-
十、Spring Boot 安全管理(4)
本章概要
- OAuth 2
10.4.1 OAuth 2 简介
OAuth 是一个开放标准,该标准允许用户让第三方应用访问该用户在某一网站上存储的私密资源(如头像、照片、视频等),而在这个过程中无须将用户名和密码提供给第三方应用。
实现这一功能是通过一个令牌(token),而不是用户名和密码来访问他们存放在特定服务提供者的数据。每一个令牌授权一个特定的网站在特定的时间段内访问特定的资源。
这样 OAuth 让用户可以授权第三方网站灵活的访问存储在另一些资源服务器的特定信息,而非所有内容。例如,用户想通过 QQ 登录知乎,这时知乎就是一个第三方应用,知乎要访问用户的一些基本信息就需要得到用户的授权,如果用户把自己的 QQ 用户名和密码告诉知乎,那么知乎就能访问用户的所有数据,并且只有用户修改密码才能收回权限,这种授权方式安全隐患很大,如果使用 OAuth ,就能很好的解决这一问题。
采用令牌的方式可以让用户灵活的对第三方应用授权或者收回权限。OAuth 2 是 OAuth 协议的下一版本,但不向下兼容 OAuth 1.0 。
OAuth 2 关注客户端开发者的简易型,同时为Web应用、桌面应用,移动设备、起居室设备提供专门的认证流程。传统的 Web 开发登录认证一般都是基于 Session 的,但是前后端分离的架构中继续使用 Session 会有许多不便,因为移动端(Android、IOS、微信小程序等)要么不支持 Cookie(微信小程序),要么使用非常不便,对于这些问题,使用 OAuth 2 认证都能解决。10.4.2 OAuth 2 角色
先了解 OAuth 2 中几个基本的角色
- 资源所有者:即用户,具有头像、照片、视频等资源
- 客户端:即第三方应用
- 授权服务器:用来验证用户提供的信息是否正确,并返回一个令牌给第三方应用
- 资源服务器:提供给用户资源的服务器,例如头像、照片、视频等资源
一般来说,授权服务器和资源服务器可以是同一台服务器。
10.4.2 OAuth 2 授权流程
步骤01:客户端(第三方应用)向用户请求授权。
步骤02:用户单击客户端所呈现的服务授权页面上的同意授权按钮后,服务端返回一个授权许可凭证给客户端。
步骤03:客户端拿着授权许可证去授权服务器申请令牌。
步骤04:授权服务器验证信息无误后,发放令牌给客户端。
步骤05:客户端拿着令牌去资源服务器访问资源。
步骤06:资源服务器验证令牌无误后开放资源。10.4.4 授权模式
OAuth 协议的授权模式共分为 4 种,如下
- 授权码模式:授权码(authorization code)是功能最完整、流程最严谨的授权模式。它的特点就是通过客户端的服务器与授权服务器进行交互,国内常见的第三方平台登录功能基本都是使用这种模式
- 简化模式:简化模式不需要客户端服务器参与,直接在浏览器中向授权服务器申请令牌,一般若是纯静态页面,则可以采用这种方式
- 密码模式:用户把用户名密码直接告诉客户端,客户端使用这些信息向授权服务器申请令牌。这需要用户对客户端高度信息,例如客户端应用和服务提供商是同一家公司
- 客户端模式:客户端使用自己的名义而不是用户的名义想服务提供者申请授权。严格来说,客户端模式并不能算作 OAuth 协议要解决的问题的一种解决方案,但是,对于开发者而言,在一些前后端分离应用或者为移动端提供的认证授权服务器上使用这种模式还是非常方便的
4 种模式各有千秋,分别适用于不同的开发场景,开发者根据实际情况进行选择
10.4.5 实践
此处介绍的是在前后端分离应用(或为移动端、微信小程序等)提供的认证服务器中如何搭建 OAuth 服务,因此主要介绍密码模式。
1. 创建项目,添加依赖
创建 Spring Boot Web 项目,添加如下依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>io.lettucegroupId> <artifactId>lettuce-coreartifactId> exclusion> exclusions> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clientsgroupId> <artifactId>jedisartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security.oauthgroupId> <artifactId>spring-security-oauth2artifactId> <version>2.3.3.RELEASEversion> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
