-
Java——String类常见方法
目录
🍦 赋值字符串构造
🍦 通过字符数组构造
🍎 求字符串长度
🍧 ==的使用
🍧 boolean equeal(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较是否相同
🍧 int compareTo(String s) 方法:按照字典序比较大小
🍧 boolean equalsIgnoreCase(Object anObject) 方法:忽略大小写比较是否相等
🍧 int compareToIgnoreCase(String s) 方法:忽略大小比较字符串大小
🍨 char charAt(int index) 方法:得到指定位置的字符
🍨 int indexOf(int ch) 方法:得到指定字符首次出现的位置
🍨 int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始找字符ch第一次出现的位置
🍨 int indexOf(String s) 方法:得到字符串s第一次出现的位置
🍨 int indexOf(String s, int fromIndex) 方法:得到字符串s从fromIndex位置开始第一次出现的位置
🍨 int lastIndexOf(int ch) 方法:从后往前找,得到字符ch第一次出现的位置
🍨 int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找,得到ch第一次的位置
🍨 int lastIndexOf(String s) 方法:从后往前找,得到字符串s在整个字符串中第一次出现的位置
🍨 int lastIndexOf(String s, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找,得到字符串第一次的位置
💎转化
☕️ 其他类型转为字符串:
🍺 数字转字符串
🍺 布尔类型转字符串
☕️ 字符串转为其他类型:
☕️ 字符串与数组之间转化:
🍺 字符串转数组
🍺 数组转字符串
☕️ 大小写转化:
🍺 小写转大写
🍺 小写转大写
☕️ 格式化:
🍹 Sting replaceAll() 方法:用给定字符串替换所有指定的字符串
🍹 String replaceFirst() 方法:只替换原字符串中第一次出现的指定字符串
🍰 将字符串全部拆分
🍰 以 . 号拆分
🍰 以 \ 号拆分
✨ 截取指定长度

本篇文章清楚总结了一些常用String类中包含的方法,熟练运用后即可在题海中节省大量时间

字符串构造
赋值字符串构造
- //通过字符串构造
- String str1 = "hello";
- System.out.println("str1 = " + str1);
通过new对象构造
- //通过new对象构造
- String str2 = new String("hello");
- System.out.println("str2 = " + str2);
通过字符数组构造
- //通过字符数组构造
- char[] arr = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
- String str3 = new String(arr);
- System.out.println("str3 = " + str3);

字符串数组本质
因为String属于引用类型,所以str内存储的并不是字符串内容本身。
我们进入String源码可以看到str数组内部存储的是对象的地址,字符串内容其实是存在字符数组value[ ]中的:

调试起来看:

这是它的简化内存布局图:

字符串长度
求字符串长度
返回值:字符串或数组长度
- String str1 = "hello";
- System.out.println(str1.length());
判断字符串长度是否为0
为0返回ture;
不为0返回false
- String str1 = "hello";
- System.out.println(str1.isEmpty());
String对象比较
==的使用
内置类型:比较两个变量的值是否相等;
引用类型:比较的是引用的地址.
返回值:相同返回true,否则返回false.
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int a = 10;
- int b = 10;
- System.out.println(a == b);
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("hello");
- System.out.println(s1 == s2);
- }

具体的在下文中字符串常量池中。
boolean equeal(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较是否相同
返回值:相同返回true,否则返回false.
我们知道所有类都继承着Object这个父类,虽然Object中的equal方法是按照==来比较的,但是在
String类中重写了equal方法,这样就可以按照字面值来比较了:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("hello");
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
- }

int compareTo(String s) 方法:按照字典序比较大小
通过comparaTo源码可以看到:
返回值是int类型:
如果有不同的字符,返回字符的ASCII值差值;
如果没有不同的字符,返回长度的差值.

