-
金仓数据库 KingbaseGIS 使用手册(6.16. 聚类函数)
6.16. 聚类函数
6.16.1. ST_ClusterDBSCAN
ST_ClusterDBSCAN — 基于 2D 空间中的 Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) 算法返回每个输入几何对象的聚类号。 与 ST_ClusterKMeans 函数不同,该算法不需要预先指定聚类数,而是基于期望距离(eps)和密度(minpoints)参数来生成每个聚类。
用法
integer ST_ClusterDBSCAN(geometry winset geom, float8 eps, integer minpoints);
描述
基于 2D 空间中的 Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) 算法返回每个输入几何对象的聚类号。 与 ST_ClusterKMeans 函数不同,该算法不需要预先指定聚类数,而是基于期望距离(eps)和密度(minpoints)参数来生成每个聚类。
一个输入的几何对象满足下列条件之一时,将会被加入一个聚类:
-
它距离至少 minpoints 个输入几何对象(包括它自己)的距离小于 eps,会被作为“核心对象 ”加入;
-
它距离一个“核心对象” 的距离小于 eps,会被作为一个“边界对象”加入;
需要注意的是,边界对象可能位于多个聚类的核心对象的 eps 距离内。在这种情况下,无论分到哪个类别下都是正确的,并且边界对象会被分配到其中任意一个类别下。 这有可能使得生成的正确类别所包含的几何对象数小于 minpoints。 当边界对象的分类存在歧义时, 如果在窗口定义中包含 Order By 子句,反复调用ST_ClusterDBSCAN 将能产生一致的结果,但可能与同一算法的其他实现返回的结果不同。
注意
无法满足聚类条件的输入几何对象,其聚类号将为 NULL。
样例
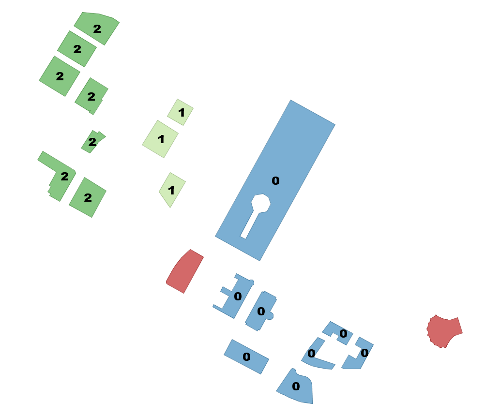
每个类别至少 包含 2 个对象,且对象间距在 50m 以内,孤立对象的 cid 为 NULL
SELECT name, ST_ClusterDBSCAN(geom, eps := 50, minpoints := 2) over () AS cid FROM boston_polys WHERE name > '' AND building > '' AND ST_DWithin(geom, ST_Transform( ST_GeomFromText('POINT(-71.04054 42.35141)', 4326), 26986), 500); name | bucket -------------------------------------+-------- Manulife Tower | 0 Park Lane Seaport I | 0 Park Lane Seaport II | 0 Renaissance Boston Waterfront Hotel | 0 Seaport Boston Hotel | 0 Seaport Hotel & World Trade Center | 0 Waterside Place | 0 World Trade Center East | 0 100 Northern Avenue | 1 100 Pier 4 | 1 The Institute of Contemporary Art | 1 101 Seaport | 2 District Hall | 2 One Marina Park Drive | 2 Twenty Two Liberty | 2 Vertex | 2 Vertex | 2 Watermark Seaport | 2 Blue Hills Bank Pavilion | NULL World Trade Center West | NULL (20 rows)使用命名参数绑定的方式调用,将同一类别中的几何对象合并成一个图块。
SELECT cid, ST_Collect(geom) AS cluster_geom, array_agg(parcel_id) AS ids_in_cluster FROM ( SELECT parcel_id, ST_ClusterDBSCAN(geom, eps := 0.5, minpoints := 5) over () AS cid, geom FROM parcels) sq GROUP BY cid;
参考
ST_DWithin, ST_ClusterKMeans, ST_ClusterIntersecting, ST_ClusterWithin
6.16.2. ST_ClusterIntersecting
ST_ClusterIntersecting — 将给定几何对象集合中相互之间存在交集的对象聚合成一类,返回一个由几何对象集合组成的数组。 每个数组元素代表一个类别。
用法
geometry[] ST_ClusterIntersecting(geometry set g);
描述
ST_ClusterIntersecting 是一个聚合函数。它返回一个由几何对象集合组成的数组,每个 几何对象集合代表一组相互之间有交集的几何对象。
样例
WITH testdata AS (SELECT unnest(ARRAY['LINESTRING (0 0, 1 1)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (5 5, 4 4)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (6 6, 7 7)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (0 0, -1 -1)'::geometry, 'POLYGON ((0 0, 4 0, 4 4, 0 4, 0 0))'::geometry]) AS geom) SELECT ST_AsText(unnest(ST_ClusterIntersecting(geom))) FROM testdata; --result st_astext --------- GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(LINESTRING(0 0,1 1),LINESTRING(5 5,4 4),LINESTRING(0 0,-1 -1),POLYGON((0 0,4 0,4 4,0 4,0 0))) GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(LINESTRING(6 6,7 7))参考
ST_ClusterDBSCAN, ST_ClusterKMeans, ST_ClusterWithin
6.16.3. ST_ClusterKMeans
ST_ClusterKMeans — 根据给定的聚类数,采用 K-Means 算法进行聚类,返回每个输入的几何对象到聚类中心的距离。
用法
