-
C++阶段05笔记03【C++提高编程资料(string容器、vector容器、deque容器、stack容器)】
目录
3、STL常用容器
3.1、string容器
3.1.1、string基本概念
本质:string是C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类。
string和char*区别:1.char*是一个指针;2.string是一个类,类内部封装了char*管理这个字符串,其是一个char*型的容器。
特点:
string类内部封装了很多成员方法,例如:查找find、拷贝copy、删除delete、替换replace、插入insert。
string管理char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责。
3.1.2、string构造函数
构造函数原型:
-
string();//创建一个空的字符串,例如:string str; -
string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化 -
string(const string& str);//使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象 -
string(int n, char c);//使用n个字符c初始化
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- /*
- 构造函数原型:
- 1、string(); //创建一个空的字符串,例如:string str;
- 2、string(const char* s); //使用字符串s初始化
- 3、string(const string& str); //使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象
- 4、string(int n, char c); //使用n个字符c初始化
- */
- //string的构造函数
- void test01() {
- string s1;//创建空字符串,调用默认无参构造函数
- cout << "str1 = " << s1 << endl;//str1 =
- const char *str = "hello world";
- string s2(str);//把c_string转换成了string
- cout << "str2 = " << s2 << endl;//str2 = hello world
- string s3(s2);//调用拷贝构造函数
- cout << "str3 = " << s3 << endl;//str2 = hello world
- string s4(10, 'a');
- cout << "str4 = " << s4 << endl;//str4 = aaaaaaaaaa
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:string的多种构造方式没有可比性,灵活使用即可。
3.1.3、string赋值操作
功能描述:给string字符串进行赋值。
赋值的函数原型:
-
string& operator=(const char* s);//char*类型字符串赋值给当前的字符串 -
string& operator=(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前的字符串 -
string& operator=(char c);//字符赋值给当前的字符串 -
string& assign(const char *s);//把字符串s赋给当前的字符串 -
string& assign(const char *s, int n);//把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串 -
string& assign(const string &s);//把字符串s赋给当前字符串 -
string& assign(int n, char c);//用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //赋值
- void test01() {
- string str1;
- str1 = "hello world";
- cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
- string str2;
- str2 = str1;
- cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
- string str3;
- str3 = 'a';
- cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
- string str4;
- str4.assign("hello c++");
- cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
- string str5;
- str5.assign("hello c++", 5);
- cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
- string str6;
- str6.assign(str5);
- cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
- string str7;
- str7.assign(5, 'x');
- cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:string的赋值方式很多,
operator=这种方式是比较实用的。3.1.4、string字符串拼接
功能描述:实现在字符串末尾拼接字符串。
函数原型:
-
string& operator+=(const char* str);//重载+=操作符 -
string& operator+=(const char c);//重载+=操作符 -
string& operator+=(const string& str);//重载+=操作符 -
string& append(const char *s);//把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾 -
string& append(const char *s, int n);//把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾 -
string& append(const string &s);//同operator+=(const string& str) -
string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n);//字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //string字符串拼接
- void test01() {
- string str1 = "我";
- str1 += "爱玩游戏";
- cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
- str1 += ':';
- cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
- string str2 = "LOL DNF";
- str1 += str2;
- cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
- string str3 = "I";
- str3.append(" love ");
- cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
- str3.append("game abcde", 4);
- //str3.append(str2);
- str3.append(str2, 4, 3);//从下标4位置开始,截取3个字符拼接到字符串末尾
- cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:字符串拼接的重载版本很多,初学阶段记住几种即可。
3.1.5、string查找和替换
功能描述:1.查找:查找指定字符串是否存在;2.替换:在指定的位置替换字符串。
函数原型:
-
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;//查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找 -
int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;//查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找 -
int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;//从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置 -
int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;//查找字符c第一次出现位置 -
int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const;//查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找 -
int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const;//查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找 -
