-
【数据结构与算法】<==>栈
作者:旧梦拾遗186
专栏:数据结构成长日记

每日励志
没有一个冬天不可逾越,没有一个春天不会来临。最慢的步伐不是跬步,而是徘徊,最快的脚步不是冲刺,而是坚持。
前言:
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。 栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出 LIFO ( Last In First Out )的原则。压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈 / 压栈 / 入栈, 入数据在栈顶 。出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。 出数据也在栈顶 。目录
栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。 进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。 栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出 LIFO ( Last In First Out )的原则。压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈 / 压栈 / 入栈, 入数据在栈顶 。出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。 出数据也在栈顶 。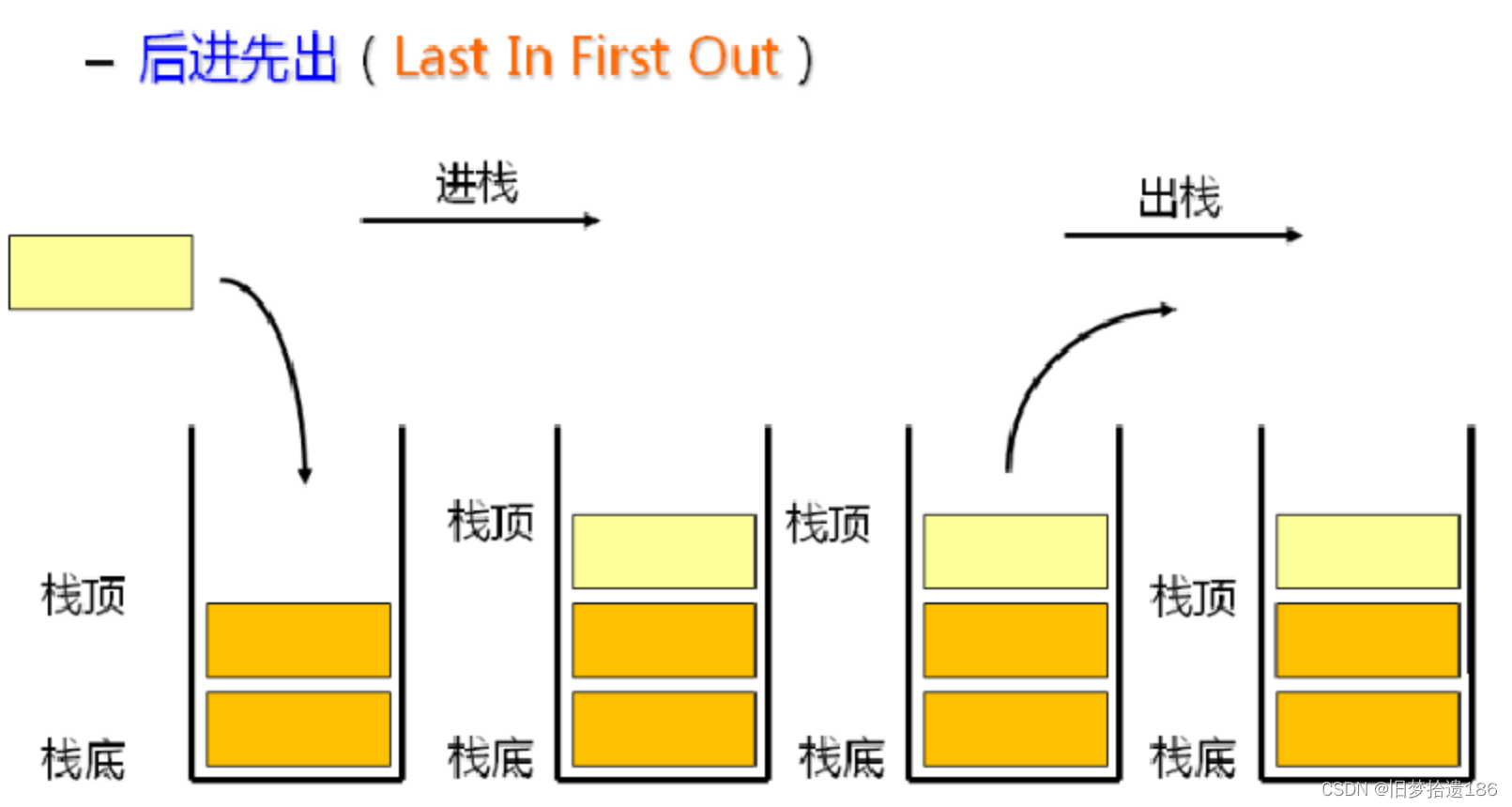

