-
第十二天Tensorflow基础和简单的线性回归实现
Tensorflow基本操作
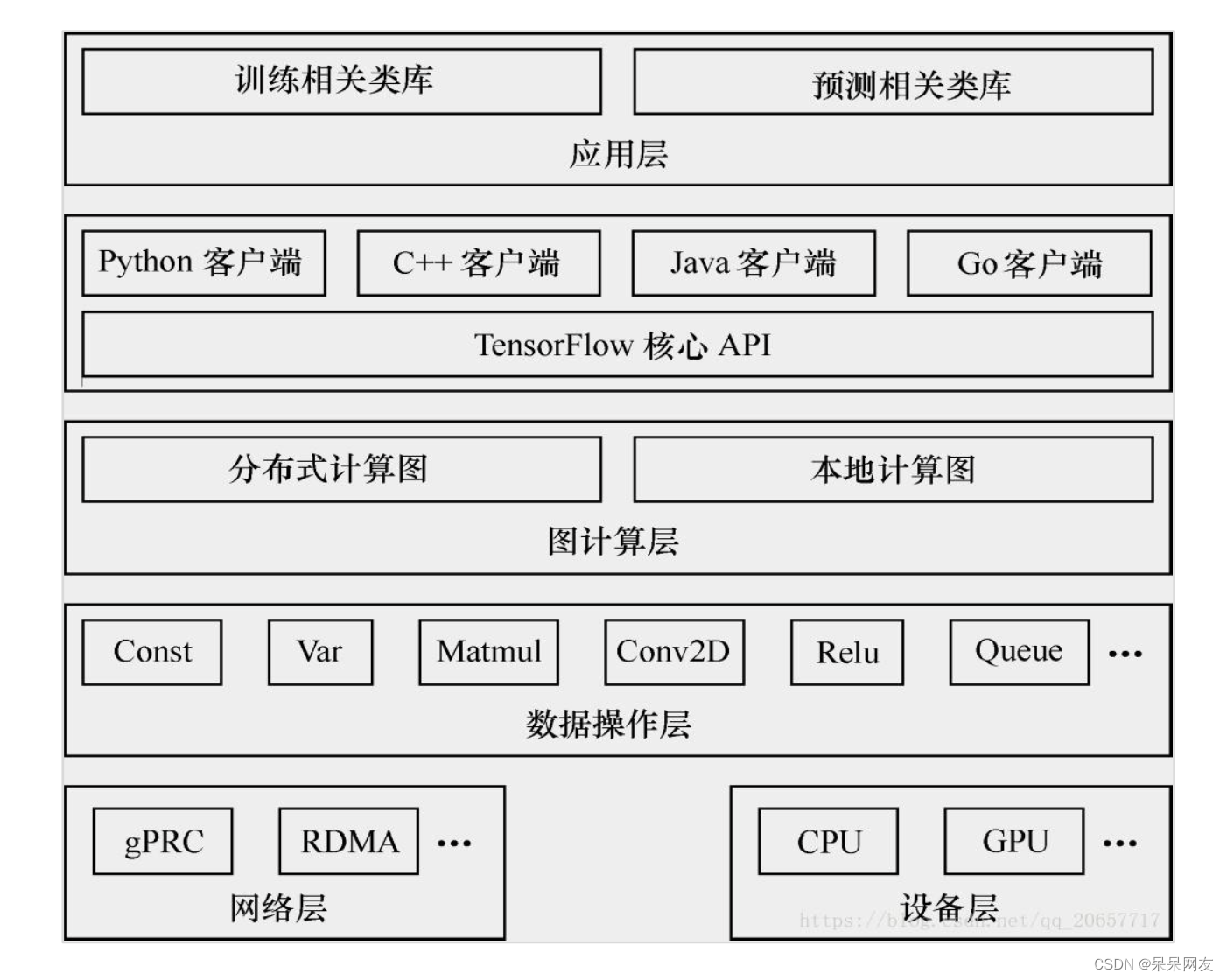
作者在Python3.6版本下使用Tensorflow1.14.0实现一下代码。相比较与二版本,这个版本有些过程需要使用对话,原因在于Tensorflow的使用有点类似于BS模式,Python语言更像是与其对话的客户端,Tensorflow像是服务器,通过对话接收前台的操作对象,在后台运行并计算,最后得出结果。下面是作者学到的Tensorflow体系结构:

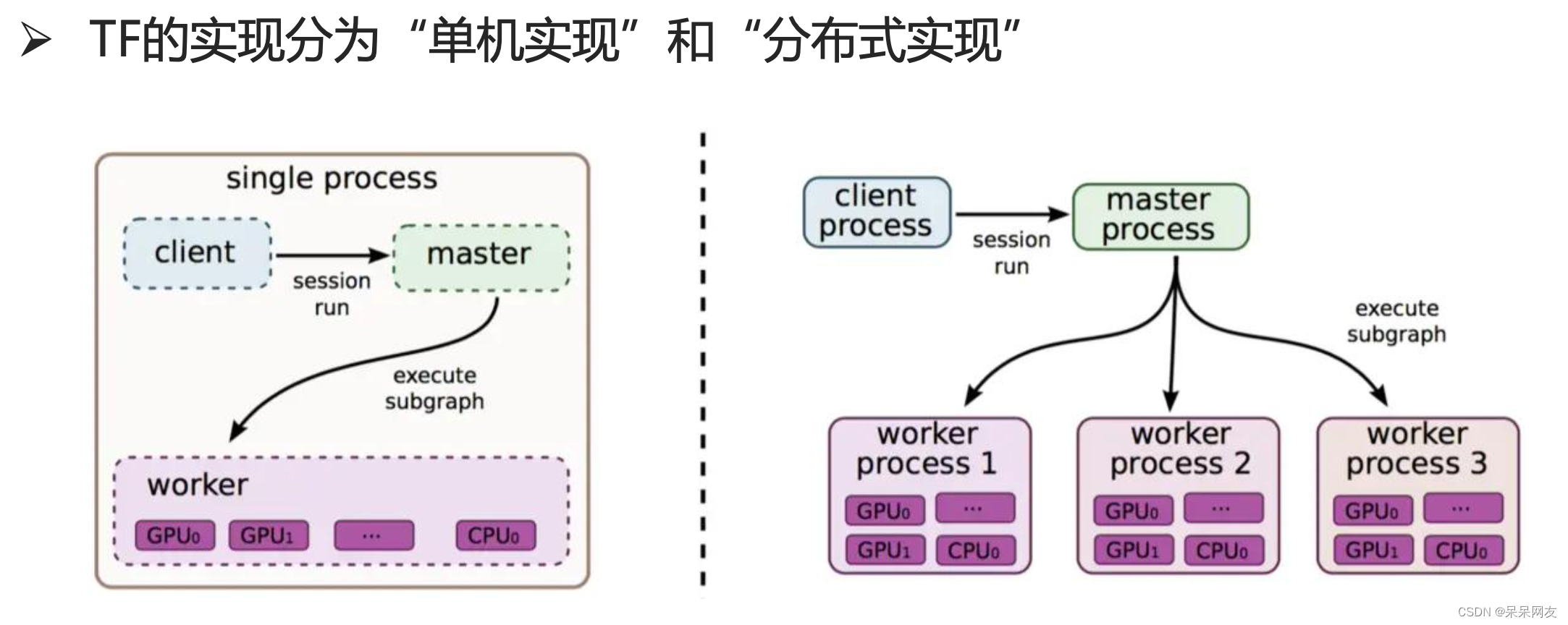
在单机与分布式情况下工作情况:
后端逻辑结构:
这里先看一下二版本和一版本下的一些区别,代码中cons1 = tf.constant(100.0)相当于定义一个计划,也就是操作对象,但是并没有执行,只有交给对话才执行了,同时需要知道Tensorflow中所有的计算都构建在图中会话(Session)是用来执行图的运算,下面的代码实现了简单的张量加运算。在Tensorflow中,变量(Variable)是一种操作,变量是一种特殊的张量, 能够进行存储持久化(张量不能进行持久化),它的值是张量。持久化存储就是写入文件中,所以模型参数用变量创建
占位符(placeholder)是变量占位符,当不能确定变量的值时,可以先声 明一个占位符,真正执行时再传入变量。一般用于样本数据中,因为样本输入的样本数并不确定,所有常用占位符
import tensorflow as tf #定义 2版本下可以直接运行 cons1 = tf.constant(100.0) cons2 = tf.constant(200.0) res = tf.add(cons1, cons2) print(res) ''' 低版本下 #执行1 sess = tf.Session() print(sess.run(res)) sess.close() #执行2 with tf.Session as sess: print(sess.run(res)) '''- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
图
TensorFlow 程序通常被组织成一个构建阶段和一个执行阶段。在构建阶段, op 的执行步骤 被描述成一个图. 在执行 阶段, 使用会话执行执行图中的 op。