使用方法:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("hello"); //h:104
- String s2 = new String("aello"); //a:97
- int ret1 = s1.compareTo(s2); //104 - 97 = 7
- System.out.println(ret1);
- String s3 = new String("abc"); //长度为3
- String s4 = new String("ab"); //长度为2
- int ret2 = s3.compareTo(s4); // 3 - 2 = 1
- System.out.println(ret2);
- }

boolean equalsIgnoreCase(Object anObject) 方法:忽略大小写比较是否相等
返回值:与equal一样
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("Hello");
- System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
- String s3 = new String("hello");
- String s4 = new String("aello");
- System.out.println(s3.equalsIgnoreCase(s4));
- }

int compareToIgnoreCase(String s) 方法:忽略大小比较字符串大小
返回值:与compareTo一样
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = new String("hello");
- String s2 = new String("Hello");
- System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));
- String s3 = new String("hello");
- String s4 = new String("aello");
- System.out.println(s3.compareToIgnoreCase(s4));
- }

字符串查找
char charAt(int index) 方法:得到指定位置的字符
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- char ch = s1.charAt(4);
- System.out.println("第四个字符是:" + ch);
- }

如果指定位置为负或者越界:抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException异常。
int indexOf(int ch) 方法:得到指定字符首次出现的位置
返回值:存在则返回第一次出现的位置;否则返回-1;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- int ch = s1.indexOf('l');
- System.out.println("字符o第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始找字符ch第一次出现的位置
返回值:存在则返回在整个字符串中的位置;否则返回-1;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- int ch = s1.indexOf('o',5);//位置5处是空格
- System.out.println("从位置5开始字符o第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int indexOf(String s) 方法:得到字符串s第一次出现的位置
返回值:存在返回首字符第一次出现的位置;否则返回-1;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- int ch = s1.indexOf("llo");
- System.out.println("字符llo第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int indexOf(String s, int fromIndex) 方法:得到字符串s从fromIndex位置开始第一次出现的位置
返回值:存在则返回在整个字符串中的位置;否则返回-1;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello world";
- int ch = s1.indexOf("llo",4);
- System.out.println("从位置4开始字符llo第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int lastIndexOf(int ch) 方法:从后往前找,得到字符ch第一次出现的位置
返回值:存在则返回从后往前第一次出现的位置;否则返回-1
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello world"; //第一个o在4位置 第二个o在10位置 第三个o在13位置
- int ch = s1.lastIndexOf('o');
- System.out.println("从后往前找,字符o第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找,得到ch第一次的位置
返回值:存在则返回所在位置;否则返回-1
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello world"; //第一个o在4位置 第二个o在10位置 第三个o在13位置
- int ch = s1.lastIndexOf('o',12);
- System.out.println("从12位置起,从后往前找,字符o第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }

int lastIndexOf(String s) 方法:从后往前找,得到字符串s在整个字符串中第一次出现的位置
返回值:找到返回s的首元素在整个字符串中第一次出现的位置;否则返回-1
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello world";
- int ch = s1.lastIndexOf("llo");
- System.out.println("从后往前找,字符串llo第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }
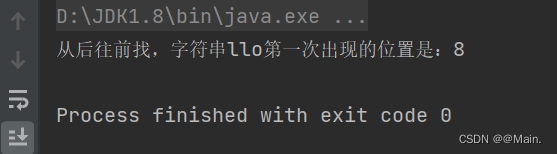
int lastIndexOf(String s, int fromIndex) 方法:从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找,得到字符串第一次的位置
返回值:同上
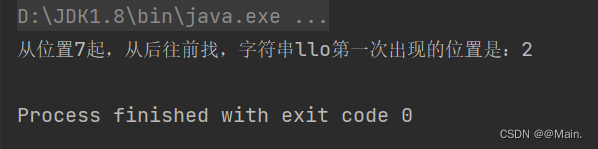
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello world";
- int ch = s1.lastIndexOf("llo",7);
- System.out.println("从位置7起,从后往前找,字符串llo第一次出现的位置是:" + ch);
- }
转化
其他类型转为字符串:
数字转字符串
- String s1 = String.valueOf(100);
- String s2 = String.valueOf(3.1415);
布尔类型转字符串
- String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
- String s4 = String.valueOf(false);
实例化对象转字符串
- class Student{
- public String name;
- public int age;
- public Student(String name, int age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = String.valueOf(new Student("张三",18));
- }
- }
字符串转为其他类型:
字符串转数字
- int num1 = Integer.parseInt("123321");
- double num2 = Double.parseDouble("3.1415926");
字符串转布尔类型
- boolean flag1 = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
- boolean flag2 = Boolean.parseBoolean("false");
字符串与数组之间转化:
字符串转数组
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello";
- char[] ch = s1.toCharArray();
- for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(ch[i]);
- }
- }