由于 Spring Boot 中的 OAuth 协议是在 Spring Security 的基础上完成的,因此首先要添加 Spring Security 依赖,要用到 OAuth 2,因此添加 OAuth 2 相关依赖,令牌可以存储在 Redis 缓存服务器上,同时 Redis 具有过期等功能,很适合令牌的存储,因此也加入 Redis 依赖。
配置 application.propertiesspring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.host=ip地址 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password=root spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1ms spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2. 配置授权服务器
授权服务器和资源服务器可以是同一台服务器,也可以是不同服务器,此处假设是同一台服务器,通过不同的配置分别开启授权服务器和资源服务器,首先是授权服务器:
@Configuration @EnableAuthorizationServer public class AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired AuthenticationManager authenticationManager; @Autowired RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory; @Autowired UserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } @Override public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception { clients.inMemory() .withClient("password") .authorizedGrantTypes("password", "refresh_token") .accessTokenValiditySeconds(1800) .resourceIds("rid") .scopes("all") .secret("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq"); } @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception { endpoints.tokenStore(new RedisTokenStore(redisConnectionFactory)) .authenticationManager(authenticationManager) .userDetailsService(userDetailsService); } @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception { security.allowFormAuthenticationForClients(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
代码解释:
- 自定义类继承自 AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter ,完成对授权服务器的配置,然后通过 @EnableAuthorizationServer 注解开启授权服务器
- 注入 AuthenticationManager 用来支持 password 模式
- 注入 RedisConnectionFactory 用来完成 Redis 缓存,将令牌信息储存到 Redis 缓存中
- 注入 UserDetailsService 该对象为刷新 token 提供支持
- 在 configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) 方法中配置 password 授权模式,authorizedGrantTypes 表示 OAuth 2 中的授权模式为 password 和 refresh_token 两种,在标准的 OAuth 2 协议中,授权模式并不包括 refresh_token ,但是在 Spring Security 的实现中将其归为一种,因此如果要实现 access_token 的刷新,就需要添加这样一种授权模式;accessTokenValiditySeconds 方法配置了 access_token 的过期时间;resourceIds 配置了资源 id;secret 方法配置了加密后的密码,明文是 123
- configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) 方法配置了令牌的存储,AuthenticationManager 和 UserDetailsService 主要用于支持 password 模式以及令牌的刷新
- configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) 方法配置表示支持 client_id 和 client_secret 做登录认证
3. 配置资源服务器
@Configuration @EnableResourceServer public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception { resources.resourceId("rid").stateless(true); } @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin") .antMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("user") .anyRequest().authenticated(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
代码解释:
- 自定义类继承自 ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter ,并添加 @EnableResourceServer 注解开启资源服务器配置
- resources.resourceId(“rid”).stateless(true); 配置资源 id,这里的资源 id 和授权服务器中的资源 id 一直,然后设置这些资源仅基于令牌认证
- configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法配置 HttpSecurity
4. 配置 Security
@Configuration public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Bean @Override public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception { return super.authenticationManagerBean(); } @Bean @Override protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService() { return super.userDetailsService(); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin") .password("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq") .roles("admin") .and() .withUser("sang") .password("$2a$10$RMuFXGQ5AtH4wOvkUqyvuecpqUSeoxZYqilXzbz50dceRsga.WYiq") .roles("user"); } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.antMatcher("/oauth/**").authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/oauth/**").permitAll() .and().csrf().disable(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
这里两个 Bean 将注入授权服务器配置类中使用,另外,这里的 HttpSecurity 配置主要是配置 /oauth/** 模式的 URL ,这一类的请求直接放行。在 Spring Security 配置和资源服务器配置中,一共涉及两个 HttpSecurity ,其中 Spring Security 中的配置优先级高于资源服务器中的配置,即请求地址先经过 Spring Security 的 HttpSecurity ,再经过资源服务器的 HttpSecurity。