TensorFlow Python 库有一个默认图 (default graph), op 构造器可以为其 增加节点. 这个默认图对 许多程序来说已经足够用了,也可以创建新的图来 描述计算过程。
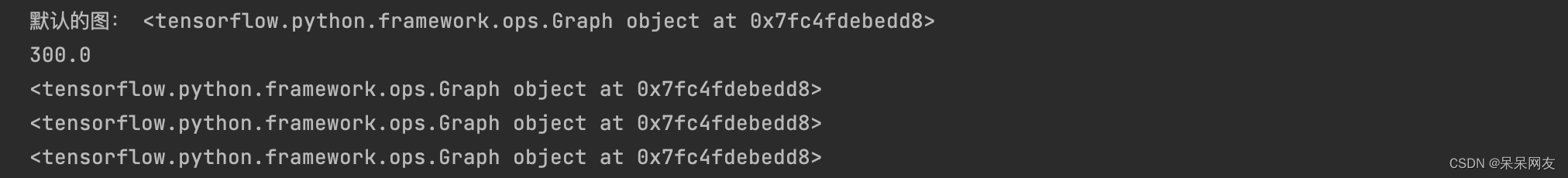
在Tensorflow中,op/session/tensor都有graph属性。
#定义 const1 = tf.constant(100.0) const2 = tf.constant(200.0) res = tf.add(const1, const2) #获取默认的图 graph = tf.get_default_graph() print('默认的图:', graph) #运行 with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(res)) print(const1.graph) print(const2.graph) print(res.graph)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
会话及相关操作、占位符
会话
会话(session)用来执行图中的计算,并且保存了计算张量对象的上下文
信息。会话的作用主要有:- 运行图结构
- 分配资源
- 掌握资源(如变量、队列、线程)
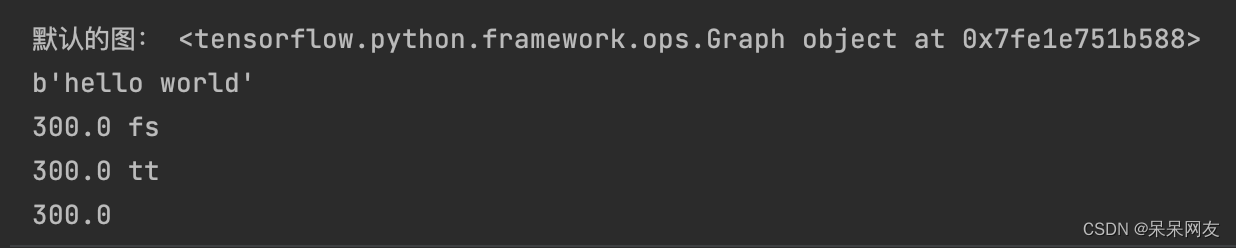
一个session只能执行一个图的运算。可以在会话对象创建时,指定运行的 图。如果在构造会话时未指定图形参数,则将在会话中使用默认图。如果 在同一进程中使用多个图(使用tf.graph( )创建),则必须为每个图使用不 同的会话,但每个图可以在多个会话中使用。
#定义 const1 = tf.constant(100.0) const2 = tf.constant(200.0) res = tf.add(const1, const2) #获取默认的图 graph = tf.get_default_graph() print('默认的图:', graph) #新建一个图 new_graph = tf.Graph() with new_graph.as_default(): new_op = tf.constant('hello world') #运行 with tf.Session(graph=new_graph) as sess: #print(sess.run(res)) print(sess.run(new_op)) #运行 with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess: print(sess.run(res), 'fs') sess2 = tf.Session() #一个会话中还能再创建会话 print(sess2.run(res), 'tt') sess2.close() #运行 with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess: print(sess.run(res))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30

调用run()方法时,可能会出现的错误及原因- RuntimeError:Session处于无效(如关闭)
- TypeError:fetches或feed_dict的键是不合适的值
- ValueError:fetches或feed_dict的键无效或引用的值不存在
下面案例中将说明如何传入参数构建的字典。
占位符
不确定张量内容情况下,可以使用占位符先占个位置,然后执行计算时,通过 参数传入具体数据执行计算(通过feed_dict参数指定)。placeholder节点被 声明的时候是未初始化的, 也不包含数据, 如果没有为它供给数据, 则 TensorFlow运算的时候会产生错误。
使用eval()也可以给占位符传参数
plhd = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 3]) #行数是样本数量,所以不固定,但是列数是神经元个数,那么一定会固定 data = np.arange(1, 7).reshape(2, 3) with tf.Session() as sess: print(sess.run(plhd, feed_dict={plhd: data})) [[1. 2. 3.] [4. 5. 6.]]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

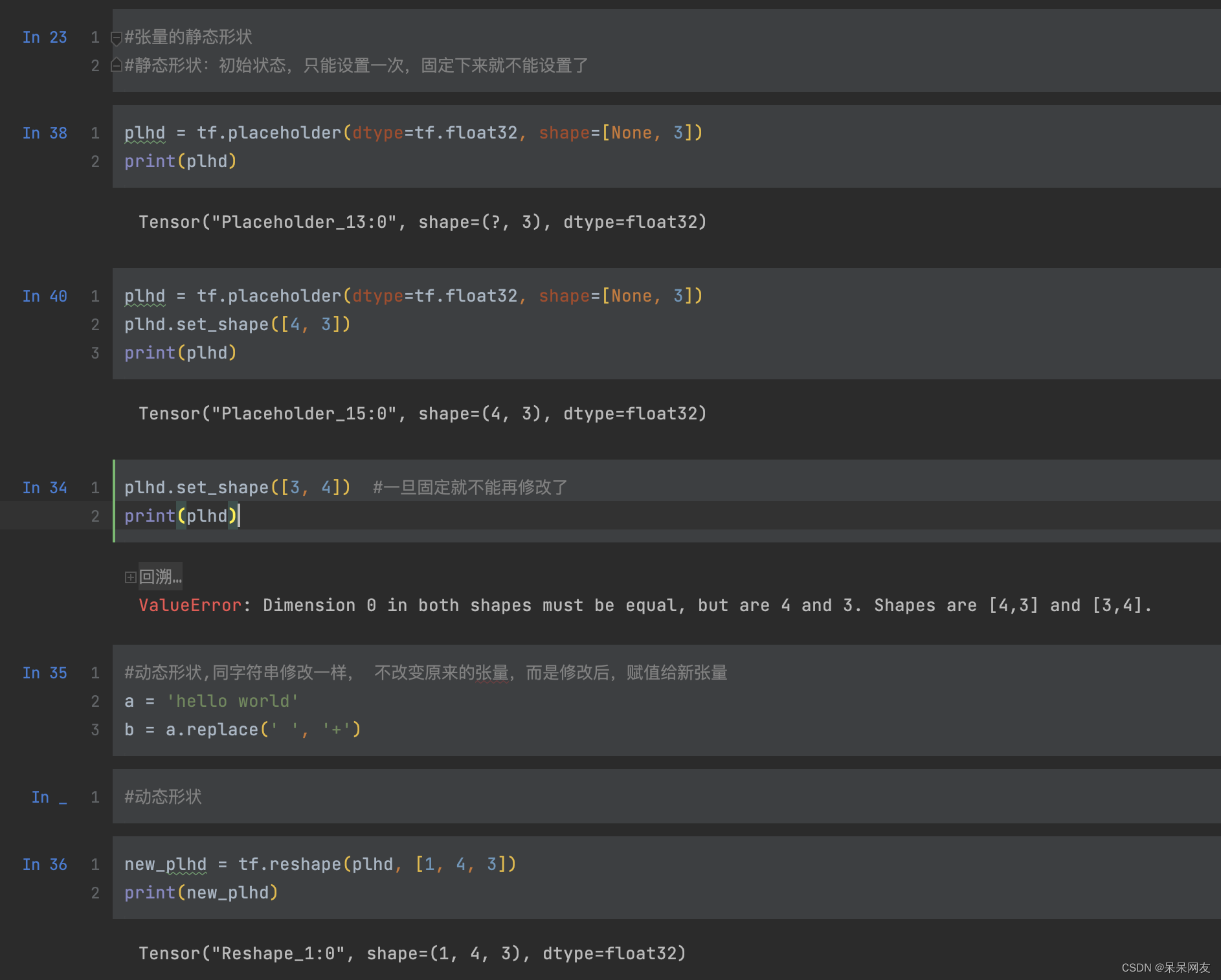
图中说明了静态形状只能改变一次值,改变后就无法再进行修改了,同时有一点需要注意第二个代码块,plhd.set_shape([4, 3])如果写成plhd.set_shape([3, 4])也会报错,是因为和占位符冲突了,因为占位符固定了特征只有3个。
张量常用属性