int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;//从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置 -
int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const;//查找字符c最后一次出现位置 -
string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str);//替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串str -
string& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s);//替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s
示例:
- #include
//查找和替换 - #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {//查找
- string str1 = "abcdefgde";
- int pos = str1.find("de");
- if (pos == -1) {
- cout << "未找到字符串!" << endl;
- } else {
- cout << "已找到字符串,pos = " << pos << endl;
- }
- //rfind,rfind和find区别:rfind从右往左查找、find从左往右查找
- pos = str1.rfind("de");
- cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;
- }
- void test02() {//替换
- string str1 = "abcdefgde";
- str1.replace(1, 3, "1111");//从1号位置起的3个字符替换为"1111"
- cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- test02();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
find查找是从左往后,rfind从右往左;
-
find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1;
-
replace在替换时,要指定从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串。
3.1.6、string字符串比较
功能描述:字符串之间的比较。
比较方式:字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比,1.=返回0;2.>返回1;3.<返回-1。
函数原型:
-
int compare(const string &s) const;//与字符串s比较 -
int compare(const char *s) const;//与字符串s比较
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {//字符串比较
- string s1 = "hello";
- string s2 = "aello";
- int ret = s1.compare(s2);
- if (ret == 0) {
- cout << "s1 等于 s2" << endl;
- } else if (ret > 0) {
- cout << "s1 大于 s2" << endl;
- } else {
- cout << "s1 小于 s2" << endl;
- }
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:字符串对比主要是用于比较两个字符串是否相等,判断谁大谁小的意义并不是很大。
3.1.7、string字符存取
string中单个字符存取方式有两种:
-
char& operator[](int n);//通过[]方式取字符 -
char& at(int n);//通过at方法获取字符
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {
- string str = "hello world";
- //cout << "str = " << str << endl;
- //1、通过[]访问单个字符
- for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
- cout << str[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //2、通过at方式访问单个字符
- for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
- cout << str.at(i) << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //字符修改(修改单个字符)
- str[0] = 'x';
- cout << "str = " << str << endl;
- str.at(1) = 'x';
- cout << "str = " << str << endl;
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:string字符串中单个字符存取有两种方式,利用[]或at。
3.1.8、string插入和删除
功能描述:对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作。
函数原型:
-
string& insert(int pos, const char* s);//插入字符串 -
string& insert(int pos, const string& str);//插入字符串 -
string& insert(int pos, int n, char c);//在指定位置插入n个字符c -
string& erase(int pos, int n = npos);//删除从Pos开始的n个字符
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {//字符串插入和删除
- string str = "hello";
- str.insert(1, "111");//插入
- cout << "str = " << str << endl;//str = h111ello
- str.erase(1, 3);//删除,从1号位置开始3个字符
- cout << "str = " << str << endl;//str = hello
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:插入和删除的起始下标都是从0开始。
3.1.9、string子串
功能描述:从字符串中获取想要的子串。
函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const;//返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {//子串
- string str = "abcdefg";
- string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);
- cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;
- //实用操作:从邮件地址中获取用户名信息
- string email = "hello@sina.com";
- int pos = email.find("@");
- string userName = email.substr(0, pos);
- cout << "userName:" << userName << endl;
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:灵活的运用求子串功能,可以在实际开发中获取有效的信息。
3.2、vector容器
3.2.1、vector基本概念
功能:vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组。
vector与普通数组区别:不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vector可以动态扩展。
动态扩展:并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间。
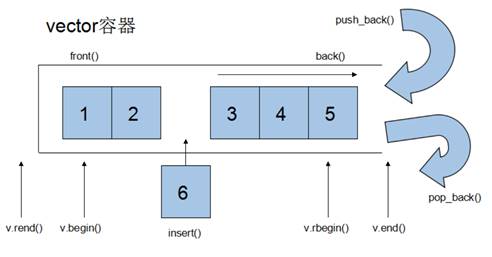
vector容器的迭代器是支持随机访问的迭代器。
3.2.2、vector构造函数
功能描述:创建vector容器。
函数原型:
-
vector//采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数。v; -
vector(v.begin(), v.end());//将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 -
vector(n, elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 -
vector(const vector &vec);//拷贝构造函数。
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
- for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //vector容器构造
- void test01() {
- //构造方式1、默认构造(无参构造)