数组转字符串
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- char[] ch = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
- String s1 = new String(ch);
- System.out.println(s1);
- }
大小写转化:
小写转大写
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello";
- System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
- }

小写转大写
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "HELLO";
- System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());
- }

格式化:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = String.format("%d - %d - %d",2022,8,12);
- System.out.println(s);
- }

字符串替换
Sting replaceAll() 方法:用给定字符串替换所有指定的字符串
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello World";
- String s2 = s1.replaceAll("ll","a");
- System.out.println(s2);
- }

String replaceFirst() 方法:只替换原字符串中第一次出现的指定字符串
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello hello World";
- String s2 = s1.replaceFirst("ll","a");
- System.out.println(s2);
- }

字符串拆分
可以将字符串按照字符串内已有符号进行分割;
将字符串全部拆分
返回值:数组
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello@hello@world";
- String[] s2 = s1.split("@");
- for (String s: s2) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }

将字符串拆分成指定组
返回值:数组
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello@hello@world";
- String[] s2 = s1.split("@",2);
- for (String s: s2) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }

以下是特殊的:
以 . 号拆分
需要加两个转义字符:
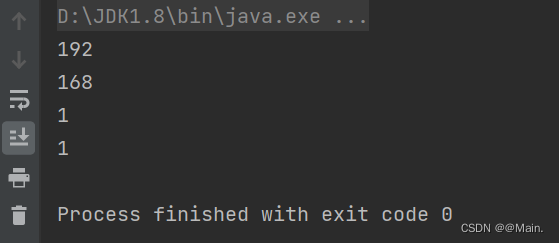
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "192.168.1.1";
- String[] s2 = s1.split("\\.");
- for (String s: s2) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }
以 \ 号拆分
因为\\表示一个\,所以需要在前面再加两个\\:
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "2022\\08\\12";
- System.out.println("原来是:" + s1);
- String[] s2 = s1.split("\\\\");
- System.out.println("现在是:");
- for (String s: s2) {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }

多次拆分(分步拆分)
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "mp.csdn.net/2022";
- System.out.println("原来是:" + s1);
- System.out.println("现在是:");
- String[] s2 = s1.split("/");
- for (String s: s2) {
- String[] ss = s.split("\\.");
- for (String temp: ss) {
- System.out.println(temp);
- }
- }
- }

字符串截取
从一个完整的字符串中截取部分;
从指定位置截取到结尾
返回值:字符串
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- String s2 = s1.substring(6);
- System.out.println(s2);
- }

截取指定长度
长度是(起始位置,终点位置):左闭右开
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = "hello world";
- String s2 = s1.substring(6,10);
- System.out.println(s2);
- String s3 = s1.substring(6,11);
- System.out.println(s3);
- }

去掉字符串左右空格,保留中间空格
trim() 可以字符串开头和结尾的空格、制表符、回车等;
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s1 = " hello world \t " +
- " ";
- String s2 = " " +
- " tomorrow ";
- System.out.println( "[" + s1.trim() + s2.trim() + "]");
- }

-
相关阅读:
SSM框架集成
安泰:功率放大器的工作原理以及注意事项有哪些
要想不踩SaaS那些坑,得先了解“SaaS架构”
Java面试题01
深入了解MySQL中的JSON_ARRAYAGG和JSON_OBJECT函数
敏捷是怎么提高工作效率的
kotlin 之几个常见的内联函数(二)
pandas dataframe drop函数
偶数科技亮相2023中国程序员节——数据库技术高峰论坛
响应的结构与Http常见状态码
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_65190367/article/details/126308342