#定义 const1 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], dtype=tf.int64) #const2 = tf.constant(2) 这样的张量是一个标量 with tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess: print(sess.run(const1)) print('name', const1.name) print('dtype', const1.dtype) print('shape', const1.shape) print('op', const1.op) print('graph', const1.graph) [1 2 3 4 5 6 7] name Const_4:0 dtype <dtype: 'int64'> shape (7,) ===================== op name: "Const_4" op: "Const" attr { key: "dtype" value { type: DT_INT64 } } attr { key: "value" value { tensor { dtype: DT_INT64 tensor_shape { dim { size: 7 } } tensor_content: "\001\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\002\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\003\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\004\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\005\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\006\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\007\000\000\000\000\000\000\000" } } } ****************** graph <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x7fb3d0f4c908>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
生成张量
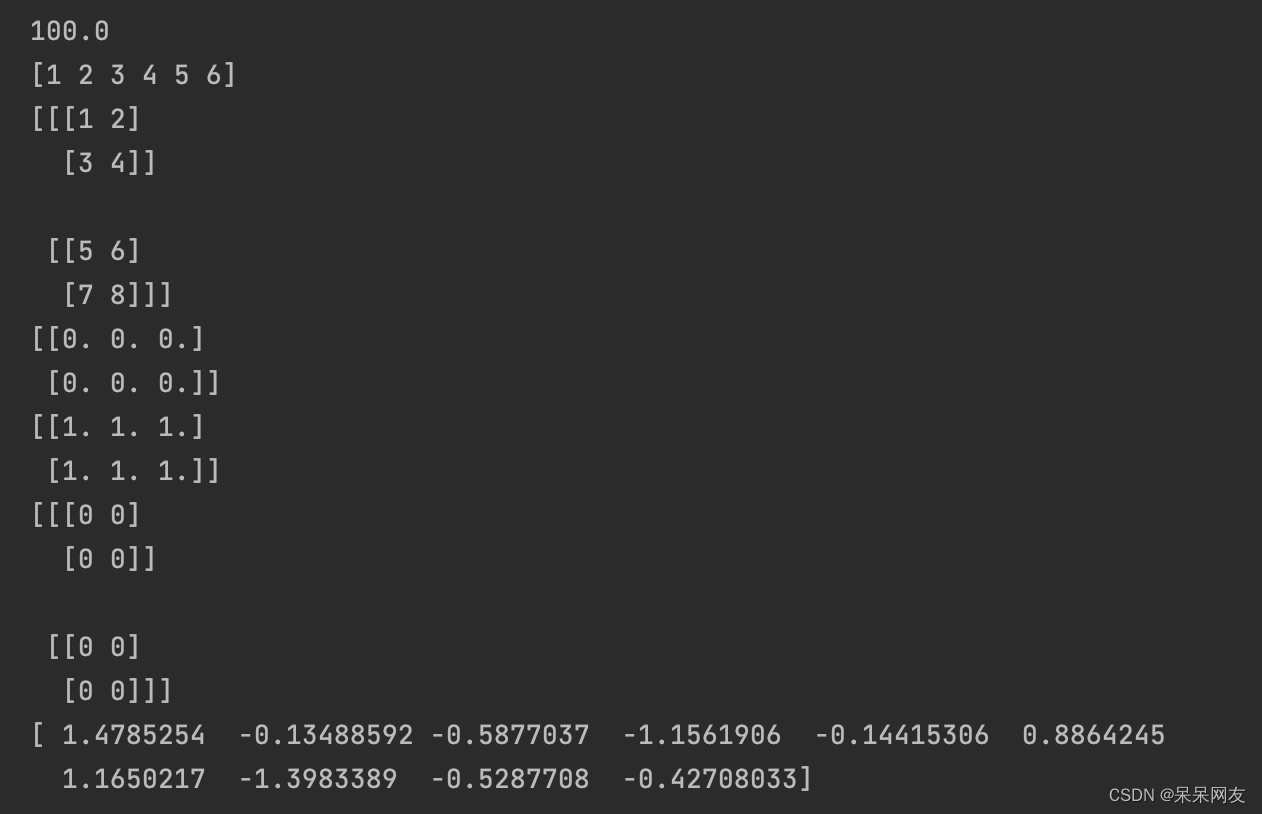
#定义 const1 = tf.constant(100.0) const2 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) const3 = tf.constant(np.arange(1, 9).reshape(2, 2, 2)) zeros = tf.zeros(shape=[2, 3], dtype='float32') ones = tf.ones(shape=[2, 3], dtype=tf.float32) zeros_like = tf.zeros_like(const3) random = tf.random_normal(shape=[10], mean=0.0, stddev=1, dtype=tf.float32) #运行 with tf.Session() as sess: print(const1.eval()) print(const2.eval()) print(const3.eval()) print(zeros.eval()) print(ones.eval()) print(zeros_like.eval()) print(random.eval())- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
张量数据类型的转换
ones = tf.ones(shape=[2, 3], dtype='int64') tensor1 = tf.constant([1.1, 2.2, 3.3], dtype='float32') temp = tf.cast(ones, 'float32') temp_str = tf.cast(tensor1, tf.string) with tf.Session() as sess: print(temp.eval()) #print(temp_str.eval()) #浮点类型不能转字符串 [[1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1.]]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
张量的数学运算
x = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype='float32') y = tf.constant([[4, 3], [2, 1]], dtype='float32') add = tf.add(x, y) mul = tf.matmul(x, y) log = tf.log(x) #自然对数 reduce_sum = tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=1) #水平方向求和 #计算片段和 data = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]) ids = tf.constant([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2]) segment = tf.segment_sum(data=data, segment_ids=ids) with tf.Session() as sess: print(add.eval()) print(mul.eval()) print(log.eval()) print(reduce_sum.eval()) print(segment.eval()) [[5. 5.] [5. 5.]] [[ 8. 5.] [20. 13.]] [[0. 0.6931472] [1.0986123 1.3862944]] [3. 7.] [ 6 30 19]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
变量,用到变量必须进行初始化,初始化也是op
weight = tf.random_normal(shape=[2, 3]) var = tf.Variable(initial_value=weight) #初始化 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) #当定义一个变量时,需要在会话中进行初始化 print(sess.run(var)) [[ 1.3942643 0.26474926 0.25010285] [-1.3674018 0.65457994 0.79963946]]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
将图中的计算逻辑写入事件文件中,并在tensorboard中显示
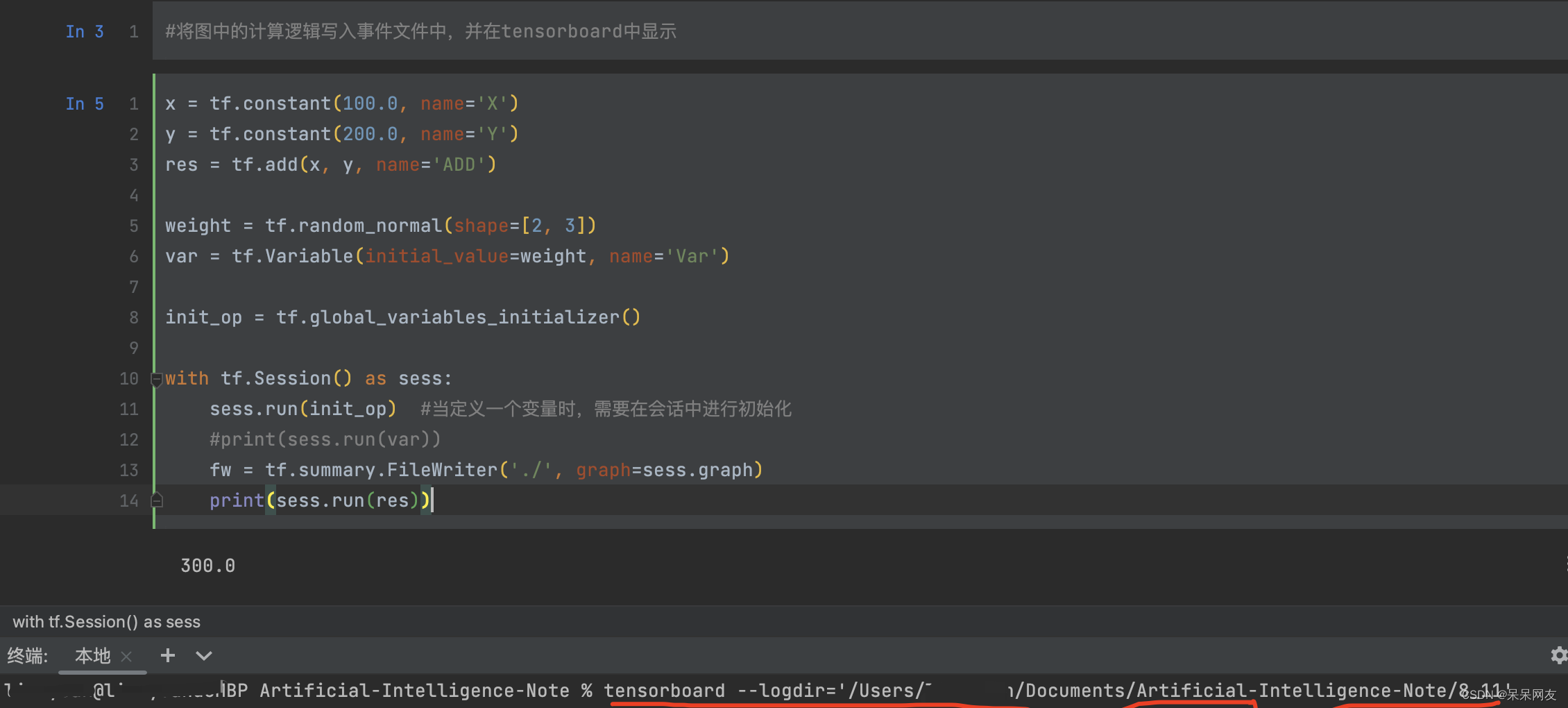