理解了栈的概念及其结构,我们可以连做一些比较常见的选择题:
1.一个栈的初始状态为空。现将元素1、2、3、4、5、A、B、C、D、E依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,则元素出
栈的顺序是( )。
A 12345ABCDE
B EDCBA54321
C ABCDE12345
D 54321EDCBA解析:非常简单,根据后进先出,选B
2.若进栈序列为 1,2,3,4 ,进栈过程中可以出栈,则下列不可能的一个出栈序列是()
A 1,4,3,2
B 2,3,4,1
C 3,1,4,2
D 3,4,2,1解析:学校的考试选择题最喜欢出这种了,我们可以边进边出,A、B、D是可以的。而对于C:要想出3,肯定要先入1、2、3,而要出1是不可能的,还有个2呢。
栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用 数组或者链表实现 ,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。

注意:
-
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
-
栈的作用还是挺大的:递归如果深度太深,可以利用栈来实现非递归
-
我们直接来进行栈的实现:数据结构这里不要直接去访问结构数据,我们最好还是通过函数接口进行访问
对于栈的插入操作,我们需要知道top的初始位置是在哪里,是-1呢还是0呢?


很明显,这里我们在初始化的时候设置成0了。同时,插入的时候我们需要去考虑有必要扩容的问题。
- void Stackpush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->top == ps->capaticy)
- {
- int newcapaticy =ps->capaticy== 0 ? 4 : ps->capaticy * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapaticy);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("false");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capaticy = newcapaticy;
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
test.c
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
- #include"Stack.h"
- void TestStack()
- {
- ST st;
- StackInit(&st);
- Stackpush(&st, 1);
- Stackpush(&st, 2);
- Stackpush(&st, 3);
- Stackpush(&st, 4);
- Stackpush(&st, 5);
- //访问栈
- while (!StackEmpty(&st))
- {
- printf("<==>%d ", StackTop(&st));
- Stackpop(&st);
- }
- //把栈顶数据拿出来
- printf("\n");
- }
- int main()
- {
- TestStack();
- return 0;
- }

Stack.c
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
- #include"Stack.h"
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->capaticy = ps->top = 0;
- ps->a = NULL;
- }
- //销毁
- void StackDestory(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->capaticy = ps->top = 0;
- }
- void Stackpush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->top == ps->capaticy)
- {
- int newcapaticy =ps->capaticy== 0 ? 4 : ps->capaticy * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapaticy);
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("false");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capaticy = newcapaticy;
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- 打印
- //void Stackprint(ST* ps)
- //{
- // assert(ps);
- // ps->top = 0;
- // while (ps->top!=ps->capaticy)
- // {
- // printf("<==>%d", ps->a[ps->top]);
- // ps->top++;
- // }
- //}
- //退栈
- void Stackpop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }
- //判断栈空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
- }
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;



Stack.h
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* a;
- int top;
- int capaticy;
- }ST;
- //初始化
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- //销毁
- void StackDestory(ST* ps);
- //插入数据
- void Stackpush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
- 打印
- //void Stackprint(ST* ps);
- //退栈
- void Stackpop(ST* ps);
- //判断栈空
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
- //查看栈顶
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- //元素个数
- int StackSize(ST* ps);

测试

栈的OJ题
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
示例 2:输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例 3:输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
示例 4:输入:s = "([)]"
输出:false
示例 5:输入:s = "{[]}"
输出:true
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 仅由括号 '()[]{}' 组成- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- //静态栈
- //#define N 100
- //typedef int STDataType;
- //typedef struct Stack
- //{
- // STDataType a[N];
- // int top;
- //}ST;
- //动态栈
- typedef char STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType*a;
- int top;
- int capacity;
- }ST;
- void StackInit(ST* ps);
- void StackDestory(ST* ps);
- void StackPush(ST* ps,STDataType x);
- void StackPop(ST* ps);
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
- bool StackEmpty(ST*ps);
- int StackSize(ST* ps);
- void StackInit(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
- }
- void StackDestory(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
- }
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
- if (NULL == tmp)
- {
- perror("malloc fail");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- void StackPop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
- }
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- int StackSize(ST* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }
- bool isValid(char * s){
- ST st;
- StackInit(&st);
- while(*s)
- {
- if(*s == '{' || *s=='[' ||*s=='(')
- {
- StackPush(&st,*s);
- }
- else
- {
- //可能只有右括号,而栈为空,数量不匹配
- if(StackEmpty(&st))
- return false;
- char top = StackTop(&st);
- StackPop(&st);
- if((*s == '}'&&top != '{')
- ||(*s == ']'&&top != '[')
- ||(*s == ')'&&top != '('))
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- ++s;
- }
- //栈不为空,数量不匹配
- bool flag = StackEmpty(&st);
- StackDestory(&st);
- return flag;
- }

-
-
相关阅读:
医学图像分割利器:U-Net网络详解及实战
flume1.11.0安装部署
61-Java-分布式开发框架Dubbo
阶段性工作总结
Verilog generate
Linux 手动卸载jdk
A child container failed during start之解决方法
Flink之KeyedState
自己动手从零写桌面操作系统GrapeOS系列教程——16.封装打印字符串函数
Typescript 中根据某个字段判断其他字段是否必传
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_67900732/article/details/126278859

 https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/