integer ST_ClusterKMeans(geometry winset geom, integer number_of_clusters);
描述
基于 K-Means 聚类数,返回每个输入几何对象到聚类中心的距离。 对于 2D 几何对象, 返回的是其几何中心到所属类别中心的距离;对于 3D 几何对象, 返回的是其边界盒中心到所属类别中心的距离。 对于输入的 POINT 对象, M 坐标被视为权重值, 因此必须大于 0。
样例
CREATE TABLE parcels AS SELECT lpad((row_number() over())::text,3,'0') As parcel_id, geom, ('{residential, commercial}'::text[])[1 + mod(row_number()OVER(),2)] As type FROM ST_Subdivide(ST_Buffer('SRID=3857;LINESTRING(40 100, 98 100, 100 150, 60 90)'::geometry, 40, 'endcap=square'),12) As geom;
原始图块

基于聚类号(cid)作颜色编码后的图块
SELECT ST_ClusterKMeans(geom, 5) OVER() AS cid, parcel_id, geom FROM parcels; -- result cid | parcel_id | geom -----+-----------+--------------- 0 | 001 | 0103000000... 0 | 002 | 0103000000... 1 | 003 | 0103000000... 0 | 004 | 0103000000... 1 | 005 | 0103000000... 2 | 006 | 0103000000... 2 | 007 | 0103000000... (7 rows) -- Partitioning parcel clusters by type SELECT ST_ClusterKMeans(geom,3) over (PARTITION BY type) AS cid, parcel_id, type FROM parcels; -- result cid | parcel_id | type -----+-----------+------------- 1 | 005 | commercial 1 | 003 | commercial 2 | 007 | commercial 0 | 001 | commercial 1 | 004 | residential 0 | 002 | residential 2 | 006 | residential (7 rows) -- Clustering points around antimeridian can be done in 3D XYZ CRS, EPSG:4978: SELECT ST_ClusterKMeans(ST_Transform(ST_Force3D(geom), 4978), 3) over () AS cid, parcel_id, type FROM parcels; -- result ┌─────┬───────────┬─────────────┐ │ cid │ parcel_id │ type │ ├─────┼───────────┼─────────────┤ │ 1 │ 001 │ commercial │ │ 2 │ 002 │ residential │ │ 0 │ 003 │ commercial │ │ 1 │ 004 │ residential │ │ 0 │ 005 │ commercial │ │ 2 │ 006 │ residential │ │ 0 │ 007 │ commercial │ └─────┴───────────┴─────────────┘ (7 rows)
参考
ST_ClusterDBSCAN, ST_ClusterIntersecting, ST_ClusterWithin, ST_Subdivide
6.16.4. ST_ClusterWithin
ST_ClusterWithin — 返回一个几何对象集合数组,每个集合都由一组相距不超过指定距离几何对象构成。 (距离采用 SRID 指定的坐标系中的笛卡儿距离)
用法
geometry[] ST_ClusterWithin(geometry set g, float8 distance);
描述
ST_ClusterWithin 是一个聚合函数。它返回一个几何对象集合数组,每个集合都由一组相距不超过指定距离几何对象构成。(距离采用 SRID 指定的坐标系中的笛卡儿距离)。
样例
WITH testdata AS (SELECT unnest(ARRAY['LINESTRING (0 0, 1 1)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (5 5, 4 4)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (6 6, 7 7)'::geometry, 'LINESTRING (0 0, -1 -1)'::geometry, 'POLYGON ((0 0, 4 0, 4 4, 0 4, 0 0))'::geometry]) AS geom) SELECT ST_AsText(unnest(ST_ClusterWithin(geom, 1.4))) FROM testdata; --result st_astext --------- GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(LINESTRING(0 0,1 1),LINESTRING(5 5,4 4),LINESTRING(0 0,-1 -1),POLYGON((0 0,4 0,4 4,0 4,0 0))) GEOMETRYCOLLECTION(LINESTRING(6 6,7 7))参考
ST_ClusterDBSCAN, ST_ClusterKMeans, ST_ClusterIntersecting
-
-
相关阅读:
HTTP协议中的Cookie 和 Session
开题报告:基于java企业公司网站系统 毕业设计论文开题报告模板
ZooKeeper 避坑实践:如何调优 jute.maxbuffer
ElasticSearch学习笔记:内容有点多,但很实用(包含安装、使用、安全、部署)
js防抖、节流以及他们的应用场景
Redis事务、pub/sub、PipeLine-管道、benchmark性能测试详解
redis学习(008 实战:黑马点评:缓存介绍)
【Redis】为什么要学 Redis
PyTorch学习笔记-Non-linear Activations与Linear Layers
就业喜报:产品岗位提升的底层能力是产品思维
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/arthemis_14/article/details/126303232