x = tf.constant(100.0, name='X') y = tf.constant(200.0, name='Y') res = tf.add(x, y, name='ADD') weight = tf.random_normal(shape=[2, 3]) var = tf.Variable(initial_value=weight, name='Var') init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) #当定义一个变量时,需要在会话中进行初始化 #print(sess.run(var)) fw = tf.summary.FileWriter('./', graph=sess.graph) print(sess.run(res)) 300- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
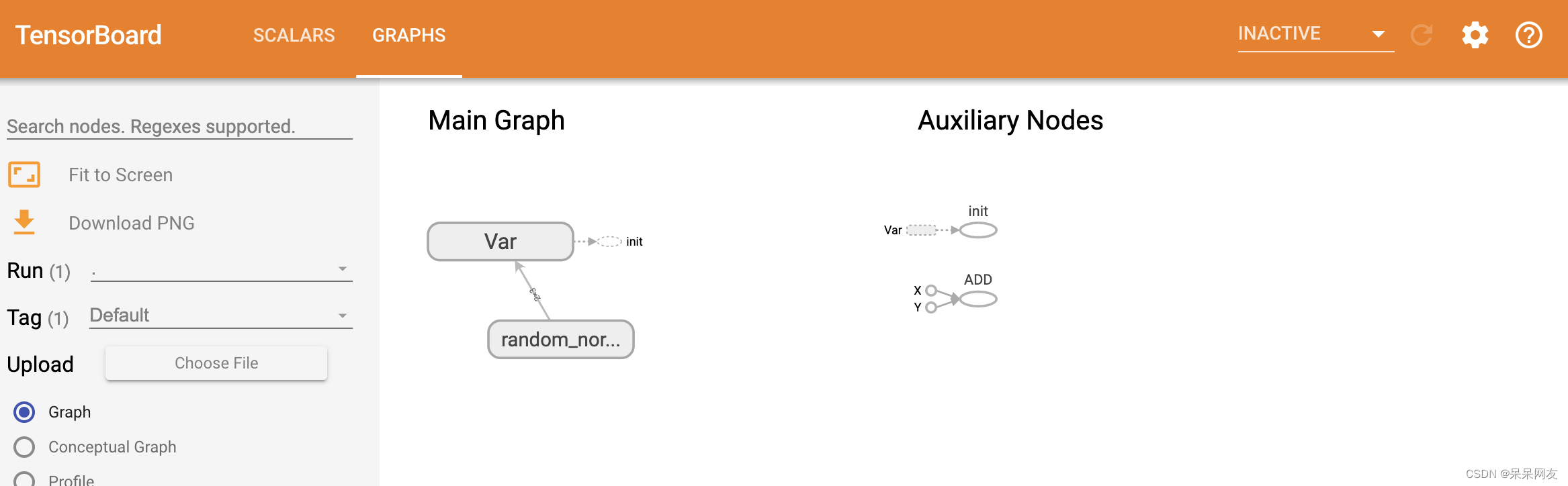
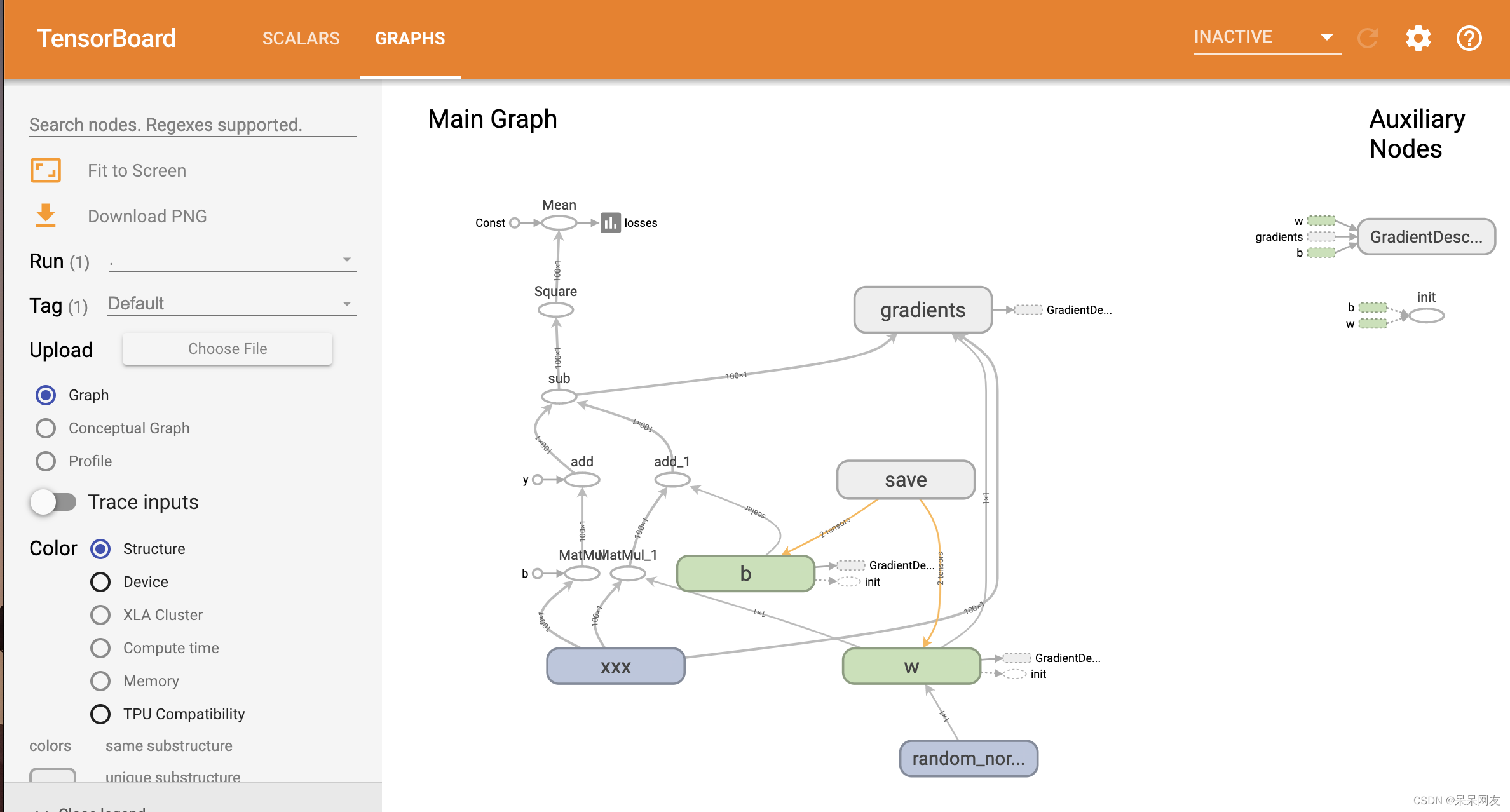
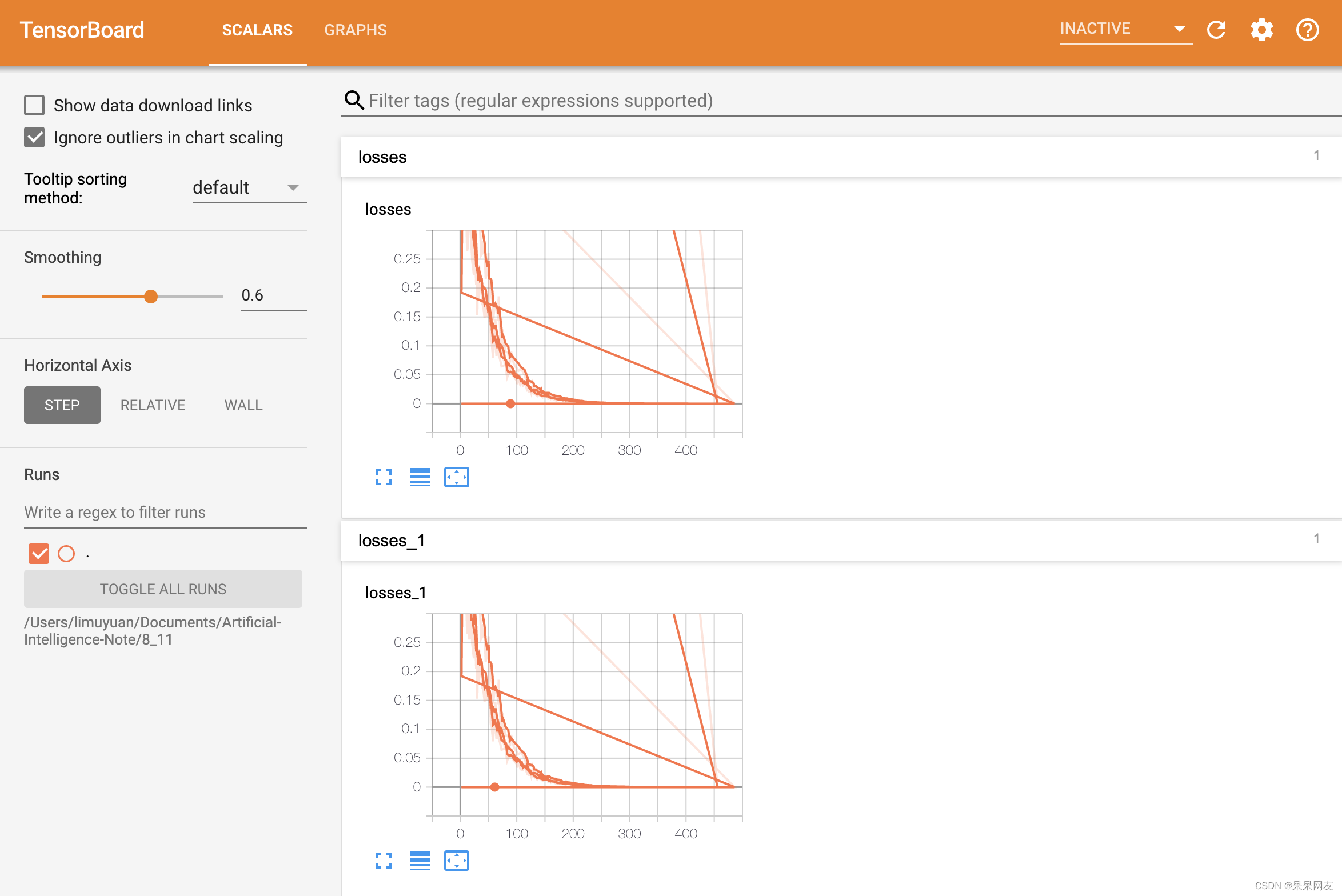
红色为启动命令,后面附上运行结果:
简单线性回归到实现
import tensorflow as tf import os #数据准备 x = tf.random_normal([100, 1], mean=1.75, stddev=0.5, name='xxx') #根据y=2x+5算出来 y = tf.matmul(x, [[2.0]]) + 5.0 #构建线性模型 weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal([1, 1]), name='w', trainable=True) #w需要是二维的 bias = tf.Variable(0.0, name='b', trainable=True) pred_y = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias #构建损失函数 均方误差 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - pred_y)) #梯度下降优化器 train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(loss) #初始化 init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer() #收集标量 