5. 验证测试
首先创建三个简单的请求地址
@RestController public class HelloController { @GetMapping("/admin/hello") public String admin() { return "Hello admin!"; } @GetMapping("/user/hello") public String user() { return "Hello user!"; } @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "hello"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
根据前文的配置,要请求这三个地址,分别需要 admin 角色、user 角色以及登录后访问。
所有都配置完成后,启动 Redis 服务器,再启动 Spring Boot 项目,首先发送一个 POST 请求获取 token,请求地址如下(注意这里是一个 POST 请求,为了显示方便,将参数写在地址栏中):http://localhost:8080/oauth/token?username=sang&password=123&grant_type=password&client_id=password&scope=all&client_secret=123
请求地址中包含的参数有用户名、密码、授权模式、客户端 id 、scope 以及客户端密码,基本就是授权服务器中所配置的数据,请求结果如图
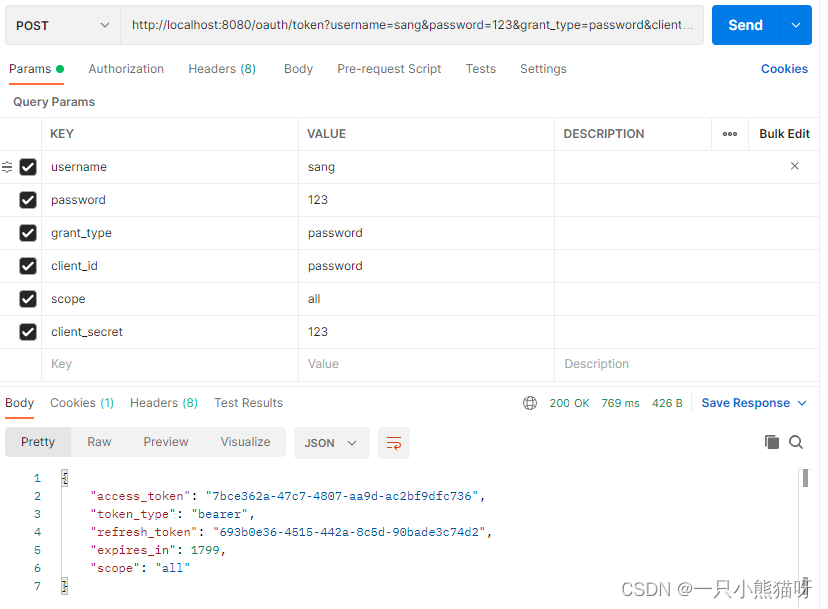
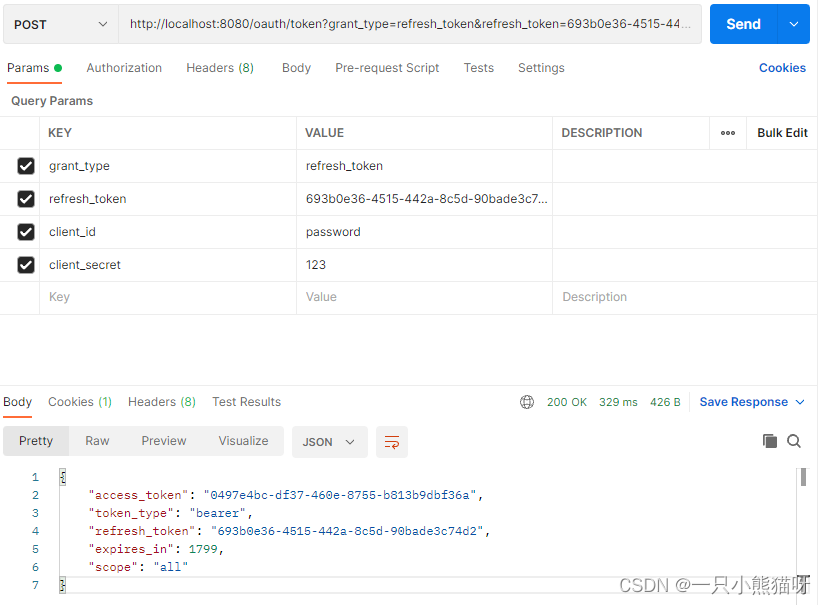
其中 access_token 是获取其它资源时要用的令牌,refresh_token 用来刷新令牌,expires_in 表示 access_token 过期时间,当 access_token 过期后,使用 refresh_token 重新获取新的 access_token (前提是 refresh_token 未过期),请求地址(注意也是POST请求):http://localhost:8080/oauth/token?grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=693b0e36-4515-442a-8c5d-90bade3c74d2&client_id=password&client_secret=123
获取新的 access_token 时需要携带上 refresh_token ,同事授权模式设置为 refresh_token ,在获取的结果中 access_token 会变化,同时 access_token 有效期也会变化,如图
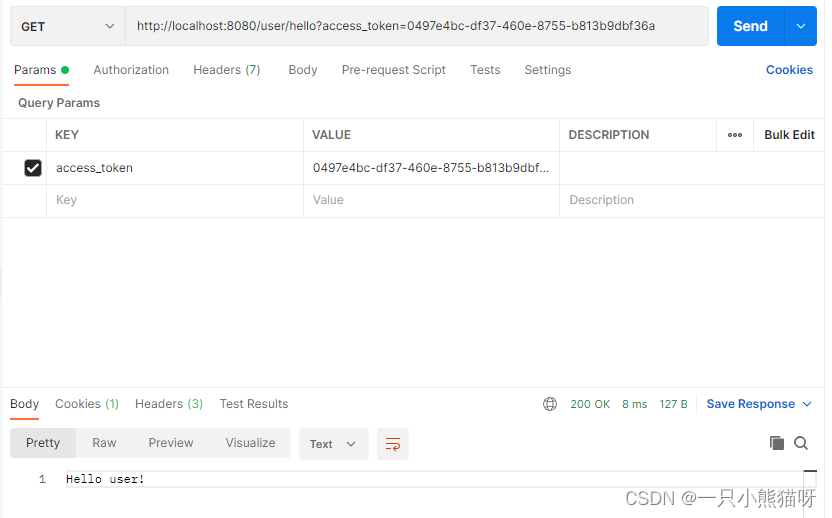
接下来访问所有资源,携带上 access_token 参数即可,例如 /user/hello 接口:http://localhost:8080/user/hello?access_token=0497e4bc-df37-460e-8755-b813b9dbf36a,访问结果如图
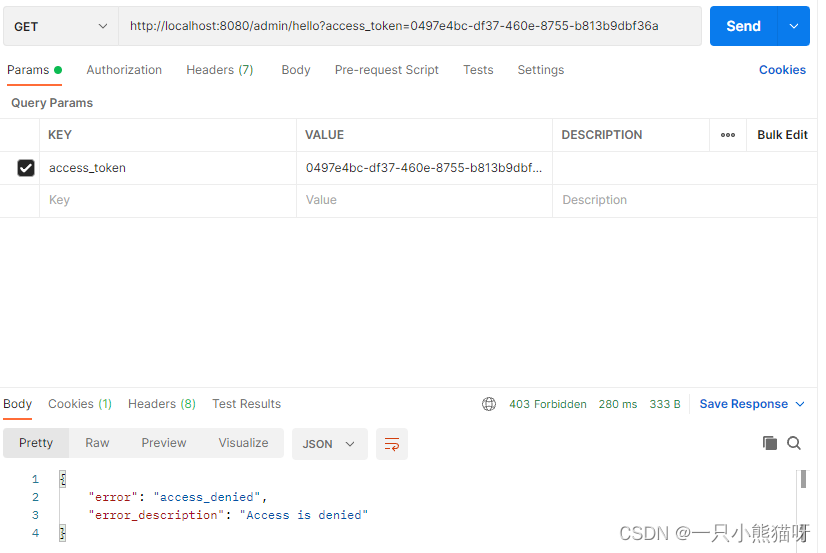
如果非法访问一个资源,例如 sang 用户访问 /admin/hello 接口,结果如图
到此,一个 password 模式的 OAuth 认证体系就搭建成功了。
OAuth 中的认证模式有 4 中,开发者需要结合自己开发的实际情况选择其中一种,此处介绍的是在前后端分离应用中常用的 password 模式,其它的授权模式也都有自己的使用场景。
整体来讲,Spring Security OAuth 2 的使用还是较复杂的,配置也比较繁琐,如果开发者的应用场景比较简单,完全可以按照此处介绍的授权流程自己搭建 OAuth 2 认证体系。 -
相关阅读:
【python绘图】Matplotlib绘图2维+3维(2D图像和3D图像)
bizlog通用操作日志组件(使用篇)
证书科普 | 国内主流BIM证书,原来差距这么大
SOA(面向服务架构)是什么?
SpringBoot SpringBoot 原理篇 1 自动配置 1.8 bean 的加载方式【六】
Java版企业电子招标采购系统源码—企业战略布局下的采购寻源
重看工厂模式
尚医通(三)
如何进行Java项目的构建和部署?
设计模式 - 解释器模式
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/GXL_1012/article/details/126280733