- vector<int> v1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- v1.push_back(i);
- }
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- //构造方式2、通过区间方式进行构造
- vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
- printVector(v2);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- //构造方式3、n个elem方式构造
- vector<int> v3(10, 100);
- printVector(v3);//100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- //构造方式4、拷贝构造
- vector<int> v4(v3);
- printVector(v4);//100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:vector的多种构造方式没有可比性,灵活使用即可。
3.2.3、vector赋值操作
功能描述:给vector容器进行赋值。
函数原型:
-
vector& operator=(const vector &vec);//重载等号操作符。 -
assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 -
assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
- for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //vector赋值操作
- void test01() {
- vector<int> v1;//无参构造
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- v1.push_back(i);
- }
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- //赋值方式1:operator=
- vector<int> v2;
- v2 = v1;
- printVector(v2);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- //赋值方式2:assign
- vector<int> v3;
- v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
- printVector(v3);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- //赋值方式3:n个elem方式赋值
- vector<int> v4;
- v4.assign(10, 100);
- printVector(v4);//100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:vector赋值方式比较简单,使用operator=,或者assign都可以。
3.2.4、vector容量和大小
功能描述:对vector容器的容量和大小操作。
函数原型:
-
empty();//判断容器是否为空 -
capacity();//容器的容量 -
size();//返回容器中元素的个数 -
resize(int num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 -
resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
- for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //vector容器的容量和大小操作
- void test01() {
- vector<int> v1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- v1.push_back(i);
- }
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- if (v1.empty()) {//为真代表容器为空
- cout << "v1为空!" << endl;
- } else {
- cout << "v1不为空!" << endl;
- cout << "v1的容量为:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
- cout << "v1的大小为:" << v1.size() << endl;
- }
- //resize重新指定大小:若指定的更大,默认用0填充新位置,可以利用重载版本替换默认填充
- v1.resize(15, 100);//利用重载版本,可以指定默认填充值,参数2。如果重新指定的比原来长了,默认用0填充新的位置
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 100 100 100 100 100
- //resize重新指定大小:若指定的更小,超出部分元素被删除
- v1.resize(5);//如果重新指定的比原来短了,超出部分会删除掉
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
判断是否为空——empty;
-
返回元素个数——size;
-
返回容器容量——capacity;
-
重新指定大小——resize。
3.2.5、vector插入和删除
功能描述:对vector容器进行插入、删除操作。
函数原型:
-
push_back(ele);//尾部插入元素ele -
pop_back();//删除最后一个元素 -
insert(const_iterator pos, ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele -
insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele -
erase(const_iterator pos);//删除迭代器指向的元素 -
erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);//删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素 -
clear();//删除容器中所有元素
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- /*vector插入和删除
- 1、push_back(ele);//尾部插入元素ele
- 2、pop_back();//删除最后一个元素
- 3、insert(const_iterator pos, ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
- 4、insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);//迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
- 5、erase(const_iterator pos);//删除迭代器指向的元素
- 6、erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);//删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
- 7、clear();//删除容器中所有元素
- */
- void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
- for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- void test01() {//插入和删除
- vector<int> v1;
- //尾插
- v1.push_back(10);
- v1.push_back(20);
- v1.push_back(30);
- v1.push_back(40);
- v1.push_back(50);
- printVector(v1);//遍历,10 20 30 40 50
- //尾删
- v1.pop_back();
- printVector(v1);//遍历,10 20 30 40
- //插入,第一个参数是迭代器
- v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);
- printVector(v1);//遍历,100 10 20 30 40
- v1.insert(v1.begin(), 2, 1000);
- printVector(v1);//遍历,1000 1000 100 10 20 30 40
- //删除,参数也是迭代器
- v1.erase(v1.begin());
- printVector(v1);//遍历,1000 100 10 20 30 40
- //清空
- //v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());
- v1.clear();
- printVector(v1);
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
尾插——push_back;
-
尾删——pop_back;
-
插入——insert(位置迭代器);
-
删除——erase(位置迭代器);
-
清空——clear。
3.2.6、vector数据存取
功能描述:对vector中的数据的存取操作。
函数原型:
-
at(int idx);//返回索引idx所指的数据 -
operator[];//返回索引idx所指的数据 -
front();//返回容器中第一个数据元素 -
