); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(sleepTimeInSecond); } catch (InterruptedException ie) { //ignore } } finally { transaction.complete(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
客户端发送一个http请求到服务端的/notifications/v2接口。服务端不会立刻返回,而是通过Spring DeferredResult把请求挂起,如果60s内没有该客户端关心的配置发布,那么会返回http状态码304给客户端,为什么是60s呢?这个不重要,但重要的是这个时间要小于客户端设置的超时时间90s,否则客户端会经常timeout。若该客户端关心的配置有更新,则会立刻返回。客户端从返回的结果中获取到配置变化的namespace后,会立刻请求config service获取该namespace的最新配置。
下面我们简单看下服务端的代码:
NotificationControllerV2: public DeferredResult<ResponseEntity<List<ApolloConfigNotification>>> pollNotification( @RequestParam(value = "appId") String appId, @RequestParam(value = "cluster") String cluster, @RequestParam(value = "notifications") String notificationsAsString, @RequestParam(value = "dataCenter", required = false) String dataCenter, @RequestParam(value = "ip", required = false) String clientIp) { List<ApolloConfigNotification> notifications = null; try { notifications = gson.fromJson(notificationsAsString, notificationsTypeReference); } catch (Throwable ex) { Tracer.logError(ex); } if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(notifications)) { throw new BadRequestException("Invalid format of notifications: " + notificationsAsString); } Map<String, ApolloConfigNotification> filteredNotifications = filterNotifications(appId, notifications); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(filteredNotifications)) { throw new BadRequestException("Invalid format of notifications: " + notificationsAsString); } DeferredResultWrapper deferredResultWrapper = new DeferredResultWrapper(bizConfig.longPollingTimeoutInMilli()); Set<String> namespaces = Sets.newHashSetWithExpectedSize(filteredNotifications.size()); Map<String, Long> clientSideNotifications = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(filteredNotifications.size()); for (Map.Entry<String, ApolloConfigNotification> notificationEntry : filteredNotifications.entrySet()) { String normalizedNamespace = notificationEntry.getKey(); ApolloConfigNotification notification = notificationEntry.getValue(); namespaces.add(normalizedNamespace); clientSideNotifications.put(normalizedNamespace, notification.getNotificationId()); if (!Objects.equals(notification.getNamespaceName(), normalizedNamespace)) { deferredResultWrapper.recordNamespaceNameNormalizedResult(notification.getNamespaceName(), normalizedNamespace); } } Multimap<String, String> watchedKeysMap = watchKeysUtil.assembleAllWatchKeys(appId, cluster, namespaces, dataCenter); Set<String> watchedKeys = Sets.newHashSet(watchedKeysMap.values()); /** * 1、set deferredResult before the check, for avoid more waiting * If the check before setting deferredResult,it may receive a notification the next time * when method handleMessage is executed between check and set deferredResult. */ deferredResultWrapper .onTimeout(() -> logWatchedKeys(watchedKeys, "Apollo.LongPoll.TimeOutKeys")); deferredResultWrapper.onCompletion(() -> { //unregister all keys for (String key : watchedKeys) { deferredResults.remove(key, deferredResultWrapper); } logWatchedKeys(watchedKeys, "Apollo.LongPoll.CompletedKeys"); }); //register all keys for (String key : watchedKeys) { this.deferredResults.put(key, deferredResultWrapper); } logWatchedKeys(watchedKeys, "Apollo.LongPoll.RegisteredKeys"); logger.debug("Listening {} from appId: {}, cluster: {}, namespace: {}, datacenter: {}", watchedKeys, appId, cluster, namespaces, dataCenter); /** * 2、check new release */ List<ReleaseMessage> latestReleaseMessages = releaseMessageService.findLatestReleaseMessagesGroupByMessages(watchedKeys); /** * Manually close the entity manager. * Since for async request, Spring won't do so until the request is finished, * which is unacceptable since we are doing long polling - means the db connection would be hold * for a very long time */ entityManagerUtil.closeEntityManager(); List<ApolloConfigNotification> newNotifications = getApolloConfigNotifications(namespaces, clientSideNotifications, watchedKeysMap, latestReleaseMessages); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(newNotifications)) { deferredResultWrapper.setResult(newNotifications); } return deferredResultWrapper.getResult(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
RemoteConfigRepository
RemoteConfigRepository定时轮询Config Service的配置读取/configs/{appId}/{clusterName}/{namespace:.+}
详细请查看com.ctrip.framework.apollo.configservice.controller.ConfigController的configs/{appId}/{clusterName}/{namespace:.+}接口RemoteConfigRepository: protected synchronized void sync() { Transaction transaction = Tracer.newTransaction("Apollo.ConfigService", "syncRemoteConfig"); try { //缓存中的apolloConfig ApolloConfig previous = m_configCache.get(); //从configServer获得apolloConfig ApolloConfig current = loadApolloConfig(); //reference equals means HTTP 304 //如果不相等说明有更新,更新缓存 if (previous != current) { logger.debug("Remote Config refreshed!"); m_configCache.set(current); //发布事件,由监听的listener进行消费 this.fireRepositoryChange(m_namespace, this.getConfig()); } if (current != null) { Tracer.logEvent(String.format("Apollo.Client.Configs.%s", current.getNamespaceName()), current.getReleaseKey()); } transaction.setStatus(Transaction.SUCCESS); } catch (Throwable ex) { transaction.setStatus(ex); throw ex; } finally { transaction.complete(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
SpringValueRegistry
private void initialize() { Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ApolloThreadFactory.create("SpringValueRegistry", true)).scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { public void run() { try { SpringValueRegistry.this.scanAndClean(); } catch (Throwable var2) { var2.printStackTrace(); } } }, 5L, 5L, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } private void scanAndClean() { Iterator iterator = this.registry.values().iterator(); while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && iterator.hasNext()) { Multimap<String, SpringValue> springValues = (Multimap)iterator.next(); Iterator springValueIterator = springValues.entries().iterator(); while(springValueIterator.hasNext()) { Entry<String, SpringValue> springValue = (Entry)springValueIterator.next(); if (!((SpringValue)springValue.getValue()).isTargetBeanValid()) { springValueIterator.remove(); } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
将符合条件的属性封装成一个
SpringValue对象,放在一个Map中。当clien检测到配置发生变化时,就会更新这个Map里面的值,从而达到自动更新的目的。参考:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/-hUaQPzfsl9Lm3IqQW3VDQ
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ALRSZCvtgv7m8q4tC8qlUg
https://www.jianshu.com/p/915b893eae20
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40378034/article/details/114778207
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1878847
https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv11916999/
https://blog.csdn.net/pdwljhlg/article/details/89459786
-
-
相关阅读:
美团面试——算法岗(4个面试案例)
一文读懂HTML的头部内容,希望有所帮助
Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos 的 2 种健康检查机制!
CAP 7.0 版本发布通告 - 支持延迟消息,性能炸了?
计算机毕设(附源码)JAVA-SSM基于的学生事务管理系统
【k8s】Kubernetes 原理剖析与实战应用(更新中)
初识Java
MySQL 主从复制与读写分离
程序员常用的19款办公软件和开发工具推荐!
图解http
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013978512/article/details/126336350