tf.summary.scalar('losses', loss) #合并摘要 merged = tf.summary.merge_all() #创建模型保存对象 saver = tf.train.Saver() #运行 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) print('weight:{},bias:{}'.format(weight.eval(), bias.eval())) fw = tf.summary.FileWriter('./', graph=sess.graph) #在训练前检查是否有模型保存 if os.path.exists('./model/linear_model/checkpoint'): saver.restore(sess, './model/linear_model/') #开始训练 for i in range(100): sess.run(train_op) #执行合并 summary = sess.run(merged) fw.add_summary(summary, i + 1) print("epoch:{},weight:{},bias:{}".format(i + 1, weight.eval(), bias.eval())) #保存模型 saver.save(sess, './model/linear_model/')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
-
相关阅读:
uview的真机演示,微信小程序,当两个input框的时候,从一个input切换到两一个input的时候,键盘调不起来
requests 库:发送 form-data 格式的 http 请求 (python)
python办公自动化(应用方向)
【GD32F427开发板试用】+demo的正确打开方式(一)
Redis主从复制+哨兵选举机制分析
flink1.15 savepoint 超时报错 java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
使用 PyTorch 的计算机视觉简介 (3/6)
[数据可视化] 南丁格尔玫瑰图
51单片机汇编代码规范
数据结构作业:传输数据的增删改
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45256637/article/details/126292244