back();//返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例:
- #include
//vector容器-数据存取 - #include
- using namespace std;
- void test01() {
- vector<int> v1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- v1.push_back(i);
- }
- //利用[]方式访问数组中元素
- for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
- cout << v1[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //利用at方式访问元素
- for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
- cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //获取第一个元素
- cout << "第一个元素为:" << v1.front() << endl;//0
- //获取最后一个元素
- cout << "最后一个元素为:" << v1.back() << endl;//9
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
除了用迭代器获取vector容器中元素,[ ]和at也可以;
-
front返回容器第一个元素,back返回容器最后一个元素。
3.2.7、vector互换容器
功能描述:实现两个容器内元素进行互换。
函数原型:
swap(vec);//将vec与本身的元素互换示例:

swap互换容器_收缩内存解析图 - #include
//vector容器互换 - #include
- using namespace std;
- void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
- for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //1、基本使用
- void test01() {
- vector<int> v1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- v1.push_back(i);
- }
- cout << "交换前:" << endl;
- printVector(v1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- vector<int> v2;
- for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) {
- v2.push_back(i);
- }
- printVector(v2);//10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- cout << "交换后:" << endl;
- v1.swap(v2);//互换容器
- printVector(v1);//10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
- printVector(v2);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- cout << endl;
- }
- //2、实际用途-巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
- void test02() {
- vector<int> v;
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- v.push_back(i);
- }
- cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;//v的容量为:131072
- cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl << endl;//v的大小为:100000
- v.resize(3);//重新指定大小
- cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;//v的容量为:131072
- cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl << endl;//v的大小为:3
- //巧用swap收缩内存,按照v目前所用的空间来初始化匿名对象
- vector<int>(v).swap(v);//匿名对象
- cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;//v的容量为:3
- cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;//v的容量为:3
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- test02();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:swap可以使两个容器互换,可以达到实用的收缩内存效果。
3.2.8、vector预留空间
功能描述:减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数。
函数原型:
reserve(int len);//容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //vector容器-预留空间
- void test01() {
- vector<int> v;
- v.reserve(100000);//利用reserve预留空间
- int num = 0;//统计开辟次数
- int *p = NULL;
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- v.push_back(i);
- if (p != &v[0]) {//指针是否指向首地址
- p = &v[0];
- num++;
- }
- }
- cout << "num = " << num << endl;//num = 1
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:如果数据量较大,可以一开始利用reserve预留空间。
3.3、deque容器
3.3.1、deque容器基本概念
功能:双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作。
deque与vector区别:
-
vector对于头部的插入删除效率低,数据量越大,效率越低;
-
deque相对而言,对头部的插入删除速度回比vector快;
-
vector访问元素时的速度会比deque快,这和两者内部实现有关。

deque内部工作原理:deque内部有个中控器,维护每段缓冲区中的内容,缓冲区中存放真实数据。中控器维护的是每个缓冲区的地址,使得使用deque时像一片连续的内存空间。

deque容器的迭代器也是支持随机访问的。
3.3.2、deque构造函数
功能描述:deque容器构造。
函数原型:
-
dequedeqT; //默认构造形式 -
deque(beg, end);//构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。 -
deque(n, elem);//构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。 -
deque(const deque &deq);//拷贝构造函数
示例:
- #include
//deque构造函数 - #include
- using namespace std;
- void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- //*it = 100;//const限定容器只读,容器中的数据不可以修改了
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- void test01() {
- deque<int> d1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- d1.push_back(i);
- }
- printDeque(d1);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- deque<int> d2(d1.begin(), d1.end());
- printDeque(d2);//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- deque<int> d3(10, 100);
- printDeque(d3);//100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- deque<int> d4(d3);
- printDeque(d4);//100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:deque容器和vector容器的构造方式几乎一致,灵活使用即可。
3.3.3、deque赋值操作
功能描述:给deque容器进行赋值。
函数原型:
-
deque& operator=(const deque &deq);//重载等号操作符 -
assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。 -
assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //deque容器赋值操作
- void test01() {
- deque<int> d1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- d1.push_back(i);
- }
- printDeque(d1);
- //operator=赋值
- deque<int> d2;
- d2 = d1;
- printDeque(d2);
- //assign赋值
- deque<int> d3;
- d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end());
- printDeque(d3);
- deque<int> d4;
- d4.assign(10, 100);
- printDeque(d4);
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:deque赋值操作也与vector相同,需熟练掌握。
3.3.4、deque大小操作
功能描述:对deque容器的大小进行操作。
函数原型:
-
deque.empty();//判断容器是否为空 -
deque.size();//返回容器中元素的个数 -
deque.resize(num);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。 -
deque.resize(num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置;如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例:
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //deque容器大小操作
- void printDeuqe(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- void test01() {
- deque<int> d1;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- d1.push_back(i);
- }
- printDeuqe(d1);
- if (d1.empty()) {//判断容器是否为空
- cout << "d1为空!" << endl;
- } else {
- cout << "d1不为空!" << endl;
- cout << "d1的大小为:" << d1.size() << endl;//统计大小
- //deque容器没有容量概念
- }
- //重新指定大小
- //d1.resize(15);
- d1.resize(15, 1);
- printDeuqe(d1);
- d1.resize(5);
- printDeuqe(d1);
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
deque没有容量的概念;
-
判断是否为空——empty;
-
返回元素个数——size;
-
重新指定个数——resize。
3.3.5、deque插入和删除
功能描述:向deque容器中插入和删除数据。
函数原型:
两端插入操作:
-
push_back(elem);//在容器尾部添加一个数据 -
push_front(elem);//在容器头部插入一个数据 -
pop_back();//删除容器最后一个数据 -
pop_front();//删除容器第一个数据
指定位置操作:
-
insert(pos,elem);//在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。 -
insert(pos,n,elem);//在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。 -
insert(pos,beg,end);//在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。 -
clear();//清空容器的所有数据 -
erase(beg,end);//删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。 -
erase(pos);//删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
示例:
- #include
- #include
//deque容器插入和删除 - using namespace std;
- void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //两端操作
- void test01() {
- deque<int> d1;
- //尾插
- d1.push_back(10);
- d1.push_back(20);
- //头插
- d1.push_front(100);
- d1.push_front(200);
- printDeque(d1);//200 100 10 20
- //尾删
- d1.pop_back();
- printDeque(d1);//200 100 10
- //头删
- d1.pop_front();
- printDeque(d1);//100 10
- }
- //插入
- void test02() {
- deque<int> d1;
- d1.push_back(10);
- d1.push_back(20);
- d1.push_front(100);
- d1.push_front(200);
- printDeque(d1);//200 100 10 20
- //insert插入
- d1.insert(d1.begin(), 1000);
- printDeque(d1);//1000 200 100 10 20
- d1.insert(d1.begin(), 2, 10000);
- printDeque(d1);//10000 10000 1000 200 100 10 20
- //按照区间进行插入
- deque<int> d2;
- d2.push_back(1);
- d2.push_back(2);
- d2.push_back(3);
- d1.insert(d1.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end());
- printDeque(d1);//1 2 3 10000 10000 1000 200 100 10 20
- }
- //删除
- void test03() {
- deque<int> d1;
- d1.push_back(10);
- d1.push_back(20);
- d1.push_front(100);
- d1.push_front(200);
- printDeque(d1);
- //删除
- deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin();
- it++;
- d1.erase(it);
- printDeque(d1);//200 10 20
- d1.erase(d1.begin());
- printDeque(d1);
- //按区间方式删除
- //d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end());//清空操作
- //清空
- d1.clear();
- printDeque(d1);
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- test02();
- test03();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
尾插——push_back;
-
尾删——pop_back;
-
头插——push_front;
-
头删——pop_front;
-
插入和删除提供的位置是迭代器!
3.3.6、deque数据存取
功能描述:对deque中的数据的存取操作。
函数原型:
-
at(int idx);//返回索引idx所指的数据 -
operator[];//返回索引idx所指的数据 -
front();//返回容器中第一个数据元素 -
back();//返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例:
- #include
- #include
//deque容器数据存取 - using namespace std;
- void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- //数据存取
- void test01() {
- deque<int> d;
- d.push_back(10);
- d.push_back(20);
- d.push_back(30);
- d.push_front(100);
- d.push_front(200);
- d.push_front(300);
- //1、通过[]方式访问元素
- for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) {
- cout << d[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;//300 200 100 10 20 30
- //2、通过at方式访问元素
- for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) {
- cout << d.at(i) << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;//300 200 100 10 20 30
- //访问头尾元素
- cout << "第一个元素front为:" << d.front() << endl;//300
- cout << "最后一个元素back:" << d.back() << endl;//30
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:
-
除了用迭代器获取deque容器中元素,[ ]和at也可以;
-
front返回容器第一个元素;back返回容器最后一个元素。
3.3.7、deque排序
功能描述:利用算法实现对deque容器进行排序。
算法:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end)//对beg和end区间内元素进行排序示例:
- #include
- #include
- #include
//标准算法头文件 - using namespace std;
- void printDeque(const deque<int> &d) {
- for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- void test01() {//deque容器排序
- deque<int> d;
- d.push_back(10);
- d.push_back(20);
- d.push_back(30);
- d.push_front(100);
- d.push_front(200);
- d.push_front(300);
- printDeque(d);//300 200 100 10 20 30
- //排序-默认排序规则:从小到大升序
- //对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以利用sort算法直接对其进行排序
- //vector容器也可以利用sort进行排序
- sort(d.begin(), d.end());
- cout << "排序后:" << endl;
- printDeque(d);
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:sort算法非常实用,使用时包含头文件algorithm即可。
3.4、案例-评委打分
3.4.1、案例描述
有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分。
3.4.2、实现步骤
-
创建五名选手,放到vector中;
-
遍历vector容器,取出来每一个选手,执行for循环,可以把10个评分打分存到deque容器中;
-
sort算法对deque容器中分数排序,去除最高和最低分;
-
deque容器遍历一遍,累加总分;
-
获取平均分。
示例代码:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- using namespace std;
- //有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分。
- //选手类
- class Person {
- public:
- Person(string name, int score) {
- this->m_Name = name;
- this->m_Score = score;
- }
- string m_Name; //姓名
- int m_Score; //平均分
- };
- void createPerson(vector
&v) { - string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- string name = "选手";
- name += nameSeed[i];
- int score = 0;
- Person p(name, score);
- v.push_back(p);//将创建的person对象放入到容器中
- }
- }
- //打分
- void setScore(vector
&v) { - for (vector
::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { - //将评委的分数放入到deque容器中
- deque<int> d;
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- int score = rand() % 41 + 60;//0-40,60-100
- d.push_back(score);
- }
- cout << "选手:" << it->m_Name << ",打分:" << endl;
- for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) {
- cout << *dit << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- sort(d.begin(), d.end());//排序
- //去除最高和最低分
- d.pop_back();
- d.pop_front();
- //取平均分
- int sum = 0;
- for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++) {
- sum += *dit;//累加每个评委的分数
- }
- int avg = sum / d.size();
- it->m_Score = avg;//将平均分赋值给选手身上
- }
- }
- void showScore(vector
&v) { - for (vector
::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { - cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << ",平均分:" << it->m_Score << endl;
- }
- }
- int main() {
- srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));//随机数种子
- //1、创建5名选手
- vector
v;//存放选手的容器 - createPerson(v);
- //测试
- for (vector
::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { - cout << "姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << ",分数: " << (*it).m_Score << endl;
- }
- //2、给5名选手打分
- setScore(v);
- //3、显示最后得分
- showScore(v);
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结: 选取不同的容器操作数据,可以提升代码的效率。
3.5、stack容器
3.5.1、stack基本概念
概念:stack是一种先进后出(First In Last Out,FILO)的数据结构,它只有一个出口。


栈中只有顶端的元素才可以被外界使用,因此栈不允许有遍历行为。
栈中进入数据称为——入栈
push,栈中弹出数据称为——出栈pop。生活中的栈:


3.5.2、stack常用接口
功能描述:栈容器常用的对外接口。
构造函数:
stack//stack采用模板类实现, stack对象的默认构造形式stk; stack(const stack &stk);//拷贝构造函数
赋值操作:
stack& operator=(const stack &stk);//重载等号操作符数据存取:
-
push(elem);//向栈顶添加元素 -
pop();//从栈顶移除第一个元素 -
top();//返回栈顶元素
大小操作:
-
empty();//判断堆栈是否为空 -
size();//返回栈的大小
示例:
- #include
- #include
//栈stack容器 - using namespace std;
- void test01() {//栈容器常用接口
- //特点:符合先进后出数据结构
- stack<int> s;//创建栈容器,栈容器必须符合先进后出
- //向栈中添加元素,叫做:压栈、入栈
- //入栈
- s.push(10);
- s.push(20);
- s.push(30);
- s.push(40);
- cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl;//4
- //只要栈不为空,查看栈顶,并且执行出栈操作
- while (!s.empty()) {
- //查看栈顶元素
- cout << "栈顶元素为:" << s.top() << endl;//输出栈顶元素
- s.pop();//出栈//弹出栈顶元素
- }//40 30 20 10
- cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl;//0
- }
- int main() {
- test01();
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
总结:1.入栈——push;2.出栈——pop;3.返回栈顶——top;4.判断栈是否为空——empty;5.返回栈大小——size。
-
-
相关阅读:
CPP-Templates-2nd--第 21 章 模板和继承
PyTorch相关笔记(不断补充)
【python入门专项练习】-N06.循环语句
QEMU背景知识
2023东华理工大学计算机考研信息汇总
wordcloud—根据文本生成词云—Python第三方库
IIS 网站初始化与 Keep alive
K8SYaml文件详解及编写示例
独享IP是原生IP吗?
大一学生网页课程作业 南京介绍网页设计 学生家乡网页设计作品静态 HTML网页模板源码 html我的家乡网页作业
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44949135/article/details/126232366
